高糖环境下beclin2介导的自噬增强绒毛膜滋养层细胞凋亡
纪璐璐,熊国平,汪琳*
(1武汉大学基础医学院组织学与胚胎学教研室,武汉 430071;2武汉市中心医院妇产科,武汉 430014)
高糖环境下beclin2介导的自噬增强绒毛膜滋养层细胞凋亡
纪璐璐1,熊国平2,汪琳1*
(1武汉大学基础医学院组织学与胚胎学教研室,武汉 430071;2武汉市中心医院妇产科,武汉 430014)
目的探讨高糖对人绒毛膜滋养层细胞早期凋亡及自噬水平的影响。方法取足月妊娠的正常及妊娠期糖尿病(gestational diabetes mellitus, GDM)患者的胎盘组织,透射电镜观察滋养层细胞超微结构的改变。体外用不同浓度的含糖培养基培养滋养层细胞系HTR8/Svneo细胞24h,分为低糖组(1.57mmol/L或LG2 2.25mmol/L),正常对照组(5.57mmol/L)和高糖组(10.57mmol/L、15.57mmol/L或40.57mmol/L);流式细胞术检测细胞早期凋亡率;q-PCR检测细胞内beclin1、beclin2和ATG7等自噬相关基因的mRNA表达水平;Western blot检测Ⅱ型自噬标志蛋白微管相关蛋白1轻链3(LC3-II)和p62蛋白表达水平。结果透射电镜下可见GDM组滋养层细胞中存在自噬小体且空泡数目明显多于正常足月妊娠组,其游离面微绒毛出现明显倒覆及坍塌现象;在体外培养的滋养层细胞中,流式细胞术检测显示1.57mmol/L低糖组及40.57mmol/L高糖组较正常对照组HTR8/SVneo细胞的早期凋亡率均明显增加;q-PCR分析发现40.57mmol/L高糖组beclin2及ATG7 mRNA表达水平较正常对照组升高,beclin1 mRNA表达无差异;Western blot检测表明,与正常对照组比较,40.57mmol/L高糖组LC3-II蛋白表达水平升高,p62蛋白表达水平降低。结论高糖可通过beclin2介导的自噬信号途径增强滋养层细胞自噬水平进而导致细胞凋亡,并可能与不良的妊娠结局相关。
妊娠期糖尿病;HTR8/SVneo;自噬;凋亡;beclin2
妊娠期糖尿病(gestational diabetesmellitus, GDM)是一种伴有糖耐量异常的代谢性疾病,在妊娠期间出现或者被首次诊断出来[1]。流行病学研究发现,妊娠期糖尿病可影响3%~30%的妊娠期妇女[2]。胎盘是一个非常特殊的器官,是给胎儿提供营养物质、气体交换及排除代谢物质的主要场所,对维持正常妊娠非常重要。在妊娠早期,滋养层细胞能够侵入母体子宫蜕膜、重塑母体脉管系统以形成低抵抗、高容量的血管系统,这对正常胎盘的形成及正常妊娠的维持必不可少。而抗血管生成因子、促炎环境因素导致的GDM、子痫等妊娠期疾病会损害滋养层细胞的侵袭和迁移,引起浅的胎盘植入最终导致不利于胎儿生长及母胎界面形成的环境[3-5]。
在真核细胞中,自噬对细胞的存活、分化以及细胞稳态的维持必不可少[6]。在一些应激状况下,细胞内的自噬会被上调,如细胞内应激(错误折叠蛋白的累积、氧化应激的增加、DNA受损),或是细胞外环境的影响(饥饿、缺氧、激素刺激)[7]。自噬对胎盘的形成、滋养层细胞的入侵必不可少,而且自噬能为不同阶段的妊娠维持起保护作用[8,9]。与正常妊娠相比,子痫前期及胎儿宫内发育迟缓的胎盘组织中自噬水平增高[10]。但是在GDM状态下,自噬的水平及其对胎盘形成的影响目前尚不清楚。本研究通过透射电镜观察GDM和正常妊娠胎盘滋养层细胞的超微结构,并用HTR8/SVneo细胞株来探讨高糖对人绒毛膜滋养层细胞(HTR8/SVneo)早期凋亡及自噬水平的影响。
材料和方法
1 胎盘组织
2015年9月至2015年11月于武汉市中心医院妇产科取足月剖宫产分娩的正常(社会因素剖宫产)(NP)及GDM患者的胎盘组织各9例,平均年龄26 ± 2.7岁。
2 细胞
人绒毛膜滋养层细胞系HTR8/SVneo购自ATCC细胞库。
3 试剂
RPMI-1640培养基购自Hyclone公司,胎牛血清购自美国Gibco公司,Trizol reagent购自Invitrogen公司,ATG7、beclin2、beclin1、GAPDH引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成,Prime ScriptT-MRT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser购自日本Takara公司,SYBR®Green Realtime PCR Master Mix购自日本TOYOBO公司;GAPDH (内参蛋白)、HRP标记山羊抗兔IgG(二抗)、p62多克隆抗体购自武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司,LC3B抗体购自美国CST公 司,Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection Kit购自凯基生物公司。
4 胎盘组织电镜术
胎盘样本去除胎膜后,取约1mm×1mm×1mm胎盘组织块,经2.5%戊二醛固定、1%锇酸固定、脱水、环氧树脂618包埋,超薄切片后醋酸铀-柠檬酸铅染色,透射电镜下观察。
5 细胞培养与分组
HTR8/SVne细胞在普通RPMI-1640培养基(含10%胎牛血清,100U/ml青霉素,100μg/ml链霉素)中常规培养,培养条件为5%CO2,37℃。细胞接种到6孔板上时,用不含糖的RPMI-1640培养基并另外加葡萄糖至实验所需不同的浓度。所有实验细胞均取自对数生长期,台盼蓝拒染率均在95%以上。
实验分为3组,低糖组:1.57mmol/L(LG1)和2.57mmol/L (LG2);正常糖组:5.57mmol/L;高糖 组:10.57mmol/L (HG1)、15.57mmol/L(HG2)和40.57mmol/L(HG3),均培养24h。
6 细胞总RNA的提取和q-PCR扩增
根据说明书裂解细胞,所得总RNA用无RNase去离子水溶解,在Nana DropTM2000上测浓度并作为逆转录聚合酶链反应的模板,反应体系和操作步骤按TAKARA说明书进行。各引物序列见表1。PCR反应条件:Pattern 1:反转录反应37℃15min,85℃ 5sec;Pattern 2:q-PCR反应95℃ 5sec,60℃ 30sec,共40个循环;收集荧光信号。每1个样本做3个平信管。基因表达的相对变化采用2-ΔΔCt法处理。
7 Western blot
收集细胞,用含有蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液冰上裂解的细胞30min(6孔板,200μl/孔),收集裂解产物12000r/min、4℃离心10min,BCA法测定上清中蛋白浓度;经SDS-PAGE电泳后,将蛋白条带转印至0.22μm的PVDF膜上(90min),然后用含5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭2h,再用1∶1000稀释的纯化一抗4℃孵育过夜,再用1∶5000二抗室温孵育2h,最后用ECL化学发光试剂盒(Millipore公司,美国)显色,UVP化学发光检测仪检测目的蛋白的表达,ImageJ扫描分析灰度值。

表1 目的基因PCR引物序列Tab.1 The primer sequences of target genes for real-time PCR
8 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡
用不含EDTA的胰酶消化收集细胞,PBS洗涤细胞两次(2000r/min、5min)收集的细胞密度为1×105/ml,加400μl 1×Binding Bufer重新悬浮细胞,加5μl Annexin V-FITC于细胞悬液中,混匀后4℃避光孵育20min,加10μl Propidium Iodide于细胞悬液中,混匀,4℃避光孵育5min,1h内用流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率。
9 统计学分析
采用SPSS17统计学软件进行统计学分析,数值均以均值±标准差来表示,多组间的比较采用单因素方差分析,组间差异性用LSD检测,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
1 GDM胎盘滋养层细胞游离面微绒毛倒覆且胞内有大量空泡结构
透射电镜术结果显示,正常妊娠组胎盘绒毛膜滋养层细胞内细胞器结构清晰可见,胞质内未见明显膜性空泡,滋养层细胞微绒毛排列密集整齐(图1A)。GDM组滋养层细胞胞质中观察到自噬小体,且可见大量空泡状结构。此外,在GDM组的滋养层细胞上可见坍塌倒覆的微绒毛(图1B)。

图1 正常妊娠与GDM胎盘组织超微结构。A,正常妊娠组;B,妊娠期糖尿病组;箭头,胎盘游离面微绒毛;*,自噬小体;#,空泡状结构;比例尺,500nmFig.1 Placenta ultrastructure observed by transmission electron microscopy. A, normal group; B, GDM group; arrowheads, microvilli; *, autophagosome, #, vacuole; scale bar, 500nm
2 高糖及低糖组HTR8/SVneo细胞早期凋亡率增高
流式细胞术分析显示,与正常对照组相比,低糖组细胞凋亡增多,且随着糖浓度的降低细胞早期凋亡增多(图2A),糖浓度为1.57mmol/L(LG1)时,细胞凋亡率明显增加(图2B);高糖组细胞较正常对照组细胞凋亡增加,糖浓度达到15.57mmol/L(HG2)时细胞早期凋亡开始增加(图2A),当浓度增加到40.57mmol/L(HG3)时,大部分处于凋亡状态(图2B)。

图2 不同糖浓度对HTR8/SVneo细胞早期凋亡率的影响。A,细胞早期凋亡率的影响的流式细胞术检测;B,细胞早期凋亡率的统计学分析;**,1.57mmol/L组与5.57mmol/L组比较,P < 0.01;****,40.57mmol/L组与5.57mmol/L组比较,P<0.0001Fig. 2 The efect of diferent glucose concentrations on the early apoptosis rate of HTR8/SVneo cells. A, fow cytometry assessment of early apoptosis rates; B, statistical analysis of early apoptosis rates; **, P<0.01, 1.57mmol/L vs. 5.57mmol/L; ****, P<0.0001, 40.57mmol/L vs. 5.57mmol/L
3 高糖增强HTR8/SVneo细胞自噬相关基因表达
用含40.57mmol/L葡萄糖的培养基培养细胞24h后,提取细胞总RNA,q-PCR检测各组细胞中自噬相关分子(beclin1、beclin2和ATG7)的mRNA表达水平。结果显示,与NC相比,HG3组细胞中beclin2及ATG7 mRNA表达水平显著增高,但是beclin1 mRNA表达水平两组之间无差异(图3)。
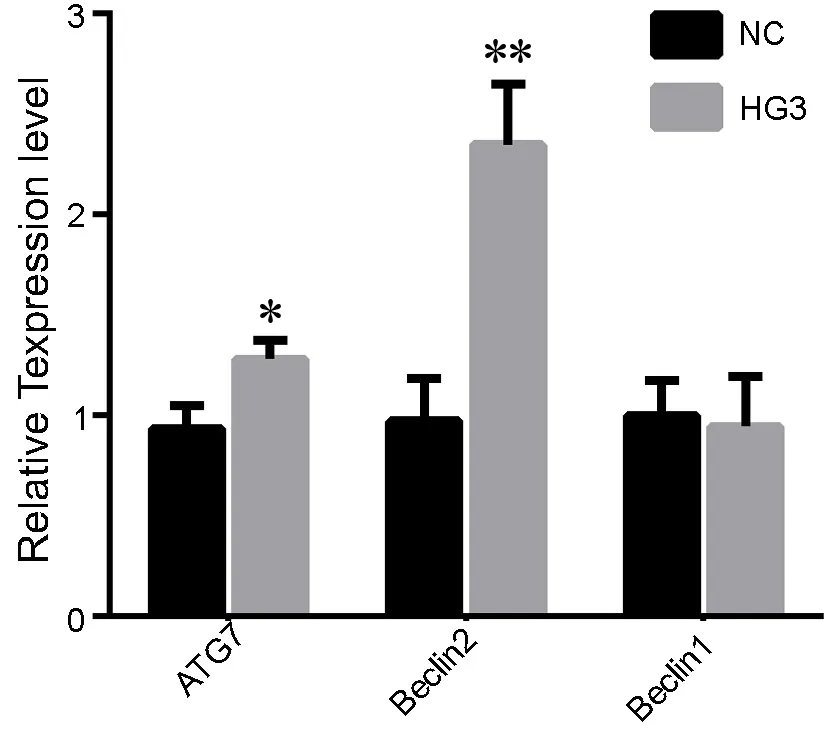
图3 高 糖 对HTR8/SVneo中ATG7、beclin1和 beclin2 mRNA表达影响的q-PCR检测。NC, 5.57mmol/L正常对照组;HG3, 40.57mmol/L高糖组;*,0.01<P<0.05;**,P<0.01Fig. 3 qPCR detection of the effect of high glucose on the levels of ATG7, beclin1 and beclin2 mRNA in HTR8/SVneo cells. NC, 5.57mmol/L normal control group; HG3, 40.57mmol/L high glucose group; *, 0.01<P<0.05; **, P<0.01

图4 高糖对HTR8/SVneo中LC3-II和p62水平的影响。A,LC3-II和p62水平的Western blot检测;B,LC3-II和p62水平的统计学分析;NC, 5.57mmol/L正常对照组;HG3, 40.57mmol/L高糖组;*,0.01<P<0.05, **,P<0.01Fig.4 The efect of high glucose on the levels of LC3-II and p62 protein in HTR8/SVneo cells. A, western blot detection of LC3-II and p62. B, statistical analysis of the levels of LC3-II and p62. NC, 5.57mmol/L normal control group; HG3, 40.57mmol/L high glucose group; *, 0.01<P<0.05; **, P<0.01
4 高糖增强HTR8/SVneo细胞中LC3-II蛋白表达,降低p62蛋白表达
本研究同时检测了自噬标志蛋白LC3-II及p62蛋白表达水平。Western blot分析显示,与NC相比,HG3组LC3-II蛋白表达水平显著升高,p62蛋白表达水平降低(图4)。
讨 论
虽然许多研究表明自噬在胎盘形成的过程中所发挥的作用是必不可少的,但GDM中胎盘绒毛膜滋养层的自噬水平及其功能还未知。我们推测高糖作为一种应激因素,可能会增强胎盘的自噬水平。因此,我们在GDM胎盘组织和HTR8/SVneo中进行了关于自噬的研究。首先,本研究通过透射电镜对GDM患者的胎盘进行了观察,发现滋养层细胞胞质中有大量的囊泡状结构存在,其游离面微绒毛出现了明显的坍塌、倒覆及数目减少的现象。其次,用HTR8/SVneo模拟高糖环境的体外研究实验表明:细胞中beclin2 、ATG7 mRNA和LC3-II蛋白高表达,p62蛋白低表达,但是在本研究中与自噬表达相关的beclin1基因表达水平并未升高。
作为维持细胞稳态的生物学过程,自噬可能参与高糖环境下细胞状态的改变。有超过20多种自噬相关基因参与自噬形成的分子过程,其中ATG7在自噬小泡的形成过程中发挥着关键性作用[11]。在特异敲除肝脏ATG7基因的小鼠中,经由糖异生作用把氨基酸转化为葡萄糖来维持血糖水平的途径受到抑制,导致饥饿时低血糖状态[12]。在胚胎早期植入的过程中检测到了LC3,ATG7这些自噬相关基因的转录[13]。除了ATG7外,beclin2作为哺乳动物特有的蛋白和beclin1一样通过与class IIIPI3K 复合物及Bcl-2相互作用来调节自噬,但是它的降解途径却异于beclin1。同时作为一个汇合的调节器,beclin2在自噬与G蛋白偶联受体之间发挥调节作用,它能够增强beclin家族在自噬中功能和机制多样性、胞内溶酶体运输和代谢的功能,并且在胎盘、子宫中高表达[14]。在本实验中,高糖环境下滋养层细胞自噬水平的增高,是beclin2而不是beclin1发挥关键作用。
本研究还发现,随着糖浓度的变化,细胞凋亡程度呈现出不同的变化趋势,当糖浓度小于5.57 mmol/L时,凋亡率随着糖浓度的减少而增多,而当糖浓度大于5.57mmol/L至15.57mmol/L时细胞凋亡水平开始发生变化,至40.57mmol/L细胞凋亡水平显著升高,这表明糖浓度对细胞凋亡发挥了非常重要的作用。在本实验中我们着重观察高糖对滋养层细胞的影响。有研究证实自噬在凋亡诱导的细胞死亡中发挥着一定的作用,抑制Hdac1而激活细胞自噬能导致细胞死亡[15];在哺乳动物细胞中过表达Beclin1也能诱导细胞死亡[16],这些可能都与细胞过度自噬而激活细胞凋亡途径最终导致细胞死亡相关。近期的研究表明处于长期的自噬激活状态能导致胚胎的凋亡[13]。因此,本研究表明:高糖环境下Beclin2介导的过度自噬与细胞凋亡相关;推测过度自噬诱导细胞凋亡进而导致胎盘浅植这一过程与妊娠期糖尿病的不良妊娠结局密切相关。
[1] American Diabetes Association. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care, 2004, 27 (Suppl 1)∶S88-90.
[2] American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2011. Diabetes Care, 2011, 34 (Suppl 1)∶S11-61.
[3] Bowen RS, Gu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Hypoxia promotes interleukin-6 and -8 but reduces interleukin-10 production by placental trophoblast cells from preeclamptic pregnancies. J Soc Gynecol Investig, 2005, 12(6)∶ 428-432.
[4] Redman CW, Sargent IL. Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science, 2005, 308(5728)∶ 1592-1594.
[5] Han CS, Herrin MA, Pitruzzello MC, et al. Glucose and metformin modulate human frst trimester trophoblast function∶ a model and potential therapy for diabetes-associated uteroplacental insufciency. Am J Reprod Immunol, 2015, 73(4)∶ 362-371.
[6] Levine B, Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell, 2008, 132(1)∶ 27-42.
[7] Green DR, Levine B. To be or not to be? How selective autophagy and cell death govern cell fate. Cell, 2014, 157(1)∶65-75.
[8] Signorelli P, Avagliano L, Virgili E, et al. Autophagy in term normal human placentas. Placenta, 2011, 32(6)∶ 482-485.
[9] Chifenti B, Locci MT, Lazzeri G, et al. Autophagy-related protein LC3 and Beclin-1 in the frst trimester of pregnancy. Clin Exp Reprod Med, 2013, 40(1)∶ 33-37.
[10] Hung TH, Chen SF, LO LM, et al. Increased autophagy in placentas of intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. PloS One, 2012, 7(7)∶ e40957.
[11] Komatsu M, Wang QJ, Holstein G, et al. Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2007, 104(36)∶14489-94.
[12] Ezaki J, Matsumoto N, Takeda-ezaki M, et al. Liver autophagy contributes to the maintenance of blood glucose and amino acid levels. Autophagy, 2011, 7(7)∶ 727-736.
[13] Song BS, Yoon SB, Kim JS, et al. Induction of autophagy promotes preattachment development of bovine embryos by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biol Reprod, 2012, 87(1)∶ 8, 1-11.
[14] He C, Wei Y, Sun K, et al. Beclin 2 functions in autophagy, degradation of G protein-coupled receptors, and metabolism. Cell, 2013, 154(5)∶ 1085-1099.
[15] Xie HJ, Noh JH, Kim JK, et al. HDAC1 inactivation induces mitotic defect and caspase-independent autophagic cell death in liver cancer. PloS One, 2012, 7(4)∶ e34265.
[16] Scott RC, Juhasz G, Neufeld T P. Direct induction of autophagy by Atg1 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptotic cell death. Curr Biol , 2007, 17(1)∶ 1-11.
High glucose induces apoptosis of chorionic trophoblast cells via beclin2-mediated autophagy
Ji Lulu1, Xiong Guoping2, Wang Lin1*(1Department of Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences,Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China;2Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Wuhan 430014, China )
ObjectiveTo investigate the efect of high glucose on the early apoptosis and autophagy of human chorionic trophoblast cells.MethodsFull-term placenta tissue was sampled from normal cases and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) cases, and the changes in the ultrastructure of trophoblast cells were observed by transmission electron microscopy. HTR8/SVneo trophoblast cells were cultured in vitro in low, normal and high glucose conditions (LG1∶ 1.57mmol/L, LG2∶ 2.25mmol/L, NC∶ 5.57mmol/L, HG1∶ 10.57mmol/L, HG2∶ 15.57mmol/L, HG3∶ 40.57mmol/L) for 24 hours. The early apoptosis rate was measured by fow cytometry. The mRNA levels of autophagy-related genes Beclin2, ATG7 and Beclin1 were analyzed by qPCR. The levels of LC3-II and p62 protein were detected by western blot.ResultsAutophagosomes were observed by transmission electron microscopy in trophoblast cells in the GDM group, as well as an increased number of vacuoles compared with that of the normal group. Remarkable collapse of microvilli on the free surface was also observed in the GDM group. The fow cytometry results showed that the early apoptosis rate was signifcantly higher in groups LG1 and HG3 than in group NC. The qPCR test displayed that the levels of beclin2 and ATG7 mRNA increased obviously in group HG3, while that of beclin1 mRNA showed no signifcant diference from group NC. The western blot results showed that the level of LC3-II protein was higher and that of p62 lower in group HG3 than in group NC.ConclusionHigh glucose promotes the autophagy of trophoblast cells via Beclin2-mediated signaling, which results in cell apoptosis and may lead to adverse fetal outcomes.
Gestational diabetes mellitus; HTR8/SVneo; autophagy; apoptosis; beclin2
R329.1
A
10.16705/ j. cnki. 1004-1850.2017.02.003
2017-01-11
2017-03-30
纪璐璐,女(1990年),汉族,医学硕士
*通讯作者(To whom correspondence should be addressed):lin.wang@whu.edu.cn

