不确定拟哈密顿系统的随机最优控制*
胡荣春 应祖光朱位秋
(浙江大学航空航天学院力学系,杭州 310027)
不确定拟哈密顿系统的随机最优控制*
胡荣春 应祖光†朱位秋
(浙江大学航空航天学院力学系,杭州 310027)
本文提出了不确定拟哈密顿系统、基于随机平均法、随机极大值原理和随机微分对策理论的一种随机极大极小最优控制策略.首先,运用拟哈密顿系统的随机平均法,将系统状态从速度和位移的快变量形式转化为能量的慢变量形式,得到部分平均的Itô随机微分方程;其次,给定控制性能指标,对于不确定拟哈密顿系统的随机最优控制,根据随机微分对策理论,将其转化为一个极小极大控制问题;再根据随机极大值原理,建立关于系统与伴随过程的前向-后向随机微分方程,随机最优控制表达为哈密顿控制函数的极大极小条件,由此得到最坏情形下的扰动参数与极大极小最优控制;然后,将最坏扰动参数与最优控制代入部分平均的Itô随机微分方程并完成平均,求解与完全平均的Itô随机微分方程相应的Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov(FPK)方程,可得受控系统的响应量并计算控制效果;最后,将上述不确定拟哈密顿系统的随机最优控制策略应用于一个两自由度非线性系统,通过数值结果说明该随机极大极小控制策略的控制效果.
不确定性,极大极小最优控制,极大值原理,随机平均法
引言
工程结构动力学大多可以通过拟哈密顿系统建立数学模型,拟哈密顿系统的随机最优控制研究具有重要的理论与实际意义.基于随机动态规划原理的随机最优控制已有较多研究[1-3].然而,随机极大值原理是随机最优控制的另一个基本原理[2],基于此的随机最优控制研究相对较少,需要进一步深入研究.此外,实际结构系统例如参数总存在一定的随机性,相应的数学模型具有不确定性.不确定拟哈密顿系统的基于随机极大值原理的随机最优控制有待于研究发展.不确定系统的鲁棒控制已有很多研究,而微分对策理论是解决不确定系统最优控制的一个重要方法.本文简要介绍一个不确定拟哈密顿系统的随机最优控制策略,它综合运用随机平均法、随机极大值原理与微分对策理论.
1 随机平均控制系统
考虑如下多自由度受控的具有不确定参数的拟哈密顿系统:
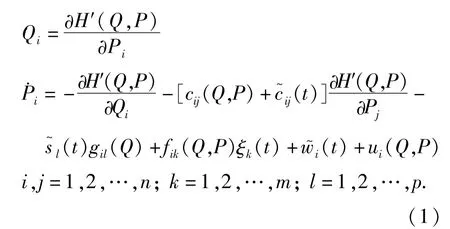
式中Qi、Pi分别为广义位移与广义动量,Q=[Q1,Q2,…,Qn]T,P=[P1,P2,…,Pn]T;H′=H′(Q,P)为具有连续偏导数的哈密顿函数;cij=cij(Q,P)表示拟线性阻尼系数;gil=gil(Q)表示非线性恢复力;fik=fik(Q,P)表示随机激励幅值;为ξk(t)随机过程;分别表示参数与激励的扰动部分;ui=ui(Q,P)表示反馈控制力.假定系统扰动及控制力的量级分别为,其中ε为小量.扰动参数都是有界的,即以及.
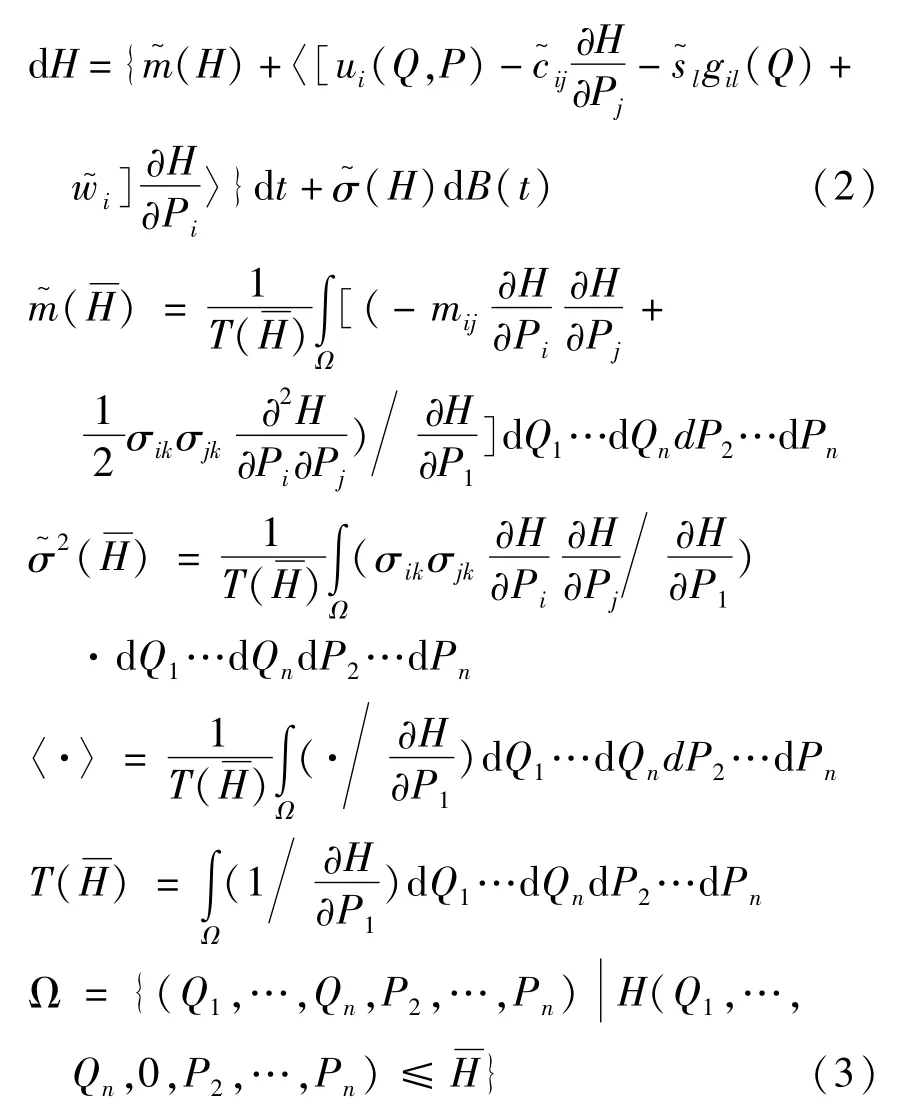
式中H为平均的哈密顿函数,B为标准Wiener过程.类似地,对于可积非共振情形,拟可积哈密顿系统的平均方程为:
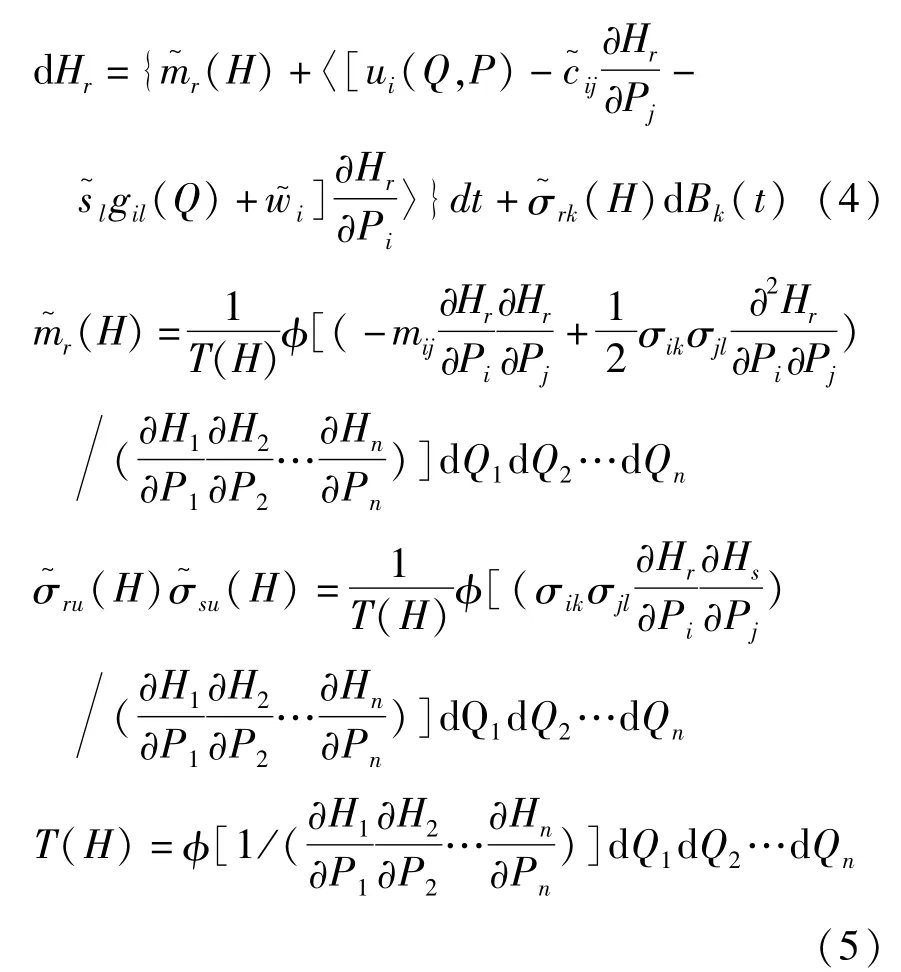
式中H为独立积分向量.系统控制的性能指标[5],如不确定拟不可积哈密顿系统(2)的有限时间控制指标
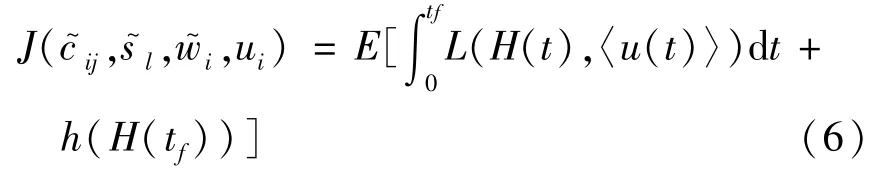
式中E[.]表示平均算子;tf是控制的终止时间;L称为成本函数;h为终止成本.
2 基于极大极小的随机最优控制
方程(2)和(6)组成不确定系统的随机最优控制问题.根据随机微分对策理论,该控制问题可以表达为下列极小极大控制问题:
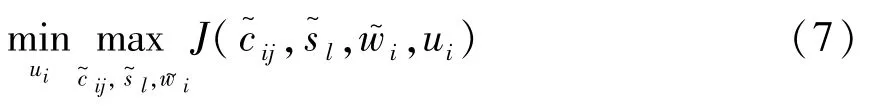
根据随机极大值原理[2],极小极大控制问题可以转化为哈密顿函数Hc的极大极小控制问题,Hc满足前后向随机微分方程.哈密顿函数的极大极小条件为
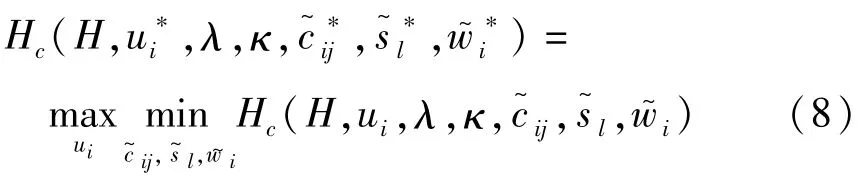
式中λ、κ是伴随过程,
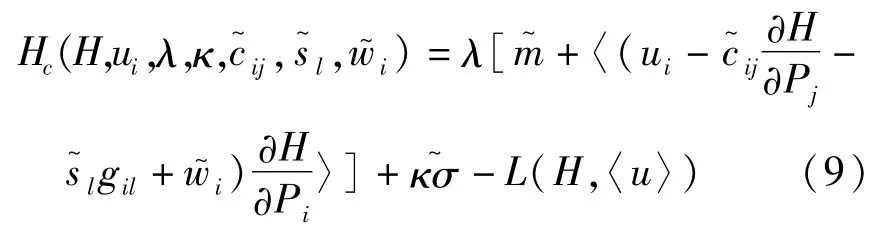

对于二次型控制力的函数L:
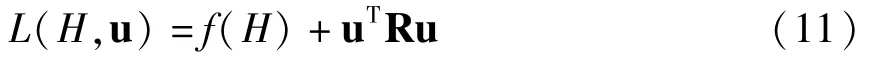
式中R对称正定,f(H)>0.由式(9)右端项关于ui极大化,可得最优控制[5]:
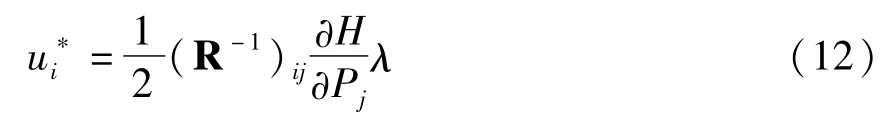
将最优控制(12)和最坏扰动(10)代入式(2),得到平均系统方程:
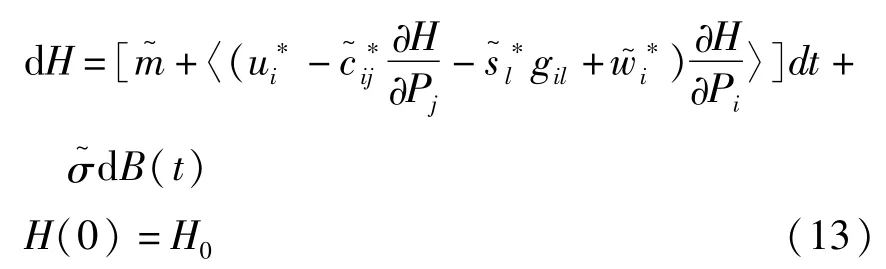
相应的随机极大值原理确定的一阶伴随方程为
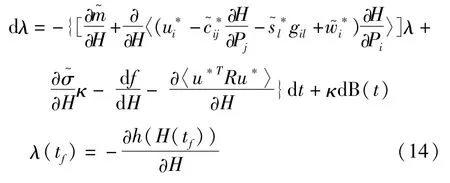
方程(13)和(14)组成确定哈密顿函数Hc的前后向随机微分方程,求解该方程得到受控系统的响应和伴随过程,从而确定最优控制(12).
假设伴随过程λ(t)仅仅通过系统能量而随时间t变化,即:

这里λ(H)是某个确定性函数.对等式(15)应用Itô微分得到关于λ的微分方程,与(14)比较可得关于λ和κ的方程,简化后得到关于λ(H)的方程:
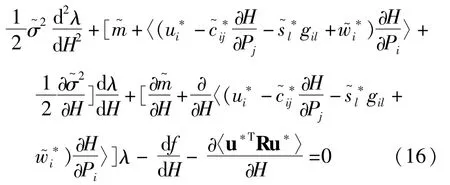
给定边界条件,求解该二阶常微分方程,得到伴随函数λ(H),代入式(12)即得最坏扰动下的最优控制[7].
3 应用简例
考虑一个两自由度不确定非线性控制系统:
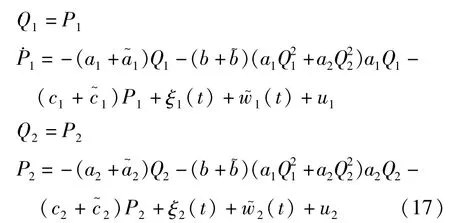
式中a1,a2,b,c1和c2为理想情形的刚度和阻尼系数;为有界扰动,满足及;ξk(t)是强度为2Dk的独立高斯白噪声;ui为反馈控制力.该系统为拟不可积系统,运用拟不可积哈密顿系统的随机平均法,可得平均的Itô微分方程(2).对于性能指标(6),根据极大极小控制策略确定最坏扰动:
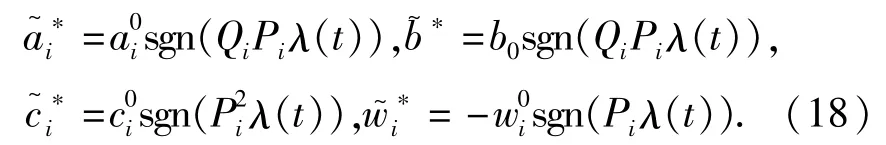
进一步确定最优控制力:

相应的伴随过程可由式(16)确定,其中f(H)=s0+s1H+s2H2+s3H3,u=(u1,u2),R=(R1,R2).将最坏扰动(18)和最优控制力(19)代入式(13),得到平均方程,建立相应的FPK方程,求解之可得概率密度,从而可估计受控系统的响应方差,及系统响应的相对降低,即:
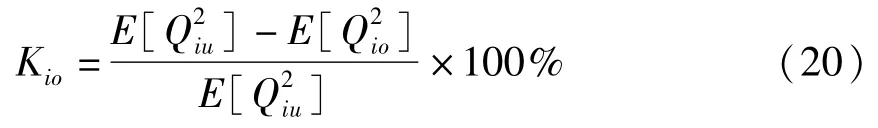
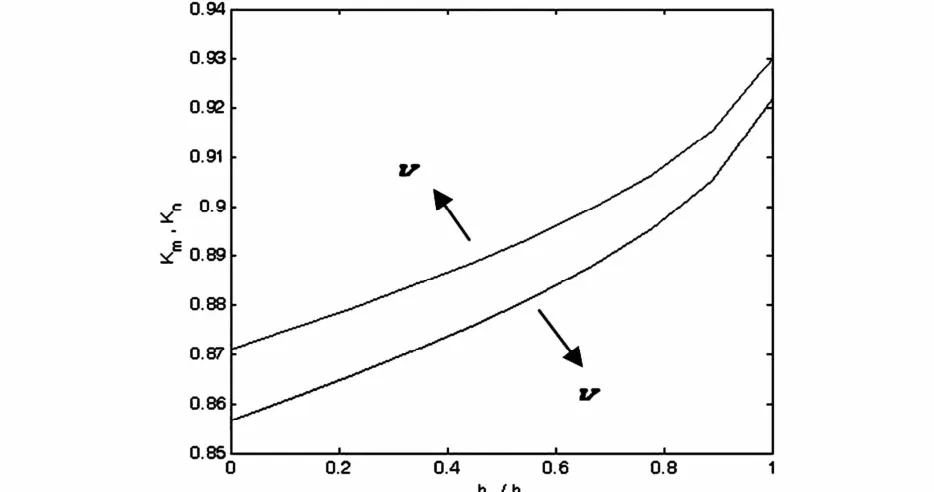
图1 系统第一个自由度位移的相对降低随参数相对扰动界b0/b的变化(Km是本文最优控制的效果,Kn是平均参数系统最优控制的效果)Fig.1 The relationships of control effectiveness(Km/Kn)to the ratio of parameter disturbance(b0/b)for the first DOF of the system(where Kmfor minimax control and Knfor nominal control)
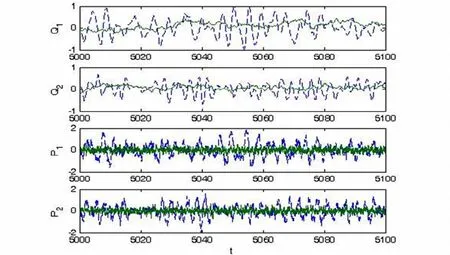
图2 极大极小控制系统与未控系统的位移和速度(虚线为未控系统响应,实线为控制系统响应)Fig.2 Time history of the system displacement and velocity(where dashed line for uncontrolled system,while solid line for minimax controlled system)
选取无量纲量参数值a1=1,a2=2,b=2,c1=c2=0.5,R1=R2=0.4,s1=0,s2=2.0,s3=0,b0=0.2,λ(0)=-3.7.图1给出系统第一个自由度位移的相对降低随参数相对扰动界b0/b的变化情况,可见系统响应的相对降低即控制效果随扰动参数界b0的增大而非线性地提高.本文介绍的极大极小最优控制效果高于相应的平均参数系统最优控制.图2为极大极小最优控制前后系统的位移和速度样本图.研究表明:本文提出的极大极小最优控制策略能有效地降低系统的速度和位移等响应量,在控制效果方面明显优于平均参数系统最优控制,而相应的控制效率尚则有待于进一步研究.
1 Stengel R F.Stochastic optimal control.New York,Wiley,1986
2 Yong JM,Zhou X Y.Stochastic controls,hamiltonian systems and HJB equations.New York,Springer-Verlag,1999
3 朱位秋,应祖光.拟哈密顿系统非线性随机最优控制.力学进展,2013,43(1):39~55(Zhu W Q,Ying Z G.Nonlinear stochastic optimal control of quasi-Hamiltonian systems.Advances in Mechanics,2013,43(1):39~55(in Chinese))
4 应祖光,洪沁.一种基于随机平均的最优时滞控制方法.动力学与控制学报,2008,6(3):260~264(Ying Z G,Hong Q.An optimal time delay control method based on the stochastic averaging.Journal of Dynamics and Control,2008,6(3):260~264(in Chinese))
5 陈林聪,朱位秋.随机扰动下简单电力系统的可靠度反馈最大化.动力学与控制学报,2010,8(1):19~23(Chen L C,Zhu W Q.Feedback maximization of reliability of a simple power system under random perturbations.Journal of Dynamics and Control,2010,8(1):19~23(in Chinese))
6 Zhu W Q,Yang Y Q.Stochastic averaging of quasi non-integrable Hamiltonian systems.ASME Journal of Applied Mechanics,1997,64(1):157~164
7 Zhu W Q,Ying Z G,Soong T T.An optimal nonlinear feedback control strategy for randomly excited structural systems.Nonlinear Dynamics.,2001,24(1):31~51
8 Ying ZG.A minimax stochastic optimal control for bounded-uncertain systems.Journal of Vibration and Control,2010,16(11):1591~1604
9 Hu R C,Ying ZG,Zhu W Q.Stochastic minimax optimal control strategy for uncertain quasi-Hamiltonian systems using stochastic maximum principle.Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization,2014,49(1):69~80
Received 12 January 2015,revised 4 February 2015.
*The project Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(11432012,11572279)
†Corresponding author E-mail:yingzg@zju.edu.cn
STOCHASTIC OPTIMAL CONTROL OF UNCERTAIN QUASI-HAMILTONIAN SYSTEMS*
Hu Rongchun Ying Zuguang†Zhu Weiqiu
(Department of Mechanics,School of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310027,China)
In this paper,a stochastic minimax optimal control strategy for uncertain quasi-Hamiltonian systems is proposed based on stochastic averaging method,stochastic maximum principle and stochastic differential game theory.Firstly,the partially averaged Itô stochastic differential equations are derived using the stochastic averaging method for quasi-Hamiltonian systems,while the system state transits from rapid variable of velocity and displacement into the slow variable of energy.Secondly,the stochastic optimal control of Hamiltonian system with a given performance index is converted into a minimax control problem based on the stochastic differential game theory.Thirdly,forward-backward stochastic differential equations of the system and the adjoint process were established according to stochastic maximum principle.The worst disturbances are generated by minimizing the Hamiltonian function,while maximizing the minimal Hamiltonian function results in the worst-case optimal controls.The worst disturbances and the worst-case optimal controls are then substituting into the partially averaged Itô equation in order to obtain the fully averaged Itô equation.The responses of controlled system are predicted by solving the Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov(FPK)equation associated with the fully averaged Itô equation.Meanwhile,the control effectiveness can also be computed.Finally,the proposed stochastic optimal control of uncertain quasi-Hamiltonian system is applied into a two-DOF nonlinear system.The effectiveness of the minimax control strategy is validated by numerical results.
Hamiltonian system,uncertainty,minimax optimal control,stochastic maximum principle,stochastic averaging method
10.6052/1672-6553-2016-065
2015-01-12收到第1稿,2015-02-04收到修改稿.
*国家自然科学基金资助项目(11432012,11572279)
†通讯作者E-mail:yingzg@zju.edu.cn

