热缺血再灌注损伤早期大鼠肝脏基因表达谱的实验研究
李文川++高良奎++李浩航++许佐明++罗宗将++汪建初++陆涛 浦涧

【摘要】目的探讨热缺血再灌注损伤(WIRI)早期大鼠肝脏基因表达谱的差异。
方法建立SD大鼠肝脏热缺血再灌注损伤模型,取再灌注30 min和再灌注1 h肝组织标本,采用基因表达谱芯片技术检测各组基因表达的变化情况,确定差异表达基因。
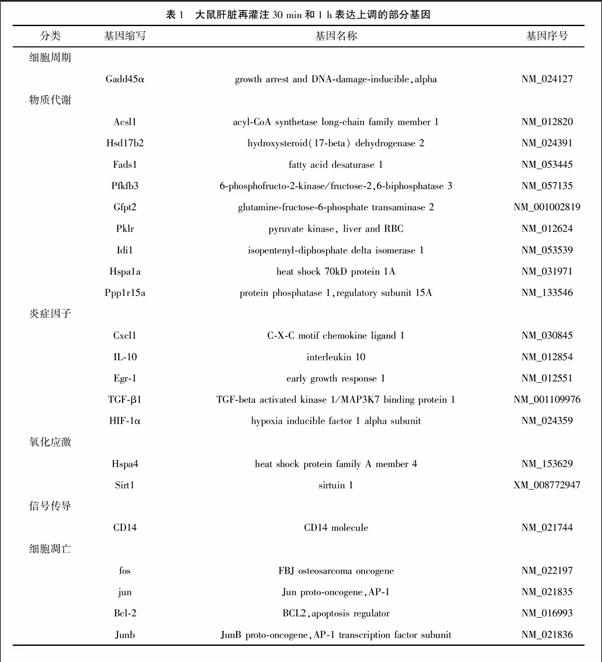
结果筛选出大鼠肝脏再灌注30 min、再灌注1 h两组共同差异表达基因有77条,其中表达上调56条,表达下调21条。 再灌注30 min或1 h表达上调的基因数均多于表达下调基因数,再灌注1 h表达发生变化的基因总数多于再灌注30 min。
結论大鼠肝脏热缺血再灌注损伤伴随多基因的表达谱改变,再灌注损伤早期的差异表达基因为研究肝脏WIRI的分子机制提供实验依据。
【关键词】肝脏;基因表达;再灌注损伤
中图分类号:R657.3文献标识码:ADOI:10.3969/j.issn.10031383.2017.01.006
A experimental study on gene expression profiles in rats liver at early phase of warm ischemia and reperfusion injury
[HJ1][HJ]
LI Wenchuan1,GAO Liangkui1,LI Haohang1,XU Zuoming1,LUO Zongjiang1,WANG Jianchu2,LU Tao2,PU Jian2▲
(1.Graduate School,2.Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of Affiliated Hospital,Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities,Baise 533000,China)
[HJ2][HJ]
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo explore difference of gene expression profiles in rats liver at early phase of warm ischemia and reperfusion injury(WIRI).
MethodsLiver WIRI model of SD rats was established,and liver tissue samples with 30 min and 1 h of reperfusion were taken.Gene expression microarray was used to detect changes of gene expression in each group,so as to identify differential expressed genes(DEGs).
ResultsThe analysis data of the microarray showed that there were 77 common DEGs including 56 upregulated genes and 21 downregulated genes at both 30 min and 1 h of reperfusion.The number of upregulated genes at 30 min or 1 h of reperfusion was larger than that of downregulated genes.And the number of DEGs at 1 h of reperfusion was larger than that 30 min of reperfusion.
ConclusionWIRI of rats livers are always complicated with profile changes of multi gene expression,and differential expressed genes at early phase of reperfusion injury can provide experimental basis to molecular mechanism of liver WIRI.
【Key words】liver;gene expression;reperfusion injury
肝脏热缺血再灌注损伤(warm ischemia and reperfusion injury,WIRI)是肝移植和肝脏切除术中出现的主要临床问题[1]。其主要特征在于肝细胞损伤、无菌性炎症及术后肝功能障碍[2]。研究表明[3~4]热缺血诱导的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)生成及许多炎症介质的释放有助于并加重再灌注早期诱导组织损伤。因此,本实验采用基因表达芯片技术对WIRI早期大鼠肝脏基因表达谱的改变进行大规模、高通量、并行分析,初步筛选再灌注损伤早期调节其表达显著的功能基因,并讨论与以前研究的相似性和差异性,为进一步阐明热缺血再灌注损伤早期的分子调控机制提供理论基础。
1材料与方法
1.1实验动物模型的建立
SPF级雄性SpragueDawley(SD)大鼠16只,体重320~380 g,由右江民族医学院动物中心(许可证号:SCXK桂20120003)提供。术前禁食但可适量饮水。称重后采用10%水合氯醛300 mg/kg腹腔注射麻醉,取腹部纵切口,离断镰状韧带及左右三角韧带,分离肝胃韧带,游离门静脉及肝固有动脉。3 min后将门静脉和肝固有动脉阻断30 min,造成原位肝脏热缺血模型,切取标本,即热缺血30 min组。再灌注损伤组为阻断30 min后恢复肝脏血流后30 min、1 h分别切取标本。假手术组仅常规进腹后,游离但不予结扎肝十二指肠韧带内血管,30 min后切取标本。

