腹腔镜胃旁路术治疗肥胖合并2型糖尿病的临床效果①
鲍 峰,向荣超,鲜于剑波,王 东,李国强,邓志刚,向春华,智 星,刘 文
(绵阳市中心医院,四川 绵阳,621000)
·论 著·
腹腔镜胃旁路术治疗肥胖合并2型糖尿病的临床效果①
鲍 峰,向荣超,鲜于剑波,王 东,李国强,邓志刚,向春华,智 星,刘 文
(绵阳市中心医院,四川 绵阳,621000)
目的:探讨腹腔镜Roux-en-Y胃旁路术(laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass,LRYGB)治疗肥胖合并2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)的临床效果。方法:回顾分析2009年3月至2013年5月为7例肥胖合并T2DM患者行LRYGB的临床资料,随访3年,分析手术前后糖脂代谢指标的变化。结果:7例手术均获成功,无一例中转开腹,术前体重指数(body mass index,BMI)≥27.5 kg/m2,与术前相比,术后3年BMI下降[(26.47±1.24) vs.(29.87±2.17),P<0.05],空腹血糖[(5.90±0.76) vs.(8.24±2.19),P<0.05]、糖化血红蛋白HbA1c[(6.28±0.42) vs.(8.06±1.73),P<0.05]、总胆固醇[(4.27±0.22) vs. (5.10±0.49),P<0.05]、三酰甘油[(1.59±0.10) vs. (1.97±0.14),P<0.05]、低密度脂蛋白[(2.67±0.32) vs.(3.22±0.12),P<0.05]、高密度脂蛋白[(1.14±0.06) vs.(1.04±0.05),P<0.05]较术前均有明显改善。术后患者均无严重并发症发生。结论:LRYGB治疗肥胖合并T2DM可显著降低患者的BMI,改善血糖、血脂水平,手术安全、有效,值得临床推广应用。
肥胖症;糖尿病,2型;腹腔镜检查;胃旁路术
近年,腹腔镜Roux-en-Y胃旁路术(laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass,LRYGB)已成为治疗肥胖合并2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)的有效方法[1-6],不仅可有效降低体重,还可缓解甚至治愈T2DM及其多种并发症[3,7-8]。国际糖尿病联盟(international diabetes federation,IDF)公布的糖尿病治疗指南(2011版)中已将亚洲人群糖尿病手术治疗的适应证调整至体重指数(body mass index,BMI)≥27.5 kg/m2[9]。然而,对于手术治疗肥胖合并T2DM临床效果的长期随访资料仍较少[10-11]。自2009年我院普通外科开展LRYGB治疗肥胖合并T2DM以来,其中BMI≥27.5 kg/m2并随访3年的患者共7例,现回顾性分析7例患者的临床资料,探讨LRYGB治疗肥胖合并T2DM的临床效果。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料 2009年3月至2013年5月共7例患者,其中男2例,女5例;36~63岁,平均(50.3±8.8)岁,BMI为27.5~33.0 kg/m2,平均(29.9±2.2) kg/m2,糖尿病病程2~12年,平均(5.4±3.4)年。术前均不同程度使用胰岛素治疗。术前由内分泌科医生按照2009年美国糖尿病学会(American diabetes association,ADA)糖尿病指南明确诊断为T2DM[12]。患者均被告知手术风险并知情同意,经医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 手术方法 均行常规LRYGB,符合指南操作要求[13]。常规气管插管,全身麻醉,采用5孔法行LRYGB。助手拨开肝左叶,术者游离胃大弯至His角,于胃左动脉第1分支以下无血管区分离肝胃韧带进入网膜囊,直线切割闭合器分次将胃底横行切断,建立小胃囊,容积15~25 ml;Treitz韧带下75~150 cm处横断空肠,远端空肠在横结肠前方上提至小胃囊处,行小胃囊与小肠侧侧吻合,近端空肠在胃空肠吻合口下75~100 cm与空肠行“Y”形吻合。检查吻合口无渗漏后,分别于右肝下、脾窝放置腹腔引流。见图1。

图1 手术操作方法。A:分离肝胃韧带进入网膜囊。B:直线切割闭合器分次将胃底横行切断,建立小胃囊,容积15~25 ml。C:近端空肠在胃空肠吻合口下75~100 cm与空肠行“Y”形侧侧吻合。D:缝合空肠侧侧吻合开口。E:小胃囊与小肠侧侧吻合。F:缝合胃空肠侧侧吻合口开口。
1.3 术后指导及随访 术后第1~2天:禁食、抑酸、控制血糖、肠外营养支持,鼓励患者早期下床活动;术后第3天:上消化道造影未见吻合口渗漏后拔除胃管,开始少量饮水及进流质饮食;术后第5~7天出院。出院后长期口服补充复合维生素及铁、叶酸等。术后第3、6、12个月回院复查,此后每年复查1次,随访截至2016年5月10日。
1.4 观察指标 BMI,空腹血糖(fasting plasma glucose,FPG)、糖化血红蛋白A1c (hemoglobin A1c,HbA1c);三酰甘油(triacylglycerol,TG)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、低密度脂蛋白(low density lipoprotein,LDL)及高密度脂蛋白(high density lipoprotein,HDL)。
1.5 统计学处理 应用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计分析,配对样本均数比较采用配对t检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
7例均顺利完成LRYGB,并获得术后随访。无一例中转开腹或死亡病例。术后均未发生吻合口狭窄、梗阻、瘘等并发症,术后营养不良2例,轻度贫血4例,对症处理后好转。术后3个月时,7例患者均无需使用任何药物,血糖水平保持长期正常。术前BMI平均(29.87±2.17) kg/m2,术后第3年平均(26.47±1.24) kg/m2,与术前相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。患者术后第3年FPG、HbA1c、TG、TC、HDL、LDL较术前均有明显改善(P<0.05)。见表1、图2~图4。
3 讨 论
肥胖症与T2DM是在世界范围内广泛流行的危害人类健康的两种重要疾病。减肥手术是目前最成功的治疗肥胖症的方法,手术在取得显著、持久减肥效果的同时显著缓解了并发的T2DM。目前,减肥手术已被美国糖尿病协会写入T2DM治疗指南,成为T2DM的重要治疗方案之一[14]。
胃旁路术最早由Mason医生于1967年报道[15],手术方式几经改进,最后发展为目前的Roux-en-Y胃旁路术(Roux-en-Y gastric bypass,RYGB),这是目前最主要的减肥术式之一,对T2DM的有效缓解率高达84%[16],是目前治疗肥胖及T2DM的常见术式[17-19],对血糖的改善及体重下降方面优于非手术治疗[20-22]。RYGB不仅可纠正肥胖及T2DM患者的代谢紊乱,并有研究表明对多种代谢相关性疾病均具有良好的治疗作用[23-24]。近年,RYGB治疗肥胖合并T2DM在国内得到快速发展,其治疗效果也得到了不少临床研究的验证[25-26],为手术治疗肥胖合并T2DM提供了依据。
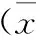
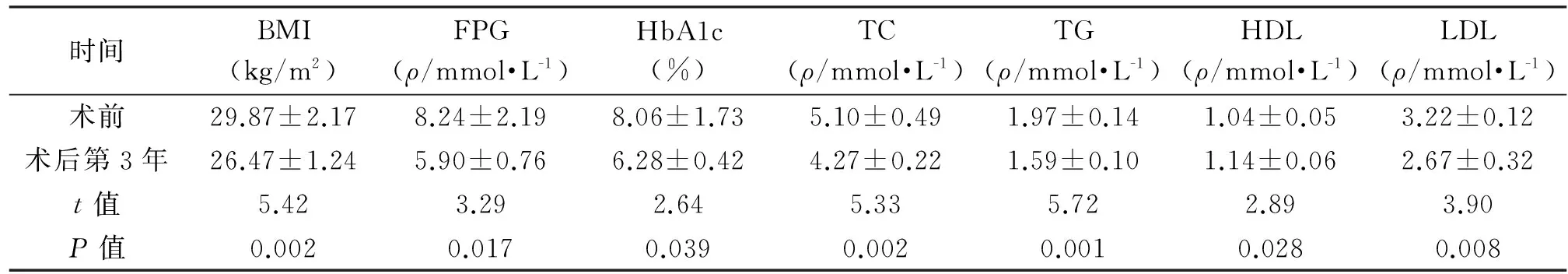
时间BMI(kg/m2)FPG(ρ/mmol·L-1)HbA1c(%)TC(ρ/mmol·L-1)TG(ρ/mmol·L-1)HDL(ρ/mmol·L-1)LDL(ρ/mmol·L-1)术前29.87±2.178.24±2.198.06±1.735.10±0.491.97±0.141.04±0.053.22±0.12术后第3年26.47±1.245.90±0.766.28±0.424.27±0.221.59±0.101.14±0.062.67±0.32t值5.423.292.645.335.722.893.90P值0.0020.0170.0390.0020.0010.0280.008
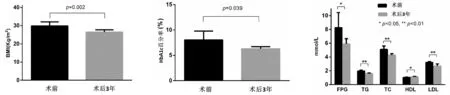
图2 术前及术后3年BMI变化 图3 术前及术后3年HbA1c百分率变化 图4 术前及术后3年糖脂代谢指标变化
目前手术治疗肥胖合并T2DM对患者BMI有较严格的要求,中国肥胖、T2DM外科治疗指南(2014)对于BMI<27.5 kg/m2的患者推荐为慎重开展手术。对于BMI<27.5 kg/m2的患者有研究表明术后临床效果欠佳。吴良平等[27]为20例BMI<28 kg/m2的T2DM患者行胃旁路术,随访3年发现与术前相比,术后BMI差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),术后HbA1c控制达标率仅为55.0%。但BMI并非影响手术效果的唯一因素,Dixon等[28]通过对154例华人病例行RYGB后1年血糖情况的logistic回归分析,认为影响手术效果的因素主要有BMI、糖尿病病程长短、空腹C肽及体重下降情况。
对手术治疗肥胖合并T2DM的术式选择,目前开展较多且被广泛认可的主要有:RYGB、胆胰转流及十二指肠转流术、胃袖状切除术(sleeve gastrectomy,SG)、可调节胃束带术、迷你胃旁路术等[29]。LRYGB与腹腔镜胃袖状切除术是目前手术治疗肥胖合并T2DM的常用术式,均具有较好的控制体重及血糖的作用[1,30]。汤聪等[31]通过对RYGB及SG对肥胖合并T2DM近、远期疗效的Meta 分析后认为,RYGB及SG手术均是治疗肥胖合并T2DM 的有效措施,其近、远期疗效随随访时间无明显下降,但RYGB术后T2DM缓解率较SG高,认为RYGB治疗T2DM 的疗效优于SG 手术。Dogan等[8]通过对52例严重肥胖合并T2DM患者行LRYGB术后随访(6.9±2.3)年后发现,此术式对于肥胖合并的糖尿病、血脂紊乱、高血压等均有明显的长期改善作用。因此RYGB是目前治疗肥胖合并T2DM的首选术式[29]。本组7例肥胖合并T2DM患者术后3年效果良好,糖脂代谢均较术前显著改善(P<0.05)。表明手术治疗肥胖合并T2DM的疗效显著。
综上,LRYGB治疗肥胖合并T2DM安全、有效,可显著降低患者的BMI,改善血糖、血脂水平。相信随着相关研究的不断深入,会促进其更加广泛的应用于临床。
[1] Lee WJ,Chong K,Ser KH,et al.Gastric bypass vs sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes mellitus:a randomized controlled trial[J].Arch Surg,2011,146(2):143-148.
[2] Schauer PR,Kashyap SR,Wolski K,et al.Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes[J].N Engl J Med,2012,366(17):1567-1576.
[3] Ikramuddin S,Korner J,Lee WJ,et al.Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes,hypertension,and hyperlipidemia:the Diabetes Surgery Study randomized clinical trial[J].JAMA,2013,309(21):2240-2249.
[4] Liang Z,Wu Q,Chen B,et al.Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension:a randomized controlled trial[J].Dia Res Clin Pract,2013,101(1):50-56.
[5] Wentworth JM,Playfair J,Laurie C,et al.Multidisciplinary diabetes care with and without bariatric surgery in overweight people:a randomised controlled trial[J].Lancet,2014,2(7):545-552.
[6] Schauer PR,Bhatt DL,Kirwan JP,et al.Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes--3-year outcomes[J].N Engl J Med,2014,370(21):2002-2013.
[7] Zou J,Zhang P,Yu H,et al.Effect of Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery on Obstructive Sleep Apnea in a Chinese Population with Obesity and T2DM[J].Obes Surg,2015,25(8):1446-1453.
[8] Dogan K,Betzel B,Homan J,et al.Long-term effects of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on diabetes mellitus,hypertension and dyslipidaemia in morbidly obese patients[J].Obes Surg,2014,24(11):1835-1842.
[9] Dixon JB,Zimmet P,Alberti KG,et al.Bariatric surgery:an IDF statement for obese Type 2 diabetes[J].Dia Med,2011,28(6):628-642.
[10] Lebovitz HE.Metabolic surgery for type 2 diabetes with BMI <35 kg/m(2):an endocrinologist's perspective[J].Obes Surg,2013,23(6):800-808.
[11] Maggard-Gibbons M,Maglione M,Livhits M,et al.Bariatric surgery for weight loss and glycemic control in nonmorbidly obese adults with diabetes:a systematic review[J].JAMA,2013,309(21):2250-2261.
[12] American Diabetes A.Standards of medical care in diabetes-2009[J].Diabetes Care,2009,32 Suppl 1:S13-61.
[13] 刘金刚,郑成竹,王勇.中国肥胖和2型糖尿病外科治疗指南(2014)[S].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(11):1005-1010.
[14] American Diabetes A.Standards of medical care in diabetes--2014[J].Diabetes Care,2014,37 Suppl 1:S14-80.
[15] Mason EE,Ito C.Gastric bypass in obesity[J].Surg Clin North Am,1967,47(6):1345-1351.
[16] Buchwald H,Estok R,Fahrbach K,et al.Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery:systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Am J Med,2009,122(3):248-256,e245.
[17] Yip S,Plank LD,Murphy R.Gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes:a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes[J].Obes Surg,2013,23(12):1994-2003.
[18] Pournaras DJ,Aasheim ET,Sovik TT,et al.Effect of the definition of type II diabetes remission in the evaluation of bariatric surgery for metabolic disorders[J].Br J Surg,2012,99(1):100-103.
[19] Hayes MT,Hunt LA,Foo J,et al.A model for predicting the resolution of type 2 diabetes in severely obese subjects following Roux-en Y gastric bypass surgery[J].Obes Surg,2011,21(7):910-916.
[20] Dorman RB,Serrot FJ,Miller CJ,et al.Case-matched outcomes in bariatric surgery for treatment of type 2 diabetes in the morbidly obese patient[J].Ann Surg,2012,255(2):287-293.
[21] Demssie YN,Jawaheer J,Farook S,et al.Metabolic outcomes 1 year after gastric bypass surgery in obese people with type 2 diabetes[J].Med Prin Pract,2012,21(2):125-128.
[22] Serrot FJ,Dorman RB,Miller CJ,et al.Comparative effectiveness of bariatric surgery and nonsurgical therapy in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and body mass index <35 kg/m2[J].Surgery,2011,150(4):684-691.
[23] Sharkey KA.Animal models of bariatric/metabolic surgery shed light on the mechanisms of weight control and glucose homeostasis:view from the chair[J].Int J Obes(Lond),2011,35 Suppl 3:S31-34.
[24] Hofso D,Nordstrand N,Johnson LK,et al.Obesity-related cardiovascular risk factors after weight loss:a clinical trial comparing gastric bypass surgery and intensive lifestyle intervention[J].Eur J Endoc,2010,163(5):735-745.
[25] Sovik TT,Aasheim ET,Taha O,et al.Weight loss,cardiovascular risk factors,and quality of life after gastric bypass and duodenal switch:a randomized trial[J].Ann Int Med,2011,155(5):281-291.
[26] Carlsson LM,Peltonen M,Ahlin S,et al.Bariatric surgery and prevention of type 2 diabetes in Swedish obese subjects[J].N Engl J Med,2012,367(8):695-704.
[27] 吴良平,文其武,曾松华,等.腹腔镜胃旁路术治疗2型糖尿病44例疗效分析[J].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(11):1060-1063.
[28] Dixon JB,Chuang LM,Chong K,et al.Predicting the glycemic response to gastric bypass surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Care,2013,36(1):20-26.
[29] 程中,杜潇.2型糖尿病外科治疗术式合理选择及评价[J].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(11):1030-1032.
[30] 廉东波,朱斌,樊庆,等.腹腔镜胃旁路术和胃袖状切除术治疗肥胖合并2型糖尿病疗效对比分析[J].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(11):1056-1059.
[31] 汤聪,梁文丰,岑宏,等.袖状胃切除及胃旁路手术对合并肥胖2型糖尿病近、远期疗效的Meta分析[J/CD].中华普通外科学文献(电子版),2014,8(4):321-331.
(英文编辑:杨庆芸)
Clinical effect of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for the treatment of obesity with type 2 diabetes mellitus
BAOFeng,XIANGRong-chao,XIANYUJian-bo,etal.
DepartmentofGeneralSurgery,MianyangCentralHospital,Mianyang621000,China
Objective:To investigate the clinical effect of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) for the treatment of obesity with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.Methods:The clinical data of 7 patients of obesity with T2DM performed LRYGB surgery between Mar.2009 and May 2013 in the department of general surgery of Mianyang Central Hospital were analyzed retrospectively.The changes of glucose and lipid metabolism indicators of 7 patients were analyzed after 3 years of follow-up.Results:All 7 cases of obesity with T2DM were successfully operated,and no case was converted to laparotomy,all the patients’ preoperative body mass index (BMI) were ≥27.5 kg/m2.Compared with the preoperative data,postoperative patients’ BMI decreased significantly [(26.47±1.24) vs. (29.87±2.17),P<0.05],and the fasting plasma glucose [(5.90±0.76) vs. (8.24±2.19),P<0.05],the hemoglobin HbA1c [(6.28±0.42) vs. (8.06±1.73),P<0.05],the total cholesterol [(4.27±0.22) vs. (5.10±0.49),P<0.05],the triacylglycerol [(1.59±0.10) vs. (1.97±0.14),P<0.05],the low density lipoprotein [(2.67±0.32) vs. (3.22±0.12),P<0.05],the high density lipoprotein [(1.14±0.06) vs. (1.04±0.05),P<0.05] were significantly improved.There were no severe complications after operation.Conclusions:LRYGB for treatment of obesity with T2DM significantly reduces the patient’s BMI,improves the patient’s blood glucose and blood lipid levels,it is a safe and effective treatment method,worthy of clinical application.
Obesity;Diabetes mellitus,type 2;Laparoscopy;Gastric bypass
1009-6612(2017)01-0012-04
10.13499/j.cnki.fqjwkzz.2017.01.012
鲍 峰(1984—)男,四川省绵阳市中心医院普通外科主治医师,主要从事胃肠外科的研究。
R589.1
A
2016-06-11)
①*通讯作者:向荣超,E-mail:xiangrongchao@163.com

