离子通道型嘌呤受体P2X4在中枢神经系统中的作用及其作为神经系统疾病干预靶标的前景
马雪飞,于 烨(上海交通大学医学院药理与化学生物学系,上海 200025)
ATP一直被认为是一种细胞内能源物质。研究发现,ATP也可作为一个重要的细胞外信号分子[1]。ATP下游信号主要通过激活嘌呤受体传导,嘌呤受体分为P1和P2两大类。其中,P1是G蛋白偶联受体,P2受体包含P2X离子通道和P2Y G蛋白偶联受体[2]。P2X受体是一种非选择性阳离子通道,有7个亚型(P2X1~P2X7),允许Na+,K+和Ca2+等阳离子通过。其结构由同源或异源的3个亚基组成三聚体[3]。
P2X受体在体内广泛表达,往往都是较低水平的表达。另外,在脑和脊髓中,未观测到内源性ATP释放引起动作电位发放。目前已建立起多个P2X敲除小鼠,但在相关报道中均未发现明显的中枢神经相关的表型。这些现象一方面表明,ATP可能主要是通过激活突触前P2X受体充当神经调节物质[4];另一方面表明,P2X受体可能更多在病理情况下起重要作用。研究表明,大多数神经元细胞和小胶质细胞中都能发现P2X4受体[5-6],在一定条件下,P2X4受体表达上调,介导多种病理过程,如神经性疼痛[7]、乙醇摄入和偏好[8]、癫痫[9]、卒中缺血或神经退行性疾病恢复[10]和神经炎症[11]。P2X4受体可作为一个潜在的治疗靶标,但由于P2X4受体缺少有效的选择性抑制剂,非常不利于P2X4受体的功能研究。P2X4受体特异性抑制剂的发现,可促进P2X4受体生理病理功能的研究,也可为治疗上述疾病提供新的药理学方法。
1 P2X4受体在中枢神经系统中的分布及功能
P2X4最早在小鼠大脑中克隆,是第一个在中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)中检测到的P2X4受体[12]。随后在人类大脑中也克隆到P2X4[13]。在大脑皮质神经元中发现具有功能的P2X4受体,伊维霉素(ivermectin,IVM,一类P2X4受体功能增强剂)可增强ATP诱导的电流[14];通过激活P2X受体可诱导大脑皮质快速兴奋突触后电流,影响突触可塑性[15]。在海马体中ATP影响突触可塑性[16],ATP的释放与海马体的长时程增强(long-term potentiation,LTP)有关[17],在海马体神经元中,P2X受体激活会刺激或抑制谷氨酸释放[18]。P2X4受体在海马体的锥体细胞层、中间神经元以及海马CA1,CA2和CA3锥体细胞中高水平表达[19]。相比野生型小鼠,P2X4敲除的小鼠中LTP减少,在野生型小鼠中IVM可增加LTP,但P2X4敲除小鼠中无此作用[20],说明P2X4受体在LTP时可增强突触活性。在海马体CA1区锌离子可通过调节P2X4受体而提高LTP[21]。
P2X4受体在小脑皮质大量表达,在浦肯野细胞层和颗粒细胞层,及星状细胞和篮状细胞中均检测到P2X4受体的表达[22]。P2X4受体在舌下神经核中表达,可调节舌下神经的活性[23]。在室旁核和垂体前叶也检测到P2X4受体的表达[24]。视上神经元表达了有功能的突触前和突触外P2X4受体,可调节谷氨酸和γ-氨基丁酸(γ-aminobutyrate,GABA)的释放[25]。在小丘脑神经元中增加P2X4受体的表达会导致GABA能电流减小,P2X4受体和GABAA受体相互作用共同调节突触信号[26]。在下丘脑弓状核的刺鼠肽基因相关蛋白-神经肽神经元中高表达P2X4受体。电生理实验表明,P2X4受体介导突触前GABA释放到阿片-促黑素细胞皮质素原神经元,这些神经元都称为集中投射神经元,在食欲的调节中发挥重要作用[27]。促黄体生成激素释放激素的释放也与P2X4受体有关[28]。
P2X4受体在躯体感觉神经元[14]、三叉神经元[29]、视网膜神经节和双极细胞[30]以及脊髓[31]均有表达。在脊髓胶质细胞中发现大量的P2X4受体,在周围神经损伤损伤后,P2X4的转录、翻译水平均上调[6]。在脊髓中周围神经损伤引起的疼痛可被P2X4受体的阻断剂反转[7],敲除P2X4可缓解小鼠炎症和神经性疼痛[6]。
2 P2X4受体参与的中枢神经系统相关疾病
P2X4受体参与CNS许多生理病理过程,包括慢性痛、乙醇摄入、癫痫、阿尔茨海默病(AD)、帕金森病(PD)和卒中,P2X4可作为治疗神经性疾病的一个重要潜在靶标。
2.1 慢性痛
近年来,P2X4受体对慢性痛的作用受到了广泛的关注,而之前的研究主要是针对以神经元为中心的机制:原发性或者二级感受神经元的改变引起的过度兴奋性,越来越多的研究证明了胶质细胞微环境的变化会引起周围感觉神经元的超兴奋性和疼痛应答。研究发现,随着周围神经的损伤,脊髓小胶质细胞P2X4受体在细胞膜上的表达量上升。而且P2X4受体抑制剂可反转神经损伤引起的痛觉过敏,所以提出P2X4受体可能是治疗这种神经疼痛的潜在靶标。小神经胶质细胞活化可诱发神经元超兴奋性,这个信号通路的关键分子是脑源性神经营养因子(brain derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)[32],BDNF的释放依赖ATP激活小胶质细胞的P2X4受体[33]。BDNF激活脊髓背角Ⅰ层神经元的TrkB受体,诱导K+/Cl-转运体下调,使神经元内的氯离子升高,脊髓背角Ⅰ层神经元阴离子逆转电位(EAnion)的去极化发生改变,并减少GABAA受体和甘氨酸对兴奋性的抑制,从而产生疼痛[32]。所以,在小胶质细胞中,P2X4受体异常表达促成了周围神经损伤诱导的神经疼痛,因此P2X4受体表达上调也成为研究对象。其中干扰素调节因子5(interferon regulatory factor-5,IRF-5)是参与P2X4受体转录调控的转录因子,缺少IRF-5的小鼠在周围神经损伤后,脊髓中P2X4受体表达未上调,也未表现出对疼痛异常敏感[34]。
Src家族激酶Lyn对神经疼痛也具有重要作用。Lyn参与小胶质细胞活化,在神经损伤后,Lyn表达水平显著上升,而在Lyn敲除小鼠随着神经损伤并未出现P2X4受体表达上调和异常性疼痛[35]。Lyn可激活PI3K-Akt引起P2X4受体表达增加,所以,Lyn可能是调节小胶质细胞P2X4受体上调的关键激酶[36]。趋化因子CCL21也参与增加P2X4受体的表达,缺少CCL21可防止脊髓背角小胶质细胞P2X4受体的过表达,而使用CCL21可使小胶质细胞P2X4受体表达上调[37]。
神经损伤后诱发神经疼痛的机制存在性别差异,在雄性小鼠中小神经胶质细胞的P2X4受体表达上调并伴随着P38丝分裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogenactivated protein kinase,MAPK)激活和BDNF的释放,而在雄性小鼠中未出现P2X4受体表达上调,阻断通路中的任何一步都不能有效治愈疼痛[38]。因此,上述疼痛机制不适用在雄性小鼠。
最近发现,P2X4受体与吗啡耐受[39]和吗啡诱导的痛觉过敏[40]有关。吗啡诱导的痛觉过敏也需要阿片受体介导的脊髓小胶质细胞P2X4受体的上调[40]。由此说明,P2X4受体在疼痛通路中的重要作用。
2.2 乙醇摄入相关疾病
乙醇使用障碍已成为比较严重的健康问题,针对乙醇使用障碍的药物开发是一个相对年轻的领域。目前被美国FDA批准的药物有双硫仑、环丙甲羟二羟吗啡酮和阿坎酸[41-42]。但这些还远不够,因此,关于开发有效的治疗乙醇使用障碍的药物的研究越来越多。体外研究发现,乙醇可特异性地抑制P2X4受体电流[43],而不抑制其他P2X4受体的功能。进一步研究表明,乙醇抑制P2X4受体是由于降低了ATP对P2X4受体的亲和力[44],乙醇会阻止P2X4受体开放状态,但不影响受体失活。乙醇作用P2X4受体的关键位点Trp46,His241,Asp331和 Met336[45-46]也被发现。
研究表明,P2X4受体在特定的脑区表达水平较高,这些脑区都参与增强乙醇和其他药物的性能[47]。一些研究发现,P2X4受体在乙醇诱导的行为中起作用,P2X4受体在维持多巴胺体内稳态中起重要作用,因此参与饮酒行为[48]。P2X4受体表达水平与乙醇摄入相关,偏好乙醇的小鼠P2X4表达水平低于不喜乙醇的小鼠[49]。因此,乙醇摄入存在遗传倾向,突出了在治疗乙醇使用障碍的药物开发中遗传异质性的重要意义。P2X4受体敲除小鼠的乙醇摄入量明显高于野生型小鼠[50]。相比野生型小鼠,敲除P2x4受体小鼠表现出不同的乙醇摄入、乙醇的镇定催眠作用,小脑GABAA受体表达升高[51]。P2X4受体参与调节GABA的神经传递,意味着P2X4受体参与调节GABA介导的乙醇摄入调节。IVM可抑制乙醇对P2X4受体的作用,是因为干扰了乙醇在P2X4受体的结合位点[52]。IVM可能通过P2X4受体影响一些神经信号系统,例如GABA、谷氨酸和多巴胺,都参与乙醇摄入。因此,IVM可充当研究P2X4在乙醇摄入中功能的药理学工具。
前期临床证明,IVM可减少乙醇消耗,但作用有限[53]。IVM在大脑中无法达到较高的浓度,所以需要开发新的化合物,既可增强IVM在CNS中的滞留能力,还要保持减少乙醇摄入的能力和安全性。随后发现的两种IVM相关的大环内脂阿维菌素(abamectin)和司拉克丁(selamectin),它们可穿过血脑屏障,减少乙醇摄入,改变GABAA受体的调节以及P2X4受体表达,相比IVM在大脑中浓度较高[54]。莫西菌素(moxidectin)具有作为乙醇使用障碍的新型药物治疗的潜力[55]。在中脑边缘系统中,P2X4受体调节多巴胺能神经传递,在中脑边缘系统的多巴胺能神经元中,P2X4受体在饮酒行为中具有重要作用,P2X4受体活性与其他多巴胺能神经传递相关的行为也有关[48]。
2.3 神经炎症相关疾病
在大脑和脊髓中发生的炎症响应一般称为神经性炎症,小神经胶质细胞是CNS的先天性免疫细胞,在介导神经炎症响应中起关键作用[56]。神经炎症反应需要一些关键因子,包括促炎症细胞因子(IL-1β,IL-6和TNF-α)、趋化因子(CCL2,CCL5和CXCL1)和第二信使(一氧化氮和前列腺素),这些都由激活CNS中小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞而产生[56]。
在脊髓损伤、外伤性脑损伤和脑缺血后受伤组织的P2X4受体表达增加。炎性体是多蛋白复合体,可促进炎症细胞因子成熟,如IL-1β,可能参与调控神经炎症过程。使用P2X4敲除小鼠检测脊髓损伤后P2X4受体对炎性体激活和神经炎症的作用,发现P2X4敲除小鼠在脊髓损伤后炎性体激活,促炎症细胞因子和炎症细胞浸润均显著减少。因此,P2X4受体在神经元介导的先天性神经炎症中起重要作用[57]。在P2X4敲除小鼠中,癫痫发作后神经损伤和炎症发生改变,P2X受体家族成员可能在癫痫的病理生理学中发挥重要作用,为癫痫发作控制和神经保护提供新的靶点[58]。将P2X4敲除小鼠诱导成持续癫痫状态,48 h后小胶质细胞活化的部分功能被损害,如细胞招募、电压依赖钾通道上调[9]。
神经退行性疾病,如AD和PD也与神经炎症相关[59],其中小神经胶质起到重要作用[60-61]。P2X4受体参与调节小神经胶质细胞的信号通路,因此证明P2X4受体在各类与小胶质炎症相关的疾病中具有重要作用。在多发性硬化动物模型中小神经胶质细胞P2X4受体表达上调[62],在脂多糖诱导的神经炎症中,用P2X4抑制剂可减少小神经胶质细胞的活性。急性缺血损伤导致严重神经元损伤的关键机制是炎症。急性缺血导致死亡神经元和非神经元释放过量的ATP,激活P2X4受体,P2X4受体在CNS高表达,尤其是在脊髓中,小胶质细胞是CNS中的免疫细胞,响应脑功能破坏,如缺血性卒中,卒中后小神经胶质细胞形态发生变化,产生炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α[63-64],这些变化都伴随着小神经胶质细胞活化和P2X4受体表达上调,P2X4敲除小鼠在脊髓损伤[57]和过敏原诱导的呼吸道炎症[65]后,炎性体信号减少,在这些损伤模型中,P2X4阳性受体白细胞是释放促炎症细胞因子主要来源。这些结果表明,P2X4受体阳性小神经胶质细胞也是促炎症细胞因子的重要来源。因此,P2X4受体参与神经性炎症主要是通过P2X4受体调节小神经胶质细胞的信号通路。
3 P2X4受体特异性抑制剂
由于缺少特异性P2X4受体抑制剂,P2X4受体研究受到阻碍,之前的研究都用非选择性P2X4受体抑制剂(TNP-ATP和BBG)研究P2X4受体,但它们对P2X4亲和力小,效果不明显。随着研究发现,P2X4受体越来越重要,针对P2X4受体特异性抑制剂的研究也越来越受到关注,其发现可为针对P2X4受体治疗提供新途径。遗憾的是这些化合物与P2X4受体的作用机制并不清楚。根据已经解析的斑马鱼P2X4受体(zfP2X4)晶体结构,结合其他手段发现P2X4受体特异性抑制剂的作用位点,可为这些化合物的改造提供分子水平基础。
3.1 5-BDBD
5-BDBD是第一个被发现的有效的P2X4受体特异性抑制剂,在HEK-293细胞表达人源P2X4(hP2X4)受体IC50值为1.2 μmol·L-1,2种不同浓度的5-BDBD导致ATP浓度依赖曲线右移,说明5-BDBD是竞争抑制剂[66]。但后来也有研究表明,5-BDBD并非竞争性抑制剂,而是变构调节剂[67],在应用方面,敲除P2X4或使用5-BDBD可以缓解小鼠呼吸道炎症,表明5-BDBD在临床上有潜在应用价值。
3.2 BX430
最近发现的一个P2X4受体抑制剂BX430,IC50值为0.54 μmol·L-1,相比其他P2X受体具有高选择性,是非竞争性变构调节剂。BX430对P2X4受体的抑制作用具有种属特异性,目前发现它可抑制hP2X4和zfP2X4,但只能较弱抑制小鼠源和大鼠源P2X4受体的功能[68]。
3.3 PSB
PSB-12054是一个强效的hP2X4受体抑制剂,IC50值为0.189 μmol·L-1,在小鼠和大鼠的效果稍低一些,相比其他P2X受体,也同样具有高的选择性。其类似物PSB-12062效率相比之前的低,但在人、小鼠和大鼠3个种属抑制效率相似[69]。
3.4 NP-1815-PX
NP-1815-PX是一个新的P2X4抑制剂,在人源P2X4 上,IC50值为 0.26 μmol·L-1,对小鼠源和大鼠源也同样具有抑制作用。相比其他P2X受体,它对P2X4具有高选择性。在慢性痛模型中,NP-1815-PX可缓解神经损伤相关的疼痛[70]。
4 结语
大量研究表明,P2X4受体在CNS中的重要作用(图1)。当周围神经损伤、脊髓损伤、外伤性脑损伤以及脑缺血时,引起P2X4受体表达上调,通过相关的信号转导最终导致慢性痛、神经炎症、乙醇使用障碍和多发性硬化等疾患。因此,P2X4受体可作为潜在的药物靶点在这些疾病中发挥作用。随着P2X4受体晶体结构的相继解析,对P2X4受体结构有了更深入的研究,为研究P2X4受体与抑制剂和增强剂的结合机制提供了结构基础。多个内源性或外源性的物质或者药物分子都可以调节P2X4受体的功能。新型P2X4受体特异性抑制剂或者增强剂的发现,有助于研究P2X4受体在疾病中的作用,为治疗相关疾病提供新的潜在药物。
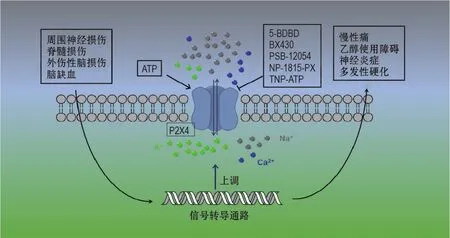
图1 P2X4受体在中枢神经系统中的重要作用及目前已知的靶向P2X4受体的抑制剂.
[1 ]Burnstock G.Historical review:ATP as a neurotransmitter[J].Trends Pharmacol Sci,2006,27(3):166-176.
[2]Ralevic V,Burnstock G.Receptors for purines and pyrimidines[J].Pharmacol Rev,1998,50(3):413-492.
[3 ]Saul A,Hausmann R,Kless A,Nicke A.Heteromeric assembly of P2X subunits[J/OL].Front Cell Neurosci,2013,7:250[2013-12-18].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3866589/
[4 ]Cunha RA,Ribeiro JA.ATP as a presynaptic modulator[J].Life Sci,2000,68(2):119-137.
[5 ]Burnstock G,Knight GE.Cellular distribution and functions of P2 receptor subtypes in different systems[J].Int Rev Cytol,2004,240:31-304.
[6]Ulmann L,Hatcher JP,Hughes JP,Chaumont S,Green PJ,Conquet F,et al.Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain[J].J Neurosci,2008,28(44):11263-11268.
[7 ]Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S,Mizokoshi A,Kohsaka S,Salter MW,et al.P2X4 Receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury[J].Nature,2003,424(6950):778-783.
[8 ]Wyatt LR, Finn DA, Khoja S, Yardley MM,Asatryan L,Alkana RL,et al.Contribution of P2X4 receptors to ethanol intake in male C57BL/6 mice[J].Neurochem Res,2014,39(6):1127-1139.
[9]Ulmann L,Levavasseur F,Avignone E,Peyroutou R,Hirbec H,Audinat E,et al.Involvement of P2X4 receptors in hippocampal microglial activation after status epilepticus[J].Glia,2013,61(8):1306-1319.
[10 ]Burnstock G.Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2008,7(7):575-590.
[11 ]Guo LH,Trautmann K,Schluesener HJ.Expression of P2X4 receptor by lesional activated microglia during Formalin-induced inflammatory pain[J].J Neuroimmunol,2005,163(1-2):120-127.
[12 ]Soto F,Garcia-Guzman M,Karschin C,Stühmer W.Cloning and tissue distribution of a novel P2X receptor from rat brain[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,1996,223(2):456-460.
[13 ]Garcia-Guzman M,Soto F,Gomez-Hernandez JM,Lund PE,Stühmer W.Characterization of recombinant human P2X4 receptor reveals pharmacological differences to the rat homologue[J].Mol Pharmacol,1997,51(1):109-118.
[14 ]Lalo U,Verkhratsky A,Pankratov Y.Ivermectin potentiates ATP-induced ion currents in cortical neurones:evidence for functional expression of P2X4 receptors?[J].Neurosci Lett,2007,421(2):158-162.
[15 ]Pankratov Y,Lalo U,Krishtal OA,Verkhratsky A.P2X Receptors and synaptic plasticity[J].Neuroscience,2009,158(1):137-148.
[16 ]Amadio S,Montilli C,Picconi B,Calabresi P,Volonté C.Mapping P2X and P2Y receptor proteins in striatum and substantia nigra:an immunohistological study[J].Purinergic Signal,2007,3(4):389-398.
[17 ]Wieraszko A.Extracellular ATP as a neurotransmitter:its role in synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus[J].Acta Neurobiol Exp(Wars),1996,56(2):637-648.
[18 ]Wieraszko A,Ehrlich YH.On the role of extracellular ATP in the induction of long-term potentiation in the hippocampus[J].J Neurochem,1994,63(5):1731-1738.
[19 ]Lê KT,Villeneuve P,Ramjaun AR,McPherson PS,Beaudet A,Séguéla P.Sensory presynaptic and widespread somatodendritic immunolocalization of central ionotropic P2X ATP receptors[J].Neuroscience,1998,83(1):177-190.
[20 ]Sim JA,Chaumont S,Jo J,Ulmann L,Young MT,Cho K,et al.Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2X4 knock-out mice[J].J Neurosci,2006,26(35):9006-9009.
[21 ]Lorca RA,Rozas C,Loyola S,Moreira-Ramos S,Zeise ML,Kirkwood A,et al.Zinc enhances longterm potentiation through P2X receptor modulation in the hippocampal CA1 region[J].Eur J Neurosci,2011,33(7):1175-1185.
[22 ]García-Lecea M, Sen RP, Soto F, Ma MP,Castro E.P2 receptors in cerebellar neurons:molecular diversity of ionotropic ATP receptors in Purkinje cells[J].Drug Dev Res,2010 ,52(1-2):104-113.
[23 ]Funk GD,Kanjhan R,Walsh C,Lipski J,Comer AM,Parkis MA,et al.P2 receptor excitation of rodent hypoglossal motoneuron activity in vitro and in vivo:a molecular physiological analysis[J].J Neurosci,1997,17(16):6325-6337.
[24 ]Zemkova H,Kucka M,Li S,Gonzalez-Iglesias AE,Tomic M,Stojilkovic SS.Characterization of purinergic P2X4 receptor channels expressed in anterior pituitary cells[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2010,298(3):E644-E651.
[25 ]Vavra V,Bhattacharya A,Zemkova H.Facilitation of glutamate and GABA release by P2X receptor activation in supraoptic neurons from freshly isolated rat brain slices[J].Neuroscience,2011,188:1-12.
[26 ]Jo YH,Donier E,Martinez A,Garret M,Toulmé E,Boué-Grabot E.Cross-talk between P2X4 and gamma-aminobutyric acid,type A receptors determines synaptic efficacy at a central synapse[J].J Biol Chem,2011,286(22):19993-20004.
[27 ]Xu J,Bernstein AM,Wong A,Lu XH,Khoja S,Yang XW,et al.P2X4 receptor reporter mice:sparse brain expression and feeding-related presynaptic facilitation in the arcuate nucleus[J].J Neurosci,2016,36(34):8902-8920.
[28 ]Terasawa E,Keen KL,Grendell RL,Golos TG.Possible role of 5′-adenosine triphosphate in synchronization of Ca2+oscillations in primate luteinizing hormonereleasing hormone neurons [J].Mol Endocrinol,2005,19(11):2736-2747.
[29 ]Luo J,Yin GF,Gu YZ,Liu Y,Dai JP,Li C,et al.Characterization of three types of ATP-activated current in relation to P2X subunits in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons[J].Brain Res,2006,1115(1):9-15.
[30 ]Wheeler-Schilling TH,Marquordt K,Kohler K,Guenther E,Jabs R.Identification of purinergic receptors in retinal ganglion cells[J].Brain Res Mol Brain Res,2001,92(1-2):177-180.
[31 ]Kobayashi K,Fukuoka T,Yamanaka H,Dai Y,Obata K,Tokunaga A,et al.Differential expression patterns of mRNAs for P2X receptor subunits in neurochemically characterized dorsal root ganglion neurons in the rat[J].J Comp Neurol,2005,481(4):377-390.
[32]Coull JA,Beggs S,Boudreau D,Boivin D,Tsuda M,Inoue K,et al.BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain[J].Nature,2005,438(7070):1017-1021.
[33 ]Trang T,Beggs S,Wan X,Salter MW.P2X4-receptor-mediated synthesis and release of brainderived neurotrophic factor in microglia is dependent on calcium and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation[J].J Neurosci,2009,29(11):3518-3528.
[34 ]Masuda T,Iwamoto S,Yoshinaga R,Tozaki-Saitoh H,Nishiyama A,Mak TW,et al.Transcription factor IRF5 drives P2X4R+/-reactive microglia gating neuropathic pain[J/OL].Nat Commun,2014,5:3771.[2014-05-13].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4024744/
[35]Tsuda M,Tozaki-Saitoh H,Masuda T,Toyomitsu E,Tezuka T,Yamamoto T,et al.Lyn tyrosine kinase is required for P2X4 receptor upregulation and neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury[J].Glia,2008,56(1):50-58.
[36]Tsuda M,Toyomitsu E,Kometani M,Tozaki-Saitoh H,Inoue K.Mechanisms underlying fibronectin-induced up-regulation of P2X4R expression in microglia:distinct roles of PI3K-Akt and MEK-ERK signalling pathways[J].J Cell Mol Med,2009,13(9B):3251-3259.
[37]Biber K,Tsuda M,Tozaki-Saitoh H,Tsukamoto K,Toyomitsu E,Masuda T,et al.Neuronal CCL21 up-regulates microglia P2X4 expression and initiates neuropathic pain development[J].EMBO J,2011,30(9):1864-1873.
[38 ]Mapplebeck JC,Beggs S,Salter MW.Sex differences in pain:a tale of two immune cells[J].Pain,2016,157(Suppl 1):S2-S6.
[39]Horvath RJ,Romero-Sandoval EA,De Leo JA.Inhibition of microglial P2X4 receptors attenuates morphine tolerance,Iba1,GFAP and mu opioid receptor protein expression while enhancing perivascular microglial ED2[J].Pain,2010,150(3):401-413.
[40 ]Ferrini F,Trang T,Mattioli TA,Laffray S,Del′Guidice T,Lorenzo LE,et al.Morphine hyperalgesia gated through microglia-mediated disruption of neuronal Cl-homeostasis[J].Nat Neurosci,2013,16(2):183-192.
[41]Harris AH,Kivlahan DR,Bowe T,Humphreys KN.Pharmacotherapy of alcohol use disorders in the Veterans Health Administration [J].Psychiatr Serv,2010,61(4):392-398.
[42]Litten RZ,Egli M,Heilig M,Cui C,Fertig JB,Ryan ML,et al.Medications development to treat alcohol dependence:a vision for the next decade[J].Addict Biol,2012,17(3):513-527.
[43]Davies DL,Kochegarov AA,Kuo ST,Kulkarni AA,Woodward JJ,King BF,et al.Ethanol differentially affects ATP-gated P2X3 and P2X4 receptor subtypes expressed in Xenopus oocytes[J].Neuropharmacology,2005,49(2):243-253.
[44 ]Xiong K,Hu XQ,Stewart RR,Weight FF,Li C.The mechanism by which ethanol inhibits rat P2X4 receptors is altered by mutation of histidine 241[J].Br J Pharmacol,2005,145(5):576-586.
[45 ]Popova M,Asatryan L,Ostrovskaya O,Wyatt LR,Li K,Alkana RL,et al.A point mutation in the ectodomain-transmembrane 2 interface eliminates the inhibitory effects of ethanol in P2X4 receptors[J].J Neurochem,2010,112(1):307-317.
[46 ]Popova M,Trudell J,Li K,Alkana R,Davies D,Asatryan L.Tryptophan 46 is a site for ethanol and ivermectin action in P2X4 receptors[J].Purinergic Signal,2013,9(4):621-632.
[47 ]Kimpel MW,Strother WN,McClintick JN,Carr LG,Liang T,Edenberg HJ,et al.Functional gene expression differences between inbred alcohol-preferring and-non-preferring rats in five brain regions[J].Alcohol,2007,41(2):95-132.
[48 ]Khoja S, Shah V, Garcia D, Asatryan L,Jakowec MW,Davies DL.Role of purinergic P2X4 receptors in regulating striatal dopamine homeostasis and dependent behaviors[J].J Neurochem,2016,139(1):134-148.
[49 ]Franklin KM,Hauser SR,Lasek AW,Bell RL,McBride WJ.Involvement of purinergic P2X4 receptors in alcohol intake of high-alcohol-drinking(HAD)rats[J].Alcohol Clin Exp Res,2015,39(10):2022-2031.
[50 ]Asatryan L,Nam HW,Lee MR,Thakkar MM,Saeed Dar M,Davies DL,et al.Implication of the purinergic system in alcohol use disorders[J].Alcohol Clin Exp Res,2011,35(4):584-594.
[51]Franklin KM,Asatryan L,Jakowec MW,Trudell JR,Bell RL,Davies DL.P2X4 receptors(P2X4Rs)represent a novel target for the development of drugs to prevent and/or treat alcohol use disorders[J/OL].Front Neurosci,2014,8:176.[2014-06-24].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4068020/
[52 ]Asatryan L,Popova M,Perkins D,Trudell JR,Alkana RL,Davies DL.Ivermectin antagonizes ethanol inhibition in purinergic P2X4 receptors[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2010,334(3):720-728.
[53 ]Yardley MM,Wyatt L,Khoja S,Asatryan L,Ramaker MJ,Finn DA,et al.Ivermectin reduces alcohol intake and preference in mice[J].Neuropharmacology,2012,63(2):190-201.
[54 ]Asatryan L,Yardley MM,Khoja S,Trudell JR,Hyunh N,Louie SG,et al.Avermectins differentially affect ethanol intake and receptor function:implications for developing new therapeutics for alcohol use disorders[J].Int J Neuropsychopharmacol,2014,17(6):907-916.
[55]Huynh N,Arabian N,Naito A,Louie S,Jakowec MW,Asatryan L,et al.Preclinical development of moxidectin as a novel therapeutic for alcohol use disorder[J].Neuropharmacology,2017,113(Pt A):60-70.
[56 ]DiSabato DJ,Quan N,Godbout JP.Neuroinflammation:the devil is in the details[J].J Neurochem,2016,139(Suppl 2):136-153.
[57 ]de Rivero Vaccari JP, Bastien D, Yurcisin G,Pineau I,Dietrich WD,De Koninck Y,et al.P2X4 receptors influence inflammasome activation after spinal cord injury[J].J Neurosci,2012,32(9):3058-3066.
[58 ]Henshall DC,Diaz-Hernandez M,Miras-Portugal MT,Engel T.P2X receptors as targets for the treatment of status epilepticus[J/OL].Front Cell Neurosci,2013,7:237.[2013-11-26].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3840793/
[59 ]Ransohoff RM.How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration[J].Science,2016,353(6301):777-783.
[60 ]Wes PD,Sayed FA,Bard F,Gan L.Targeting microglia for the treatment of Alzheimer′s disease[J].Glia,2016,64(10):1710-1732.
[61 ]Joers V,Tansey MG,Mulas G,Carta AR.Microglial phenotypes in Parkinson′s disease and animal models of the disease[J].Prog Neurobiol,2017,155:57-75.
[62 ]Vázquez-Villoldo N,Domercq M,Martín A,Llop J,Gómez-Vallejo V,Matute C.P2X4 receptors control the fate and survival of activated microglia[J].Glia,2014,62(2):171-184.
[63 ]Ritzel RM, Patel AR,Grenier JM,Crapser J,Verma R,Jellison ER,et al.Functional differences between microglia and monocytes after ischemic stroke[J/OL].J Neuroinflammation,2015,12:106.[2015-05-29].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4465481/
[64 ]Lambertsen KL,Biber K,Finsen B.Inflammatory cytokines in experimental and human stroke[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2012,32(9):1677-1698.
[65 ]Zech A,Wiesler B,Ayata CK,Schlaich T,Dürk T,Hoßfeld M,et al.P2RX4 deficiency in mice alleviates allergen-induced airway inflammation[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(49):80288-80297.
[66 ]Balázs B,Dankó T,Kovács G,Köles L,Hediger MA,Zsembery A.Investigation of the inhibitory effects of the benzodiazepine derivative,5-BDBD on P2X4 purinergic receptors by two complementary methods[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2013,32(1):11-24.
[67 ]Abdelrahman A, Namasivayam V, Hinz S,Schiedel AC,Köse M,Burton M,et al.Characterization of P2X4 receptor agonists and antagonists by calcium influx and radioligand binding studies[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2017,125:41-54.
[68 ]Ase AR,Honson NS,Zaghdane H,Pfeifer TA,Séguéla P.Identification and characterization of a selective allosteric antagonist of human P2X4 receptor channels[J].Mol Pharmacol,2015,87(4):606-616.
[69 ]Hernandez-Olmos V,Abdelrahman A,El-Tayeb A,Freudendahl D,Weinhausen S,Müller CE.N-substituted phenoxazine and acridone derivatives:structure-activity relationships of potent P2X4 receptor antagonists[J].J Med Chem,2012,55(22):9576-9588.
[70]Matsumura Y,Yamashita T,Sasaki A,Nakata E,Kohno K,Masuda T,et al.A novel P2X4 receptorselective antagonist produces anti-allodynic effect in a mouse model of herpetic pain[J/OL].Sci Rep,2016,6:32461.[2016-08-31].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5006034/

