VEGF逆转miR-200b促进非小细胞肺癌增殖的作用
罗卫民,张军,余宗涛,林称意,郭家龙
(湖北医药学院附属十堰市太和医院心胸外科1、检验科2,湖北 十堰 442000)
VEGF逆转miR-200b促进非小细胞肺癌增殖的作用
罗卫民1,张军1,余宗涛2,林称意1,郭家龙1
(湖北医药学院附属十堰市太和医院心胸外科1、检验科2,湖北 十堰 442000)
目的探讨血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)在miR-200b抑制非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)增殖中的作用及机制。方法选择2013年2月至2014年5月在本院经手术治疗的65例NSCLC患者的肿瘤组织,qRT-PCR检测NSCLC组织中miR-200b与VEGF的表达,并统计分析NSCLC组织中miR-200b与VEGF表达的相关性;常规培养A549、H460及16HBE细胞,qRT-PCR检测各组细胞中miR-200b与VEGF的表达;将常规培养的A549细胞随机分为四组,即miR-200b mimics+vector、miR-200b mimics+VEGF组、miR-200b inhibitor+scramble组、miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA组,其中miR-200b mimics+vector组与miR-200b inhibitor+scramble组作为阴性对照,采用MTT法检测各组吸光度值(OD值)。结果qRT-PCR结果显示,miR-200b在NSCLC组织的表达水平为(0.682± 0.106),VEGF在NSCLC组织的表达水平为(2.731±0.597),相关性分析显示在NSCLC组织中miR-200b与VEGF的表达呈负相关(r=-0.514,P<0.001);miR-200b在A549、H460细胞中的表达显著低于16HBE细胞,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000),而VEGF在A549、H460细胞中的表达明显高于16HBE细胞,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000);MTT结果显示,miR-200b mimics+VEGF组A549细胞在48 h、72 h的细胞增殖率明显高于miR-200b mimics+vector组,miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA组A549细胞在48 h、72 h的细胞增殖率明显低于miR-200b inhibitor+scramble组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论miR-200b与VEGF在NSCLC组织及细胞中表达呈负相关;VEGF逆转miR-200b对NSCLC细胞增殖的作用。
miR-200b;非小细胞肺癌;血管内皮生长因子;增殖
肺癌是全球死亡率最高的恶性肿瘤,70%~80%的肺癌是非小细胞肺癌(non samll cell lung cancer,NSCLC),包括鳞状细胞癌、腺癌、大细胞癌[1]。非小细胞肺癌的预后很差,尽管今年化疗药物研究进展及治疗手段有所进步,NSCLC的5年总体生存率仍不超过11%。其主要死亡原因是化疗耐药性和转移,但NSCLC转移的机制仍不十分清楚[2]。
微小RNA(miRNAs)是一组包含19~25个核苷酸的非编码小分子单链RNA,是基因表达的一个重要调控因子。通过与靶基因3′-UTR(3′-非编码区)形成完全或不完全地碱基配对,miRNA可导致靶mRNA的翻译抑制或降解,并在转录后水平上调控靶基因表达。miRNA同时也参与多种细胞生物学行为,包括细胞的分化、增殖、迁移、代谢及凋亡等过程。过去的研究已经证明miRNA表达谱在不同的肿瘤中的作用,同时也表明了miRNA的表达异常与肿瘤的发生发展息息相关[3-4]。据报道,目前已有一些研究证实miRNA在NSCLC中能发挥抗肿瘤作用,如miR-145[5],而还有许多miRNA能在NSCLC中促进肿瘤的转移,如miR-141[6],miRNA-197[7]。miR-200b能抑制支气管上皮细胞的上皮间叶转化(EMT)及肿瘤细胞转移[8],同时miR-200b还能下调E盒结合锌指蛋白2(ZEB2)及E2F3的表达,增加E-钙连接素表达,从而抑制耐药性NSCLC细胞增殖,并促进肿瘤细胞凋亡[9-10]。
血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)是一种重要的血管生成促成因子,通过与特异性受体结合从而刺激血管内皮细胞增殖,增加血管通透性,诱导肿瘤新生血管及淋巴管形成,其过度表达与肿瘤的形成、发展、转移等病理过程密切相关[11]。研究表明VEGF在多种实体肿瘤中高表达,如胃癌[3]、肝癌[12]、乳腺癌[13]、NSCLC[14];Fossella等[14]研究表明在NSCLCⅠ~Ⅳ临床分期中,临床分期越高患者血清中VEGF水平也升高。此外,miR-200b通过靶向作用于VEGF及其受体负性调控VEGF信号通路,从而抑制肿瘤细胞血管的生成[15]。而NSCLC中,miR-200b与VEGF的表达调控关系尚无报道。本研究拟通过研究miR-200b在NSCLC中对VEGF表达调控的作用,探讨miR-200b抑制NSCLC侵袭转移的机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞培养 NSCLC细胞株A549、H460及正常的肺支气管上皮细胞系人支气管上皮细胞(16HBE),从美国标准生物品收藏中心(ATCC)购买。细胞培养基:DMEM,10%胎牛血清,2µmol/L谷氨酰胺,100 IU/mL青霉素及100µg/mL硫酸链霉素,在37℃、5%二氧化碳环境培养。
1.2 临床标本收集及资料 人非小细胞肺癌取自本院2013年2月至2014年5月手术治疗的65例患者,所有患者均无接受手术前化疗。记录患者年龄、性别、组织学分级、肿瘤大小、浸润深度和淋巴结转移等资料。本研究经医学伦理委员会批准。
1.3 试剂 miR-200b mimics、miR-200b inhibitor、VEGF过表达载体、vector、VEGF siRNA、scramble购自Genecopoeia公司。转染试剂为Lipofectamine 2000,购自invitrogen公司。
1.4 总RNA提取、逆转录 用Trizol(invitrogen)提取RNA。用Nanodrop 2000(Thermo)测定RNA浓度及纯度。用cDNA合成试剂盒及miRNA特异性检测试剂盒(Genecopeoia)。cDNA合成的条件为:50℃,30 min;85℃,5 min。
1.5 细胞分组与转染 将NSCLCA549细胞分为miR-200b mimics+vector组(共转染miR-200b mimics与vector)、miR-200b mimics+VEGF组(共转染miR-200b mimics与VEGF)、miR-200b inhibitor+scramble组(共转染miR-200b inhibitor与scramble)、miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA组(共转染miR-200b inhibitor与VEGF-siRNA),其中miR-200b mimics+vector组与miR-200b inhibitor+scramble组作为阴性对照。将A549细胞接种于6孔板,将上述转染用的质粒分别转染细胞。根据转染试剂说明书进行操作。
1.6 MTT实验 将上述转染48 h后的4组A549细胞接种于96孔板中,每组设5个复孔,分别培养24 h、48 h、72 h至临近90%饱和度,每孔加灭菌MTT液(5 mg/mL)20 μL,孵育4 h后取出,每孔中加入DMSO 150 μL,低速振荡10 min,选择波长为570 nm,在酶标仪上测定各孔吸光值,记录结果,实验重复3次。
1.7 荧光实时定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR,qRT-PCR)PCR扩增反应体系为20 μL,其中包括MiR-PCR primers(5 mmol/L)0.4 μL,miRNA RT product 2.0 μL,Taq DNA polymerase 5 U/μL)0.2 μL,2×SYBR Mix 10 μL,灭菌蒸馏水7.4 μL。循环体系为:95℃,3 min;95℃,12 s;62℃,35 s;72℃,30 s,一共40个循环。以β-actin为内参,所测定的miR-200b的相对表达量采用2-ΔΔCT法分析。
1.8 统计学方法 采用SPSS13.0统计软件对实验数据进行分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(±s)表示,两组间均数比较采用t检验,多组间均数比较采用方差分析,相关性分析用Pearson检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 miR-200b与VEGF在NSCLC组织及细胞中的表达 qRT-PCR检测了NSCLC组织及细胞中miR-200b与VEGF的表达。结果显示,miR-200b在NSCLC组织的表达水平为(0.682±0.106),VEGF在NSCLC组织的表达水平为(2.731±0.597),相关性分析显示在NSCLC组织中miR-200b与VEGF的表达呈负相关(r=-0.514,P<0.001)。miR-200b在NSCLC细胞中的表达显著低于16HBE,差异有统计学意义(F= 214.670,P=0.000),而NSCLC中VEGF的表达明显高于16HBE,差异有统计学意义(F=107.820,P=0.000),miR-200b及VEGF在NSCLC及16HBE细胞中的表达相反,见表1。
表1 miR-200b及VEGF在NSCLC细胞及肺支气管上皮细胞中表达(±s)
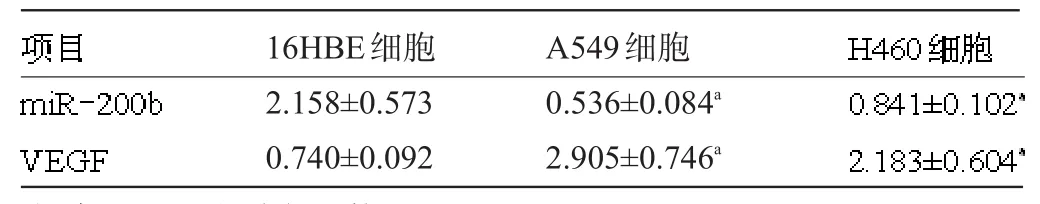
表1 miR-200b及VEGF在NSCLC细胞及肺支气管上皮细胞中表达(±s)
注:与16HBE细胞相比较,aP<0.01。
16HBE细胞A549细胞2.158±0.573 0.740±0.092 0.536±0.084a2.905±0.746a
2.2 VEGF逆转miR-200b对NSCLC细胞增殖的作用 MTT结果显示,在转染miR-200b mimics+ VEGF组的A549细胞48 h与72 h的OD值高于miR-200b mimics+vector组,差异有统计学意义;在转染miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA组的A549细胞48 h与72 h的OD值低于miR-200b inhibitor+scramble,差异有统计学意义(48 h:miR-200b mimics+VEGF组t=4.695,P=0.009;miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA组t=9.035,P=0.001;72 h:miR-200b mimics+VEGF组t=5.266,P=0.006;miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA组t=7.046,P=0.002)。
表2 miR-200b与VEGF对NSCLC细胞增殖的影响(±s)
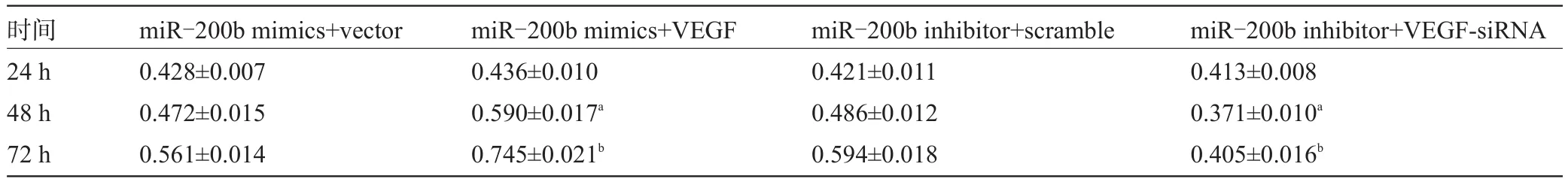
表2 miR-200b与VEGF对NSCLC细胞增殖的影响(±s)
注:与miR-200b mimics+vector组或miR-200b inhibitor+scramble组相比较,aP<0.05,bP<0.01。
时间24 h 48 h 72 h miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA 0.413±0.008 0.371±0.010a0.405±0.016bmiR-200b mimics+vector 0.428±0.007 0.472±0.015 0.561±0.014 miR-200b mimics+VEGF 0.436±0.010 0.590±0.017a0.745±0.021bmiR-200b inhibitor+scramble 0.421±0.011 0.486±0.012 0.594±0.018
3 讨 论
研究证实,miRNAs在NSCLC发生发展过程中发挥重要作用[16]。miRNAs作为肿瘤抑制或致癌基因参与肿瘤发展的多个过程,包括细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移和侵袭[17]。miR-200b在多种肿瘤中发挥抑瘤作用。最近有研究表明,miR-200b能靶向调节Bmi-1癌基因抑制舌癌细胞上皮间质转化[18],还能增强前列腺癌细胞对化疗药物的敏感性,抑制其增殖及转移[19]。此外,miR-200b通过靶向Ras鸟苷酸结合蛋白超家族的新成员(RND3)来调节细胞周期蛋白D1(cyclin D1)表达水平从而促进宫颈癌细胞周期停滞[20]。在肺癌中,miR-200b通过靶向作用转录调控因子E2F3逆转肺癌对多西他赛化疗耐药[9],还能通过靶向血管内皮生长因子受体1(FLT1/VEGFR1)抑制肺癌细胞迁移和增殖[21]。
VEGF是一种重要的血管生成调节因子,主要由肿瘤细胞分泌。人VEGF存在5种同型异构体,其中VEGF165是生物活性最强的分子类型,而VEGF已被看作是许多不同恶性肿瘤生长和扩散转移过程中的一个关键的致癌基因[22]。早期的研究发现,VEGF参与肺癌浸润与转移机制存在两种形式,一种方式可能通过与内皮细胞上的VEGFR结合,经过旁分泌形式促进肿瘤新生血管形成及增加血管通透性从而导致肺癌细胞浸润与转移;另一种方式可能通过自分泌机制促进肺癌的生长和浸润转移[23]。Brussino等[24]研究发现在NSCLC细胞中VEGF阳性表达量较正常细胞明显增高,本实验与Brussino等[24]的研究结果基本一致。此外,VEGF与NSCLC淋巴结的转移密切相关,VEGF表达阳性者,淋巴结转移显著增高[25]。同时还有研究表明,VEGF在许多肿瘤中的表达受一些miRNA调控,其中包括miR-200b[15,26-27]。但miR-200b与VEGF在肺癌中的表达调控未见报道。作为miR-200b的靶基因,VEGF是否参与了miR-200b对NSCLC细胞功能的调控?于是,本研究检测了miR-200b与VEGF共同对NSCLC细胞增殖的影响。结果证实,miR-200b与VEGF共同高表达组细胞增殖率明显高于miR-200b高表达组,miR-200b与VEGF共同表达抑制组细胞增殖率低于miR-200b高表达组。这说明VEGF作为miR-200b的靶基因逆转了miR-200b抑制NSCLC细胞增殖的作用。
本研究证实了NSCLC组织及细胞中miR-200b与VEGF表达呈负相关,并且VEGF可逆转miR-200b对NSCLC细胞增殖抑制作用。但是VEGF的这种作用调控的下游信号通路尚不清楚,这成为我们后续研究的方向。
[1]Jemal A,Bray F,Center MM,et al.Global cancer statistics[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2011,61(2):69-90.
[2]Gao D,Vahdat LT,Wong S,et al.Microenvironmental regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer[J].Cancer Res,2012, 72(19):4883-4889.
[3]Tang H,Deng M,Tang Y,et al.miR-200b and miR-200c as prognostic factors and mediators of gastric cancer cell progression[J].Clin Cancer Res,2013,19(20):5602-5612.
[4]Tang H,Kong Y,Guo J,et al.Diallyl disulfide suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through Wnt-1 signaling pathway by up-regulation of miR-200b and miR-22[J]. Cancer Lett,2013,340(1):72-81.
[5]Chen Z,Zeng H,Guo Y,et al.miRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting c-Myc[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2010,29:151.
[6]Mei Z,He Y,Feng J,et al.MicroRNA-141 promotes the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating expression of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2[J].FEBS Lett,2014,588(17):3055-3061.
[7] Du L,Schageman JJ,Subauste MC,et al.miR-93,miR-98,and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor gene FUS1[J]. Mol Cancer Res,2009,7(8):1234-1243.
[8]Wang Z,Zhao Y,Smith E,et al.Reversal and prevention of arsenic-induced human bronchial epithelial cell malignant transformation by microRNA-200b[J].Toxicol Sci,2011,121(1):110-122.
[9]Feng B,Wang R,Song HZ,et al.MicroRNA-200b reverses chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting E2F3[J].Cancer,2012,118(13):3365-3376.
[10]Fang S,Zeng X,Zhu W,et al.Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2)regulated by miR-200b contributes to multi-drug resistance of small cell lung cancer[J].Exp Mol Pathol,2014,96(3):438-444.
[11]Hainsworth JD,Spigel DR,Farley C,et al.PhaseⅡ trial of bevacizumab and erlotinib in carcinomas of unknown primary site: the Minnie Pearl Cancer Research Network[J].J Clin Oncol,2007, 25(13):1747-1752.
[12]Guo LY,Zhu P,Jin XP.Association between the expression of HIF-1 α and VEGF and prognostic implications in primary liver cancer[J]. Genet Mol Res,2016,15(2):doi:10.4238/gmr.15028107.
[13]Scherbakov AM,Gershtein ES,Korotkova EA,et al.Regulatory proteins of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and some components of VEGF signaling pathway in breast cancer[J].Bull Exp Biol Med, 2016,160(6):802-806.
[14]Fossella FV,DeVore R,Kerr RN,et al.Randomized phase III trial of docetaxel versus vinorelbine or ifosfamide in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy regimens.The TAX 320 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Study Group[J].J Clin Oncol,2000,18(12):2354-2362.
[15]Choi YC,Yoon S,Jeong Y,et al.Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling by miR-200b[J].Mol Cells,2011,32(1): 77-82.
[16]Yang YR,Li YX,Gao XY,et al.MicroRNA-137 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting bone morphogenetic protein-7(BMP7) in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2015,8 (9):10847-10853.
[17]Guo J,Xia B,Meng F,et al.miR-137 suppresses cell growth in ovarian cancer by targeting AEG-1[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013,441(2):357-363.
[18]Sun L,Yao Y,Liu B,et al.MiR-200b and miR-15b regulate chemotherapy-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human tongue cancer cells by targeting BMI1[J].Oncogene,2012,31(4):432-445.
[19]Yu J,Lu Y,Cui D,et al.miR-200b suppresses cell proliferation,migration and enhances chemosensitivity in prostate cancer by regulating Bmi-1[J].Oncol Rep,2014,31(2):910-918.
[20]Xia W,Li J,Chen L,et al.MicroRNA-200b regulates cyclin D1 expression and promotes S-phase entry by targeting RND3 in HeLa cells[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2010,344(1-2):261-266.
[21]Roybal JD,Zang Y,Ahn YH,et al.miR-200 Inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by targeting Flt1/VEGFR1[J]. Mol Cancer Res,2011,9(1):25-35.
[22]Nakayama M,Nakayama A,van Lessen M,et al.Spatial regulation of VEGF receptor endocytosis in angiogenesis[J].Nat Cell Biol, 2013,15(3):249-260.
[23]Decaussin M,Sartelet H,Robert C,et al.Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)and its two receptors(VEGF-R1-Flt1 and VEGF-R2-Flk1/KDR)in non-smallcelllung carcinomas (NSCLCs):correlation with angiogenesis and survival[J].J Pathol, 1999,188(4):369-377.
[24]Brussino L,Culla B,Bucca C,et al.Inflammatory cytokines and VEGF measured in exhaled breath condensate are correlated with tumor mass in non-small cell lung cancer[J].J Breath Res,2014,8(2): 027110.
[25]Li Q,Dong X,Gu W,et al.Clinical significance of co-expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in non-small cell lung cancer[J].Chin Med J(Engl),2003,116(5):727-730.
[26]Takahashi Y,Koyanagi T,Suzuki Y,et al.Vasohibin-2 expressed in human serous ovarian adenocarcinoma accelerates tumor growth by promoting angiogenesis[J].Mol Cancer Res,2012,10(9):1135-1146.
[27]Liu GT,Chen HT,Tsou HK,et al.CCL5 promotes VEGF-dependent angiogenesis by down-regulating miR-200b through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells[J].Oncotarget, 2014,5(21):10718-10731.
VEGF reverses the inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer proliferation induced by miR-200b.
LUO Wei-min1, ZHANG Jun1,YU Zong-tao2,LIN Cheng-yi1,GUO Jia-long1.Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery1,Department of Clinical Laboratory2,the Affiliated Shiyan Taihe Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine,Shiyan 442000,Hubei,CHINA
ObjectiveTo investigate the function of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)in the process of miR-200b inhibiting the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC).MethodsSixty-five patients with NSCLC who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital from February 2013 to May 2014 were enrolled.Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR(qRT-PCR)was conducted to detect the expression of miR-200b and VEGF in NSCLC tissues.The correlation between miR-200b and VEGF in NSCLC tissues was statistically analyzed.A549,H460 and 16HBE cells were routinely cultured,the expression of miR-200b and VEGF in A549,H460 and 16HBE cells were detected by qRT-PCR.The normal cultured A549 cells were randomly divided into four groups:miR-200b mimics+vectorgroup,miR-200b mimics+VEGF group,miR-200b inhibitor+scramble group,miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA group.miR-200b mimics+vector group and miR-200b inhibitor+scramble group were selected as the negative control. The tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay(MTT)was used to measure the OD value of each group.ResultsQRT-PCR showed that the expression levels of miR-200b and VEGF in NSCLC tissues were respectively(0.682±0.106)and (2.731±0.597),and the correlation analysis showed that miR-200b was negatively correlated with VEGF expression in NSCLC tissues(r=-0.514,P<0.001).The expression of miR-200b in A549 and H460 cells was significantly lower than that in 16HBE cells(P=0.000),while the expression of VEGF in A549 and H460 cells was significantly higher than that in 16HBE cells(P=0.000).MTT showed that the proliferation rates of miR-200b mimics+VEGF group at 48 h and 72 h were significantly higher than that of miR-200b mimics+vector group(P<0.05),while the cell proliferation rates of miR-200b inhibitor+VEGF-siRNA group were significantly lower than that of miR-200b inhibitor+scramble group at 48 h and 72 h(P<0.05).ConclusionThe expression of miR-200b is negatively correlated with the expression of VEGF in NSCLC tissues and cells.VEGF reverses the effect of miR-200b in the proliferation of NSCLC cell.
miR-200b;Non-small cell lung cancer;Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF);Proliferation
R734.2
A
1003—6350(2017)01—0005—04
2016-07-19)
湖北省教育厅课题(编号:B2015477)
罗卫民。E-mail:luoweiming0803@sina.com
10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2017.01.002

