锥冰晶石型氟化物K5V3F14的水热法制备及其磁性能
赫丽杰, 张 冬, 谭广雷, 牟 涛, 刘海燕, 杜 鹏
(1. 营口理工学院 化学与材料工程系,辽宁 营口 115014;2. 吉林大学 物理学院 新型电池物理与技术教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012)
·快递论文·
锥冰晶石型氟化物K5V3F14的水热法制备及其磁性能
赫丽杰1, 张 冬2*, 谭广雷1, 牟 涛1, 刘海燕1, 杜 鹏1
(1. 营口理工学院 化学与材料工程系,辽宁 营口 115014;2. 吉林大学 物理学院 新型电池物理与技术教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012)
采用水热法制备了锥冰晶石型氟化物K5V3F14(1),其结构和性能经元素分析,XRD, SEM, TG-DTA和磁性分析表征。结果表明:1属四方晶系,空间群P4/mnc,晶胞参数a=0.762 9 nm,b=0.762 9 nm,c=1.166 7 nm。 1的热分解温度>400 ℃。 T<16 K时,1为亚铁磁性;T=0 K时,1出现磁饱和现象。
水热法; 制备; 锥冰晶石型氟化物; 磁性能
为减少环境污染和设备腐蚀,提高FC产品质量,本文首次报道了采用水热法制备锥冰晶石型FC(K5V3F14, 1)的方法,其结构和性能经元素分析,XRD, SEM, TG-DTA和磁性分析表征。该方法具有操作简便,反应条件温和等优点。
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器与试剂
JEOL JSM-6700F型扫描电镜(加速电压30 kV); Rigaku D/Max 2550 V/PC型X-射线衍射仪(CuKα辐射,λ=1.541 8 Å,管电压40 kV,管电流200 mA,步长0.02 °·step-1,扫描范围15°≤2θ≤120°; TGS-2型热重分析仪(氮气保护,加热速率10 ℃·min-1); Quantum MPMS-XL SQUIDS型磁性测量仪(测量范围2~350 K,外加磁场100 Oe, ZFC和FC条件下测量磁化率)。
K2S2O3·2H2O, KF, V2O3,分析纯,北京化工厂;其余所用试剂均为分析纯。
1.2 合成
在烧杯中加入V2O30.075 g, K2S2O30.196 g和去离子水20 mL,搅拌使其混合均匀;加入KF 0.393 g,将反应液移入内衬聚四氟乙烯的反应釜中(填充度约80%),于180 ℃晶化3 d。冷却至室温,倒入烧杯,用乙醇洗涤得绿色透明片状晶体1,于50 ℃干燥备用。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 合成
合成过程中,影响1形成的因素较多,其中过饱和KF溶液、反应温度和还原剂作用较明显。KF作矿化剂,不仅可为目标产物提供K+和F-,也是反应体系的pH缓冲剂。结晶过程中,只有当反应温度高于180 ℃,才能制得1。 K2S2O3作还原剂,可稳定溶液中的V3+。若不加K2S2O3, 1中可能存在蓝色晶体(NH4)2NaVOF5(V3+被氧化为V4+)。
2.2 表征
(1) SEM
图1为1的SEM照片。由图1可以看出,1结晶度较好,具有规则的几何外形。
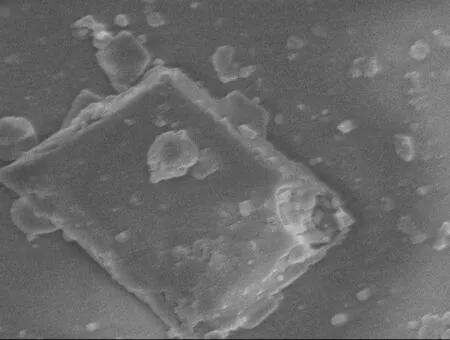
图1 1的SEM照片Figure 1 SEM image of 1
(2) 元素分析和XRD
表1为1的元素分析结果,图2为1的XRD谱图。从图2可以看出,1具有很强的衍射峰,说明结晶度较好。这与SEM照片结果一致。
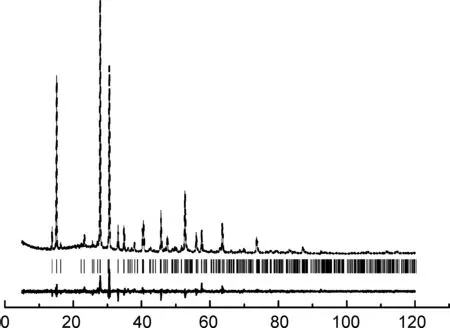
2θ/(°)图2 1的XRD谱图Figure 2 XRD pattern of 1表1 1的元素分析结果Table 1 Elemental analysis of 1

计算值测试值K5V3F14K5.05V2.98F14.07
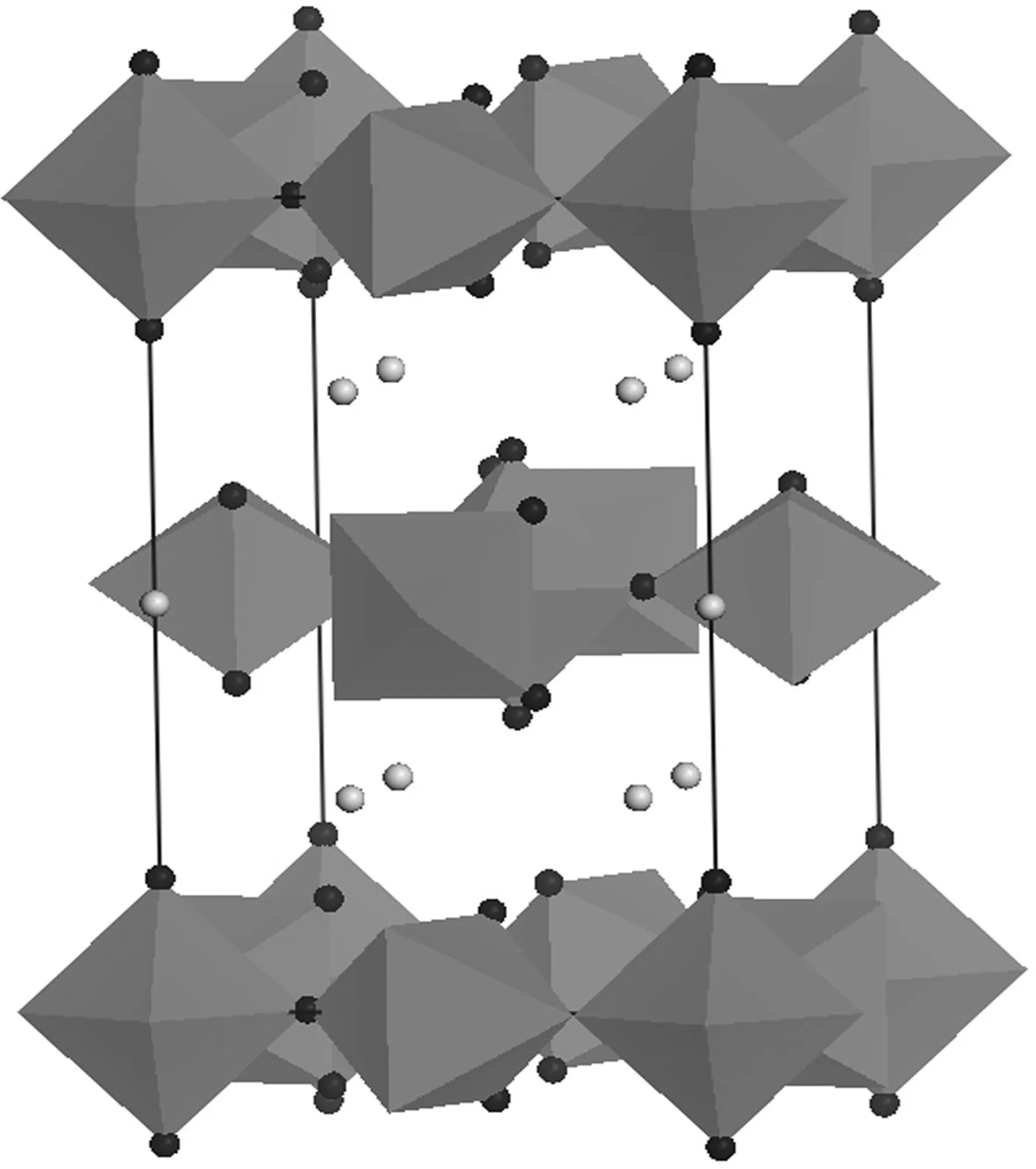
(a)[VF6]3-八面体
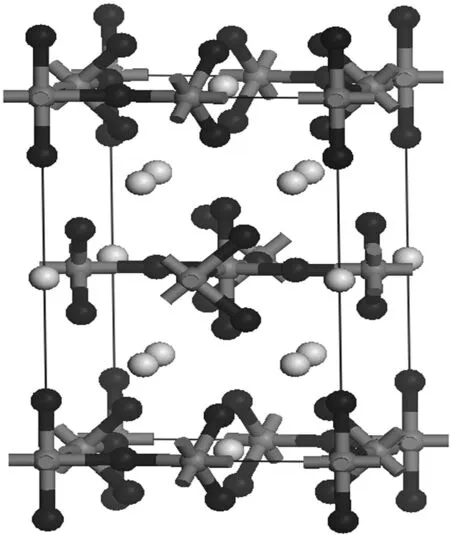
(b)沿c轴向结构图3 1的晶体结构Figure 3 Crystal structure of 1表2 1的晶胞参数和原子位置Table 2 Parameters and atom positions of 1
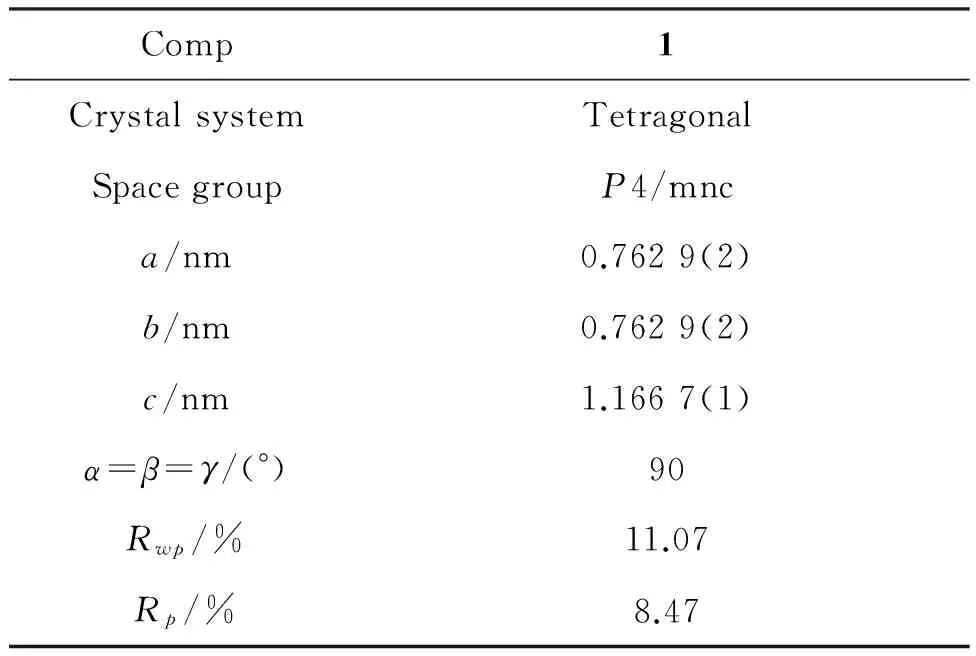
Comp1CrystalsystemTetragonalSpacegroupP4/mnca/nm0.7629(2)b/nm0.7629(2)c/nm1.1667(1)α=β=γ/(°)90Rwp/%11.07Rp/%8.47
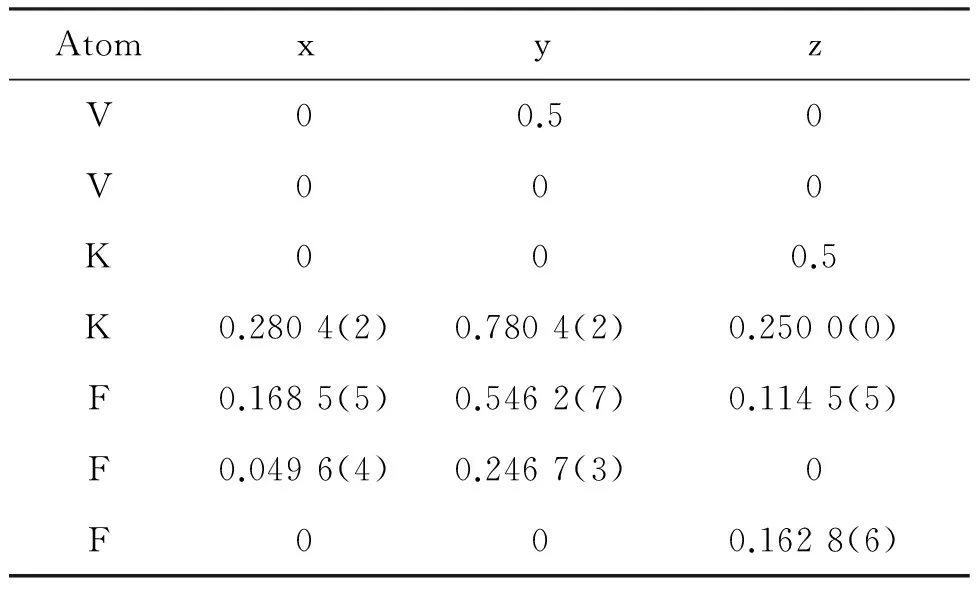
AtomxyzV00.50V000K000.5K0.2804(2)0.7804(2)0.2500(0)F0.1685(5)0.5462(7)0.1145(5)F0.0496(4)0.2467(3)0F000.1628(6)
2.3 性能
(1) 热稳定性
图4为1的TG-DTA曲线。由图4可以看出,1加热至400 ℃时仍保持稳定。
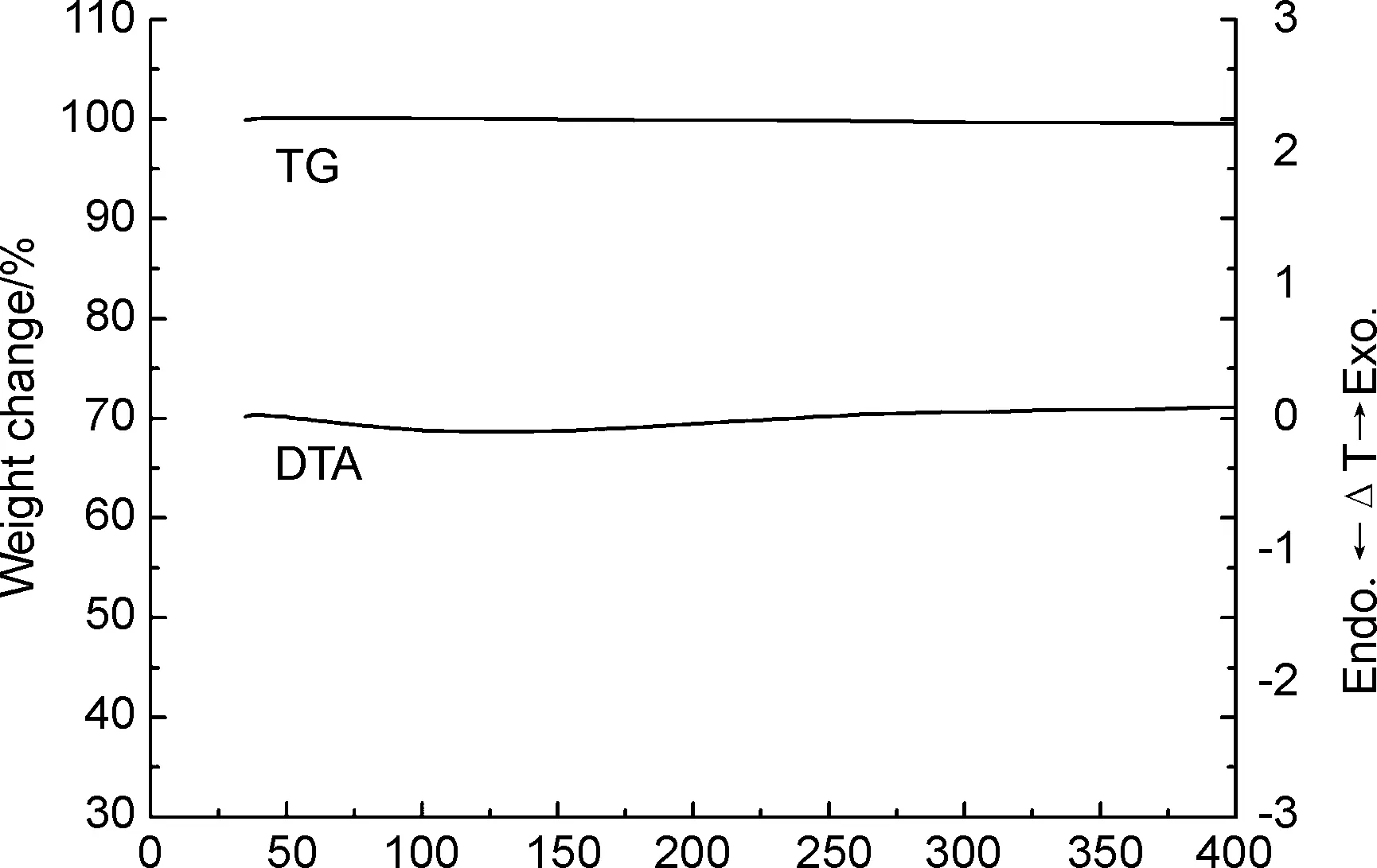
Temperature/℃图4 1的TG-DTA曲线Figure 4 TG-DTA curves of 1
BIIIF6八面体排列形成一系列孤立磁单元、一维链、二维层状和三维网状结构。氟化物磁性与电子强烈定域的晶体学特征有关[25]。图5为1在4~300 K内的磁性曲线(磁场强度4×105 A·m-1)。从图5可以看出,1在高温区化合物的磁性行为遵守居里-外斯定律,其磁性参数为Tc=16 K, C=1.233 9 cm3·K·mol-1,θ=-43.04 K。1在高温区的有效磁矩为3.19 μeff·μB-1,与V3+单自旋有效磁矩(2.828 μeff·μB-1)很接近。磁性测量结果表明,1在温度低于16 K时表现为亚铁磁性,在0 K时饱和磁化强度为2.15。这与Cros C等[26]采用高温熔融法制备的1磁性相同。此外,1在64 K时产生拟合曲线与实验曲线分离的现象。氟八面体是刚性单元,不易发生八面体变形。这种随着温度降低,两条曲线线性偏离的现象,可能是晶体学对称性改变诱导V3+发生自旋有序倾斜所致。
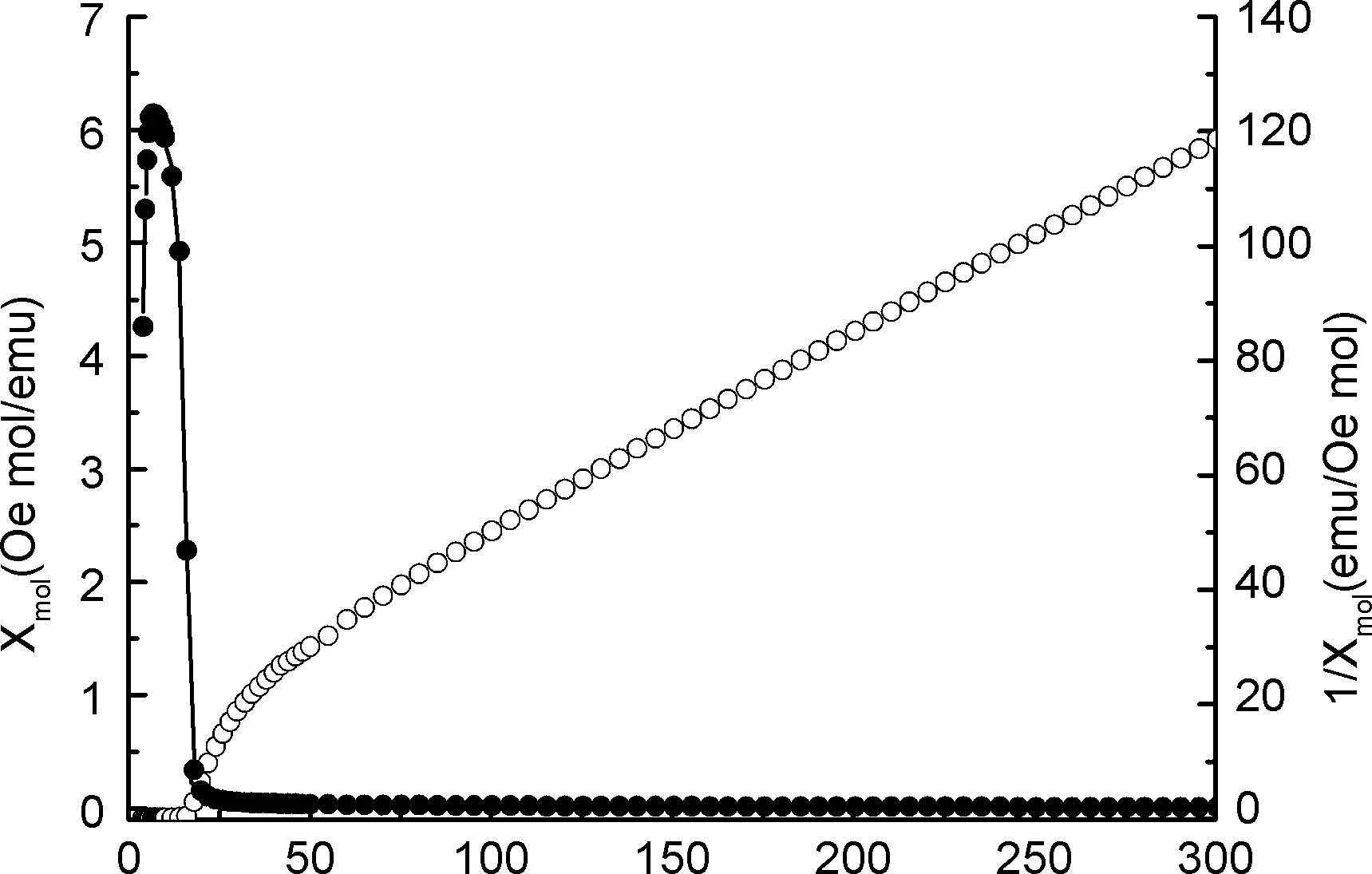
Temperature/K图5 1的磁性曲线Figure 5 Magnetization curves of 1
采用水热法合成了锥冰晶石型氟化物K5V3F14(1)。1属四方晶系,晶胞参数a=0.762 9 nm,b=0.762 9 nm,c=1.166 7 nm。 1的热分解温度>400 ℃。 T<16 K时,1为亚铁磁性;T=0 K时,1出现磁饱和现象。1在磁电耦合和多铁性有序材料中有潜在的应用价值。
致谢:感谢营口理工学院院级科研立项基金(QN-L-201403)和国家自然科学基金(21201073)的资助。
[1] McLain E S, Dolgos R M, Tennant A D,etal. Magnetic behaviour of layered Ag(II) fluorides[J].Nature Materials,2006,5(7):561-565.
[2] ScatturinV, Corliss L, Elliott N,etal. Magnetic structures of 3d transition metal double fluorides,KMeF3[J].J Magn Mater,1961,14(1):19-26.
[3] Dupont N, Gredin P, Pierrard A,etal. Magnetic properties of two copperII fluorides:Ba2Cu2AlF11and Ba5Sc2CuF18[J].Solid State Sciences,2000,2(5):531-537.
[4] Chicklis E P, Naiman C S, Folweiler R C,etal. High-efficiency room-temperature 2.06 μm laser using sensitized Ho3+:YLF[J].Appl Phys Lett,1971,19(4):119-121.
[5] Claude E, Nicola A S. Origin of ferroelectricity in the multiferroic barium fluorides BaMF4[J].Phys Rev B,2006,74(2-1):024102-024110.
[6] Robert B, Gašper T, Boris Žemva,etal. Weak ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity in K3Fe5F15[J].J Appl Phys,2008,103(7):074114-074118.
[7] O’Keeffe M. Ionic conductivity of yttrium fluoride and lutetium fluoride[J].Science,1973,180(180): 1276-1277.
[8] Underwood C C, McMillen C D, Chen H,etal. Hydrothermal chemistry,structures,and luminescence studies of alkali hafnium fluorides[J].Inorg Chem,2013,52(1):237-244.
[9] Xu Z H, Li C X, Yang P P,etal. Rare earth fluorides nanowires/nanorods derived from hydroxides:Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescence properties[J].Crystal Growth & Design,2009,9(11):4752-4758.
[10] Arnaud A, Cindy C, Samuel D,etal. High specific surface area metal fluorides as catalysts for the fluorination of 2-chloropyridine by HF[J].Applied Catalysis A:General,2013,453(1):20-27.
[11] Groß U, Rüdiger S, Kemnitz E. Alkaline earth fluorides and their complexes:A sol-gel fluorination study[J].Solid State Sci,2007,9(9):838-842.
[12] Yue Y C, Hu Z G, Chen C T. Flux growth of BaAlBO3F2crystals[J].J Cryst Growth,2008,310(6):1264-1267.
[13] Wangkiyn B M. Flux growth of crystals of some transition metal fluorides[J].J Mater Sci,1975,16(14):1487-1943.
[14] Wang X, Zhuang J, Peng Q,etal. Hydrothermal synthesis of rare-earth fluoride nanocrystals[J].Inorg Chem,2006,45(17):6661-6665.
[15] 何菲,闫共芹. 尖晶石型铁氧体空心纳微球的水热法制备及其性能研究进展[J].合成化学,2015,23(12):1178-1183.
[16] 李桂,张菁玲,王继明,等. 新型单核镍配合物的原位合成及其荧光性能[J].合成化学,2016,24(2):102-106.
[17] 彭文,胡彬,陈岩,等. 新型Keggin型钨簇合物{[Et3N]5[H3BW12O40]2·2H2O}的合成及其光催化性能[J].合成化学,2016,24(2):139-143.
[18] Liu X T, Zhang Y L, Shi C S,etal. Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescent properties of BaBeF4:RE(RE=Eu,Tb)[J].J Solid State Chem,2005,178(6):2167-2174.
[19] Xu Z H, Li C X, Yang P P,etal. Rare earth fluorides nanowires/nanorods derived from hydroxides:Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescence properties[J].Crystal Growth Design,2009,9(11):4752-4758.
[20] Wang X, Zhuang J, Peng Q,etal. Hydrothermal synthesis of rare-earth fluoride nanocrystals[J].Inorg Chem,2006,45(17):6661-6665.
[21] He L J, Zhang D, Feng S H,etal. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of perovskite oxide AgTaO3[J].Chem Res Chinese Universities,2012,28(5):760-763.
[22] He L J, Yuan H M, Huang K K,etal. Hydrothermal syntheses,structures,and magnetic properties of (NH4)2NaVF6and Na3VF6[J].J Solid State Chem,2009,182(2):2208-2212.
[23] Wanklyn B M , Garrard B J, Wondre F. Flux growth of some fluoride crystals under reducing conditions(VF2,K5V3F14, KTiF4)III[J].J Crystal Growth,1976,33(1):165-168.
[24] Jacoboni C, Leble A, Rousseau J J. Détermination precise de la structure de la chiolite Na5Al3F14et etude par R.P.E. de Na5Al3F14:Cr3+[J].J Solid State Chem,1981,36(3):297-304.
[25] Bukovec P, Bukovec N, Demšar A. Thermal analysis of complex fluorides[J].J Therm Anal,1990,36(5):1751-1760.
[26] Cros C, Dance J M, Grenier J C,etal. Sur les proprietes magnetiques du fluorure K5V3F14de type chiolite[J].Mater Res Bull,1977,12(4):415.
Hydrothermal Preparation of Chiolite-type Fluoride K5V3F14and Its Magnetic Property
HE Li-jie1, ZHANG Dong2*, TAN Guang-lei1,MU Tao1, LIU Hai-yan1, DU Peng1
(1. Department of Chemical and Material Engineering, Yingkou Institute of Technology, Yingkou 115014, China;2. Key Laboratoryof Ministry of Education of Physics and Technology for Advanced Batteries,College of Physics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China)
Chiolite-type fluoride K5V3F14(1) was prepared by hydrothermal method. The structure and property were characterized by elemental analysis, XRD, SEM, TG-DTA and magnetism analysis. The results indicated that 1 belongs to tetragonal, space groupP4/mnc witha=0.762 9 nm,b=0.762 9 nm,c=1.166 7 nm. Thermal decomposition temperature of 1 was above 400 ℃. 1 exhibited ferrimagnetism below 16 K and saturation magnetization at 0 K.
hydrothermal method; preparation; chiolite-type fluoride; magnetic property
2016-05-22;
2016-11-09
国家自然科学基金资助项目(21201073); 营口理工学院院级科研立项基金资助项目(QN-L-201403)
赫丽杰(1980-),女,汉族,吉林大安人,博士,副教授,主要从事固体功能材料合成的研究。 E-mail: helijie80@163.com
张冬,博士后,副教授, E-mail: dongzhang@jlu.edu.cn
0611.4
A
10.15952/j.cnki.cjsc.1005-1511.2017.02.16129

