Stathmin和p27在胃癌演变过程中的表达变化及与Hp感染的关系
胡桂梅 叶国良 秦丽君
Stathmin和p27在胃癌演变过程中的表达变化及与Hp感染的关系
胡桂梅 叶国良 秦丽君
目的 观察Stathmin和p27在胃癌演变过程中的表达变化,探讨其与幽门螺杆菌(Hp)的关系。方法 选取本院胃癌手术标本90例,胃镜活检标本160例及同期行内镜下黏膜剥离术后病理证实为早期胃癌标本56例,应用免疫组化法检测慢性胃炎黏膜(n=80)、上皮内瘤变(n=80)、早期胃癌(n=56)和进展期胃癌(n=90)组织中Stathmin和p27蛋白的表达水平。用14C呼气试验和组织学改良Giemsa染色方法联合检测胃癌中Hp感染情况,分析Stathmin、p27与Hp感染的关系。结果 与胃炎组和上皮内瘤变组相比,进展期胃癌组Stathmin和p27的表达水平差异均存有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。在上皮内瘤变组与胃炎组Stathmin表达水平差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),而p27表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同胃癌分化类型、浸润深度、TNM分期及淋巴转移与否者Stathmin和p27的表达水平差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。Hp感染者Stathmin蛋白表达增多,p27蛋白表达下降,均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。结论 p27联合Stathmin蛋白测定可以早期预测胃癌发生,更可以作为反映胃癌良恶性表型及预后的重要指标。
胃癌 上皮内瘤变 Stathmin p27 幽门螺杆菌
胃癌是常见的消化道恶性肿瘤之一,其发生及演变进展机制复杂。Stathmin是一种高度保守的胞质磷酸蛋白,有改变细胞增殖、分化等生物学行为[1]。近年来,国内外研究证实在多种肿瘤中Stathmin均有高水平表达,抑制其表达可以干扰恶性细胞的增殖[2]。p27是一种抑癌基因,在多种肿瘤包括胃癌中均发现该蛋白表达水平下降[3]。研究发现,Stathmin和p27两者相互作用,Stathmin能调节p27的细胞迁移作用[4]。本文探讨Stathmin和p27在胃癌演变过程中的表达变化及其与幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染的关系,现报道如下。
1 对象和方法
1.1 对象 选取我院2011年6月至2014年6月胃癌手术标本90例(进展期胃癌组),患者中男58例,女32例,年龄37~78(59.7±9.4)岁。胃癌分期采用1997年国际抗癌联盟制定的TNM分期法。所有胃癌病例均经病理证实,并附有完整的临床病理资料,根据病理结果分为两组,分别为高、中分化组50例,低、未分化组40例,患者术前均未接受化疗或放疗。选取同期胃镜活检标本共160例,患者中男98例,女62例,年龄16~85(57.1±11.0)岁;慢性胃炎80例(慢性胃炎组),上皮内瘤变80例(上皮内瘤变组)。同年在我院行内镜下黏膜剥离(ESD)术,术后病理证实为早期胃癌标本56例(早期胃癌组),患者中男38例,女18例,年龄35~72(58.9±8.6)岁。
1.2 试剂和方法 Stathmin单克隆抗体购自德国ABD Serotec公司,p27单克隆抗体、SP试剂盒和DAB染色剂均购自北京中山生物技术有限公司。常规免疫组织化学SP法(具体步骤按试剂盒说明书进行),DAB显色,分别用已知的阳性片作阳性对照,PBS代替一抗作阴性对照。Stathmin蛋白染色主要定位于细胞质中,p27染色主要定位于细胞核上,采用简单随机化方法选择10个高倍(×400)视野,根据染色程度及染色细胞百分率进行评分,阳性细胞百分率<10%,1分;10%~50%,2分;>50%,3分。肿瘤显色深浅按基本不着色,0分;色淡,1分;色中,2分;色深,3分。计算两者乘积,以得0分或1分为阴性,得2分、3分或4分为阳性(+),≥6分为强阳性(++)。所有切片均由2位有经验的病理医师经仔细阅片2次,确保结果的可重复性。
1.3 Hp检查 采用14C呼气试验和组织学改良Giemsa染色方法联合检测Hp,两项检查结果均为阳性者判定为Hp阳性,全部为阴性者判定为Hp阴性,剔除两种检测方法结果不一致的病例。
1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS17.0统计软件,计量资料以表示,组间比较采用方差分析;计数资料以百分率表示,组间比较采用校正χ2检验。
2 结果
2.1 Stathmin在各组中表达的阳性率比较 见表1、图1。

表1 Stathmin在各组中表达的阳性率比较[例(%)]

图1 Stathmin在各组中表达情况(a:慢性胃炎组Stathmin呈阴性表达;b:上皮内瘤变组Stathmin呈阳性表达;c:胃癌组Stathmin呈阴性表达;d:胃癌组Stathmin呈阳性表达;免疫组化染色,×200)
由表1可见,进展期胃癌组Stathmin的表达情况与慢性胃炎组、上皮内瘤变组相比差异均有统计学意义(χ2=61.232、15.359,均P<0.01),与早期胃癌组相比差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.241,P>0.05)。上皮内瘤变组与胃炎组、早期胃癌组相比差异均有统计学意义(χ2= 20.401、8.827,均P<0.01)。
2.2 p27在各组中表达的阳性率比较 见表2、图2。

图2 p27在各组中表达情况(a:慢性胃炎组p27呈阳性表达;b:上皮内瘤变组p27呈阳性表达;c:胃癌组p27呈阴性表达;d:胃癌组p27呈阳性表达;免疫组化染色,×100)

表2 p27在各组中表达的阳性率比较[例(%)]
由表2可见,p27在慢性胃炎组、上皮内瘤变组中的表达水平差异无统计学意义(χ2=4.410,P>0.05),与慢性胃炎组、上皮内瘤变组相比,p27在进展期胃癌组中的表达水平降低,差异均有统计学意义(χ2= 47.985、33.632,均P<0.05),但与早期胃癌组比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.095,P>0.05)。
2.3 Stathmin的表达与胃癌临床病理特征的关系 见表3。

表3 Stathmin的表达与胃癌临床病理特征的关系[例(%)]
由表3可见,不同性别、年龄胃癌患者中Stathmin阳性率比较差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),在分化类型、浸润深度、淋巴转移、TNM分期方面阳性率比较差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05),Hp感染者Stathmin阳性率高于未感染者(P<0.05)。
2.4 p27表达与胃癌临床病理特征的关系 见表4。
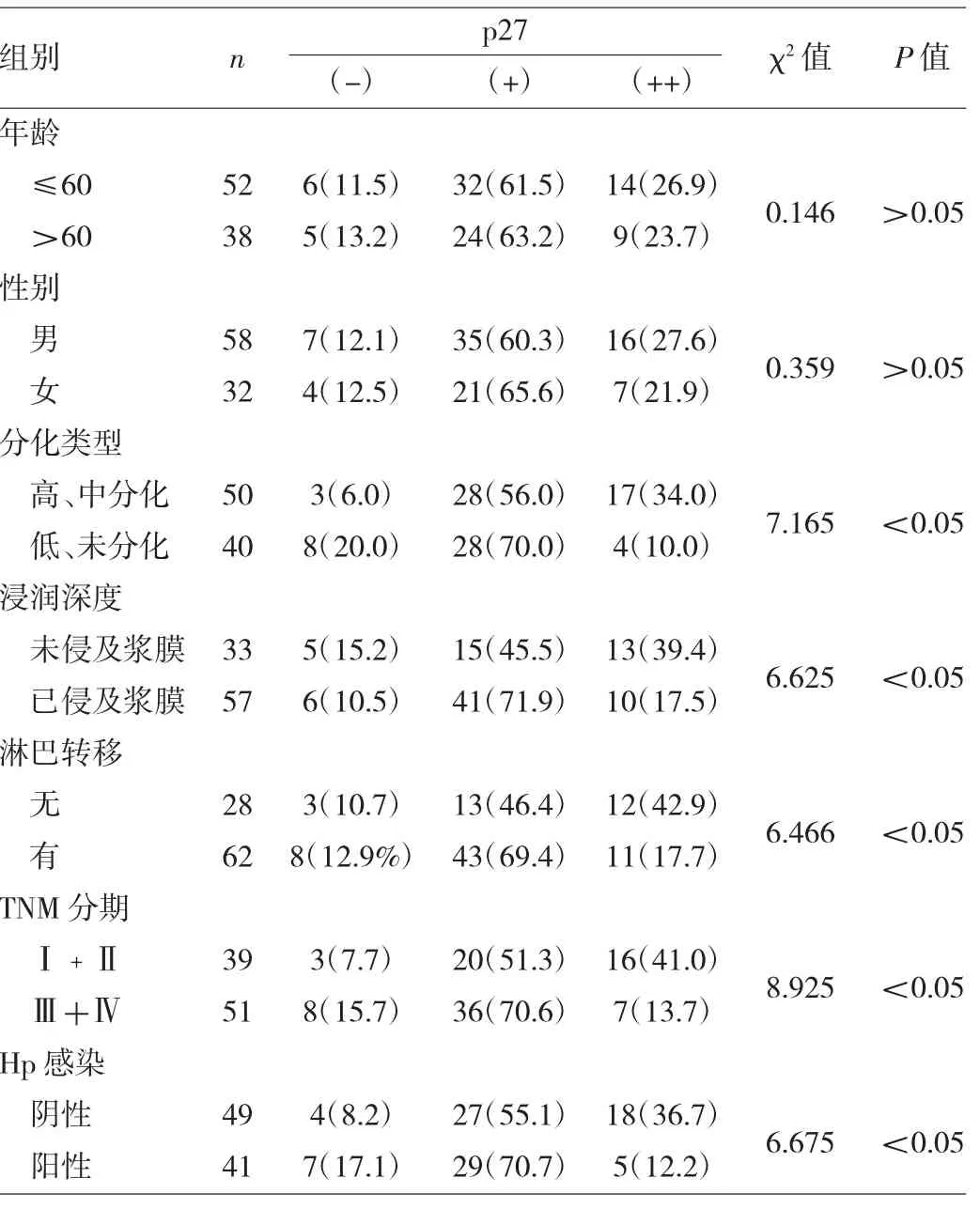
表4 p27表达与胃癌临床病理特征的关系[例(%)]
由表4可见,不同性别、年龄胃癌患者中p27阳性率比较差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),在分化类型、浸润深度、淋巴转移、TNM分期方面阳性率比较差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05),Hp感染者p27阴性率高于未感染者(P<0.05)。
3 讨论
胃癌是世界上最常见的消化道恶性肿瘤之一,全球癌症发病率位列第4位,病死率居癌症死因的第2位[5]。胃癌的发生并不是单一因素引起的,是多种因素共同作用的结果,不仅与癌基因的激活和抑癌基因的失活有关,还与细胞的增殖基因作用密切相关。Stathmin是一种主要的微管不稳定蛋白,通过调节微管系统的动力学平衡,控制细胞周期,并以此改变细胞的增殖、分化、活性等生物学行为,其表达情况与肿瘤细胞增殖及转移有关[6]。Jeon等[7]对226例弥漫型胃癌研究发现,Stathmin表达与肿瘤的淋巴转移、TNM分期、脉管浸润及肿瘤复发均呈正比,认为Stathmin的表达可作为评估胃癌预后的指标和胃癌治疗靶向基因。本研究结果显示,Stathmin在胃癌中表达阳性率高,多呈阳性或强阳性表达,与上皮内瘤变组相比差异有统计学意义;其表达强度在肿瘤分化类型、浸润深度、淋巴结转移、TNM分期等临床病理参数中差异均有统计学意义。因此,Stathmin的表达可预测胃癌发生可能,其高表达在胃癌的预后及发生、发展中均发挥了重要作用。
p27作为细胞周期负性调节因子,具有阻止细胞通过G1/S期转换的“关卡”作用,从而抑制细胞增殖导致细胞凋亡[8]。国外Aoyagi等[9]对75例胃癌研究中发现p27阴性者的淋巴转移率明显高于p27阳性者,p27阳性者的病变侵犯浆膜率明显低于p27阴性者,p27阴性者的平均增殖细胞核抗原指数明显高于p27阳性者,p27阳性者的生存指数明显高于p27阴性者。本研究结果显示,p27在胃炎及上皮内瘤变中蛋白表达阳性率均较高,两组间差异无统计学意义,而在胃癌组织中的表达阳性率显著下降;胃癌中p27的表达强度在肿瘤分化类型、浸润深度、淋巴转移、TNM分期等临床病理参数中差异均有统计学意义,在分化差或未分化、浆膜侵犯、淋巴结转移、TNM分期晚的胃癌中p27表达强度降低。因此,认为p27的表达可作为预测胃癌预后的指标。
1994年WHO国际癌症研究机构将Hp列为人类Ⅰ类致癌因子,相关研究证实Hp感染是胃癌发生的最重要危险因素之一,70%的胃癌发生与Hp感染有关[10]。研究认为Hp可通过调节G蛋白耦合的阿片受体→抑制p27启动因子的组胺乙酰化作用→p27表达下降[11];同时长期慢性Hp感染可使p27的胞浆错位,使其从抑癌转变为癌基因促使胃癌的发生、发展[12]。Baldassarre等[13]研究发现,Stathmin可以直接与p27结合,抑制Stathmin的表达和微管解离活性,从而降低肉瘤细胞的运动和侵袭性,而p27不仅与Stathmin结合,还可抑制Stathmin活性,促进微管稳定,使细胞不迁移;同时p27也可影响细胞形态和活性,其与Stathmin表达平衡在细胞骨架和细胞行为中起决定性作用[14]。最近Watanabe等[15]研究发现,Stathmin与p27结合,从而抑制p27功能,促进肿瘤细胞增殖,同时提高了肿瘤细胞的抗药性。本研究发现,在Hp阳性的胃癌中p27表达明显下降,而Stathmin表达明显增多。我们推测,Hp感染可能通过影响p27表达,从而促使Stathmin的表达增加。
综上所述,Stathmin和 p27相互作用,p27联合Stathmin测定能早期预测胃癌发生,甚至作为反映胃癌良、恶性表型及预后的重要指标。
[1]Rubin C I,Arweh G F.The role of Stathmin in the regulation of the cellcycle[J].J CellBiochem,2004,93(2):242.
[2]Liu Z,Lu H,Shi H,et al.PUMA overexpression induces reactive oxygen species generation and proteasome-mediated Stathmin degradation in colorectalcancer cells[J].Cancer Res,2005,65(5): 1647-1654.
[3]Kim D H,Lee H I,Nam E S,et al.Reduced expression of the cell-cycle inhitor P27Kipl is associated with progression and lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma[J].Histopathology, 2000,36(1):245-251.
[4]Ianetr Ruhin C,Atwch G F.p27(Kipl)and stammin share the stage for the first time[J].Trends CellBiol,2005,15(7):346-348.
[5]于吉人.进展期胃癌的治疗进展[J].浙江医学,2010,32(6):795-796.
[6]Singer S,Ehemann V,Brauckhoff A,et al.Protumorigenic overexpression of stathmin/Op18 by gain-of-function mutation in p53 in human hepatocarcinogenesis[J].Hepatology,2007,46(3):759-768.
[7]Jeon T Y,Han M E,Lee Y W,et al.Overexpression of Stathmin in the diffuse type of gastric cancer and its roles in proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells[J].Br J Cancer,2010,102(4): 710-718.
[8]Chu I M,Hengst L,Slingerland J M.The Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer:prognostic potential and relevance to anticancer therapy [J].Nat Rev Cancer,2008,8(4):253-264.
[9]AoyagiK,KouhujiK,MiyagiM,et al.Expression of p27Kip1 protein in gastric carcinoma[J].Hepatogastroenterology,2013,60(122): 390-394.
[10]Peek R M Jr,Blaser M J.Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2002,2(1):28-37.
[11]Byun S W,Chang Y J,Chung I S,et al.Helicobacter pylori decreases p27 expression through the delta opioid receptor-mediated inhibition of histone acetylation within the p27 promoter [J].Cancer Lett,2012,326(1):96-104.
[12]Sicheng Wen,Yoshiya So,Kamaljeet Singh,et al.Promotion of cytoplasmic mislocalization of p27 by Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer[J].Oncogene,2012,31(14):1771-1780.
[13]Baldassarre G,Bellett I B,Nicoloso M S,et al.p27(Kip1)-stathmin in interaction influences sarcoma cell migration and invasion[J]. Cancer Cell,2005,7(1):51-63.
[14]Belletti B,Pellizzari I,Berton S,et al.p27kip1 controls cell morphology and motility by regulating microtubule-dependent lipid raft recycling[J].MolCellBiol,2010,30(9):2229-2240.
[15]Watanabe A1,Suzuki H,Yokobori T,et al.Stathmin regulates p27 expression,proliferation and drug resistance,resulting in poor clinicalprognosis in cholangiocarcinoma[J].Cancer Sci,2014,105 (6):690-696.
Changes of stathmin and p27 expression in evolution of gastric cancer and their relation to infection of Helicobacter pylori
HU Guimei,YE Guoliang,QIN Lijun.Department of Gastroenterology,the Affiliated Hospital of Medical School of Ningbo University, Ningbo 315020,China
Objective To study the expression of the stathmin and p27 protein in the gastritis,intraepithelial neoplasia and gastric cancer and their relation to Helicobacter pylori(Hp)infection. Methods Immunohistochemical method were employed to detect stathmin and p27 protein expressions in gastritis,gastric intraepithelial neoplasia and gastric cancer specimen.The 14C-urea breath test and methylene blue method were used to detect Hp infection.The correlation of stathmin and p27 expression with Hp infection was analyzed. Results Compared with gastritis and gastric intraepithelial neoplasia,the expression of the stathmin and p27 in the gastric cancer were significantly increased(P<0.05).There was significant difference in stathmin expression between gastritis and intraepithelial neoplasia,but no difference in p27 expression between two groups.The expression of the stathmin and p27 protein was correlated with degree of differentiation,depth of invasion,lymph node metastasis,and TNM stage of gastric carcinoma.The expressions of stathmin and p27 were significantly correlated with Hp infection (P<0.05). Conclusion Stathmin and p27 may be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of gastric cancer,indicating they might be a potential target for screening of early gastric cancer.
Gastric cancer Intraepithelial neoplasia Stathmin p27 H.pylori
2015-10-20)
(本文编辑:马雯娜)
315020 宁波大学医学院附属医院消化科
叶国良,E-mail:ndfyygl@163.com

