芥子酸对高糖诱导下大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响*
裴 星, 韩 勇, 张占华, 李 娜, 施 遥, 张园园, 樊一钢, 田红燕
(1西安交通大学医学院附属红会医院内科,陕西西安710054;2西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院周围血管科,陕西西安710061)
芥子酸对高糖诱导下大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响*
裴 星1, 韩 勇1, 张占华1, 李 娜1, 施 遥1, 张园园1, 樊一钢1, 田红燕2△
(1西安交通大学医学院附属红会医院内科,陕西西安710054;2西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院周围血管科,陕西西安710061)
目的:探讨芥子酸对高糖诱导下大鼠血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cells,VSMCs)增殖和凋亡的影响及机制。方法:将培养的A7r5细胞随机分组处理,MTT法检测细胞活力,BrdU法检测细胞DNA合成,流式细胞术检测细胞周期进程和细胞凋亡,ELISA检测细胞活性氧簇(reactive oxygen species,ROS)生成,Western blot检测cyclin D1、P21和P27等蛋白的表达,以及蛋白激酶C(PKC)和P38的磷酸化水平。结果:与正常组比较,高糖组细胞活力显著升高,DNA合成加快,细胞周期加快,P21和P27表达降低,cyclin D1表达增加,ROS水平增加,细胞凋亡率降低,p-PKC和p-P38蛋白水平增加(P<0.05)。而芥子酸(0.1、1和10 μmol/L)处理引起细胞增殖活性降低,DNA合成减弱,细胞周期受阻,P21和P27表达增加,cyclin D1表达降低,ROS水平降低,细胞凋亡率升高,p-PKC和p-P38蛋白水平降低,且呈一定浓度依赖性(P<0.05)。P38抑制剂SB203580和PKC抑制剂chelerythrine均显著抑制高糖诱导的PKC/P38活化和细胞活力(P<0.05)。结论:芥子酸可通过抑制PKC/P38激活降低高糖诱导的VSMCs增殖,并促进细胞凋亡。
芥子酸;高糖;血管平滑肌细胞;细胞增殖;细胞凋亡
长期髙血糖症是诱发糖尿病心血管并发症的重要因素。高糖(high glucose,HG)可引起代谢障碍,促进血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cells,VSMCs)增殖,在动脉粥样硬化发生发展中发挥重要作用。白芥子,又叫白罂粟,为十字花科芸薹属植物白芥Sinapis alba L.的干燥成熟种子,主含白芥子苷、芥子碱、多糖、黄酮、芥子酸(sinapic acid,SA)和黏液质等。其中,芥子酸具有较强的抗氧化活性[1],能显著改善糖尿病大鼠高血糖症状[2],并且其衍生物可明显抑制血管内皮细胞活性氧簇(reactive oxygen species,ROS)生成[3]。因而,本研究拟探讨芥子酸对高糖诱导下VSMCs增殖和凋亡的影响,并初步探究其可能的分子机制。
材料和方法
1 材料与试剂
大鼠VSMCs株A7r5购自ATCC;高糖DMEM培养基、低糖DMEM培养基和胎牛血清购自Gibco;胰蛋白酶购自Invitrogen;芥子酸、MTT、甘露醇、二甲基亚砜、碘化丙啶、P38抑制剂SB203580和蛋白激酶C (protein kinase C,PKC)抑制剂chelerythrine购自Sigma;兔抗p-PKC和兔抗p-P38抗体购自Cell Signaling Technology;兔抗cyclin D1、兔抗P21、兔抗P27和兔抗β-actin抗体购自Santa Cruz;HRP-标记的山羊抗兔II抗和ECL发光试剂盒购自碧云天生物技术研究所;BCA蛋白定量分析试剂盒购自Thermo;BrdU增殖检测试剂盒购自Millipore;ROS检测试剂盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所;Annexin V-FITC凋亡试剂盒购自BD Biosciences;细胞培养6孔板购自Corning。
2 方法
2.1 细胞培养和分组 A7r5细胞用含10%胎牛血清、1×105IU/L青霉素和100 mg/L链霉素的DMEM培养基,在37℃、5%CO2条件下进行培养。用25 mmol/L高浓度葡萄糖模拟糖尿病患者的体内高糖环境,设立等渗透压的甘露醇组作为对照。取对数生长期细胞用于实验,分为正常组(5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖)、甘露醇组(5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖+19.5 mmol/L甘露醇)、高糖组(25 mmol/L葡萄糖)、高糖+芥子酸(0.1、1和10 μmol/L)组、高糖+chelerythrine(10 μmol/L)组和高糖+SB203580(10 μmol/L)组。
2.2 MTT法检测细胞活力 将A7r5细胞按每孔1×104个的密度接种96孔板,每孔200 μL培养基。24 h后,细胞换液,无血清培养。24 h后,按预先的实验设计分组并更换不同处理的培养基,每组设6个复孔。分别在24 h、48 h和72 h时点,向待测孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 g/L),37℃孵育4 h后弃上清,每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜,溶解后,用酶标仪检测490 nm处各孔的吸光度(absorbance,A)值。
2.3 BrdU法检测细胞DNA合成 将A7r5细胞按每孔2×105个的密度接种6孔板,按之前步骤处理细胞。48 h后,使用BrdU增殖检测试剂盒,严格按说明书步骤,酶标仪检测450 nm处各孔的吸光度值,间接反映细胞BrdU的掺入率。
2.4 流式细胞仪检测细胞周期进程 按之前步骤处理细胞48 h后,收集细胞,经70%乙醇4℃固定过夜和0.5 mL碘化丙啶(propidium iodide,PI;50 mg/L)避光孵育30 min,上流式细胞仪检测,使用MODFIT软件分析细胞在静止期/DNA合成前期(G0/G1)、DNA合成期(S)和DNA合成后期/分裂期(G2/M)的分布百分比。
2.5 ELISA检测ROS水平 按之前步骤处理细胞48 h后,使用ROS检测试剂盒(DCFH-DA探针法),严格按说明书步骤,酶标仪测定细胞内ROS水平。
2.6 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡 按之前步骤处理细胞48 h后,收集细胞,预冷PBS洗涤,加入预冷75%乙醇,4℃固定4 h以上。离心弃上清,PBS洗涤2次后,加入500 μL binding buffer悬浮细胞。加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC混匀后,加入5 μL PI,混匀。室温下避光反应5~15 min。1 h内进行流式细胞术检测。
2.7 Western blot检测 按之前步骤处理细胞48 h后,收集细胞,加入RAPI细胞裂解液,提取全蛋白。经BCA定量后、上样、SDS-PAGE分离、转膜、封闭、I抗、II抗孵育和ECL显影等步骤,检测各组细胞中P21、P27、cyclin D1、p-PKC、p-P38和β-actin等的蛋白水平。
3 统计学处理
实验数据采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行统计学分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,各组均数间两两比较采用SNK-q检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
1 芥子酸抑制高糖诱导的A7r5细胞增殖活性
MTT结果显示,48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞活力显著升高(P<0.05);而芥子酸(0.1、1和10 μmol/L)抑制细胞活力,且呈一定的浓度依赖性(P<0.05)。流式细胞术结果显示,48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞G0/G1期比例明显减少,S期细胞比例明显增多;而芥子酸抑制细胞G0/G1期向S期转换,且呈一定的浓度依赖性。Western blot结果显示,48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞P21和P27表达明显降低,cyclin D1表达明显增加(P<0.05);而芥子酸逆转上述蛋白表达,且呈一定的浓度依赖性(P<0.05)。BrdU结果显示,48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞DNA合成加快(P<0.05);而芥子酸抑制细胞DNA合成,且呈一定的浓度依赖性(P<0.05)。因此,芥子酸可抑制高糖诱导的A7r5细胞增殖,见图1。
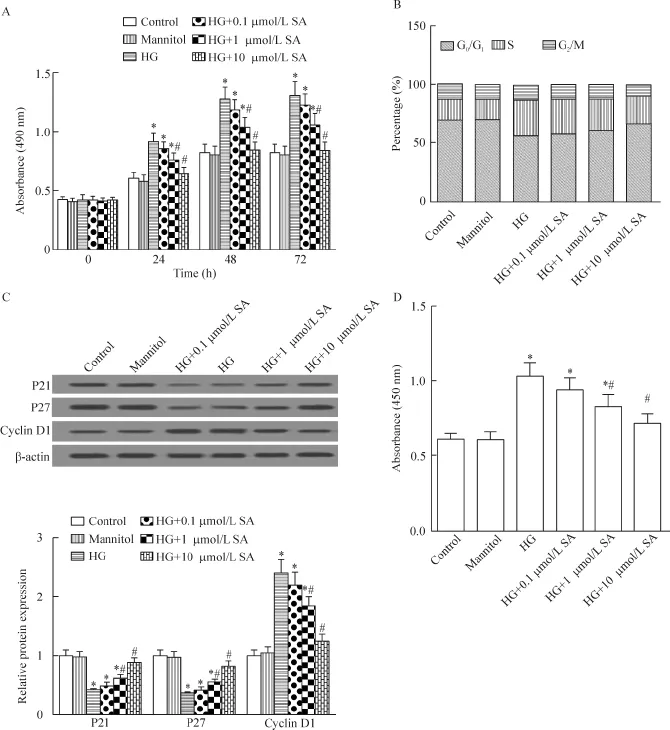
Figure 1.The effects of SA on HG-induced the proliferation of the A7r5 cells.A:the cell viability was determined by MTT assay;B: the cell cycle progression was determined by flow cytometry;C:the expression of cyclin D1,P21 and P27 was detected by Western blot;D:the DNA synthesis was measured by BrdU assay.Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05 vs control group;#P<0.05 vs HG group.图1 芥子酸对高糖引起的A7r5细胞增殖的影响
2 芥子酸抑制高糖诱导的A7r5细胞ROS生成
48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞ROS水平明显增加(P<0.05);而芥子酸(0.1、1和10 μmol/L)降低细胞ROS水平,且呈一定的浓度依赖性(P<0.05),见图2。
3 芥子酸上调高糖抑制的A7r5细胞凋亡
流式细胞术结果显示,48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞凋亡率水平明显降低(P<0.05);而芥子酸(0.1、1和10 μmol/L)上调细胞凋亡率,且呈一定的浓度依赖性(P<0.05),见图3。
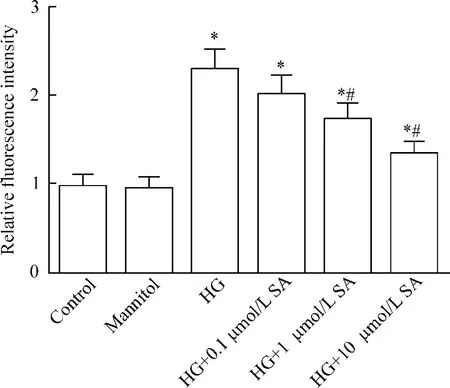
Figure 2.The effects of SA on HG-induced ROS levels in the A7r5 cells.The ROS levels were detected by ELISA assay.Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05 vs control group;#P<0.05 vs HG group.图2 芥子酸对高糖引起的A7r5细胞ROS水平的影响

Figure 3.The effects of SA on HG-induced cell apoptosis inhibition in A7r5 cells.The cell apoptosis rate was determined by flow cytometry.Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05 vs control group;#P<0.05 vs HG group.图3 芥子酸对高糖引起的A7r5细胞凋亡抑制的影响
4 芥子酸抑制高糖诱导的A7r5细胞PKC/P38活化
Western blot结果显示,48 h后,与正常组比较,高糖组细胞的p-PKC和p-P38蛋白水平明显增加;而芥子酸(0.1、1和10 μmol/L)降低细胞p-PKC和p-P38的蛋白水平,且呈一定的浓度依赖性(P<0.05),见图4。

Figure 4.The effects of SA on HG-induced p-PKC and p-P38 protein expression in the A7r5 cells.The protein levels of p-PKC and p-P38 were evaluated by Western blot.Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05 vs control group;#P<0.05 vs HG group.图4 芥子酸对高糖引起的A7r5细胞p-PKC和p-P38表达的影响
5 芥子酸通过抑制PKC/P38活化降低高糖诱导的A7r5细胞生长
Western blot结果显示,10 μmol/L SB203580和10 μmol/L chelerythrine均能显著抑制高糖诱导的PKC/P38的磷酸化水平,并下调高糖诱导的细胞生长(P<0.05),见图5。
讨论
糖尿病患者发生心血管疾病的风险比正常人显著增加,高糖环境下,VSMCs增殖加快,并迁移至动脉内膜,引起动脉壁增厚和管腔狭窄,VSMCs功能亦发生异常,是导致糖尿病大血管并发症的重要机制。长期高血糖诱导ROS生成和氧化应激,ROS生成亦促进VSMCs增殖[4],均与心血管疾病发生密切相关[5]。芥子酸,又称白芥酸或3,5-二甲氧基-4-羟基肉桂酸,属于天然酚酸类化合物,存在于紫山药、菜籽、柑橘类、酱油中以及炒白芥子、川穹、白芥子等多种药用植物中。研究表明,芥子酸可抑制结肠癌大鼠模型氧化应激反应[6],通过降低氧化应激治疗高血压性心脏病[7]和保护心脏缺血性损伤[8],并可通过自由基清除活性减轻小鼠脑神经元损伤[9]。本实验发现,芥子酸高糖可明显抑制高糖诱导的VSMCs ROS生成,提示芥子酸有可能用于糖尿病并发症的预防和治疗。
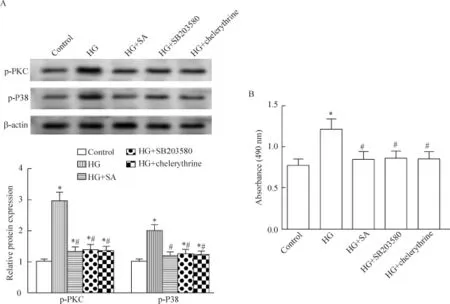
Figure 5.The effects of PKC/P38 inhibition and SA on HG-induced p-PKC and p-P38 proteins,and the changes of the viability in the A7r5 cells.A:the protein levels of p-PKC and p-P38 were evaluated by Western blot;B:the cell viability was determined by MTT assay.Mean±SD.n=4.*P<0.05 vs control group;#P<0.05 vs HG group.图5 PKC/P38抑制和芥子酸对高糖引起的A7r5细胞p-PKC、p-P38蛋白水平和细胞活力的影响
文献显示,高血糖促进VSMCs增殖,并抑制细胞凋亡[10],是糖尿病致动脉粥样硬化形成过程中的重要环节,该过程受到P21、P27和cyclin D1等因素调控[11-12]。体外研究表明,包含芥子酸的酚酸混合物能抑制乳腺癌细胞生长[13],芥子酸能抑制结肠癌细胞和Hela细胞生长[14]。本研究通过MTT法和BrdU法发现芥子酸抑制高糖诱导的VSMCs细胞增殖活性。细胞周期分析发现,在高糖环境下,VSMCs在细胞周期S期的分布比例明显增加,但芥子酸可显著逆转高糖对细胞周期的调控作用。进一步探讨芥子酸在高糖条件下抑制VSMCs增殖的分子机制表明,高糖对P21、P27和cyclin D1蛋白表达的调控作用可被芥子酸所逆转。因此,芥子酸可通过调控P21、P27和cyclin D1蛋白的表达抑制高糖诱导的促增殖效应。进一步研究表明,芥子酸可通过诱导细胞凋亡抑制HeLa细胞生长[14]。本实验流式细胞仪检测亦发现,芥子酸可明显促进高糖抑制的细胞凋亡。
PKC作为丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶家族的成员,参与氧化应激和动脉粥样硬化等病理过程,并可作为预防和治疗糖尿病血管并发症的潜在靶点[15]。P38通路激活促进VSMCs增殖迁移,与糖尿病动脉粥样硬化病理过程密切相关[16-17]。高糖促进VSMCs P38激活[11]和主动脉平滑肌细胞PKC激活,并且PKC抑制显著降低大鼠主动脉平滑肌细胞增殖活性[18-19]。而且PLC/PKC抑制能逆转血管紧张素II诱导的小鼠胚胎干细胞增殖和cyclin D1表达增加,以及P21 和P27水平降低[20];P38抑制剂SB203580可阻断人皮肤鳞状细胞癌A431细胞cyclin D1表达增加,以及P21和P27表达降低[21]。另有文献表明,芥子酸可通过抑制PLC-PKC激活提高葡萄糖利用率[2],通过负调节P38激活抑制炎症反应[22]。本实验发现,P38抑制剂SB203580和PKC抑制剂chelerythrine均能显著抑制高糖诱导的PKC/P38活化和细胞增殖活性,芥子酸亦显著抑制高糖诱导的VSMCs PKC/P38磷酸化和细胞增殖。可见,芥子酸可通过抑制PKC/ P38激活降低高糖诱导的VSMCs增殖。
综上所述,本研究发现芥子酸可通过抑制PKC/ P38激活降低高糖诱导的VSMCs过度增殖,并促进细胞凋亡,为芥子酸应用于糖尿病血管并发症治疗提供了一定的理论基础,但其作用机制和应用前景仍需进一步研究。
[1] Roy SJ,Mainzen Prince PS.Protective effects of sinapic acid on cardiac hypertrophy,dyslipidaemia and altered electrocardiogram in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2013,699(1-3): 213-218.
[2] Cherng YG,Tsai CC,Chung HH,et al.Antihyperglycemic action of sinapic acid in diabetic rats[J].J Agric Food Chem,2013,61(49):12053-12059.
[3] Zeng X,Zheng J,Fu C,et al.A newly synthesized sinapic acid derivative inhibits endothelial activation in vitro and in vivo[J].Mol Pharmacol,2013,83(5):1099-1108.
[4] 梅爱红,刘俊许,陈思锋,等.胰岛素通过活性氧的产生促进VEGF表达及血管平滑肌细胞迁移和增殖[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(2):272-277.
[5] Li H,Horke S,Forstermann U.Vascular oxidative stress,nitric oxide and atherosclerosis[J].Atherosclerosis,2014,237(1):208-219.
[6] Balaji C,Muthukumaran J,Nalini N.Effect of sinapic acid on 1,2 dimethylhydrazine induced aberrant crypt foci,biotransforming bacterial enzymes and circulatory oxidative stress status in experimental rat colon carcinogenesis [J].Bratisl Lek Listy,2015,116(9):560-566.
[7] Silambarasan T,Manivannan J,Krishna Priya M,et al.Sinapic acid prevents hypertension and cardiovascular remodeling in pharmacological model of nitric oxide inhibited rats[J].PLoS One,2014,9(12):e115682.
[8] Silambarasan T,Manivannan J,Priya MK,et al.Sinapic acid protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells against oxidative stress[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2015,456(4):853-859.
[9] Kim DH,Yoon BH,Jung WY,et al.Sinapic acid attenuates kainic acid-induced hippocampal neuronal damage in mice[J].Neuropharmacology,2010,59(1-2):20-30.
[10]Shi L,Ji Y,Jiang X,et al.Liraglutide attenuates high glucose-induced abnormal cell migration,proliferation,and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells by activating the GLP-1 receptor,and inhibiting ERK1/2 and PI3K/ Akt signaling pathways[J].Cardiovasc Diabetol,2015,14:18.
[11]Guo R,Li W,Liu B,et al.Resveratrol protects vascular smooth muscle cells against high glucose-induced oxidative stress and cell proliferation in vitro[J].Med Sci Monit Basic Res,2014,20:82-92.
[12]Chan KC,Wu CH,Huang CN,et al.Simvastatin inhibits glucose-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell migration involving increased expression of RhoB and a block of Ras/Akt signal[J].Cardiovasc Ther,2012,30(2):75-84.
[13]Kampa M,Alexaki VI,Notas G,et al.Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of selective phenolic acids on T47D human breast cancer cells:potential mechanisms of action [J].Breast Cancer Res,2004,6(2):R63-R74.
[14]Senawong T,Misuna S,Khaopha S,et al.Histone deacetylase(HDAC)inhibitory and antiproliferative activities of phenolic-rich extracts derived from the rhizome of Hydnophytum formicarum Jack.:sinapinic acid acts as HDAC inhibitor[J].BMC Complement Altern Med,2013,13:232.
15 ]Kong L,Shen X,Lin L,et al.PKC beta promotes vascular inflammation and acceleration of atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE null mice[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2013,33(8):1779-1787.
[16]Liu Z,Cao W.p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase:a critical node linking insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets,2009,9(1):38-46.
[17]Shen YJ,Zhu XX,Yang X,et al.Cardamonin inhibits angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by downregulating p38 MAPK,Akt,and ERK phosphorylation[J].Nat Med,2014,68(3): 623-629.
[18]柴大军,许昌声,宁若冰,等.RXR激动剂通过抑制PKC激活对抗高糖诱导的大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(2):266-271.
[19]Yang J,Han Y,Sun H,et al.(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by high glucose by inhibition of PKC and ERK1/2 signalings[J].J Agric Food Chem,2011,59 (21):11483-11490.
[20]Han HJ,Han JY,Heo JS,et al.ANG II-stimulated DNA synthesis is mediated by ANG II receptor-dependent Ca2+/PKC as well as EGF receptor-dependent PI3K/Akt/ mTOR/p70S6K1 signal pathways in mouse embryonic stem cells[J].J Cell Physiol,2007,211(3):618-629.
[21]Yang XS,Liu S,Liu YJ,et al.Overexpression of fucosyltransferase IV promotes A431 cell proliferation through activating MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways[J].J Cell Physiol,2010,225(2):612-619.
[22]Kook SH,Choi KC,Lee YH,et al.Raphanus sativus L.seeds prevent LPS-stimulated inflammatory response through negative regulation of the p38 MAPK-NF-κB pathway[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2014,23(2):726-734.
(责任编辑:林白霜,罗 森)
Effects of sinapic acid on proliferation and apoptosis of rat vascular smooth muscle cells induced by high glucose
PEI Xing1,HAN Yong1,ZHANG Zhan-hua1,LI Na1,SHI Yao1,ZHANG Yuan-yuan1,FAN Yi-gang1,TIAN Hong-yan2
(1Department of Internal Medicine,Hong-Hui Hospital,Xi’an Jiaotong University College of Medicine,Xi’an 710054,China;2Department of Peripheral Vascular Medicine,The First Affiliated Hospital,Xi’an Jiaotong University College of Medicine,Xi’an 710061,China.E-mail:tianhongyan21@sina.com)
AIM:To investigate the effects of sinapic acid(SA)on the proliferation and apoptosis of rat vascular smooth muscle cells(VSMCs)induced by high glucose(HG).METHODS:Cultured A7r5 cells were randomly divided and treated as indicated.The cell viability was determined by MTT assay.DNA synthesis was measured by BrdU assay.Cell cycle progression and cell apoptotic rate were determined by flow cytometry analysis.The levels of reactive oxygen species(ROS)were detected by ELISA.The protein levels of cyclin D1,P21,P27,phosphorylated protein kinase C(p-PKC),p-P38 and β-actin were evaluated by Western blot.RESULTS:Compared with control group,the viability of A7r5 cells was significantly enhanced,the DNA synthesis was increased,the cell cycle progression was promoted,the levels of ROS were elevated,the cell apoptotic rate was reduced,the protein expression of P21 and P27 was decreased,and the protein levels of cyclin D1,p-PKC and p-P38 were increased in HG group(all P<0.05).These effects were reversed by SA (0.1,1 and 10 μmol/L)treatment in a dose-dependent manner(all P<0.05).Both P38 inhibitor SB203580 and PKC inhibitor chelerythrine significantly inhibit HG-induced PKC/P38 activation and cell viability(P<0.05).CONCLUSION:SA inhibits HG-induced VSMCs proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis via reducing PKC/P38 activation.
Sinapic acid;High glucose;Vascular smooth muscle cells;Cell proliferation;Apoptosis
R587.1;R363.2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2016.07.004
1000-4718(2016)07-1174-06
2016-02-22
2016-04-05
西安市红会医院2016年院级科研基金资助项目(No.YJ2016003)
△Tel:029-85324128;E-mail:tianhongyan21@sina.com

