高频超声在类风湿关节炎患者神经卡压诊断中的应用价值
高培森,任水明,刘 磊,杜智慧,王淑敏
内蒙古鄂尔多斯市中心医院 1超声科 2风湿免疫科,内蒙古鄂尔多斯017010
·论著·
高频超声在类风湿关节炎患者神经卡压诊断中的应用价值
高培森1,任水明2,刘磊1,杜智慧1,王淑敏1
内蒙古鄂尔多斯市中心医院1超声科2风湿免疫科,内蒙古鄂尔多斯017010
摘要:目的评估高频超声在类风湿关节炎(RA)患者神经卡压诊断中的应用价值。方法以80例RA患者(研究组)和60例非RA患者为研究对象,行上肢神经超声检查,统计两组受试者的神经卡压发生率;比较有、无神经卡压症状RA患者在年龄、病程、健康评估问卷残疾指数(HAQ-DI)分值、类风湿活动性等方面的差异。结果RA组上肢神经卡压发病率明显高于对照组(15.0%比3.3%,P=0.046)。伴有神经卡压RA患者与无神经症状患者相比年龄更大[(60.2±11.4)岁比(49.2±7.9)岁;t=2.343,P=0.039],病程更长[(9.50±5.99)年比(5.88±3.87)年;t=2.639,P=0.023],HAQ-DI指数更高(1.58±0.75比0.85±0.67;t=2.490,P=0.030);两组患者在类风湿活动性指数方面差异没有统计学意义(14.50±11.68比16.62±9.24;t=1.141,P=0.278)。结论外周神经病变是RA的常见关节外表现。当RA患者疑似外周神经病变时,应行高频超声检查。
关键词:类风湿关节炎;神经卡压;超声;上肢
ActaAcadMedSin,2016,38(3):327-330
风湿性关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是一种病因不明的慢性系统性炎性疾病,以双侧对称性的多发关节炎为其特征性表现,约10%~20%的患者会合并心血管系统、呼吸系统、神经系统等关节外病变[1- 2]。Sivri等[3]研究发现,57.4%的RA患者外周神经电生理检查存在异常。RA引起的卡压、脉管炎及一些治疗药物的不良反应都有可能诱发外周神经远端的感觉或感觉-运动神经病变[4- 5]。本研究采用高频超声评估了RA患者外周神经卡压在流行病学和临床表现等方面的相关性。
对象和方法
对象2013年3月至2015年3月在内蒙古鄂尔多斯市中心医院风湿免疫科住院就诊的80例RA患者,其中,男15例,女65例,平均年龄(51.5±9.0)岁(28~78岁);所有患者均符合2012年早期RA分类诊断标准[6],平均病程(6.1±4.6)年(1~11年)。随机选取同期就诊的非RA患者60例为对照组,其中,男11例,女49例,平均年龄(51.1±10.8)岁(24~76岁)。两组患者均无骨折和外伤史,无孕产妇,RA组未排除糖尿病和甲状腺疾病患者。
仪器设备飞利浦IU22超声诊断仪,高频线阵探头L12- 5(5~12 MHz)、L15- 7(7~15 MHz)。西门子S2000超声诊断仪,高频线阵探头9L4(4~9 MHz)。
方法采用高频超声分别对两组患者的正中神经、尺神经和桡神经及其周围结构进行评价。以正中神经横截面积≥12 mm2、尺神经横截面积>10 mm2、桡神经横截面积>13 mm2,或神经局部肿大横截面积超过邻近部分20%为超声诊断标准[7- 9],所有阳性患者行肌电图检查,以肌电图检查结果为金标准,统计阳性病例及发病率。
RA组患者详细询问病史,统计患者年龄、患病时间、健康评估问卷残疾指数(Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index,HAQ-DI)分值、类风湿活动性指数(clinical disease activity index,CDAI),将RA组继续分为神经卡压阳性组(N+)和阴性组(N-),对两组患者的上述指标进行比较。
RA的活动性通过CDAI进行评价:CDAI=TJC(28个关节中的疼痛关节数)+SJC(28个关节中的肿胀关节数)+PGA(患者的总体评价0~10)+MDGA(医生的总体评价)[10]。
统计学处理采用SPSS 19.0统计软件,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,组间比较采用t检验;计数资料以百分比表示,组间比较采用卡方检验;P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
超声表现正常神经为长轴切面高回声(神经外膜)、低回声(神经束)交替分布的平行管状结构,短轴切面为边界清晰的蜂窝状结构(高回声的神经外膜包绕并分隔开的多个点状低回声)。神经卡压时,直接卡压部位神经直径明显变细(切迹),临近卡压点神经肿胀明显,神经内部回声减低、蜂窝状结构模糊消失(图1、2)。
RA组和对照组神经卡压发病率的比较RA组80
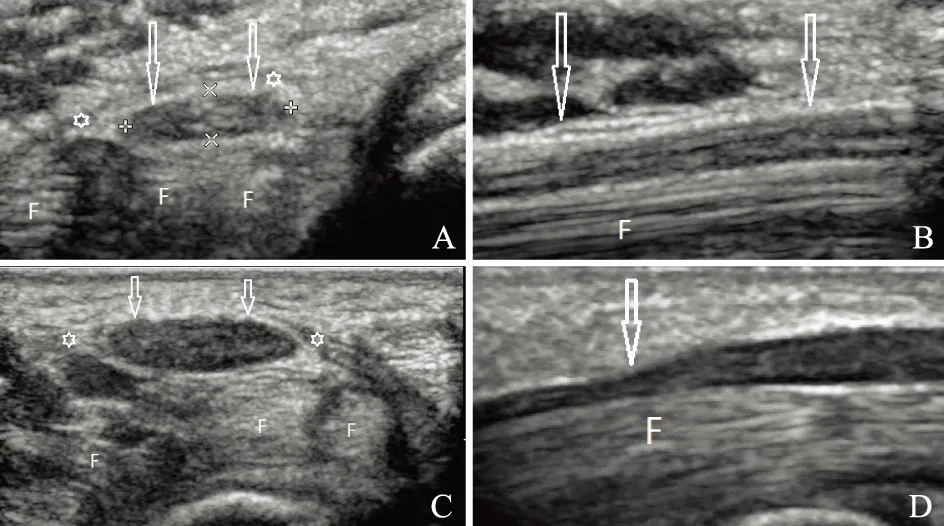
F:指屈肌腱
F:finger fiexor tendons
A. 正中神经正常超声表现(短轴,箭头);B. 正中神经正常超声表现(长轴,箭头);C. 腕管综合征患者短轴切面,正中神经明显增大(箭头),回声减低,内部结构显示不清;D. 腕管综合征患者长轴切面,正中神经受压部位可见切迹(箭头),邻近部位神经肿胀明显
A.ultrasonographic pictures of a normal median nerve (transverse sonogram,arrow);B.ultrasonographic pictures of a normal median nerve(longitudinal sonogram,arrow);C.transverse sonogram showing enlargement of the median nerve (arrow) and loss of internal structure discrimination and reduced echogenicity;D.longitudinal sonogram showing a marked caliber change noted at the compression site (arrow),and the proximal nerve was markedly swollen
图 1正中神经超声图片
Fig 1Ultrasonographic pictures of median nerve

1:肱骨内上髁;2:鹰嘴
1:medial epicondyle;2:olecroanon
A. 尺神经正常超声表现(短轴,箭头);B. 尺神经正常超声表现(长轴,箭头);C.短轴切面显示尺神经明显肿胀,内部束状结构消失(箭头);D. 长轴切面显示神经受压部位管径突然变细(箭头),邻近的神经明显肿胀
A.ultrasonographic pictures of a normal ulnar nerve(transverse sonogram,arrow);B.ultrasonographic pictures of a normal ulnar nerve(longitudinal sonogram,arrow);C.transverse sonogram shows swollen ulnar nerve and loss of fascicular discrimination(arrow);D.longitudinal showing a marked caliber change noted at the compression site(arrow),meanwhile,the proximal nerve was markedly swollen
图 2尺神经超声图片
Fig 2Ultrasonographic pictures of ulnar nerve
例患者中,有12例(15%)发生上肢神经卡压,其中,正中神经卡压10例(男2例,女8例;单侧4例,双侧6例);尺神经卡压2例(男1例,女1例,均为单侧发病)。对照组60例患者中,有2例(3.3%)发生正中神经卡压(男1例,女1例;均为单侧受压)。两组相比,差异有统计学意义(χ2=3.97,P=0.046)。
有无神经卡压RA患者间的比较伴有神经卡压RA患者与无神经症状患者相比年龄更大[(60.2±11.4)岁比(49.2±7.9)岁;t=2.343,P=0.039)],病程更长[(9.50±5.99)年比(5.88±3.87)年;t=2.639,P=0.023)],HAQ-DI指数更高(1.58±0.75比0.85±0.67;t=2.490,P=0.030);两组患者在CDAI方面差异没有统计学意义(14.50±11.68比16.62±9.24;t=1.141,P=0.278)。
讨论
外周神经疾病是RA常见的关节外病变之一。有研究显示,RA患者罹患外周神经疾病可能与神经滋养血管的脉管炎、邻近组织卡压和一些抗风湿药物的不良反应有关[4- 5,11]。外周神经病变表现多样,如感觉麻木,疼痛和肌肉萎缩。这些症状与关节炎的症状相类似,容易被忽视。
类风湿是一种慢性的系统性疾病,其主要病理特征是滑膜细胞增生,血管翳形成,侵犯关节软骨和骨组织,最终导致关节骨质破坏、增生,关节结构畸形。上肢的外周神经卡压最容易发生在腕管和肘管,腕管和肘管均为相对闭合的管道结构,其内有神经及其伴行组织走行,RA增厚的滑膜和腱鞘,肿大的肌腱和骨骼的增生变形都可以挤占管道空间,导致其内走形的神经滋养动脉受压和静脉充血,最终表现为神经的水肿,伴随着卡压时间的延长,神经鞘逐渐纤维化会对神经纤维产生进一步的危害[11]。
1992年,Buchberger等[12]首次提出直接受压部位神经直径的突然变细是神经卡压的显著超声特征,现在被认为是一个同样可以应用在其他部位神经卡压性病变的可靠诊断标准[13]。邻近病变处的神经束局限性膨大是微血管充血、水肿的表现,神经受压的严重程度与神经的横截面积呈正相关[14],严重受压的神经束通常融合在一起表现为一条粗大的低回声带,无法分辨出神经内部束样结构。超声在原发性和继发性神经卡压的诊断中有着很高的敏感性和特异性[15- 17]。
本研究结果显示,RA患者神经卡压综合征的发病率明显高于对照组,RA患者年龄越大,病程越长患病风险越高。该结果与RA疾病发展过程一致,RA患病时间越长,关节骨质增生和关节变形越严重,腕管及肘管神经通过空间减小,压力增大,更加容易导致神经卡压的发生。本研究还显示,神经卡压综合征的RA患者HAQ-DI残疾指数更高,推测其原因可能是由患者平均年龄更高,病程更长导致;此外,正中神经卡压和尺神经卡压造成的刺痛和肌肉萎缩无力也可能是重要原因之一。
本研究选取的RA患者均为住院患者,病程较长,症状较重,神经卡压的发生率有可能高于实际发病率。此外,糖尿病和甲状腺功能低下也是外周神经卡压的常见病因,RA患者合并上述疾病时,在神经卡压的超声图像和临床表现是否会有更加严重的表现,也是本研究试图探讨的问题之一,但是病例过少,且无阳性病例,未能得出有意义的结论,还需要更多的资料收集。
参考文献
[1]Turesson C,O’Fallon WM,Crowson CS,et al. Occurrence of extraarticular disease manifestations is associated with excess mortality in a community based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. J Rheumatol,2002,29(1):62- 67.
[2]Richman NC,Yazdany J,Graf J,et al.Extraarticular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis in a multiethnic cohort of predominantly Hispanic and Asian patients[J].Medicine (Baltimore),2013,92(2):92- 97.
[3]Sivri A,Guler-Uysal F. The electroneurophysiological findings in rheumatoid arthritis patients[J]. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol,1999,39(7):387- 391.
[4]Agarwal V,Singh R,Chauhan S,et al. A clinical,electrophysiological,and pathological study of neuropathy in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol,2008,27(7):841- 844.
[5]Pouget J. Vascular neuropathies[J]. Rev Prat,2000,50(7):749- 752.
[6]Singh JA,Furst DE,Bharat A, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken),2012,64(5):625- 639.
[7]Peer S,Bodner G. High resolution sonography of the peripheral nervous system[M]. 2nd ed.Berlin:Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg,2008.
[8]Volpe A,Rossato G,Bottanelli M,et al.Ultrasound evaluation of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow:correlation with electrophysiological studies[J]. Rheumatology,2009,48(9):1098- 1101.
[9]Djurdjevic T,Loizides A,Loscher W,et al.High resolution ultrasound in posterior interosseous nerve syndrome[J]. Muscle Nerve, 2014,49(1):35- 39.
[10]路晓燕,李春,赵金霞,等.2011年ACR/EULAR类风湿关节炎缓解标准与其他常用标准的比较[J]. 北京大学学报:医学版,2013,45(2):260- 263.
[11]Panahi E,O’Connor CR,Checa A. Sonographic assessment of the carpal tunnel syndrome secondary to a tenosynovitis of the flexor digitorum superficialis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis[J].J Clin Rheumatol,2014,20(5):294- 2955.
[12]Buchberger W,Judmaier W,Birbamer G, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome:diagnosis with high resolution sonography[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol,1992,159(4):793- 798.
[13]Ng ES,Vijayan J,Therimadasamy AK,et al. High resolution ultrasonography in the diagnosis of ulnar nerve lesions with particular reference to post-traumatic lesions and sites outside the elbow[J]. Clin Neurophysiol,2011,122(1):188- 193.
[14]Klauser AS,Halpern EJ,De Zordo T. Carpal tunnel syndrome assessment with US:value of additional cross-sectional area measurements of the median nerve in patients versus healthy volunteers[J].Radiology,2009,250(1):171- 177.
[15]Fujimoto K,Kanchiku T,Kido K,et al. Diagnosis of severe carpal tunnel syndrome using nerve conduction study and ultrasonography[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol,2015,41(10):1332- 1340.
[16]Kim JH,Won SJ,Rhee WI.Diagnostic cutoff value for ultrasonography in the ulnar neuropathy at the elbow[J]. Ann Rehabil Med,2015,39(2):170- 175.
[17]Scheidl E,Böhm J,Farbaky Z,et al.The significance of high-resolution ultrasonography in the diagnosis of peripheral nerve disorders[J].Ideggyogy Sz,2013,66(1- 2):4- 13.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(81260221、81460269) Supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (81260221,81460269)
通信作者:王淑敏电话:0477- 8107184,电子邮件:shuminwang2014@163.com
中图分类号:R445.1;R730.41
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1000- 503X(2016)03- 0327- 04
DOI:10.3881/j.issn.1000- 503X.2016.03.015
Corresponding author:WANG Shu-minTel:0477- 8107184,E-mail:shuminwang2014@163.com
(收稿日期:2015- 06- 15)
Value of High-frequency Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Peripheral Nerve Compression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
GAO Pei-sen1,REN Shui-ming2,LIU Lei1,DU Zhi-hui1,WANG Shu-min1
1Department of Ultrasound,2Department of Rheumatology,Ordos Hospital,Ordos,Inner Mongolia 017010,China
ABSTRACT:ObjectiveTo evaluate the value of high-frequency ultrasound (HFUS) in diagnosing peripheral nerve compression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). MethodsThe upper limb nerves were evaluated by HFUS in 80 RA patients (RA group) and 60 non-RA patients (control group),then the incidence of peripheral nerve compression was recorded respectively. RA patients with/without neurological symptoms were compared in terms of age,disease course,Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score,and clinical disease activity index (CDAI). ResultsThe incidence of upper limb nerve compression in RA group was significantly higher than that in control group(15.0% vs. 3.3%,P=0.046)。The patients with nerve compression was older [(60.2±11.4)y vs.(49.2±7.9)y;t=2.343,P=0.039] and had longer disease course [(9.50±5.99) y vs. (5.88±3.87)y;t=2.639,P=0.023] and higher HAQ-DI score (1.58±0.75 vs.0.85±0.67;t=2.490,P=0.030). These two groups had no statistical differences in CDAI (14.50±11.68 vs.16.62±9.24;t=1.141,P=0.278).ConclusionsPeripheral neuropathies are common extra-articular manifestations in RA patients. HFUS can be valuable in patients suspected of RA.
Key words:rheumatoid arthritis;nerve compression;ultrasonography;upper limb

