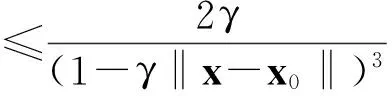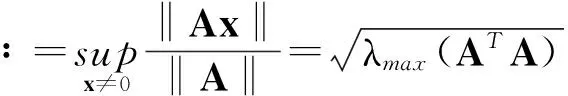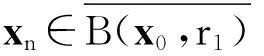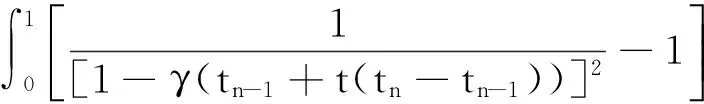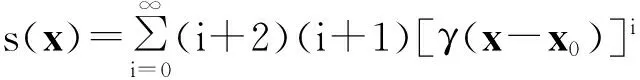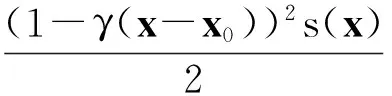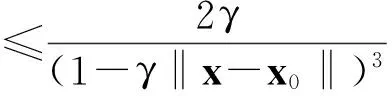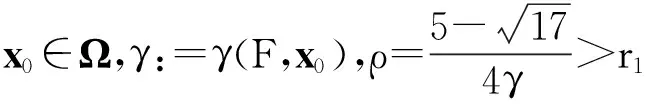解变分不等式的简单牛顿法的收敛性
周 彪,李素兰
(浙江工业大学 理学院,浙江 杭州 310023)
解变分不等式的简单牛顿法的收敛性
周彪,李素兰
(浙江工业大学 理学院,浙江 杭州 310023)
摘要:牛顿法作为求解变分不等式问题的一个重要方法,它的收敛性一直是各位学者研究的一个核心问题.当变分不等式中的函数F在内满足γ-条件时,证明了由牛顿法产生的迭代点列是适定的,而且解的序列可以被构造出来的{tn}序列控制收敛到一个变分不等式的最优解.考虑到F在内满足γ-条件这个区域性条件给进一步的研究带来了困难,因此引入了解析函数,给出了F是解析函数条件下的牛顿法的收敛性结果.数值实验表明算法是有效的.
关键词:牛顿法;变分不等式;γ-条件;半局部收敛;解析函数
变分不等式(Variational inequality)首先由Hartman和Stampacchia[1]在1966年提出,最初是用来研究偏微分方程的,它在数学、工程、物理和经济等领域有着广泛的应用背景.作为非线性互补问题的推广,它的提出统一了优化问题和均衡问题的研究,并且在数学领域中作为大量数学问题实际求解的统一框架.实际生活中的许多问题都可以归结为(或松弛成)一个凸优化问题,而凸优化的一阶必要性条件就是一个单调变分不等式.因此用变分不等式研究凸优化的求解问题,就像微积分中用导数求一元函数的极值,常常会带来很大的方便,这使得它成为数学规划中一个十分热门的研究课题[2-6].

1理论基础与符号说明
1.1符号说明
1)Rn表示n维欧式向量空间,令Ω→Rn,F:Ω→Rn表示映射F的值域和定义域都是Rn的非空子集.
2)‖x‖:向量x的2-范数.
3)‖A‖:矩阵A的2-范数.

B(x0,ρ)∶={y∈Rn|y-x0 1.2理论基础 下面给出变分不等式的一般形式: 给定一个Rn中的非空子集Ω和一个函数F:Ω→Rn,变分不等式问题记为VIP(Ω,F),是指求x*∈Ω,使得 (y-x*)TF(x*)≥0∀y∈Ω (1) 文献[13]中提到了很多数值解法,其中牛顿法是最重要的方法之一.牛顿法解函数F(x)=0时的一般迭代格式为 F′(xn-1)T(xn-xn-1)=-F(xn-1) n=1,2,3,…,∞ (2) 而在求解变分不等式时,序列{xn}是由以下不等式的解产生的:假设已知迭代起点x0∈Ω,则x1的解为 (y-x1)T(F(x1)+F′(x0)(x1-x0))≥0 ∀y∈Ω 那么假设xn-1存在,则xn为 (y-xn)T(F(xn-1)+F′(xn-1)(xn-xn-1))≥0 ∀y∈Ω (3) 的解. 定义1设Ω是Rn的一个非空的凸闭集,令ρ>0,γ>0,ργ<1.函数F:Ω→Rn在Ω上二阶可微且存在一个x0∈Ω,F′(x0)-1存在,若不等式 (4) 定义2数学上如果一个函数在邻域内的每个点都能够展开成幂级数,且收敛半径大于零,则我们称函数在邻域内是解析的. 2由牛顿法产生的序列{xn}的收敛性 2.1γ-条件 给定一个Rn中的非空子集Ω和一个函数F:Ω→Rn,变分不等式问题记为VIP(Ω,F)是指求x*∈Ω,使得 (y-x*)TF(x*)≥0∀y∈Ω (5) 牛顿法作为求解变分不等式(5)最重要的方法之一,在求解xn时文献[13]考虑的是F在xn-1处的一阶导数信息,将算法简化为每次迭代都只考虑F在x0处的一阶导数信息.故其迭代格式如下: 假设已知迭代起点x0∈Ω,则x1的解为 (y-x1)T(F(x1)+F′(x0)(x1-x0))≥0 ∀y∈Ω (6) 那么假设xn-1存在,则xn为 (y-xn)T(F(xn-1)+F′(x0)(xn-xn-1))≥0 ∀y∈Ω (7) 的解.即xn为VIP(Ω,Fn-1)的一个解.记Fn-1(xn)∶=F(xn-1)+F′(x0)(xn-xn-1). 王兴华和韩丹夫教授[15]通过引入函数 (8) 改进了Smale点估计的结论.其中β>0,R满足 此时若将式(8)中的函数L定义为 则函数h(t)为 (9) 并且定义了一个序列{tn}为 t0=0,n=0,1,… (10) 其中h(t)满足式(9). 引理1假设A∈Rn×Rn是一个正定矩阵,x∈Rn,则有 证明回顾矩阵2-范数的定义 ‖xn+1-xn‖ (11) 且{xn}收敛到变分不等式的一个解x*. 证明首先证明由牛顿法产生的序列{xn}是适定的:因为F′(x0)是正定的,那么显然Fn-1(x)是严格递增的.而Ω是Rn的一个非空的凸闭集,所以VIP(Ω,Fn-1)有一个唯一解xn.即如果F′(x0)是正定的,则由式(7)牛顿法产生的序列是有意义的[12]. (xn+1-xn)TFn-1(xn)=(xn+1-xn)T· (F(xn-1)+F′(x0)(xn-xn-1))≥0 (12) (xn-xn+1)TFn(xn+1)=(xn-xn+1)T· (F(xn)+F′(x0)(xn+1-xn))≥0 (13) 合并式(12,13),并移项得 (xn-xn+1)TF′(x0)(xn-xn+1)≤ (xn-xn+1)T[F(xn)-F(xn-1)- F′(x0)(xn-xn-1)] (14) (xn-xn+1)TF′(x0)(xn-xn+1)≥ (15) 结合式(14,15),有 (xn-xn+1)≤ (xn-xn+1)T[F(xn)- F(xn-1)-F′(x0)· (xn-xn-1)] 移项化简得 ‖xn+1-xn‖≤‖F′(x0)-1‖‖F(xn)-F(xn-1)- F′(x0)(xn-xn-1)‖= t(xn-xn-1))-F′(x0)‖· ‖xn-xn-1‖dt (16) ‖xn-xn + 1‖‖xn - 1+ t(xn-xn - 1)-x0‖dλdt = tn+1-tn (y-x*)T(F(x*)+F′(x0)(xn-xn-1))= (y-x*)T(F(x*))≥0成立,即{xn}收敛到变分不等式的一个解x*.得证. 2.2 在解析函数上的应用 (17) 如果F′(x0)不可逆,则定义γ(F,x0)=∞.因此,若 F′(x0)可逆,则由解析性得γ(F,x0)有界.以下引理说明当函数F是解析的,则F一定满足γ-条件. 证明因为函数F是解析的,可以写成幂级数的形式为 所以 又因为F′(x0)可逆,结合(17)式得 (18) (19)再次对(19)等式两边同时乘以γ(x-x0),并相减,得 移项得 再结合(18)式得 接下来,我们得到了一个关于函数F是解析函数的牛顿法序列收敛性的推论. ‖xn+1-xn‖ (20) 且{xn}收敛到变分不等式的一个解x*. 3数值结果 任意x=(ξ1,ξ2)∈R2 表1牛顿迭代的次数与数值结果 Table1ThenumberofiterationsandNumericalresultsofNewton 迭代数/次序列{xn}0(0.95,0.96)1(0.9463,0.9421)2(0.9397,0.9377)3(0.9333,0.9308)4(0.9298,0.9285)5(0.9255,0.9266)6(0.9229,0.9232)7(0.9214,0.9221)8(0.9210,0.9219)9(0.9209,0.9213)10(0.9206,0.9206)11(0.9202,0.9205)12(0.9201,0.9203)13(0.9201,0.9202)14(0.9201,0.9202) 算法在第14步趋于最优解x*=(0.92,0.92).说明牛顿算法是有效的. 4结论 参考文献: [1]HARTMAN P, STAMPACCHIA G. On some nonlinear slliptic differential functional equations[J]. Acta mathematica,1966,115:153-188. [2]FAROUQ N E. Pseudomonotone variational inequatlities: convergence of proximal methods[J]. Journal of optimization theory and applications,2001,109(2):311-326. [3]SALMON G, NGUYEN V H,STRODIOT J J. Coupling the auxiliary problem principle and epiconvergence theory to solve general variational inequalities[J]. Journal of optimization theory and applications,2000,104(3):629-657. [4]PENG J M, FUKUSHIMA M. A hybrid Newton method for solving the variational inequalities problems via the d-gap functiona[J]. Mathmatical programming,1999,86:367-386. [5]WU J H. Long-step primal path-following algorithm for monotone variational inequalities problems[J]. Journal of optimization theory and applications,1998,99(2):509-531. [6]FAROUQ N E. Pseudomonotone variational inequalities: convergence of the auxiliary problem method[J]. Journal of optimization theory and applications,2001,111(2):305-326. [7]KANTOROVICH L V,AKILOV G P. Functional analtsis[M].Qxford:Pergamon,1982. [8]KANTOROVICH L V. Functional analysis and applied mathematics[J]. Uspekhi matematicheskikh nauk, 1948(3):89-185. [9]SMALE S. Newton’s method estimates from data at one point[M]. New York: Spring,1986:185-196. [10]SMALE S. Compexity theory and numerical analysis[J] Acta number,1997(6):523-551. [11]WANG X H, HAN D F. Criterion α and Newton’s method[J]. Applied mathematics-a journal of chinese universities,1997,19:96-105. [12]CHANG D C, WANG J H, YAO J C. Newton’s method for variational inequality problems: Smale’s point estimate theory under the -condition[J]. Applicable analysis,2013(1):44-55. [13]FACCHINEI F, PANG J S. Finite-dimensioanl variation inequalities and complementarity problems[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag,2003. [14]王兴华,韩丹夫.弱条件下的α判据和Newton法[J].计算数学,1997(2):103-112. [15]WANG X H. Convergence of Newton’s method and inverse function theorem in banach space[J]. Mathematics of computation,1999,68(1):169-186. [16]WANG X H. Convergence of Newton's method and uniqueness of the solution of equations in Banach space[J]. IMA journal of numberical analysis,2000(20):123-134. [17]鲍吉锋.平衡问题和优化问题若干算法的收敛性分析[D].杭州:浙江大学,2013. (责任编辑:陈石平) Convergence of Newton method for solving variational inequalities ZHOU Biao, LI Sulan (College of Science, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China) Abstract:Newton method is an important method for solving the problem of variational inequalities, the convergence of the algorithm has been a core issue for the scholars. When the function F in variational inequalities satisfies γ-conditions in , it is proved that the iterative dot sequence produced by the Newton method is valid and can be controlled to converge to an optimal solution of the variational inequalities by a sequence {tn}, which is constructed out. Taking into account that the regional conditions of the function F satisfies γ-conditions in makes more difficult for further study, analytic functions is introduced. The convergence of Newton method under the condition that the F is analytic function is given. Numerical experiments show that the algorithm is effective. Keywords:Newton method; variational inequalities; γ-conditions; semilocal convergence; analytic functions 收稿日期:2015-12-17 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(11371325 ) 作者简介:周彪(1991—),男,浙江台州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为最优化算法与理论,E-mail:zhoubiaozjut@163.com.通信作者:李素兰副教授,E-mail:sulanli@zjut.edu.cn. 中图分类号:O224 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-4303(2016)04-0461-05