B10细胞与非肥胖型糖尿病小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的关系研究
刘丽楠 李敬华 王素莉 程 晨 侯雯莉 关树梅 张 红
(中国人民武装警察部队后勤学院附属医院内分泌科,天津300162)
B10细胞与非肥胖型糖尿病小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的关系研究
刘丽楠李敬华王素莉程晨侯雯莉关树梅张红
(中国人民武装警察部队后勤学院附属医院内分泌科,天津300162)
[摘要]目的:研究B10细胞与非肥胖型糖尿病小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的关系。方法:选择20只6周龄NOD/LT雌性小鼠进行常规培养至30周龄,根据小鼠血糖、血肌酐和体重情况将小鼠分为自身免疫性糖尿病未发生组和发生组。利用酶联吸附反应检测两组小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平。利用流式细胞分选术检测两组小鼠脾脏组织汇总B10细胞比例。将40只6周龄NOD/LT雌性小鼠分为对照组和B10组,B10组小鼠接种分离得到的B10细胞,每周一次,对照组接种同等体积生理盐水,分别于第10、15、20、25、30周龄时检测小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生情况。结果:发生组小鼠血糖和血肌酐水平显著高于未发生组(P<0.05),体重水平显著低于未发生组(P<0.05)。发生组小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平显著高于未发生组。自身免疫性糖尿病发生组小鼠脾脏组织中B10细胞含量显著高于未发生组。当小鼠处于第10、15周龄时,B10组小鼠中自身免疫性糖尿病发生率显著低于对照组,但第20、25、30周时,B10组小鼠中自身免疫性糖尿病发生率显著高于对照组。结论:B10细胞的过度积累,可能是进一步诱发NOD小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的原因之一。
[关键词]B10细胞;非肥胖型糖尿病小鼠;自身免疫性糖尿病
B细胞是机体内参与抗体分泌、抗原呈递、传递刺激信号等过程的重要免疫调节细胞,除此之外,B细胞还具有负向免疫调节功能,从而导致非肥胖型糖尿病(Nonobese diabetic,NOD)、自身免疫性脑脊髓膜炎(Experimental autoimmuneencephalomy-elitis,EAE)和系统性红斑狼疮(Systemiclupuserythe-matosus,SLE)等多种自身免疫性疾病的发生[1]。B10细胞是2008年确认鉴定出的一种重要调节性B细胞, WT小鼠被LPS+佛波酯+离子霉素+莫能菌素(Phorbol ester+ionomycin+monensin,PIM) 刺激5 h后,其脾脏组织中可分离得到的CD5+CD1dhighCD19highB细胞亚群,这类细胞是B细胞产生IL-10的主要来源,因此称为B10细胞,目前研究发现在自身免疫性疾病的发生过程中发挥重要的负向调节作用[2,3]。1型糖尿病是由于胰岛素β细胞被自身免疫系统攻击破坏后,引起胰岛素分泌障碍,导致血糖浓度升高的自身免疫性糖尿病[4]。在NOD/LT小鼠中,自身免疫性糖尿病的发生率高达80%[5]。因此,本文主要研究B10细胞与非肥胖型糖尿病小鼠的自身免疫性糖尿病发生的关系。
1材料与方法
1.1动物饲养及样本收集20只6周龄NOD/LT雌性小鼠购自上海斯莱克实验动物中心,许可证号:SCXK(沪)2003-0003。SPF级常规饲养。于NOD/LT小鼠30周龄时,称量体重,尾静脉采血,用快速血糖仪(One touch ultra)测定全血血糖,血糖>16.7 mmol/L为糖尿病小鼠,并检测血肌酐浓度,统计NOD/LT小鼠中自身免疫性糖尿病发生情况。根据发生情况将小鼠分为未发生组和发生组。1%戊巴比妥钠(50 mg/kg体重)腹腔麻醉全部小鼠,手术取小鼠脾脏组织,一部分液氮冻存用于检测IL-10水平。一部分用于分离B10细胞。重新购买40只6周龄NOD/LT雌性小鼠用于后续试验。本实验通过本院伦理协会同意。
1.2方法
1.2.1酶联吸附反应检测NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平将冻存的脾脏组织进行液氮研磨,利用IL-10 ELISA试剂盒(购自北京天根公司)检测NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平。操作根据说明书进行。
1.2.2流式细胞分选术(FACS)分选B10细胞将新鲜的NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织进行酶解消化,经200目筛网过滤,保证所分离的细胞为单个细胞,制备脾脏淋巴细胞悬液,流式抗体CD5、CD1d和CD19进行染色,采用FACS分选CD5+CD1dhighCD19highB细胞。
1.2.3B10细胞对NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的影响将新鲜的NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织进行酶解消化,经200目筛网过滤,保证所分离的细胞为单个细胞,制备脾脏淋巴细胞悬液,利用联合免疫磁珠分选术分离得到CD19high细胞,按照1x104浓度接种于24孔板中。加入10 μg/ml LPS、50 ng/ml 佛波酯、500 ng/ml 离子霉素和2 μmol/L莫能菌素刺激5 h,提高CD5+CD1dhighCD19highB细胞含量。将第二次购买的NOD/LT小鼠随机分为对照组和B10组,每组20只。将分离得到的B10细胞制备成2×104的细胞悬液,接种到B10组小鼠体内中,每周一次。对照组接种同等体积生理盐水。SPF常规培养,分别于小鼠第10、15、20、25、30周龄时取小鼠尾静脉血检测小鼠血糖水平,统计NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生情况。
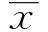
2结果
2.1NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生情况当NOD/LT小鼠培养至30周龄后,检测小鼠血糖、血肌酐和体重情况。结果显示,20只小鼠中血糖浓度高于16.7 mmol/L的小鼠共11只,低于16.7 mmol/L的小鼠共9只,即NOD/LT小鼠中自身免疫性糖尿病发生率为55%。据此将小鼠分为未发生组和发生组,统计分析两组小鼠血糖、血肌酐和体重情况,发生组小鼠血糖水平(29.24±7.48)显著高于未发生组(8.99±6.12,P<0.05),发生组小鼠血肌酐水平(24.39±2.93)显著高于未发生组(42.65±3.74,P<0.05),发生组小鼠体重水平(286.48±27.83)显著低于未发生组(153.47±25.31,P<0.05),见表1。
2.2NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平和B10细胞含量收集NOD/LT小鼠脾脏,利用ELISA是结合检测脾脏组织中IL-10水平,利用流式细胞术分析B10细胞所占淋巴细胞比例,结果显示自身免疫性糖尿病发生组IL-10水平(17.752±3.925)显著高于未发生组(8.438±1.386),同时B10细胞占比(5.61%)明显高于未发生组(1.27%,P<0.05),见图1,表2。
表1NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生情况
Tab.1Incidence of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice

GroupsnBloodglucose(mmol/L)Serumcreatinine(μmol/L)Weight(g)Noneautoimmunediabetes9(45%)8.99±6.1224.39±2.93286.48±27.83Autoimmunediabetes11(55%)29.24±7.4842.65±3.74153.47±25.31

图1 NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织中B10细胞含量Fig.1 Levels of B10 cells in spleen of NOD mice
表2NOD/LT小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平和B10细胞含量
Tab.2Levels of IL-10 and B10 cells in spleen of NOD mice
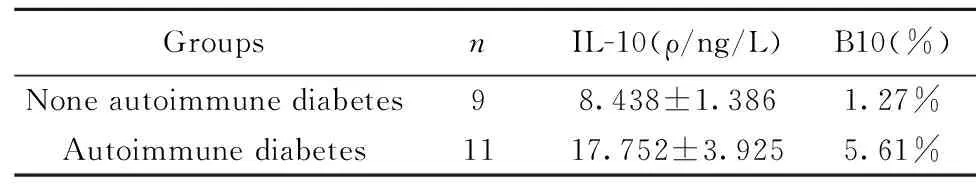
GroupsnIL-10(ρ/ng/L)B10(%)Noneautoimmunediabetes98.438±1.3861.27%Autoimmunediabetes1117.752±3.9255.61%
表3B10细胞对NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的影响[n(%)]
Tab.3Effects of B10 cells on autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice[n(%)]

Groups10weeks15weeks20weeks25weeks30weeksControlgroup2(10%)5(25%)8(40%)10(50%)12(60%)B10group0(0%)3(15%)12(60%)18(90%)20(100%)
2.3B10细胞对NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的影响将分离得到的B10细胞稀释成浓度为2×104的细胞悬液接种到6周龄NOD/LT小鼠体内,分别于小鼠第10、15、20、25、30周龄时检测小鼠血糖水平,检测NOD/LT小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生情况。结果显示B10组小鼠在第10、15、20、25、30周龄时,血糖浓度高于16.7 mmol/L的小鼠数量分别为0、3、12、18、20只,而对照组小鼠在第10、15、20、25、30周龄时时,血糖浓度高于16.7 mmol/L的小鼠数量分别为2、5、8、10、12只,因此B10组小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生率在小鼠第10(0%)和15周龄(15%)时低于对照组(10%,25%),但是在第20、25、30周龄(60%、90%、100%)时小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生率高于对照组(40%、50%、60%),见表3。
3讨论
1型糖尿病是由于胰岛素β细胞被自身免疫系统攻击破坏后,引起胰岛素分泌障碍,导致血糖浓度升高的自身免疫性糖尿病。在NOD小鼠中,自身免疫性糖尿病的发生率高达80%。目前研究认为NOD小鼠发生自发性糖尿病主要由于自身抗原缺乏耐受引起的[6]。非肥胖型糖尿病、自身免疫性脑脊髓膜炎和系统性红斑狼疮等多种自身免疫性疾病的发生都是由于B细胞的负向免疫调节功能引发的机体过度免疫反应造成的[7]。在机体内,调节性B细胞(regulatory B cells,Bregs)是参与负向免疫调节的主要B细胞亚群,其免疫功能主要通过调节白介素10(Interleukin 10,IL-10)和转化生长因子β(Transfor ming growth factor β,TGFβ)完成[8]。CD5+CD1dhighCD19highB细胞是此亚群中的主要成员,负责免疫组织中大部分IL-10的分泌,因此又称为B10细胞。因此,本文主要研究B10细胞与非肥胖型糖尿病小鼠的自身免疫性糖尿病发生的关系。
本研究中,我们选择20只6周龄NOD/LT小鼠进行常规培养,培养至30周龄时,对其血糖、血肌酐水平和体重情况进行检测,结果显示其中11只小鼠出现自身免疫性糖尿病,据此将小鼠分为未发生组和发生组,统计分析两组小鼠血糖、血肌酐和体重情况,发生组小鼠血糖和血肌酐水平显著高于未发生组(P<0.05),体重水平显著低于未发生组(P<0.05)。同时我们利用酶联免疫吸附法检测两组小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平,结果显示自身免疫性糖尿病发生组小鼠脾脏组织中IL-10水平显著高于未发生组。利用流式细胞分选术分析发现,自身免疫性糖尿病发生组小鼠脾脏组织中B10细胞含量显著高于未发生组。说明IL-10水平和B10细胞在NOD小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生过程中可能发挥着重要作用,这可能是由于小鼠自身免疫促进B10细胞的扩增引起的。
由于B10细胞除了参与抗体分泌、抗原呈递、传递刺激信号等过程之外,还可作为接触性超敏反应(Contact hypersensitivity,CHS)等疾病的特异性抗原,这有可能是引发负向免疫调节的主要原因[9]。因此我们将B10细胞接种到6周龄NOD/LT小鼠,研究B10细胞对NOD小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的影响。为了提高B10细胞浓度,我们首先利用联合免疫磁珠分选术分离得到CD19high细胞,继而利用LPS+佛波酯+离子霉素+莫能菌素处理,提高CD5+CD1dhighCD19highB细胞比例,得到浓度较高的B10细胞。将B10接种到NOD小鼠体内,分别于第10、15、20、25、30周龄时检测小鼠尾静脉血液中血糖浓度。结果显示,当小鼠处于第10,15周龄时,B10组小鼠中自身免疫性糖尿病发生率显著低于对照组,但第20周以后,B10组小鼠中自身免疫性糖尿病发生率显著高于对照组。白介素10是一种多功能的细胞因子,是目前公认的炎症与免疫抑制因子,参与调节细胞的生长与分化以及炎性和免疫反应[10]。因此我们认为在NOD小鼠成长初期,B10细胞分泌的IL-10发挥其炎症抑制作用,延缓了NOD小鼠自
身免疫性糖尿病的发生,但当B10细胞在NOD小鼠体内积累,激活小鼠体内负向免疫调节,导致NOD小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病的发生率的上升。
总之,在发生自身免疫性糖尿病的NOD小鼠中,B10细胞增多,而B10细胞的过度积累,可能是进一步诱发NOD小鼠自身免疫性糖尿病发生的原因之一。
参考文献:
[1]Vazquez MI,Catalan-Dibene J,Zlotnik A.B cells responses and cytokine production are regulated by their immune microenvironment[J].Cytokine,2015,74(2):318-326.
[2]Iwata Y,Matsushita T,Horikawa M,etal.Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells[J].Blood,2011,117(2):530-541.
[3]Candando KM,Lykken JM,Tedder TF.B10 cell regulation of health and disease[J].Immunol Rev,2014,259(1):259-272.
[4]Atkinson MA,Eisenbarth GS,Michels AW.Type 1 diabetes[J].Lancet,2014,383(9911):69-82.
[5]Ablamunits V,Henegariu O,Hansen JB,etal.Synergistic reversal of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice with anti-CD3 and interleukin-1 blockade evidence of improved immune regulation[J].DIAB,2012,61(1):145-154.
[6]Bhattacharya P,Fan J,Haddad C,etal.A novel pancreatic β-cell targeting bispecific-antibody (BsAb) can prevent the development of Type 1 diabetes in NOD mice[J].Clin Immunol,2014,153(1):187-198.
[7]Ziegler S,Gartner K,Scheuermann U,etal.Cellular immune response[J].Eur J Immunol,2014,44:1239-1244.
[8]Hoffman BE,Martino AT,Sack BK,etal.Nonredundant roles of IL-10 and TGF-β in suppression of immune responses to hepatic AAV-factor IX gene transfer[J].Mol Therapy,2011,19(7):1263-1272.
[9]Curzytek K,Kubera M,Majewska-Szczepanik M,etal.Inhibitory effect of antidepressant drugs on contact hypersensitivity reaction is connected with their suppressive effect on NKT and CD8+T cells but not on TCR delta T cells[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2015,28:1091-1096.
[10]Jin Y,Wi HJ,Choi MH,etal.Regulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β in mouse dendritic cells through treatment with clonorchis sinensis crude antigen[J].Exp Mol Med,2014,46(1):e74.
[收稿2015-09-03修回2015-09-30]
(编辑许四平)
Relationship between B10 cells and incidence of autoimmune diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice
LIU Li-Nan,LI Jing-Hua,WANG Su-Li,CHENG Chen,HOU Wen-Li,GUAN Shu-Mei,ZHANG Hong.
The Endocrinology Department of the Affiliated Hospital of Logistics Institute of Chinese People′s Armed Police Forces,Tianjin 300162,China
[Abstract]Objective:To study relationship between B10 cells and the incidence of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice.Methods: 20 NOD/LT female mice of 6 week old were cultured in normal culture to 30 weeks,and the mice were divided into two groups according the mice′s blood glucose,serum creatinine and body weight detected at their 30 weeks old.IL-10 levels in spleen tissues of the two groups were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.We used flow cytometry to detect the proportion of B10 cells in the spleen of mice in the two groups.NOD/LT mice were randomly divided into control group and B10 group.The B10 cells were inoculated in B10 groups,their blood glucose were detected when they were 10,15,20,25 and 30 weeks old.Results: The blood glucose and serum creatinine levels were significantly higher in the group than that in the autoimmune diabetes group (P< 0.05),and the body weight was significantly lower than that in the autoimmune diabetes group (P< 0.05).The level of IL-10 in the spleen tissues of the autoimmune diabetes mice was significantly higher than that in the non autoimmune diabetes group.The content of B10 cells in the spleen of the mice with autoimmune diabetes mellitus was significantly higher than that in the non autoimmune diabetes group.When mice at the age of 10,15 weeks,the incidence of autoimmune diabetes in B10 group was significantly lower than that in the control group,but the incidence of autoimmune diabetes in B10 group was significantly higher than that in control group at 20,25 and 30 weeks.Conclusion: The over accumulation of B10 cells may be one of the reasons for the further development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice.
[Key words]B10 cells;Nonobese diabetic mice;Autoimmune diabetes
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.06.009
作者简介:刘丽楠(1978年-),女,硕士,主治医师、讲师,主要从事内分泌代谢性疾病的基础与临床研究。
中图分类号R587.1
文献标志码A
文章编号1000-484X(2016)06-0812-04