B2-CuRE物理性质的第一性原理计算*
谭 旺,陈贞军,黄盼宁,陶小马,陈红梅,欧阳义芳
(广西大学物理科学与工程技术学院,广西南宁 530004)
B2-CuRE物理性质的第一性原理计算*
谭旺,陈贞军,黄盼宁,陶小马,陈红梅,欧阳义芳**
(广西大学物理科学与工程技术学院,广西南宁530004)
摘要:【目的】对17个B2-CuRE的热力学性质、力学性质、电子结构特性以及相关的热物理性质进行研究,为材料的设计和开发提供参考。【方法】利用基于密度泛函的第一性原理计算B2-CuRE (RE=Sc,Y,La-Lu)的能量、弹性常数以及电子结构特性。【结果】计算获得的晶格常数、形成焓、体积模量以及弹性常数和实验值吻合,高的B/G比表明B2-CuRE具有很好的延性。【结论】电子结构的计算可以阐明B2-CuRE的成键机制。B2-CuRE具有很好的延性。
关键词:B2-CuRE力学性质第一性原理计算
0引言
【研究意义】金属间化合物是指由两种或两种以上的金属通过金属键、共价键和离子键等混合键构成的具有特殊化学计量比的化合物。由于金属间化合物具有长程有序的超结构点阵,使得它们相对普通的金属来说,具有特殊的化学、物理、电学、磁学以及力学性质,因而备受人们的广泛关注,成为具有很大发展潜力的新材料之一。然而大多数金属间化合物在室温下都表现出低塑性和脆性,断裂抗力很小,成型性也较差,因此限制其在工程上的应用。近来,Gschneidner等[1]发现具有高度有序的B2(即CsCl结构)结构的稀土和过渡族元素形成的金属间化合物在室温下具有高延性以及高断裂韧性,并且这些稀土中间化合物的韧性不需要通过添加其它元素来提高。【前人研究进展】自Gschneidner后,关于B2结构的化合物被广大科研工作者所研究[2-16],其中有B2-AgY 和CuY[2,4-5],B2-CuDy[3],B2-AlRE[6-7]以及B2-MgRE[8-9]化合物。根据Pearson手册[17]记载,在Cu和RE(稀土)之间有10个CuRE相具有B2结构(除RE=La,Ce,Pr,Nd,Pm,Yb和 Lu外)。根据Gschneidner等[1]研究,在B2-CuRE中,CuY、CuDy、CuEr和CuHo都具有高延性。然而,至今只有少数的B2-CuRE (RE=Y,Dy) 被全面研究[2-5,10-11,15-16]。【本研究切入点】镧系稀土加上Sc和Y共有17个元素,而多数的B2-CuRE的物理性质仍然没有被系统研究,因此本研究对这17个B2-CuRE的热力学性质、力学性质、电子结构特性以及相关的热物理性质进行研究,所得结果将对具有B2结构的延性材料的进一步设计和开发有着重要的意义。【拟解决的关键问题】利用基于密度泛函的第一性原理对B2-CuRE(RE=Sc,Y和镧系稀土)的力学性能、电子结构性质等进行计算研究,为材料的设计和开发提供参考。
1计算方法
所有的第一性原理计算利用广义梯度近似下投影缀加波PAW方法[18-19]的维也纳从头计算模拟软件包VASP进行模拟计算[20-21]。广义梯度近似的交换关联势函数是用PW91[22-23]方案。计算时平面波截断能设为500 eV,布里渊区积分利用Monkhorst-Pack采点方法[24]和具有能量展宽为0.2 eV的Methfessel-Paxton技术[25]。赝势采用Cu,Sc,Y_sv,La,RE_3(RE=Ce,Pr,Nd,Pm,Sm,Gd,Tb,Dy,Go,Er,Tm,Lu),Eu_2,Yb_2进行计算。
为得到平衡体积,我们计算不同体积下的能量值,然后利用Vinet状态方程[26]进行拟合,获得平衡体积、总能量以及体积模量和体积模量对压强的导数值(∂B/∂P)T。B2-CuRE的形成焓利用以下方程进行计算:
ΔH(CuRE)=Etotal(CuRE)-Etotal(Cu)-Etotal(RE),
(1)
其中,Etotal(CuRE),Etotal(Cu)和Etotal(RE)分别是在0 K下B2-CuRE的总能量、Cu的总能量和稀土的总能量。Cu、Ce和Yb的参考态为面心立方(FCC),Eu的参考态为体心立方(BCC),La、Nd、Pr和Pm的参考态为双层六方结构(dHCP),其余的参考态为六方结构(HCP)。有关弹性常数以及多晶弹性模量的计算方法参考文献[27-31]。
2结果与分析
2.1晶格常数与形成焓
首先计算B2-CuRE的晶格常数和形成焓,如表1所示,第一原理计算的晶格常数和实验值[17]吻合得很好。并且我们可以看到无论是计算值还是实验值,晶格常数随着镧系稀土的原子序数增加而变小,表现出所谓的镧系收缩效应引起的变化。本文计算得到的形成焓都为负值,表明B2-CuRE都有着较好的合金化性质,而B2-CuLu有着最负的形成焓,说明该化合物相对稳定性最好。本文B2-CuRE形成焓的计算值与实验值[32-34]、计算相图优化值[35-40]吻合性良好。
表1B2-CuRE晶格常数和形成焓
Table 1The calculated lattice constants and formation enthalpies(ΔH) of the B2-CuRE

CuRELatticeconstants(Å)ΔH(eV/atom)PresentExp.(References[17])PresentExp.orCalphadCuSc3.24533.240-0.286-0.407(References[32])-0.366(References[33])-0.216(References[34])CuY3.48423.477-0.259--CuLa3.6604---0.147--CuCe3.6581---0.108--CuPr3.6238---0.128--CuNd3.5953---0.151--CuPm3.5683---0.175--CuSm3.54933.528-0.203--CuEu3.56173.479-0.235--CuGd3.50633.502-0.243-0.186(References[35])CuTb3.48743.481-0.256--CuDy3.46993.462-0.270-0.269(References[36])-0.279(References[37])CuHo3.45143.447-0.280-0.266(References[38])CuEr3.43613.430-0.290-0.271(References[39])CuTm3.41943.406-0.300-0.169(References[40])CuYb3.4646---0.220--CuLu3.3937---0.315--
2.2电子结构
为进一步了解B2-CuRE的成键情况,计算B2-CuRE的电子总态密度和分态密度(图1),由态密度可以看出在费米面附近的电子态密度主要来自稀土元素的贡献,成键态部分主要是Cu-d态,而反键态部分则主要是RE-d态的贡献。在费米面附近有少许的Cu-d态和RE-d态产生微弱的杂化效应。从态密度上看,几乎所有的B2-CuRE都呈现出极大的相似性。其中B2-CuRE(RE=La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Pm)的费米能级在一个急剧上升的态密度上,导致这些结构的不稳定性,因此在实验上也很难制备这些化合物,与现有的实验值保持一致性;而其他B2-CuRE的费米面则落在态密度的谷底或者态密度变化不大的地方,这样的结构就比较稳定,因而实验上也能制备出这些化合物。

图1B2-CuRE的电子总态密度和分态密度
Fig.1The total and partial electronic density of states of B2-CuRE
2.3弹性性质
弹性性质是固体材料非常重要的一个性质,从弹性常数可以获得体积模量、剪切模量、杨氏模量以及泊松比等众多的力学性质,还可以获得固体材料的声速等性质。为研究B2-CuRE的力学性质,本文利用第一性原理的方法对B2-CuRE的单晶弹性常数进行计算(表2)。因为B2结构是属于立方晶系,而立方晶系的弹性常数要满足的力学稳定性条件为C11-C12>0,C11>0,C44>0,C11+2C12>0。对照本文计算结果,所有B2-CuRE的单晶弹性常数都满足该力学稳定性条件,说明这些化合物从力学稳定性的角度上说都是稳定的。
从计算的弹性常数可以看到,含镧系稀土的B2-CuRE无论是C11,C12还是C44都呈现随着镧系稀土序数增大而增大的规律。其中由于Eu和Yb的晶体结构不同于其他元素,且Eu和Yb的f电子壳层处于半满和全满的状态,使得他们的弹性常数不同于其他化合物,这种情况在晶格常数和电子态密度中也有所体现。而B2-CuSc的弹性常数比其他元素构成的B2结构化合物的弹性常数大,说明Cu与Sc的结合很强。另外,从体积模量B可以看出B2-CuSc的体积模量达到93.1 GPa,B2-CuLu的为80.3 GPa,同时B2-CuSc和B2-CuLu的剪切模量G和杨氏模量E值最高。弹性各向异性参数A如果为1,表示化合物呈现各向同性,偏离1则表示呈现各向异性,从表2中可知,B2-CuRE的弹性各向异性参数A都偏离1,说明B2-CuRE都呈现各向异性性质;并且B2-CuSc的各向异性最大,而B2-CuY的各向异性最小。另外根据Pugh[41],B/G比值大小可以判断材料的脆韧性,当B/G 比值小于1.75时,材料呈现脆性,反之为延性,17个B2-CuRE化合物的B/G值都大于1.75,表明B2-CuRE都具有延性性质。
表2B2-CuRE的弹性常数、体积模量、剪切模量、杨氏模量、泊松比、弹性各向异性参数以及B/G比值的计算值
Table 2The calculated values of elastic constants,bulk modulus B,shear modulus G,Young’s modulus E ,Poisson’s ratio v,anisotropy A and ratio of B/G
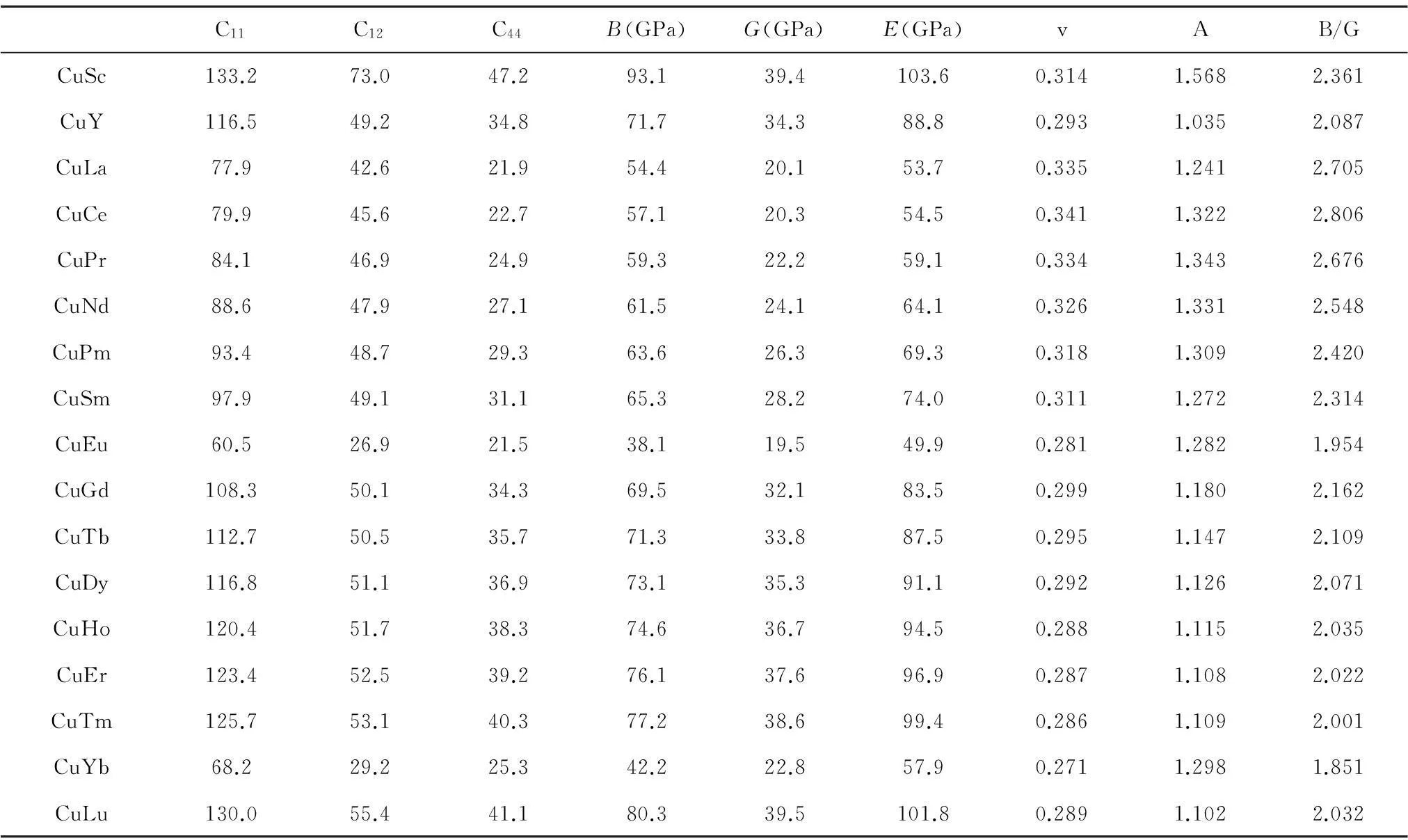
C11C12C44B(GPa)G(GPa)E(GPa)vAB/GCuSc133.273.047.293.139.4103.60.3141.5682.361CuY116.549.234.871.734.388.80.2931.0352.087CuLa77.942.621.954.420.153.70.3351.2412.705CuCe79.945.622.757.120.354.50.3411.3222.806CuPr84.146.924.959.322.259.10.3341.3432.676CuNd88.647.927.161.524.164.10.3261.3312.548CuPm93.448.729.363.626.369.30.3181.3092.420CuSm97.949.131.165.328.274.00.3111.2722.314CuEu60.526.921.538.119.549.90.2811.2821.954CuGd108.350.134.369.532.183.50.2991.1802.162CuTb112.750.535.771.333.887.50.2951.1472.109CuDy116.851.136.973.135.391.10.2921.1262.071CuHo120.451.738.374.636.794.50.2881.1152.035CuEr123.452.539.276.137.696.90.2871.1082.022CuTm125.753.140.377.238.699.40.2861.1092.001CuYb68.229.225.342.222.857.90.2711.2981.851CuLu130.055.441.180.339.5101.80.2891.1022.032
3结论
利用基于密度泛函的第一性原理的方法对B2-CuRE(RE=Sc、Y以及镧系稀土)17个化合物的晶格常数、形成焓、电子态密度、弹性常数以及弹性模量进行系统地计算。计算得到的晶格常数和形成焓与实验值以及其他理论值符合的很好。B2-CuRE(RE=La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Pm)的费米面所在的位置正好是态密度急剧变化的地方,由此可以推断出这些化合物不稳定,与实验相符。同时所计算得到的弹性常数都满足力学稳定性,并且弹性常数都随着镧系稀土的原子序数增加而增大,B/G值表明B2-CuRE都呈现良好的延展性。
参考文献:
[1]GSCHNEIDNER J R K,RUSSELL A,PECHARSKY
A,et al.A family of ductile intermetallic compounds[J].Nature Materials,2003,2(9):587-591.
[2]MORRIS J R,YE Y,LEE Y,et al.Ab initio calculation of bulk and defect properties of ductile rare-earth intermetallic compounds[J].Acta Materialia,2004,52(16):4849-4857.
[3]CAO G H,SHECHTMAN D,WU D M,et al.Determination of slip systems and their relation to the high ductility and fracture toughness of the B2 DyCu intermetallic compound[J].Acta Materialia,2007,55(11):3765-3770.
[4]SHI Y J,DU Y L,CHEN G,et al.First principle study on phase stability and electronic structure of YCu[J].Physics Letters A,2007,368(6):495-498.
[5]GSCHNEIDNER J R K A,JI M,WANG C Z,et al.Influence of the electronic structure on the ductile behavior of B2 CsCl-type AB intermetallics[J].Acta Mater,2009,57:5876-5881.
[6]TAO X,OUYANG Y,LIU H,et al.Ab initio calculations of mechanical and thermodynamic properties for the B2-based AlRE[J].Computational Materials Science,2007,40(2):226-233.
[7]TAO X,OUYANG Y,LIU H,et al.Calculation of the thermodynamic properties of B2 AlRE (RE= Sc,Y,La,Ce-Lu)[J].Physica B:Condensed Matter,2007,399(1):27-32.
[8]TAO X,OUYANG Y,LIU H,et al.Elastic constants of B2-MgRE(RE=Sc,Y,La-Lu) calculated with first-principles[J].Solid State Communications,2008,148(7):314-318.
[9]WU Y,HU W.Elastic and brittle properties of the B2-MgRE (RE= Sc,Y,Ce,Pr,Nd,Gd,Tb,Dy,Ho,Er) intermetallics[J].The European Physical Journal B,2007,60(1):75-81.
[10]WU Y,HU W,HAN S.First-principles calculation of the elastic constants,the electronic density of states and the ductility mechanism of the intermetallic compounds:YAg,YCu and YRh[J].Physica B:Condensed Matter,2008,403(19):3792-3797.
[11]XIE S,GSCHNEIDNER K A,RUSSELL A M.Microstructure and mechanical properties of the Dy50(Cu50-xNix) intermetallic B2 CsCl-type compounds[J].Scripta Materialia,2008,59(8):810-813.
[12]XIE S,RUSSELL A M,BECKER A T,et al.Dislocation core structures in YAg,a ductile B2 CsCl-type intermetallic compound[J].Scripta Materialia,2008,58(12):1066-1069.
[13]RUSSELL A M,ZHANG Z,LOGRASSO T A,et al.Mechanical properties of single crystal YAg[J].Acta Materialia,2004,52(13):4033-4040.
[14]CHEN Q,BINER S B.Stability of perfect dislocations in rare-earth intermetallic compounds:YCu,YAg and YZn[J].Acta Materialia,2005,53(11):3215-3223.
[15]ZHANG Z,RUSSELL A M,BINER S B,et al.Fracture toughness of polycrystalline YCu,DyCu,and YAg[J].Intermetallics,2005,13(5):559-564.
[16]RUSSELL A M,ZHANG Z,GSCHNEIDNER K A,et al.Mechanical properties of single crystal YCu and (Tb0.88Dy0.12)Zn B2 intermetallic compounds[J].Intermetallics,2005,13(6):565-571.
[17]CALVERT L D,VILLARS P.Pearson’s Handbook of Crystallographic Data for Intermetallic Phases[M].Materials Park,OH:ASM,1991.
[18]BLÖCHL P E.Projector augmented-wave method[J].Physical Review B,1994,50(24):17953.
[19]KRESSE G,JOUBERT D.From ultrasoft pseudopo-
tentials to the projector augmented-wave method[J].Physical Review B,1999,59(3):1758.
[20]KRESSE G,FURTHMÜLLER J.Efficient iterative
schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J].Physical Review B,1996,54(16):11169.
[21]KRESSE G,FURTHMÜLLER J.Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set[J].Computational Materials Science,1996,6(1):15-50.
[22]PERDEW J P,WANG Y.Pair-distribution function and its coupling-constant average for the spin-polarized electron gas[J].Physical Review B,1992,46(20):12947.
[23]PERDEW J P,CHEVARY J A,VOSKO S H,et al.Atoms,molecules,solids,and surfaces:Applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation[J].Physical Review B,1992,46(11):6671.
[24]MONKHORST H J,PACK J D.Special points for Bri-
llouin-zone integrations[J].Physical Review B,1976,13(12):5188.
[25]METHFESSEL M,PAXTON A T.High-precision
sampling for Brillouin-zone integration in metals[J].Physical Review B,1989,40(6):3616.
[26]VINET P,ROSE J H,FERRANTE J,et al.Universal features of the equation of state of solids[J].Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter,1989,1(11):1941.
[27]KITTEL C.Introduction to Solid State Physics[M].7th Ed.New York :Wiley,1996.
[28]REUSS A.Calculation of the flow limits of mixed crystals on the basis of the plasticity of monocrystals[J].Z Angew Math Mech,1929,9:49-58.
[29]TAO X,CHEN H,LI X,The mechanical,electronic
structure and thermodynamic properties for B2-AgRE studied from first-principles[J],Physica Scripta,2011,83:045301(9).
[30]HILL R.The elastic behaviour of a crystalline aggregate[J].Proceedings of The Physical Society:Section A,1952,65(5):349.
[31]WU Z,ZHAO E,XIANG H,et al.Crystal structures and elastic properties of superhard IrN2and IrN3from first principles[J].Physical Review B,2007,76(5):054115.
[32]GONCHARUK L V,SIDORKO V R.Thermodynamic properties of scandium-copper compounds[J].Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics,2006,45(1/2):72-75.
[33]YAMSHCHIKOV L F,SHUBIN A B,RASPOPIN S
P,et al.Thermodynamic properties of intermetallic compounds in the Sc-Cu system[J].Russian Metallurgy(USA),1992(3):191-193.
[34]WATANABE S,KLEPPA O J.Thermochemistry of
alloys of transition metals:Part IV.Alloys of copper with scandium,yttrium,lanthanum,and lutetium[J].Metallurgical Transactions B,1984,15(2):357-368.
[35]ZHANG L G,DONG H Q,HUANG G X,et al.Thermodynamic assessment of the Al-Cu-Gd system[J].Calphad,2009,33(4):664-672.
[36]ZHANG L G,HUANG G X,QI H Y,et al.Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Dy binary system[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2009,470(1):214-217.
[37]PALUMBO M,BATTEZZATI L,PASTUREL A,et
al.Thermodynamic and ab initio investigation of the Cu-Dy system[J].Calphad,2009,33(3):511-516.
[38]WANG C P,GUO S H,LIU X J,et al.Thermodynamic assessments of the Ho-X (X:Cu,Mo,V) systems[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2009,487(1):173-178.
[39]ZHANG L G,LIU L B,HUANG G X,et al.Thermodynamic assessment of the Al-Cu-Er system[J].Calphad,2008,32(3):527-534.
[40]WANG C P,GUO S H,TANG A T,et al.Thermodynamic assessments of the Cu-B and Cu-Tm systems[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2009,482(1):67-72.
[41]PUGH S F.Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals[J].Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science,1954,45(367):823-843.
(责任编辑:米慧芝)
Physical Properties of B2-CuRE Studied with First-principles Calculations
TAN Wang,CHEN Zhenjun,HUANG Panning,TAO Xiaoma,CHEN Hongmei,OUYANG Yifang
(College of Physics Sciences and Technology,Guangxi University,Nanning,Guangxi,530004,China)
Abstract:【Objective】The mechanical properties,electronic structure and thermophysical properties of 17 B2-CuREs were investigated to provide reference for the design and development of materials.【Methods】The properties of energetics,elastic constants and electronic structures of B2-CuRE(RE=Sc,Y,La-Lu) were calculated by means of first-principles based on the density function theory.【Results】The calculated lattice constants,formation enthalpies and elastic constants were all in good agreement with the experimental data available.The high B/G ratios of B2-CuRE indicated that B2-CuRE had ductility behaviors.【Conclusion】The calculation of electronic structures can elucidate the bonding mechanism in B2-CuRE compounds. The B2-CuRE has good ductility behaviors due to the high B/G ratios.
Key words:B2-CuRE,mechanical properties,first-principles calculations
收稿日期:2016-02-17
作者简介:谭旺(1989-),男,硕士研究生,主要从事金属及金属基复合材料力学性质的理论研究。
中图分类号:TG1
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1005-9164(2016)02-0174-06
修回日期:2016-03-29
*国家自然科学基金项目(11464001,51061004和51531009)和广西自然科学基金项目(2014GXNSFAA118308)资助。
**通讯作者:欧阳义芳(1965-),男,博士,教授,主要从事新材料制备和材料性能研究,E-mail:ouyangyf@gxu.edu.cn。
广西科学Guangxi Sciences 2016,23(2):174~179
网络优先数字出版时间:2016-05-11
网络优先数字出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1206.G3.20160511.1410.014.html

