尿液长链非编码RNA H19对乳腺癌的诊断价值
张开炯,张毅,罗政莲,吴立春,张莉,刘靳波
(1西南医科大学附属医院,四川泸州646000;2四川省肿瘤医院)
·临床研究·
尿液长链非编码RNA H19对乳腺癌的诊断价值
张开炯1,张毅1,罗政莲1,吴立春2,张莉2,刘靳波1
(1西南医科大学附属医院,四川泸州646000;2四川省肿瘤医院)
目的观察尿液长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)H19对乳腺癌的诊断价值。方法采用RT-PCR法检测30例乳腺癌患者(观察组)、42例健康体检者(对照组)尿液H19 mRNA水平,并分析H19与临床病理资料的关系,绘制ROC曲线分析尿液H19对乳腺癌的诊断价值。结果观察组尿液H19 mRNA相对表达量明显高于对照组,P<0.05;尿液H19 mRNA水平与c-erbB-2癌基因有关(P=0.002),而与肿瘤TNM分期、淋巴结转移、雌激素受体、孕激素受体及血管内皮生长因子受体无关(P均>0.05)。ROC曲线显示,H19曲线下面积为0.72,其诊断乳腺癌的敏感性为72.4%、特异性为67.8%。结论乳腺癌患者尿中H19水平升高,尿液H19可作为乳腺癌筛查的一个潜在的无创性生物标志物。
乳腺癌;长链非编码RNA;尿液;癌基因;生物标志物
乳腺癌是全球女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,目前发病率居于我国女性肿瘤发病率首位,病死率居于女性肿瘤第4位[1]。由于乳腺癌起病隐匿,临床确诊时多数已为晚期,治疗效果较差。目前乳腺癌的早期筛查和预后监控的血液学指标主要为糖类抗原(CA)153、27、29和癌胚抗原(CEA)等,但敏感性和特异性均较差,且对患者有一定创伤性。因此,寻找一类灵敏度高、特异性强且无创的乳腺癌新型诊断标志物成为研究热点。长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)是一类转录本>200个核苷酸,缺少特异完整的开放阅读框,无蛋白质编码功能的RNA分子[2],其可通过表观遗传学、转录及转录后水平调控肿瘤的发生、发展及转移。H19是一个具有父系印记特性的lncRNA分子,其能否作为一个无创性早期诊断靶标存在于乳腺癌患者尿液标本中目前尚无相关报道。2015年1~9月,我们检测了30例乳腺癌患尿者液中的H19 mRNA,并分析其与临床资料的关系,旨在为乳腺癌的诊断和预后判断提供临床依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1临床资料选择我院同期收治的乳腺癌初诊女性患者30例(观察组),年龄(50.30±2.45)岁,患者均术前诊断乳腺癌且术后病理确诊;TNM分期为Ⅰ~Ⅱ期21例,Ⅱ~Ⅳ期9例;伴淋巴结转移12例,未出现淋巴结转移18例;雌激素受体(ER)阳性20例,ER阴性10例;孕激素受体(PR)阳性19例,PR阴性11例;c-erbB-2癌基因阴性21例,c-erbB-2阳性9例;血管内皮生长因子受体(Ki67)≤10%者8例,Ki67>10%者22例。同时采集42例同期健康女性体检者作为对照组,年龄(48.83±1.98)岁,两组年龄差异无统计学意义。本研究经本院伦理委员会同意,两组均签署知情同意书。
1.2尿液H19 mRNA检测采用RT-PCR法。分别留存两组晨尿400~500 mL,1 500 r/min离心30 min,吸取250 μL尿沉渣置于RNA保存液中,-80 ℃保存备用。按照试剂说明书要求,提取尿标本中的总RNA,逆转录生成cDNA。以β-actin作为内参,采用相对定量2-ΔΔCt法计算两组尿液H19 mRNA水平。H19及β-actin引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成。引物序列:β-actin上游5′-TCCTCTCCCAAGTCCACACA-3′,下游5′-GCACGAA-GGCTCATCATTCA-3′;H19上游5′-GGTAGAAAAAG-CAACCACGAAGC-3′,下游:5′-ACATAAACCTCTG TCTGTGAGTGCC-3′。采用SYBRy Premix Ex TaqⅡ试剂盒(大连宝生物)检测每个扩增循环后SYBRy Green荧光信号水平,总反应体系20 μL,反应条件:95 ℃、30 s预变性;95 ℃、5 s,60 ℃、34 s,40个循环。实验重复3次。
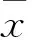
2 结果
2.1两组尿液H19 mRNA水平比较观察组和对照组尿液H19 mRNA分别为5.23±2.27和1.97±2.79,P<0.05。
2.2乳腺癌患者尿液H19 mRNA水平与临床病理特征的关系见表1。
2.3尿液H19 mRNA水平对乳腺癌的诊断价值绘制ROC曲线后发现AUC为0.72,敏感性和特异性分别为72.4%(95%CI:0.528~0.873,P<0.05)和67.8%(95%CI:0.513~0.812,P<0.05)。
3 讨论
近年研究发现,循环核酸如循环DNA、信使RNA以及微小RNA可稳定存在于人体血液、尿液、脑脊液等标本中,与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关[3]。尿液标本由于具有留取方便且无创的特点,从而成为疾病临床诊断、预后及大规模人群筛查的理想媒介。
近年来,H19被广泛地报道参与了肿瘤的发生、发展,而H19在肿瘤中的作用存在争议。研究发现,在Wilm肿瘤、胚胎横纹肌肉瘤及贝克威斯综合征中,H19被认为是肿瘤抑制基因[4],而在其他大部分肿瘤中H19发挥着癌基因的作用,如膀胱癌、子宫颈癌、食管癌及胃癌等[5~8]。在乳腺癌中,H19表达增高,其可通过生长因子、转录因子及ER调控乳腺癌细胞增殖、分化和侵袭进程[9~11]。Shore等[12]研究发现,H19在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平与ER及PR相关;其可与缺氧诱导因子、转录因子、p53等相互作用,调控乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭等过程。Matouk等[13]对乳腺癌原发灶和转移灶中的H19进行检测发现,无论在原发灶还是转移灶中H19均表达增高,且H19能够通过miR-675上调Slug表达,下调E-cadherin表达,从而调控乳腺癌上皮间质转化,并促进乳腺癌细胞的侵袭转移。最近,Vennin等[14]研究发现,H19作为miR-675的前体可在体外增强乳腺癌细胞的增殖和迁移,在体内增强肿瘤的生长和转移。此外,H19/miR-675能够下调泛素连接酶E3家族(c-Cbl、Cbl-b),促进肿瘤细胞的增殖和转移。
最近研究发现,H19能够稳定存在于胃癌患者血浆中,且血浆中H19水平能够作为胃癌早期诊断及预后监测的有效分子标记[15]。本研究发现,观察组尿液H19 mRNA水平明显高于对照组,且其水平与c-erbB-2有关。通过对尿中高表达的H19绘制ROC曲线,发现AUC为0.72,敏感度和特异性分别为72.4%和67.8%,表明乳腺癌患者尿液中的H19有望成为乳腺癌早期诊断和预后监控的新型生物标志物。然而,我们未能发现尿液H19水平与肿瘤TNM分期、淋巴结转移、ER、PR及Ki67的有关。这可能与本研究纳入标本量少有关,后续我们将扩大样本进一步分析。
[1] 陈万青,张思维,曾红梅,等.中国2010年恶性肿瘤发病与死亡[J].中国肿瘤, 2014,23(1):1-10.
[2] Van Heesch S, Van Iterson M, Jacobi J, et al. Extensive localization of long noncoding RNAs to the cytosol and mono- and polyribosomal complexes [J]. Genome Biol, 2014,15(1):6.
[3] Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS, Pantel K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011,11(6):426-437.
[4] Soejima H, Higashimoto K. Epigenetic and genetic alterations of the imprinting disorder Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and related disorders[J]. J Hum Genet, 2013,58(7):402-409.
[5] Luo M, Li Z, Wang W, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013,333(2):213-221.
[6] Feigenberg T, Gofrit ON, Pizov G, et al. Expression of the h19 oncofetal gene in premalignant lesions of cervical cancer: a potential targeting approach for development of nonsurgical treatment of high-risk lesions[J]. ISRN Obstet Gynecol, 2013,20(18):137509.
[7] Huang C, Cao L, Qiu L, et al. Upregulation of H19 promotes invasion and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in esophageal cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015,10(1):291-296.
[8] Zhang EB, Han L, Yin DD, et al. c-Myc-induced, long, noncoding H19 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer[J]. Med Oncol, 2014,31(5):914.
[9] Adriaenssens E, Lottin S, Berteaux N, et al. Cross-talk between mesenchyme and epithelium increases H19 gene expression during scattering and morphogenesis of epithelial cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2002,275(2):215-229.
[10] Berteaux N, Lottin S, Monte D, et al. H19 mRNA-like noncoding RNA promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through positive control by E2F1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005,280(33):29625-29636.
[11] Basak P, Chatterjee S, Weger S, et al. Estrogen regulates luminal progenitor cell differentiation through H19 gene expression[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2015,22(4):505-517.
[12] Shore AN, Herschkowitz JI, Rosen JM. Noncoding RNAs involved in mammary gland development and tumorigenesis: there′s a long way to go[J]. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia, 2012,17(1):43-58.
[13] Matouk IJ, Raveh E, Abu-Lail R, et al. Oncofetal H19 RNA promotes tumor metastasis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014,1843(7):1414-1426.
[14] Vennin C, Spruyt N, Dahmani F, et al. H19 non coding RNA-derived miR-675 enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer cells by downregulating c-Cbl and Cbl-b[J]. Oncotarget, 2015,6(30):29209-29223.
[15] Zhou X, Yin C, Dang Y, et al. Identification of the long non-coding RNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2015(5):11516.
Diagnostic value of urinary lncRNA H19 for breast cancer
ZHANGKaijiong1,ZHANGYi,LUOZhenglian,WULichun,ZHANGLi,LIUJinbo
(1AffiliatedHospitalofSouthwestMedicalUniversity,Luzhou646000,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the diagnostic value of urinary long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 for breast cancer. MethodsThe urinary H19 levels were detected in 30 patients with breast cancer (observation group) and 42 healthy controls (control group) by using quantitative RT-PCR, and the correlations between urinary H19 levels and clinical characteristics were further analyzed in breast cancer patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic value of urinary H19 for breast cancer. ResultsCompared with the control group, the expression level of urinary H19 in the observation group was significantly increased (P<0.05), and the expression level of urinary H19 was significantly related with c-erbB-2 (P=0.002), but was not related with TNM stages, lymph node metastasis, estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and Ki67 expression (allP>0.05). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.72, and the sensitivity and specificity were 72.4% and 67.8%, respectively. ConclusionThe expression level of urinary H19 increases in patients with breast cancer, and urinary H19 may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for the diagnosis of breast cancer.
breast carcinoma; long non-coding RNA; urine; oncogene; biomarker
四川省科学技术厅专项资金(14JC0801)。
刘靳波(E-mail: liujb7203@163.com)
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.18.014
R737.14
B
1002-266X(2016)18-0042-03
2015-12-12)

