控温方式对甲烷自扩散和局部结构影响的分子动力学模拟
徐鸣彦,史娟娟,冯华杰
(海南师范大学 化学与化工学院,海南 海口 571158)
控温方式对甲烷自扩散和局部结构影响的分子动力学模拟
徐鸣彦,史娟娟,冯华杰*
(海南师范大学 化学与化工学院,海南 海口 571158)
运用分子动力学模拟方法,通过设置两种控温方式(Andersen和Berendsen),研究了甲烷在较宽温度和压力范围的分子自扩散系数和配位数.结果表明,采用Andersen控温方式得到的甲烷自扩散系数与文献实验值相差甚远,而以Berendsen控温方式得到的甲烷自扩散系数与文献实验值较吻合,并且两种控温方式得到的甲烷平均配位数相差较小.因此,应采用Berendsen控温方式对甲烷的自扩散行为进行分子动力学模拟研究.
甲烷;自扩散;局部结构;分子动力学模拟
甲烷是天然气的主要成分,其扩散行为的研究是在天然气的开采中提高采收率的重要手段.甲烷在化工领域有着极其重要的作用,其高温分解可得炭黑,可用作颜料、油墨、油漆以及橡胶的添加剂,是生产乙炔、氢氰酸及甲醛的重要原料.因此,在实际应用中,研究甲烷的扩散行为和温度、压力、局部结构之间的关系是非常必要的.实验测量扩散系数是一项很困难的工作,需花费大量的时间和财力.目前,分子动力学(molecular dynamics,MD)模拟已经被广泛地应用于流体的研究[1-3].
Harris和Trappeniers[4]报道了110 K、140 K和160 K三个温度下甲烷的自扩散系数和密度,他们发现将甲烷的对比自扩散系数和对比密度作图时,对比自扩散系数等温线落在一条共同的曲线上.Grein⁃er-Schmid等[5]等采用脉冲场梯度核磁共振波谱技术研究了甲烷在宽广的温度和压力范围的自扩散系数,再通过硬球模型和相互作用球模型分析了测量的数据.Jorgensen教授等[6-7]通过量子化学计算和蒙特卡罗模拟开发了可用于烷烃的OPLS力场,并检验了其力场参数的可靠性.邓康等[8]采用分子动力学模拟研究了甲烷的自扩散系数,其模拟值与文献实验值的平均相对误差为10.4%.在分子动力学模拟中,常用Andersen和Berendsen两种控温方式,Weinan等[9]证明了使用Andersen控温方式可以收敛到正确的扩散系数.Mudi等[10]采用MD模拟方法探讨了Berendsen控温方式对水的动力学性质的影响,表明Berendsen控温方式在很宽的频率范围内可以非常有效地保存标记颗粒的时间相关性的波动.Carlos等[11]采用MD模拟方法研究了显式溶剂模型的蛋白Chignolin,分析Berendsen控温方式对肽演化和折叠的影响.
在分子动力学模拟过程中,一些参数设置需要通过对比结果择优确定.本文探讨不同控温方式对模拟结果的影响,分别设置控温方式为Andersen和Berendsen,研究甲烷在较宽温度和压力范围的自扩散系数和配位数.并将得到的模拟值与实验值进行比较,验证所采用的模拟参数的合理性,从而可有效地预测和研究极端条件下实验难以测量的扩散系数和局部结构.
1 模拟方法
MD模拟采用TINKER v5.0程序包,OPLS-UA联合原子模型力场[6],参数如表1.

表1 OPLS-UA力场中非键结势能参数Tab.1OPLS-UA Non-Bonded Parameters
模拟体系包含500个分子.分子间的作用势采用Lennard-Jones势,体系中的长程作用力采用Ewald[12]加和的形式.在模拟过程中,均采用周期性边界条件、Beeman算法求解运动方程.范德华力的截断半径取1.0 nm.体系的控温方式分别设置为An⁃dersen和Berendsen,时间步长为1 fs.MD模拟在NVT系综进行,先进行100万时间步平衡体系,再进行100万时间步用来计算自扩散系数和配位数.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 自扩散系数
本文中,自扩散系数D的模拟值都是通过计算均方位移获得的:
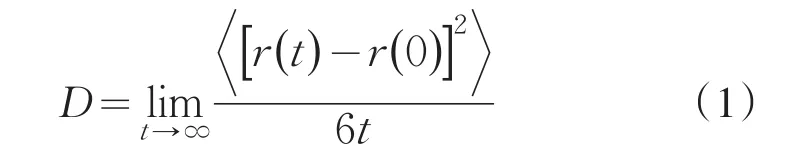
式中,r(t)表示某一分子在时间t的位置.
采用Andersen和Berendsen控温方式进行模拟得到的甲烷的分子自扩散系数与Greiner-Schmid[5]的实验数据进行比较,分别列于表2、表3、表4、表5.其中MD为模拟值,而Exp为Greiner-Schmid的实验值.总的来说,使用Andersen控温方式模拟得到的甲烷自扩散系数与实验测量值的误差很大,平均相对误差达52.0%,和实验测量数据存在严重偏差.使用Berendsen控温方式模拟得到的甲烷自扩散系数与实验测量值的误差较小,平均相对误差仅8.0%,优于文献的模拟值与实验值的平均相对误差10.4%[8].因此,使用Berendsen控温方式得到的甲烷自扩散系数比使用Andersen控温方式得到的结果更准确.
为了进一步探讨自扩散系数受温度和压力的影响,将使用Berendsen控温方式得到的甲烷自扩散系数对温度作图,见图1.从图中易看出,随着压力的升高,自扩散系数均减小.另一方面,随着温度的升高,自扩散系数均增大.很明显地,甲烷的自扩散系数受压力的影响远远大于受温度的影响,这与胺类、醇类体系的变化规律刚好相反[1,13-14].
2.2 配位数
在分子动力学模拟中,配位数(coordination num⁃bers)是反映流体局部结构性质的重要参数,配位数的意义是表示某一个粒子的最近邻粒子个数,它是由对径向分布函数积分所得到,积分公式如下

表2 甲烷的自扩散系数(10-9m2·s-1)模拟值(Andersen控温方式)与实验值的对比Tab.2Contrast between experimental and simulated(Andersen thermostat) self-diffusion coefficients for methane in 10-9m2·s-1


表3 甲烷的自扩散系数(10-9m2·s-1)模拟值(Andersen控温方式)与实验值的对比(续)Tab.3Contrast between experimental and simulated(Andersen thermostat) self-diffusion coefficients for methane in 10-9m2·s-1(continued)
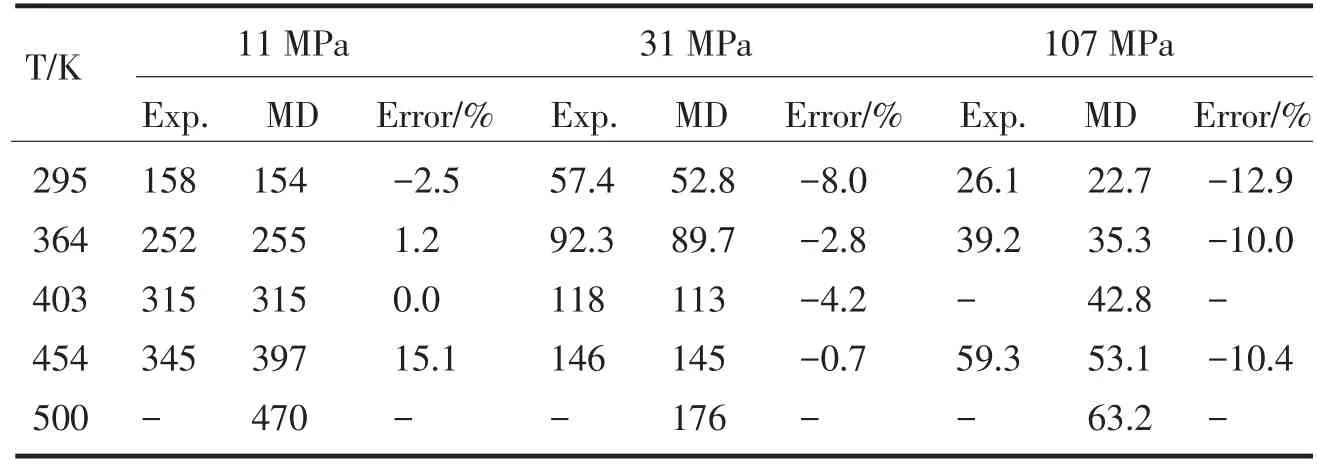
表4 甲烷的自扩散系数(10-9m2·s-1)模拟值(Berendsen控温方式)与实验值的对比Tab.4Contrast between experimental and simulated(Berendsen thermostat) self-diffusion coefficients for methane in 10-9m2·s-1

表5 甲烷的自扩散系数(10-9m2·s-1)模拟值(Berendsen控温方式)与实验值的对比(续)Tab.5 Contrast between experimental and simulated(Berendsen ther⁃mostat)self-diffusion coefficients for methane in 10-9m2·s-1(continued)
ρ0表示数密度,gij表示i和j原子的径向分布函数.
本文采用Andersen和Berendsen控温方式进行模拟得到甲烷的配位数分别于表6和表7.从表6和表7可知,两种控温方式的得到甲烷的平均配位数相差不大.在相同的温度压力条件下,采用Andersen控温方式得到甲烷的平均配位数比采用Berendsen控温方式得到的结果稍小.
同理,为了进一步探讨平均配位数受温度和压力的影响,将使用Berendsen控温方式得到的甲烷平均配位数对温度作图,见图2.从图中易看出,随着压力的升高,平均配位数均增大.另一方面,随着温度的升高,平均配位数均减小.很明显地,甲烷的平均配位数受压力的影响远远大于受温度的影响,这也与胺类、醇类体系的变化规律刚好相反[15-17].
3 结论
本文采用分子动力学模拟方法,分别设置不同的控温方式,研究了甲烷在较宽温度和压力范围的分子自扩散系数和配位数.采用Berendsen控温方式得到的甲烷自扩散系数比较准确,与文献实验值吻合得较好.而采用Berendsen和Andersen控温方式得到的甲烷平均配位数结果相差较小.因此,在较宽的温度和压力范围内,运用分子动力学模拟方法研究甲烷的自扩散行为的过程中应采用Berendsen控温方式.甲烷的自扩散系数和平均配位数都是受压力的影响远远大于受温度的影响.

图1 甲烷的自扩散系数Fig.1 Self-diffusion coefficients of methane

图2 甲烷的平均配位数Fig.2The average coordination numbers of methane

表6 甲烷的平均配位数(Andersen控温方式)Tab.6The average coordination numbers of methane (Andersen thermostat)

表7 甲烷的平均配位数(Berendsen控温方式)Tab.7The average coordination numbers of methane (Berendsen thermostat)
[1]冯华杰,聂晶晶,孙振范,等.N-甲基甲酰胺的自扩散和结构性质的分子动力学模拟[J].化工学报,2015,66(5):1683-1689.
[2]黎多来,周昌林,李东凯,等.氨的氢键数的分子动力学模拟研究[J].海南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2012,25(4):425-426.
[3]周昌林,黎多来,李东凯,等.氨的局部结构的分子动力学模拟研究[J].海南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2013,26(1):48-50.
[4]Harris K,Trappeniers N.The density dependence of the selfdiffusion coefficient of liquid methane[J].Physica A:Statisti⁃cal and Theoretical Physics,1980,104(1-2):262-280.
[5]Greiner-Schmid A,Wappmann S,Has M,et al.Self-diffusion in the compressed fluid lower alkanes:Methane,ethane,and propane[J].J Chem Phys,1991,94(8):5643-5649.
[6]Jorgensen W L,Madura J D,Swenson C J.Optimized inter⁃molecular potential functions for liquid hydrocarbons[J].J Am Chem Soc,1984,106(22):6638-6646.
[7]Jorgensen W L,Maxwell D S,Tirado-Rives J.Develop⁃ment and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on confor⁃mational energetics and properties of organic liquids[J].J Am Chem Soc,1996,118(45):11225-11236.
[8]邓康,孙振范,常勇慧,等.甲烷的自扩散系数的分子动力学模拟研究[J].广东化工,2014,41(4):6.
[9]Weinan E,Dong Li.The Andersen thermostat in molecular dynamics[J].Commun Pur Appl Math,2008,61(1):96-136.
[10]Mudi A,Chakravarty C.Effect of the Berendsen thermostat on the dynamical properties of water[J].Mol Phys,2004,102(7):681-685.
[11]Fuzo C A,Degrève L.Effect of the thermostat in the mo⁃lecular dynamics simulation on the folding of the model protein chignolin[J].J Mol Model,2012,18(6):2785-2794.
[12]Allen M P,Tildesley D J.Computer simulation of liquids [M].Oxford:Claren-don,1987.
[13]Karger N,Vardag T,Lüdemann H D.Temperature depen⁃dence of self-diffusion in compressed monohydric alcohols [J].J Chem Phys,1990,93(5):3437-3444.
[14]Chen L P,Gross T,Lüdemann H D.The density depen⁃dence of self-diffusion in some simple amines[J].Phys Chem Chem Phys,1999,1(15):3503-3508.
[15]李勇,刘锦超,芦鹏飞,等.从常温常压到超临界乙醇的分子动力学模拟[J].物理学报,2010,59(7):4880-4887.
[16]Feng H,Liu X,Gao W,et al.Evolution of self-diffusion and local structure in some amines over a wide temperature range at high pressures:a molecular dynamics simulation study[J].Phys Chem Chem Phys,2010,12(45):15007-15017.
[17]Feng H,Gao W,Sun Z,et al.The self-diffusion and hy⁃drogen bond interaction in neat liquid alkanols:A molecu⁃lar dynamic simulation study[J].Mol Simulat,2014,40(13):1074-1084.
责任编辑:刘 红
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Influence of Thermostat Algorithm on Self-diffusion and Local Structure of Methane
XU Mingyan,SHI Juanjuan,FENG Huajie*
(School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Hainan Normal University,Haikou571158,China)
Self-diffusion coefficients and coordination numbers of methane over wide range of temperature and pressure were studied by molecular dynamics simulation under Andersen and Berendsen thermostat algorithm.The result shows that the simulated self-diffusion coefficient of methane under Andersen thermostat algorithm is far from the experimental value in literature,while the simulated self-diffusion coefficient of methane under Berendsen thermostat algorithm is consistent with the experimental value in literature.On the other hand,the difference in the average coordination numbers of methane be⁃tween Andersen and Berendsen thermostat algorithm is small.Therefore,Berendsen thermostat algorithm should be used to study the self-diffusion behaviore of methane by molecular dynamics simulation.
methane;self-diffusion;local structure;molecular dynamics simulation
O 657.3
:A
:1674-4942(2016)04-0407-05
10.12051/j.issn.1674-4942.2016.04.011
2016-08-08
海南省自然科学基金项目(20162027);海南省科协青年科技英才创新计划项目(HAST201621)
*通讯作者

