The Power of Pattern Stories for Chinese Literacy
Dali Tan Northern Virginia Community College
The Power of Pattern Stories for Chinese Literacy
Helena Curtain University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee (emeritus)
Dali Tan Northern Virginia Community College
Pattern stories are stories in which elements are repeated with some variation. Pattern stories often have repeating core phrases or patterns which make it possible to predict what comes next. The rhythm or rhyme of pattern stories also helps move the language into a long-term memory. There are many different types of pattern stories but what they have in common is that at least one element is repeated. Pattern stories are available commercially but can also be teacher-created. Some pattern stories have more than one repeating element.
pattern stories; Chinese literacy; teacher-created stories
模式故事 中文读写能力 教师自编故事Tell me a story! Read me a story! These are familiar words to anyone who has spent time with children. But in the process of language learning, stories and picture books are not only for children because they build emotional connections and are the primary way humans learn about the world. Children’s picture books can be used as powerful tools to help students of all ages develop both oral and written language.
Picture books convey meaning through supportive pictures that very often connect with the text in a oneto-one correspondence and provide automatic support to help learners understand both the language and the concepts. Picture books are usually beautifully illustrated and visually appealing. Picture books provide authentic language (often in authentic cultural contexts) and examples of genuine communication. Picture books contain many kinds of stories and this article focuses on a special type of story found in picture books that is known by various names: “pattern stories”, “repetitive stories”, and “predictable stories”. For the sake of convenience, in this article we will refer to these types of stories as “pattern stories”.
What Are Pattern Stories?
Pattern stories are stories in which elements are repeated with some variation. There are repeating core phrases or patterns which make it possible to predict what comes next. Storylines, cultural sequences or concepts in pattern stories are familiar to readers. The rhythm or rhyme of pattern stories also helps move the language into a long-term memory. There are different types of pattern stories but what they have in common is that at least one element is repeated. Pattern stories are available commercially but can also be teacher-created. Some pattern stories have more than one repeating element.
What is extremely important is the fact that, even though many such stories are very simple, the narrative structure is very important and the stories must have a beginning, a middle and an end. Human brains have difficulty remembering isolated pieces of information because human brains are programmed to remember information that is organized according to the narrative structure with a beginning, a middle and an end. It is through oral stories with repetition and strong storylines that many cultures with no written language hand down their legends and traditions from generation to generation.

Figure 1.1 is an example of a non-story because there is no movement in the story and no satisfactory ending.
Why Choose Pattern Stories?
Pattern stories are especially helpful for the students who are working with Chinese literacy because they provide a meaningful context and thus help the brain link the meaning to the characters. The use of pattern stories encourages and requires readers to learn the characters embedded in logically-linked complete sentences rather than learn the characters through an isolated and scattered list of vocabulary items. Using pattern stories can help overcome a problem that mayoccur with Chinese literacy: Students may memorize the characters without understanding the meaning. This is often due to the fact that the characters are frequently learned and memorized out of context. Pattern stories facilitate and quicken the process for learners to make the connection between the form and the meaning of what they see on the page, and help transfer these connections into a long-term memory. The predictable design allows learners to understand the meanings of pattern stories more easily, thus lessening the “cognitive load” of the reading process.
The predictable nature of pattern stories provides many opportunities for repetition since the students can see the same words over and over again. As students repeat the line that appears throughout the text, they are matching oral language to the print and developing access to the written Chinese characters through the scaffolded use of repetition. The phrases that continually repeat throughout the story allow the readers to produce longer phrases or sentences by changing one central word.
Research in cognitive psychology shows that one of the best ways to practice and learn a language is through“tactful repetition”.3Pattern stories demonstrate some of the best practices in “tactful repetition” in which the learners are so intrigued by the stories that they do not realize that they are repeating the language focus and vocabulary items that are embedded in the instructional designs and lesson plans.
Pattern stories provide an opportunity for the extended listening experience as students listen to the story over and over again. Pattern stories also provide opportunities for speaking as they are sequenced and told and retold by the students. They provide chunks of language that can be building blocks for speaking and also for understanding the grammatical structure of the language.
Different Types of Pattern Stories
The following are explanations of various types of pattern stories which can be found, along with some examples of that type of story. The basic types are:
· Cumulative Story
· Familiar or Logical Sequence
· Question and Answer
· Repetition of a Word or a Phrase
· Rhyme
· Chain or Circular Story
· Combination Story
Cumulative Story
In a cumulative story each time something new happens, all the other events in the story are repeated.
The Napping House
There is a house,
A napping house,
Where everyone is sleeping.
And in that house,
There is a bed,
A cozy bed,
In a napping house,
Where everyone is sleeping.
And in that bed,
There is a granny,
A snoring granny,
On a cozy bed,
In a napping house,
Where everyone is sleeping.
And on that granny,
There is a child,
A dreaming child,
On a snoring granny,
On a cozy bed,
In a napping house,
Where everyone is sleeping.
And on that child,
There is a dog,
On a dreaming child,
On a snoring granny,
On a cozy bed,
In a napping home,
Where everyone is sleeping.
And so on so forth…
The story ends this way:
A wakeful flea,
Who bites the mouse,
Who scares the cat,
Who claws the dog,
Who thumps the child,
Who bumps the granny,
Who breaks the bed,
In the napping house,
Where no one now is sleeping.
(Adapted from https://clintoneslwiki.wikispaces.com/ file/view/Choral+Reading+-+The+Napping+House. pdf)
Familiar or Logical Sequence
The familiar or logical sequence in a pattern story can be days of the week, months of the year, seasons, the alphabet (in alphabetic languages), numbers, colors, mathematical patterns, nature patterns, and so on.
Here is an example of several sequences related to the topic of eating. Of course, the story can happen using any tense.
They ate one ...
They ate two....
They ate three....
And so on...
First they ate…
Second they ate…
Third they ate…
And so on...
In January they ate…
In February they ate…
In March they ate…
And so on…
On Monday they ate …
On Tuesday they ate…
On Wednesday they ate…
The story of “The Little Red Hen” follows the sequence of planting and harvesting. It also has a repetitive phrase.
One day as the Little Red Hen was scratching in a field, she found a grain of wheat.
“This wheat should be planted,” she said. “Who will plant this grain of wheat?”
“Not I,” said the Duck.
“Not I,” said the Cat.
“Not I,” said the Dog.
“Then I will do it myself,” said the Little Red Hen. And she did.
The story continues in this way with cutting the wheat, threshing the wheat, taking the wheat to the mill, and making the flour into bread. Each time the Little Red Hen asks the question about who will help her and each time the other animals answer “Not I,” and the Little Red Hen says, “Then I will do it myself.” Finally, she asks who will help to eat the bread, and all the animals answer “I will!” But the Little Red Hen says “No, No, I will eat it myself.”
Question and Answer
In a pattern story in the question and answer format, a similar question is repeated in every part of the story.
When they were hungry do you know what they ate?
They ate…
When they were hungry do you know what they ate?
They ate…
When they were hungry do you know what they ate?
They ate…
Repetition of a Word or a Phrase
In this type of pattern story, a phrase or a sentence is repeated. The examples below are traditional stories that follow this pattern.
In a Dark Dark Wood
In a dark dark wood, there was a dark dark path.
And on the dark dark path, there was a dark dark house.
And in the dark dark house, there was a dark dark (flight of) stairs.
And on top of the dark dark stairs, there was a dark dark room.
And in the dark dark room, there was a dark dark closet (wardrobe, bureau).
And in the dark dark closet (wardrobe, bureau), there was a dark dark box (chest).
And in the dark dark box (chest), there was…
A ghost!!!!!!!
The Little Red Riding Hood
(The Little Red Riding Hood is talking to the wolf who pretends to be her grandma.)
What big eyes you have.
All the better to see you with, my dear.
What big ears you have.
All the better to hear you with, my dear.
What big teeth you have.
All the better to eat you!
Rhyme
In a rhyming pattern story, rhyming words or rhyming patterns are used throughout the story. An example of a traditional European and North American fairy tale is “The Gingerbread Man”.
Run, run, run,
As fast as you can!
You can’t catch me.
I’m the gingerbread man.
Chain or Circular Story
In a chain or circular story, the ending leads back to the beginning so that the story begins and ends in the same place. For example:
If You Give a Mouse a Cookie
by Laura Joff Numeroff
If you give a mouse a cookie, he’s going to ask for a glass of milk.
When you give him the milk, he’s probably ask you for a straw.
When he’s finished, he’ll ask for a napkin.
Then he’ll want to look in a mirror to make sure he doesn’t have a milk mustache.
When he looks into the mirror, he might notice his hair needs a trim.
So he’ll probably ask for a pair of nail scissors.
When he’s finished giving himself a trim, he’ll want a broom to sweep up.
He’ll start sweeping.
He might get carried away and sweep every room in the house.
He may even end up washing the floors as well!
When he’s done, he’ll probably want to take a nap. You’ll have to fix up a little box for him with a blanket and a pillow.
He’ll crawl in, make himself comfortable and fluff the pillow a few times.
He’ll probably ask you to read him a story.
So you’ll read to him from one of your books, and he’ll ask to see the pictures.
When he looks at the pictures, he’ll get so excited he’ll want to draw one of his own.
He’ll ask for paper and crayons.
He’ll draw a picture.
When the picture is finished, he’ll want to sign his
name with a pen.
Then he’ll want to hang his picture on your refrigerator,
Which means he’ll need scotch tape.
He’ll hang up his drawing and stand back to look at it.
Looking at the refrigerator will remind him that he’s thirsty.
So he’ll ask for a glass of milk.
And chances are if he asks for a glass of milk, he’s going to want a cookie to go with it.
Patterns in Traditional Chinese Stories
There are a variety of pattern stories both in English and in Chinese. The Chinese pattern stories can be used as cultural rich authentic materials to help our students experience Chinese culture and also help teachers make connections with other school subjects such as math. The following are some examples of patterns found in traditional Chinese stories.
Combination of Familiar or Logical Sequence and Rhyme
七个果果
一二三四五六七,
七六五四三二一。
七个阿姨来摘果,
七个篮子手中提。
七个果子摆七样,
苹果、桃儿、石榴、 柿子、李子、栗子、梨。
Seven Fruits
One, two, three, four, five, six, seven,
Seven, six, five, four, three, two, one.
Seven aunties came to pick fruits,
Seven baskets they carry.
Seven kinds of fruits are displayed here—
Apple, peach, pomegranate, persimmon, plum, chestnut and pear.
乘法口诀儿歌
一只青蛙一张嘴,两只眼睛四条腿。
两只青蛙两张嘴,四只眼睛八条腿。
三只青蛙三张嘴,六只眼睛十二条腿。
四只青蛙四张嘴,扑通扑通跳下水!
Authentic Multiplication Children’s Rhyme
One frog, one mouth, two eyes, four legs.
Two frogs, two mouths, four eyes, eight legs.
Three frogs, three mouths, six eyes, twelve legs.
Four frogs, four mouths. Plop, plop into the water they go!
Combination of Repetition of a Word or a Phrase and Rhyme
登山
三月三,小三去登山。
上山又下山,下山又上山。
登了三次山,跑了三里三。
出了一身汗,湿了三件衫。
小三山上大声喊:
“离天只有三尺三!”
Up and Down the Mountain
March the third, Xiao San goes to climb the mountain.
Go up the mountain and go down the mountain,
Go down the mountain and go up the mountain again.
Climbed the mountain three times,
Covered three li1and three.
Sweating all over, soaked three shirts with sweat.
Xiao San shouted on the top of the mountain,
I am only three chi2and three away from the sky.
泥娃娃
泥娃娃,泥娃娃,一个泥娃娃,
也有那眉毛,也有那眼睛,眼睛不会眨;
泥娃娃,泥娃娃,一个泥娃娃,
也有那鼻子,也有那嘴巴,嘴巴不说话。
它是个假娃娃,不是个真娃娃,
它没有亲爱的妈妈,也没有爸爸。
泥娃娃,泥娃娃,一个泥娃娃,
我做她妈妈,我做她爸爸,
永远爱着她。
The Doll of Clay
The doll of clay.
The doll of clay.
She’s a doll of clay.
She has got eyebrows.
She has got eyes,
Which cannot wink.
The doll of clay.
The doll of clay.
She’s a doll of clay.
She has got a nose.
She has got a mouth,
Which cannot speak.
She’s but a doll of clay.
She’s not a living doll.
She has got no loving mom, no loving dad.
The doll of clay.
The doll of clay.
She’s a doll of clay.
I’ll be her mom.
I’ll be her dad.
Forever loving this doll of clay.
Repetition of a Word or a Phrase
抱
天空妈妈抱着小星,
大地妈妈抱着小草,
海洋妈妈抱着小鱼,
森林妈妈抱着小鸟,
大山妈妈抱着小溪,
祖国妈妈抱着小宝。
Carrying in Her Arms
The mother sky carries little stars in her arms.
The mother earth carries the little grass in her arms.
The mother ocean carries little fish in her arms.
The mother forest carries little birds in her arms.
The mother mountain carries little streams in her arms.
The motherland carries us all in her arms.
(Adapted from http://www.docin.com/p-305634654. html)
动物怎么叫?
小猫怎么叫?喵喵喵。
小狗怎么叫?汪汪汪。
小鸡怎么叫?叽叽叽。
小鸭怎么叫?嘎嘎嘎。
小羊怎么叫?咩咩咩。
老牛怎么叫?哞哞哞。
老虎怎么叫?噢噢噢。
青蛙怎么叫?呱呱呱。
大公鸡怎么叫?喔喔喔。
孩子们怎么说?你好,你好,你好!
What Does This Animal Say?
What does the cat say? Meow Meow Meow.
What does the dog say? Woof Woof Woof.
What does the chick say? Peep Peep Peep.
What does the duck say? Quack Quack Quack.
What does the lamb say? Ba Ba Ba.
What does the cow say? Moo Moo Moo.
What does the tiger say? Roar Roar Roar.
What does the frog say? Croak Croak Croak.
What does the rooster say? Cock a doodle do.
What do little children say? Nihao, Nihao, Nihao!
Note: Translated according to English mimetic words
(Adapted from http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url= cAls7QvUqE3IenB-duq2jemAl94CS83VNv ASGg8fWi5F966Jp39-IFo9u7k2rtktLhRu_ U6wAkl0XrrpyMYZNeMvaJR6IEr_a06IvFHl)
从前有座山
从前有座山,
山里有个庙,
庙里有个锅,
锅里有个盆儿,
盆儿里有个碗儿,
碗儿里有个碟儿,
碟儿里有个勺儿,
勺儿里有个豆儿,
我吃了,
你馋了,
我的故事讲完了。
Once Upon a Time There Was a Mountain
Once upon a time there was a mountain.
Inside the mountain there was a temple.
Inside the temple there was a large pot.
Inside the pot there was a large bowl.
Inside the large bowl there was a small bowl.
Inside the small bowl there was a small plate.
On the plate there was a spoon.
On the spoon there was a bean.
I ate the bean! And you wish you had the bean!
That is the end of my story.
(Adapted from http://baike.sogou.com/v67986995. htm)
Teacher-Created Pattern Stories
Pattern stories are easy and fun to write and many teachers find that the stories they write for their students are especially well-suited for their learning targets. When teachers create their own stories they can focus on the functional language and vocabulary that the students need and place them within a story that provides a meaningful context and an enjoyable experience with rhythm and patterns and of course has a satisfying narrative format of a beginning, a middle and an end. The two most commonly-used pattern stories are familiar or in a logical sequence, and have a question-and-answer pattern. You can see how pattern stories can be helpful in building the students’confidence and skills.
Familiar or Logical Sequence
你想吃什么?
今天星期一,我要吃红烧鸡。
今天星期二,我要吃羊肉串儿。
今天星期三,我要吃蛋炒饭。
今天星期四,我要吃煎饺子。
今天星期五,我要吃炸豆腐。
今天星期六,我要吃烤牛肉。
今天星期天,我要吃炸酱面。
现在我吃饱了,再见!
What Do You Want to Eat?
Today is Monday, I want to eat chicken braised in soy sauce.
Today is Tuesday, I want to eat lamb skewers.
Today is Wednesday, I want to eat egg stir-fried rice.
Today is Thursday, I want to eat fried dumplings.
Today is Friday, I want to eat deep fried tofu.
Today is Saturday, I want to eat roasted beef.
Today is Sunday, I want to eat noodles with black soybean sauce.
Now I’m full! Good-bye!
(Created by Nick Staffa for his Grade 3 Chinese students in Oak Forest Elementary School, Shelby County Schools, Memphis, Tennessee)
我爱中文
星期一我爱中文。
星期二我爱中文。
星期三我爱中文。
星期四我爱中文。
星期五我爱中文。
可是,跟中文比起来,
我更爱周末。
I Love Love Chinese
I love love Chinese on Monday.
I love love Chinese on Tuesday.
I love love Chinese on Wednesday.
I love love Chinese on Thursday.
I love love Chinese on Friday.
But…
I love love the weekend more than I love love Chinese!
(Created collectively or individually by session participants in various pattern story workshops)
Question and Answer Pattern
你喜欢做什么?
Nǐ xǐhuan zuò shénme?
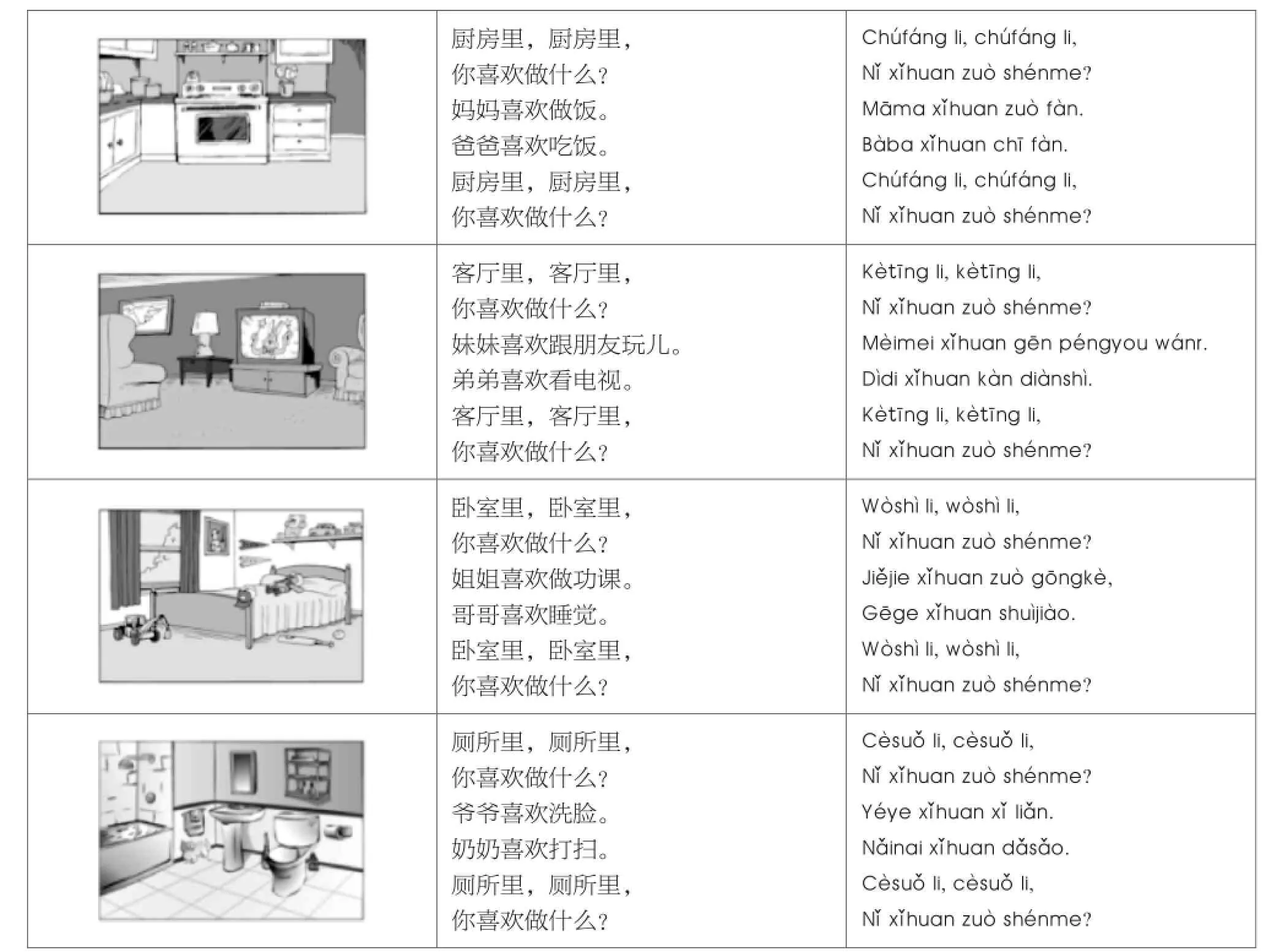
What Do You Like to Do?
In the kitchen, in the kitchen, What do you like to do?
Mom likes to cook.
Dad likes to eat.
In the kitchen, in the kitchen, What do you like to do?
In the living room, in the living room, What do you like to do?
Little sister likes to play with friends. Little brother likes to watch TV.
In the living room, in the living room, What do you like to do?
In the bedroom, in the bedroom, What do you like to do?
Elder sister likes to do her homework. Elder brother likes to sleep.
In the bedroom, in the bedroom, What do you like to do?
In the bathroom, in the bathroom, What do you like to do?
Grandfather likes to wash his face. Grandmother likes to clean.
In the bathroom, in the bathroom, What do you like to do?
(Created by Nick Staffa for his Grade 3 Chinese students in Oak Forest Elementary School, Shelby County Schools, Memphis, Tennessee)
A wonderful pattern story created by a group of middle school teachers is “Where Does the Panda Live?” Each frame asks if the panda lives in a specific country and the next frame says that certain other animals live in that country. Finally, at the end of the story we find out that the panda lives in China!
熊猫的老家在哪里?
熊猫的老家在巴西吗?
不在,熊猫的老家不在巴西。
金刚鹦鹉的老家在巴西。
熊猫的老家在美国吗?
不在,熊猫的老家不在美国。
秃鹰的老家在美国。
熊猫的老家在澳大利亚吗?
不在,熊猫的老家不在澳大利亚。
袋鼠的老家在澳大利亚。
熊猫的老家在南极吗?
不在,熊猫的老家不在南极。
企鹅的老家在南极。
熊猫的老家在印度吗?
不在,熊猫的老家不在印度。
大象的老家在印度。
熊猫的老家在津巴布韦吗?
不在,熊猫的老家不在津巴布韦。
长颈鹿、斑马、猿猴和狮子的老家在津巴布韦。
那么,熊猫的老家到底在哪里呢?
熊猫的老家在中国!
Where Does the Panda Live?
Does the panda live in Brazil?
No, the panda does not live in Brazil.
The scarlet macaw lives in Brazil.
Does the panda live in the United States?
No, the panda does not live in the United States.
The bold eagle lives in the United States.
Does the panda live in Australia?
No, the panda does not live in Australia.
The kangaroo lives in Australia.
Does the panda live in Antarctica?
No, the panda does not live in Antarctica.
The penguin lives in Antarctica.
Does the panda live in India?
No, the panda does not live in India.
The elephant lives in India.
Does the panda live in Zimbabwe?
No, the panda does not live in Zimbabwe.
The giraffe, the zebra, the monkey, and the lion live in Zimbabwe.
Well then, where does the panda live after all?
The panda lives in China!
The following stories were created collectively or individually by session participants in various pattern story workshops.
你住在哪里?
你住在哪里?我是一只松鼠,我住在树上。
你住在哪里?我是一只狐狸,我住在洞里。你住在哪里?我是一只兔子,我住在草丛里。你住在哪里?我是一只猴子,我也住在树上。我们都住在哪里?我们都住在森林里,我们都是好朋友。
Where Do You Live?
Where do you live? I am a squirrel. I live in trees.
Where do you live? I am a fox. I live in a hole in the ground.
Where do you live? I am a hare. I live in the bushes.
Where do you live? I am a monkey. I also live in trees.
Where do we all live? We all live in the forest. We are all good friends.
我的妹妹藏在哪里呢?
我的妹妹不见了!
我的妹妹藏在哪里呢?
她藏在学校里吗?她不在学校里。
她藏在后院里吗?她不在后院里。
她藏在图书馆里吗?她不在图书馆里。
她藏在公园里吗?她不在公园里。
她到底藏在哪里呢?
原来她藏在冰淇淋店里,
吃她最喜欢的巧克力冰淇淋呢!
Where Is My Younger Sister Hiding?
I could not find my younger sister.
Where is my younger sister hiding?
Is she hiding in school? No, she is not at school.
Is she hiding in the backyard? No, she is not in the backyard.
Is she hiding in the library? No, she is not in the library.
Is she hiding in the park? No, she is not in the park.
Where is she hiding after all?
It turns out that she is hiding in an ice cream store Eating her favorite chocolate ice cream!
中国十二生肖模式故事
(根据“棕熊,棕熊,你看见什么?”改编)老鼠,老鼠,你看见谁?
我看见一头牛在看我。
牛,牛,你看见谁?
我看见一只老虎在看我。
老虎,老虎,你看见谁?
我看见一只兔子在看我。
兔子,兔子,你看见谁?
我看见一条龙在看我。
龙,龙,你看见谁?
我看见一条蛇在看我。
蛇,蛇,你看见谁?
我看见一匹马在看我。
马,马,你看见谁?
我看见一只羊在看我。
羊,羊,你看见谁?
我看见一只猴子在看我。
猴子,猴子,你看见谁?
我看见一只公鸡在看我。
公鸡,公鸡,你看见谁?
我看见一只狗在看我。
狗,狗,你看见谁?
我看见一头猪在看我。
猪,猪,你看见谁?
我看见一只熊猫在看我。
Chinese Zodiac Pattern Story
(Based on “Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See?”)
Rat rat what do you see?
I see an ox looking at me.
Ox ox what do you see?
I see a tiger looking at me.
Tiger tiger what do you see?
I see a rabbit looking at me.
Rabbit rabbit what do you see?
I see a dragon looking at me.
Dragon dragon what do you see?
I see a snake looking at me.
Snake snake what do you see?
I see a horse looking at me.
Horse horse what do you see?
I see a sheep looking at me.
Sheep sheep what do you see?
I see a monkey looking at me.
Monkey monkey what do you see?
I see a rooster looking at me.
Rooster rooster what do you see?
I see a dog looking at me.
Dog dog what do you see?
I see a pig looking at me.
Pig pig what do you see?
I see a PANDA looking at me!
(Greated by Maryland Chinese Heritage School Teachers)
我的家
你家有几口人?
我家有两口人,妈妈和我。
你家有几口人?
我家有三口人,爸爸、妈妈和我。
你家有几口人?
我家有四口人,爸爸、哥哥、姐姐和我。
你家有几口人?
我家有七口人,我爸爸、我的继母、三个弟弟、一个妹妹和我。
你家有几口人?
我们家只有一口人,还有……
一只鸟、两只鸭、一只猫、一只狗和一只母鸡。
My Family
How many people are there in your family?
My family has two people, my mother and me.
How many people are there in your family?
My family has three people, my father, my mother and me.
How many people are there in your family?
My family has four people, my father, my elder brother, my elder sister and me.
How many people are there in your family?
My family has seven people, my father, my stepmother, three younger brothers, one younger sister and me.
How many people are there in your family?
My family only has one person, that’s me and…one bird, two ducks, one cat, one dog, and one hen.
(Written by Heidi Steele, the Peninsula School District in Gig Harbor, Washington)
Conclusion
The use of pattern stories encourages and requires learners to use complete sentences that are linked logically rather than a scattered list of vocabulary items. Human brains are programmed to remember a story with a beginning, a middle and an end better than some isolated pieces of information. It is through oral stories with repetition and strong storylines that many cultures with no written language hand down their legends and traditions from generation to generation. Every culture in the world has its own stories and as soon as you tell a child “once upon a time”, he or she will know that you are about to tell a story and he or she often immediately smiles and becomes interested and focused. Because of its regular repetition with some variations and its storytelling format, pattern stories are able to combine both mastery-oriented view of language forms and the meaning-oriented view of the language. Pattern stories facilitate and quicken the process for learners to make a form-meaning connection that is crucial in language learning (vocabulary and grammar concept acquisition) and help transfer their newly-acquired linguistic skills into a long-term memory. The teachercreated pattern stories can make the practice of reading those stories more aligned with the linguistic and cultural learning objectives of the unit at hand. Theuse of thoughtfully-selected, age-and-proficiencylevel-appropriate, existing Chinese pattern stories can help teachers implement the important parts of the World Readiness Standards for 21stCentury Language Learning by integrating language and culture into their instructional practice.
Research shows that most learners need between 5-16“meetings” with a linguistic item to be learned, be it a vocabulary item, a set phrase or an expression, a language chunk or a language function.4Learning Chinese characters, phrases or language functions is no exception. Chinese language learners need to practice and apply them many times in different contexts before he or she can use them appropriately. With repetition in meaningful context, pattern stories are one of the best means to help students improve their Chinese literacy by practicing and using characters in a contextualized way.
To conclude, pattern stories are a powerful tool in helping students gain access to the Chinese characters because they provide the context and repetition needed to help students remember the Chinese characters. Pattern stories are commercially available as picture books, and can also be found in traditional Chinese stories or created by teachers to provide a scaffold for literacy.
About the Authors
Helena Curtain served as associate professor at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, and her research area is appropriate pedagogical practices to build proficiency in language learning. She is the co-author (with Carol Ann Dahlberg) of Languages and Children: Making the Match (4thEd.).
Dali Tan is associate professor of Chinese language at the Northern Virginia Community College, and her research areas are issues in Chinese language teaching, such as the integration of language, culture and the content of other disciplines, intercultural exchanges and comparison, intercultural communicative competence, best practices in developing Open Educational Resource in Chinese and strategies in developing Chinese literacy.
Notes
1 a Chinese unit of length (=1/2 kilometer)
2 a Chinese unit of length (=1/3 meter)
3 Jane Kuo, Unpublished keynote address at Spring 2015 CLTAC (Chinese Language Teachers Association, California, USA) Conference, Stanford University, February 28, 2015.
4 Same as above
Pattern stories are often accompanied with supportive pictures that very often connect with the text in a one-to-one correspondence and provide automatic support to help learners understand both the language and the concepts. Pattern stories are a powerful tool in helping students gain access to Chinese characters because they provide the context and repetition needed to help students remember the characters. When saying aloud, telling or reading pattern stories, learners are actively engaged in the meaning-making process. Pattern stories facilitate and quicken the process for learners to make a form-meaning connection which is crucial in language learning and help transfer their newly-acquired oral language and character recognition skills into a longterm memory.
While all types of pattern stories are useful in helping learners develop literacy skills, teachercreated pattern stories have the additional bene fi t of making the practice of reading those stories more aligned with the linguistic and cultural learning objectives. The thoughtfully-selected, ageand-pro fi ciency-level-appropriate, existing Chinese pattern stories can help teachers implement the important parts of the World Readiness Standards for 21stCentury Language Learning by integrating language and culture into their instructional practice.
提 要模式故事是指在重复的基础上带有一定变化的故事。这类故事通常包含不断重复的核心短语或句型,读者可以据此猜测接下来发生的事情。模式故事的韵律也有助于学习者将故事内容转变为长期记忆。模式故事有很多不同的种类,如顺序逻辑类、问答类、单词或短语重复类、押韵类、混合类等,但所有的模式故事都有一个共性,即故事中至少有一个要素会重复出现。市面上可以买到很多正式出版的、带有精致插图的模式故事,教师也可以根据教学目标和教学内容自编模式故事。有些模式故事的重复要素不止一个。模式故事常常带有一对一的、与故事内容相匹配的辅助图片,学习者可以借此很自然地理解故事中的语言和概念。因为模式故事为学习者提供了语境和许多重复练习的机会,所以可以有力地帮助学习者理解和记忆汉字。当学习者在大声朗读、讲述或阅读模式故事时,他们可以积极主动地参与到解读和理解故事意义的过程中来。模式故事可以促进学习者建构语言形式和语言意义之间的联系,帮助他们把新近习得的口头语言和识字能力转变成长期记忆,而这正是语言学习的关键所在。所有类型的模式故事都有助于帮助学习者提高其文化素养,而教师自编的模式故事在教学中则更有针对性,他们可以将阅读模式故事的实践与所教单元的语言和文化教学目标更好地结合起来。根据学习者年龄和语言水平精心挑选的中文模式故事可以帮助教师将语言和文化融入到他们的教学实践中。

