延迟腓肠穿支带蒂皮瓣修复膝部软组织缺损
张功林甄平赵来绪陈克明张鹏宋涛薛钦义*
延迟腓肠穿支带蒂皮瓣修复膝部软组织缺损
张功林1甄平1赵来绪2陈克明1张鹏2宋涛2薛钦义2*
目的报告延迟腓肠内侧动脉穿支带蒂皮瓣修复膝部软组织缺损的临床应用结果。方法 自2010年1月~2014年1月,应用延迟腓肠内侧动脉穿支带蒂皮瓣修复膝部软组织缺损6例(男5,女1)。患者年龄18~46岁,平均36岁。软组织缺损范围8.5cm×7.5cm~9cm×8cm。皮瓣切取范围9.5cm×9cm~10cm×9cm。皮瓣延迟时间:8~13天,平均11天。延迟期间创面暂时应用VSD覆盖。结果 1例皮瓣发生小的皮缘裂开,术后2周自然愈合,延迟皮瓣全部成活。术后随访2~4.5年(平均3.5年),受区与供区外形较好。膝关节功能用Baily提出的膝关节评分标准评定其疗效,良5例,可1例。本组取得了较满意的临床效果。结论 该技术安全、可靠,适用于皮瓣切取较大或高风险患者。
软组织缺损;延迟皮瓣;膝关节
以腓肠内侧动脉为血供的腓肠肌内侧头肌瓣或肌皮瓣是临床用于修复膝和小腿上1/3软组织缺损的传统术式,其主要的缺点是需切取肌肉,对供区有一定的损伤,且较臃肿。随着显微解剖学的深入研究,能利用腓肠内侧动脉的肌皮穿支做为穿支皮瓣切取,由于不牺牲肌肉,扩大了手术适应证。而且,血管穿支较恒定,血运丰富。供区并发症相对小,自 Cavadas等[1]报道以来,在临床应用的报告逐渐增多[2-6]。但切取的范围有限,对膝关节周围较大面积软组织缺损的修复应用受到限制。2010年1月~2014年1月,为扩大皮瓣的切取面积,笔者修复前先采用皮瓣延迟,再行带蒂修复膝部软组织缺损,取得满意效果。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
本组6例,男5例,女1例。年龄18~46岁,平均36岁。均为膝和小腿上1/3软组织缺损伴骨和肌腱外露创面,其中,膝部软组织缺损5例,小腿上1/3 1例。左侧2例,右侧4例。1例患有糖尿病,2例有吸烟嗜好。软组织缺损的原因:交通事故伤3例,烧伤1例,重物砸伤2例。软组织缺损的范围:8.5cm×7.5cm~9cm×8cm。切取皮瓣大小:9.5cm×9cm~10cm×9cm。手术时机:本组急性创伤所致2例,行创面急症清创术的同时行皮瓣延迟术。另4例为陈旧性损伤病例,伤后时间:8~21天,平均12天,均行择期先行皮瓣延迟术。皮瓣延迟时间:8~13天,平均11天。延迟期间创面暂时应用VSD(Vacuumsealingdrainage,VSD)覆盖。
1.2 手术方法
选用腰硬联合麻醉,在充气止血带下先取平卧位行清创术,切除伤口内炎性与坏死组织,并取分泌物送培养,反复用3%双氧水和生理盐水清洗伤口。清创后,改用俯卧位,切取同侧腓肠内侧动脉穿支带蒂皮瓣[7,8]。方法:按术前Doppler测定的血管穿支点比创面稍大设计皮瓣。先切开皮瓣内侧缘至腓肠肌内侧头筋膜下,提起皮瓣缘向外分离看到至皮瓣的穿支血管后,选择较粗的一支为皮瓣供血动脉,保护好至皮瓣的穿支血管,从腓肠肌内侧头肌肉中将穿支血管从远向近逆行分离至腓肠内侧动脉、静脉血管蒂,其长度适宜后再切开皮瓣四周,遂将血管蒂从内侧头肌肉中完全游离出,将切开的内侧头肌肉行间断缝合,再将皮瓣的穿支及其穿支全部置于肌肉表面而不在肌肉内,并将血管蒂用小针细线固定在皮瓣侧,达到皮瓣延迟后二期手术不再寻找穿支及血管蒂的目的。松止血带细致止血后再将皮瓣间断缝回原位。术后10天左右,拆除延迟皮瓣四周缝线,将皮瓣从远端向近端掀起,直到上次手术分离好的血管蒂部为止。采用切开隧道方法将延迟皮瓣顺行旋转至受区修复创面缺损。供区创面经缩小缝合后,取股部中厚皮片行游离植皮修复。受区留置负压引流。
1.3 术后处理
术后应用敏感抗生素,不应用抗凝和扩血管药。经敷料包扎时的开窗孔观察皮瓣血运。抬高患肢30°左右,有利于减轻局部肿胀与改善静脉回流[9],注意腘窝内侧血管蒂处勿受压。术后48小时内拔除受区引流管。一周内局部用烤灯适当保温。应用后侧石膏托固定膝关节屈曲30°左右2周,有利于减轻血管蒂的张力。拆线后依伤口愈合情况,逐渐行伤肢功能训练。
2 结果
本组病例术后经过顺利,没有发生经过手术后穿支与周围组织粘连分离困难者,延迟后二期手术对血管蒂处理较为简单,皮瓣没有发生血管危象,全部成活。其中1例皮瓣发生小的皮缘裂开,1例出院后在家用热水袋不慎发生皮瓣中央区小的烫伤,都经2周换药处理自然愈合。所有病人随访2~4.5年(平均3.5年)。供区和受区愈合满意,没有因皮瓣修复后外形臃肿而需要行修薄以改善外观的病例。膝部功能基本恢复。小腿运动功能无明显影响。膝关节功能按 Baily提出膝关节评分标准评定[10],本组良5例,可1例。取得了满意的临床效果(典型病例见图1~6)。(彩图见插页)

图1 右膝皮肤坏死术前
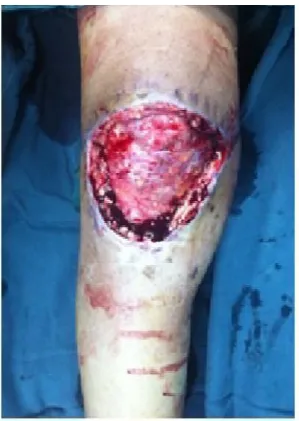
图2 术中清创术后

图3 皮瓣设计
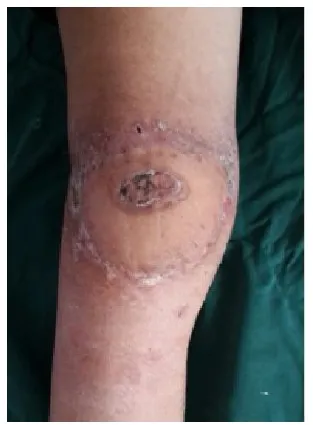
图4 修复后1月外形

图5 修复后半年外形

图6 供区外形
3 讨论
3.1 腓肠内侧动脉穿支皮瓣的优缺点
3.2 应用皮瓣延迟技术的理论基础
Dhart等[15]在为期1年的皮瓣延迟实验中,皮瓣延迟后48小时内先是出现皮瓣血管缺血期,其后血管发生逐渐的扩张,至72小时出现明显的扩张,至7天达到高峰,并较恒定的维持至1年,他把这种血管扩张称为持久性不可逆性扩张。皮瓣延迟是由于增加和扩张了chock血管,从而增加了皮瓣供血范围。达到可切取超过正常范围皮瓣的目的,使超范围的皮瓣得以成活,降低了皮瓣因供血不足所致的皮瓣坏死率。减少了皮瓣术后并发症。降低了皮瓣转移后可能发生远端部分供血不足以及会因静脉回流障碍而导致坏死的发生率[16,17]。因而,本组对所切取的皮瓣在宽度大于8cm者采用了皮瓣延迟技术,术后皮瓣成活良好。取得了满意的效果。其中,3例同时伴有糖尿病或吸烟嗜好,这类患者Ince称为高风险病人(High-riskpatients)[18],术后易于发生皮瓣部分坏死。为了提高皮瓣的供血,确保皮瓣转移后能够顺利成活,对切取超过正常范围皮瓣或高风险病人采用皮瓣延迟技术,是降低术后皮瓣发生部分坏死的一种很有效的措施,而且皮瓣延迟操作技术安全、可靠,术后过程顺利。本组没有因操作困难而临时改用其他术式者。
3.3 操作注意事
3.4 该项技术的缺点
增加了手术次数和费用以及延长了住院日是其不足。
[1]Cavadas PC,Scanz-Gimenez-Rico JR,Gutierrez-de la Camara A, et al.The medial sural artery perforator free flap[J].Plast Reconstr Surg,2001,108(6):1609-1615.
[2]Okamoto H,Sekiya I,Mizutani J,et al.Anatomical basis of the medial sural artery perforator flap in Asians[J].Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg,2007,41(3):125-129.
[3]张功林,章鸣,张金福,等.腓肠内侧动脉穿支带蒂皮瓣修复髌前软组织缺损[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(2):144.
[4]Ranson J,Rosich-Medina A,Amin K,et al.Medial Sural Artery Perforator Flap:Using the Superficial Venous System to Minimize Flap Congestion[J].Arch Plast Surg,2015,42(6):813-815.
[5]Howell A,Bartram A,Nugent M.Split table improves access for harvest of medial sural artery perforator flap[J].Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg,2015,53(9):894.
[6]Ives M,MathurB.Variedusesof the medial suralartery perforator flap[J].J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg,2015,68(6):853-858.
[7]Umemoto Y,Adachi Y,Ebisawa K.The sural artery perforator flap for coverage of defects of the knee and tibia[J].Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg,2005,39(4):209-212.
[8]Lee G,Jeong E.Coverage of defect over toes after failure of microsurgical replantation with medial sural artery perforator flap:A case report[J].Microsurgery,2016,36(2):161-164.
[9]HallockGG.Medialsural artery perforator free flap:legitimateuse as a solution for the ipsilateral distal lower extremity defect[J].J Reconstr Microsurg,2014,30(3):187-192.
[10]蒋协远,王大伟.骨科临床疗效评价标准[M].第1版,北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:180.
[11]Jeevaratnam JA,Nikkhah D,Nugent NF,et al.The medial sural artery perforator flap and its application in electrical injury to the hand[J].J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg,2014,67(11):1591-1594.
[12]Wong MZ,Wong CH,Tan BK,et al.Surgical anatomy of the medial sural artery perforator flap[J].J Reconstr Microsurg,2012,28 (80):555-560.
[13]Altaf FM.The anatomical basis of the medial sural artery perforator flaps[J].West Indian Med J,2011,60(6):622-627.
[14]Kao HK,Chang KP,Chen YA,et al.Anatomical basis and versatile application of the free medial sural artery perforator flap for head and neck reconstruction[J].Plast Reconstr Surg,2010,125(4) :1135-1145.
[15]Dhar SC,Taylor GI.The delay phenomenon:the story unfolds[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg,1999,104(7):2079-2091
[16]Ali F,Harunarashid H,Yugasmavanan K.Delayed reverse sural flap for cover of heel defect in a patient with associated vascular injury[J].A case report.Indian J Surg,2013,75(Suppl 1):148-149.
[17]Taylor GI,Chubb DP,Ashton MW.True and'choke'anastomoses between perforator angiosomes:part I.anatomical location[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg,2013,132(6):1447-1456.
[18]Ince B,Daaci M,Altuntas Z,et al.Versatility of delayed reverseflow islanded sural flap for reconstructing pretibal defects among high-risk patients[J].Ann Saudi Med,2014,34(3):235-240.
[19]张功林,甄平,陈克明,等.逆行半比目鱼肌带蒂肌瓣修复小腿远端软组织缺损[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2015,12(2): 37-39.
Delayed the medial sural artery perforator pedicled flap to repair soft-tissue defect of the knee
Zhang Gonglin1,Zhen Ping1,Zhao laixu2,et al.
1 Institute of Army Orthopaedics,Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Area,Lanzhou Gansu,730050;2 Department of Orthopaedics,Wushan County People's Hospital, Wushan Gansu,741300,China
Objective To report clinical application results of the delayed the medial sural artery perforator pedicled flap torepair soft-tissue defectoftheknee.Methods FromJan2010 to Jan 2014,6 patients(5men,1woman)withsoft-tissue defect in the knee underwent reconstruction with a delayed the medial sural artery perforator pedicled flap.They ranged in age from 18 to 46 years(mean,36y).Of them,5 cases recipient site were located on the knee and one case on the upper 1/3 of the tibia.Soft-tissue defect ranged from 8.5cm×7.5cm to 9cm×8 cm.Elevation of the flaps ranged from 9.5cm×9cm to 10cm×9cm.The delay period ranged from 8 to 13 days(mean,11d).Temporary wound coverage was achieved by VSD during the delay period.Results One patient developed small wound dehiscence,which spontaneous healed at two weeks after surgery.All the delayed flaps had survived completely.Follow-up period ranged form 2 to 4.5 years(mean,3.5y)postoperatively.A good contour was confirmed at the recipient and donor sites.The function of the knee jointswereevaluated withBailyscores.Good results were obtained in 5casesandfairin1 case.Satisfactory clinical results were obtained in this series.Conclusion This technique is safe,reliable,and particularly suitable for larger flap or high-risk patients.
Soft-tissue defect;Delayd flap;Knee
R658
B
10.3969/j.issn.1672-5972.2016.06.03
swgk2016-03-00040
张功林(1954-)男,本科,主任医师,研究方向:脊柱外科、修复与重建。
2016-03-06)
1兰州军区总医院全军骨科研究所,甘肃兰州730050;2甘肃省武山县人民医院骨科,甘肃武山741300

