国外个人信息管理现状及发展动态述评*
王文韬,谢阳群,谢笑
国外个人信息管理现状及发展动态述评*
王文韬,谢阳群,谢笑
文章探讨国外个人信息管理(PIM)研究现状和发展动态,以国外PIM相关文献和六次国际PIM会议论文为基础,通过文献内容分析得出研究现状,包括如何理解PIM、个人信息的内容及分类、PIM活动、个人信息集合、环境和空间的关系;发展动态包括个人信息类型研究细分化、研究视角和研究方法多样化、跨领域PIM研究、个人信息整合管理及PIM工具研究。
个人信息管理 现状 发展动态
0 引言
个人信息管理(personal information management,PIM)即个人以个人信息为对象,为满足自身的学习、生活和工作等需要而开展的一系列信息管理活动。PIM研究最早可追溯到20世纪初。随着计算机和信息技术发展,个人信息的数量、格式和类型等越来越多,PIM能力已不能满足个体PIM需求。这种环境下,PIM研究逐渐受到个人、学术界和产业界重视。下文在对PIM文献和六次国际PIM会议论文分析的基础上,分析国外PIM的研究现状和发展动态。
1 国外PIM研究现状
1.1 国外PIM研究阶段
国外PIM研究可分为三个阶段。
第一阶段始于20世纪上半叶,1945年美国科学家Vannevar Bush在《诚如我思》(As we may think)一文中首次提出PIM概念和MEMEX系统。通过MEMEX系统,科学家可对个人书籍、档案或信函等信息进行管理[1]。由于当时个人信息的数量和类型较少,对个人信息的研究多是对单个类型个人信息的探讨,如微文档系统(microdocumentation system)[2]、文件管理系统(zippered lists)[3]。这一阶段可视为国外PIM研究的启蒙阶段。
第二阶段。20世纪80年代末,微型计算机技术快速发展,利用其来提高PIM效率的问题得到广泛讨论。1988年Mark Lansdale在《PIM心理》(The psychology of personal information management)一文中首次提出“personal information management”(PIM)一词,认为PIM即个人分类和检索信息的方法和程序[4]。随后PIM研究进入兴起阶段。C.Moon提出用个人信息系统(personal information system)来管理个人信息的获取、存储和检索[5],主要针对科学家群体。S.Whittaker等提出个人电子邮件信息过载现象,认为电子邮件作为交流工具出现,却额外承担了任务管理和个人档案管理的任务,用户经常会迷失在过载邮件中,为此将用户分为不筛选邮件、频繁筛选、定期筛选三类,并提出解决方法[6]。Greenberg基于PDAs平台,对个人信息公开化和公共信息个体化的转换进行研究,提出以SharedNotes系统辅助个人办公[7]。
第三阶段。随着PIM研究受到越来越多的关注,2005年首届PIM会议在美国举办,到2013年PIM会议成功举办了六届。随着信息时代的到来,每个人都会遇到PIM问题,PIM进入普遍应用阶段。
1.2 PIM现状
1988年Lans dale提出PIM一词至今27年,近10年国际PIM研究活跃,但和许多新兴领域一样,PIM还有许多基础性问题没有得到解决,如对PIM的理解、个人信息内容和分类、PIM活动,以及个人信息集合、环境与空间之间的关系等等。
1.2.1 如何理解PIM
有学者将PIM定义为对个人信息进行存储、组织和检索的活动[8],强调信息管理活动的主体——个人,并没有严格界定对象——个人信息的范围。Kristina将PIM定义为关于信息的个人管理活动(personal management of information),这样既可以避免对个人信息下定义,又可以将PIM研究的重点直接放到个人而非信息、技术或系统上[9]。
本文认为,当下PIM应视为PI+PM(个人信息+个人管理),即个人对个人信息的管理,PIM的主体是个人,客体是个人信息,是个人为满足自己的学习、生活和工作等需要而开展的一系列信息管理活动。随着个人信息数量、类型和格式增多,个人对个人信息的管理越来越难,未来PM不再只是个体,通过政府、社会组织或企业等管理个人信息将是重要方式之一。
1.2.2 个人信息的内容及分类
什么是个人信息?Lally将个人信息定义为与生活有直接关系的信息,这些信息要么与我们相关,要么是由我们自身或先辈创造的信息[10]。Jones将个人已经控制和拥有的信息,与个人相关的信息,个人创造、发送、提供或出版的信息,以及个人的直接经历或间接经历等,都视为个人信息的内容[11]9。有学者认为个人信息是与个人相关,且被个人直接控制的信息[12]16。Jones[13]将个人信息分为个人所有或个人控制、与个人相关、指向个人、由个人发出、个人的经历、对个人有用等6类。
本文从物理、生理、心理和社会四个角度来理解个人信息。从物理角度看,个人信息是指个人作为大自然组成部分,由物理属性呈现出的个人信息,如肤色、血型;从生理角度看,个人信息主要表现为体貌、病理信息等;从心理角度看,个人信息主要表现为思想、思维、情绪、信仰等;从社会角度看,个人信息主要表现在个人与社会及社会中的个人进行交流的信息交换过程中产生的电子邮件、办公文档、照片和视频等信息。
1.2.3 PIM活动范围
(1)查找。Jones指出,PIM包括所有获取新信息的活动,无论这种活动是有意识的还是偶然的,只要这个活动最终是将信息组织到个人存储中或是用于个人信息的再查找或再利用[14]。可以看出,Jones认为查找应属于PIM活动范围。但Kristina认为查找不应归为PIM的一部分,他认为在开展PIM前就应具有一定的查找能力,无论这些信息是存在人的大脑中还是电子设备中或是物理形式的文档中,都属于获取前的能力,因此他认为查找应是PIM的前提[15]。PIM活动应始于对信息的获取,个人在获取信息时须已拥有一些信息,如互联网搜索、图书馆查询等都是个人获取信息时的能力。如果将发现信息的能力归结到PIM活动中来,会扩大PIM活动范围,因为在个人发现信息的能力背后还存在着信息行为或信息实践等密切相关的活动。由此可见,查找不属于PIM活动范围,PIM活动应从获取开始[16]。
随着一个学科不断发展,会与其他学科发生交叉联系。Kristina认为将查找列入PIM活动范畴,可能会扩大PIM外延的想法没有考虑到,随着PIM研究的发展,它将与心理学、计算机科学甚至人体工学产生的密切联系。因此,本文认为应将查找归入PIM活动范围,只是因此而涉及的个人信息行为和实践也可从行为科学、心理学等角度来探讨,目前多视角及跨领域的PIM研究正是学科交叉联系的结果。
(2)获取。用户的信息获取一般可分为主动的信息获取、被动的信息获取。主动的信息获取是用户在掌握一定信息查找能力后主动获取所需信息。主动获取可分为信息认知、信息创造及再造过程,信息再造就是通过对此前保存的信息进行二次加工[17]。被动的信息获取是指个人在生活、工作或学习过程中,无意发现的有用或有趣信息[18],如每天收到的非主动订阅邮件信息[19]。对“信息偶遇”这种被动的信息获取行为要考虑:一方面信息偶遇有助于个人得到感兴趣或有用的信息;另一方面过多的信息偶遇可能导致用户原始的信息查找行为暂停或终止,从而影响原有的信息查找行为。
(3)元层次活动。元层次的PIM活动由Jones等提出,是指对个人信息空间、个人信息集合等有序化的管理活动[20]13。从图1可知,PIM中元层次的活动必然要与信息的获取、存储等活动相联系,元层次活动中运用的信息查找、检索、存储方法和范式将会影响整个PIM活动效率。元层次活动相对于获取和保存活动,更抽象和隐蔽,因此更应受到关注。
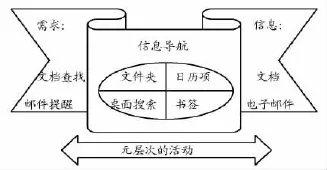
图1 元层次活动[11]
1.2.4 个人信息集合、环境和空间
国外PIM研究中的另一个基础性问题是对个人信息集合、个人信息环境和个人信息空间的概念和三者之间关系的探讨,本文通过图形的方式来阐明它们之间的关系,见图2。
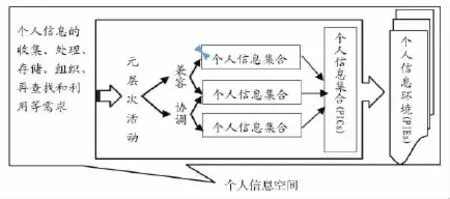
图2 个人信息集合、环境和空间关系图
从图2可看出,个人通过对个人信息的(过滤)收集、处理、存储、组织等活动来辅助个人再查找和再利用信息的行为,是个人对信息需求与信息处理矛盾之间平衡须付诸的行动。在这个过程中,用户通过借助各种软硬件设备和多种查找、检索方法在多个个人信息集合中搜索,不同的个人信息集合之间的个人信息,由于格式和存储结构等不同,存储、组织、再查找和再利用等都须通过元层次活动来完成个人信息集合间的兼容和协调。个人信息集合更偏向于个人信息类型、组织方式、配置原则和存储结构等。个人信息环境通常与个人信息设备、应用程序和个人信息活动发生的场所相关联,多个个人信息集合构成个人信息环境。
个人信息空间与个人信息环境不同的是,个人信息环境被视为个人信息空间的子集,以多种形式存在,如物理形式、数字形式或是二者兼而有之。其与个人发生关系更多是借助应用程序,如一台个人电脑可被视为一个个人信息环境,因此,用户可以有多个个人信息环境(PIEs)[21]。个人信息空间是个人信息集合(PICs)和个人信息环境的总和,每个用户只有一个个人信息空间。从PIM角度看,个人信息集合由于其偏向于某种格式类型,或是某个计划主题,因此更容易管理,但个人信息空间的管理对象较为复杂混乱,因此从个人信息集合(PICs)切入管理PIM,将更有效地提高个人信息空间的有序性。Indratmo等从个人信息的组织结构方式来探讨PIM,分析常见的个人信息的组织结构形式,如分层结构、扁平结构、线性结构、空间结构和网络结构[22]等。
2 国外PIM发展动态
2.1 研究内容细分化
国外PIM研究范围不断扩大,研究对象从研究科研人员逐渐转为普通个体。个人信息类型、媒介或载体研究范围不断扩大、细化,其中又以个人电子邮件[23]、网页[24-25]、任务或工作流[26]等研究居多,见表1。
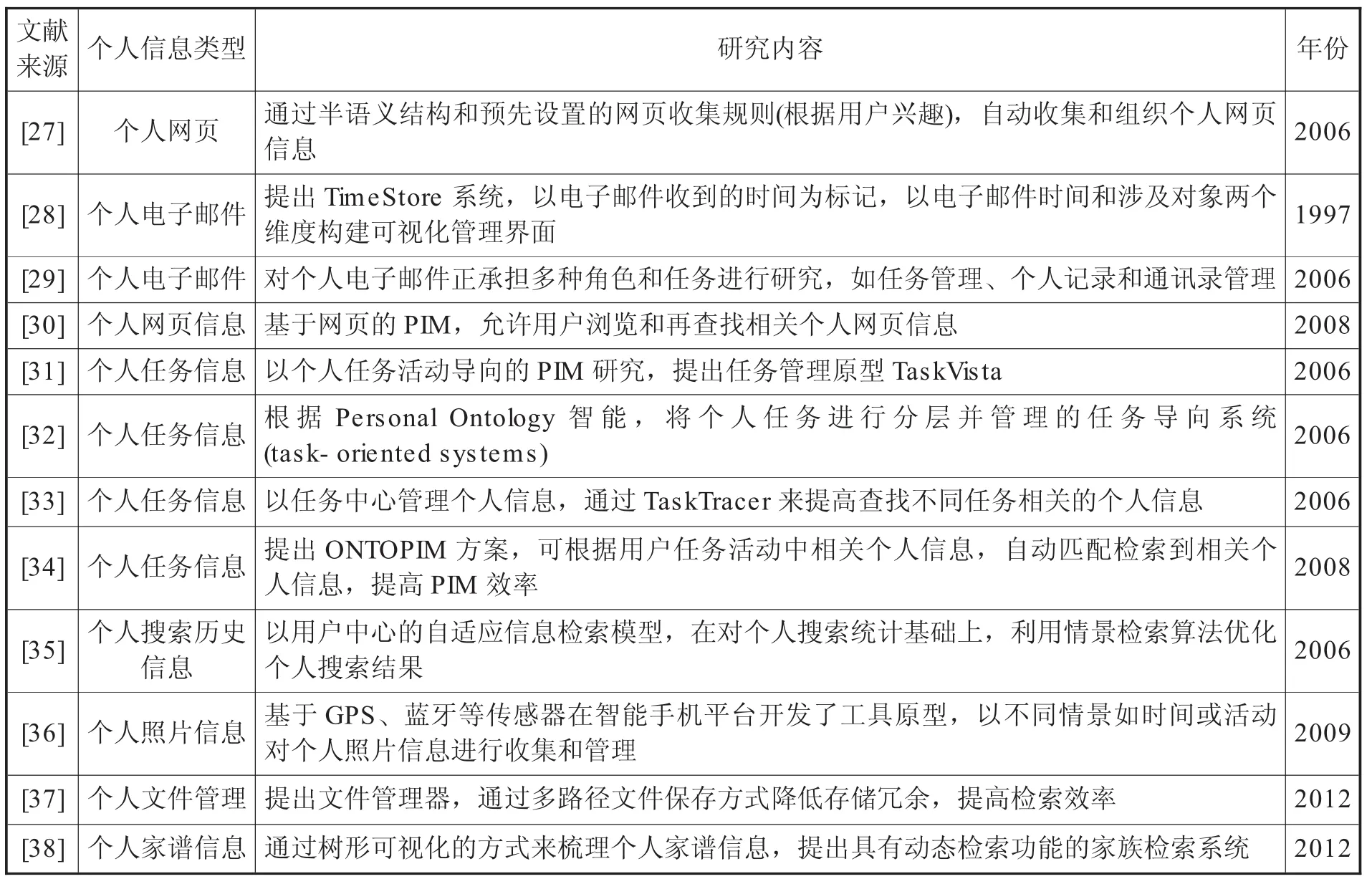
表1 个人信息类型研究
从表1可看出,个人信息格式和内容越来越细分。电子邮件最初以通讯传输方式存在,但在现代扮演更重要的角色,如日程提醒、新闻订阅、云盘存储,电子邮件逐渐变成以通讯为主搭载社交、信息备份等多种功能的个人信息管理工具。对个人网页信息的研究主要关注备份方式、兴趣推送、标签管理等,通过本地、云端等备份方式将个人网页信息进行备份,便于再查找,对时常变动的网页信息,通过本地的内容备份,即使未来服务器端的内容被删除,本地依然保存着该信息。通过大量个人网页信息搜集和计算,浏览器可提供用户可能感兴趣的网页,用户因此拥有各种各样的“标签”。
2.2 跨领域研究不断出现
由于各行各业的发展都离不开信息,PIM研究开始涉及更多领域,如医疗[39],教育[40]、图书馆[41-42]、心理学[43]等(具体见表2)。由于PIM领域涉及个人、信息等元素,与其他学科发生交叉。在信息时代,各行各业都离不开信息,个人的经历、个人特征信息,以及生活、工作和思想表达等均伴随着个人信息的产生。由于信息无孔不入,PIM研究的继续发展,除了与教育学、法学、医学、行为科学、金融学等学科关联外,将与越来越多的学科发生密切联系。
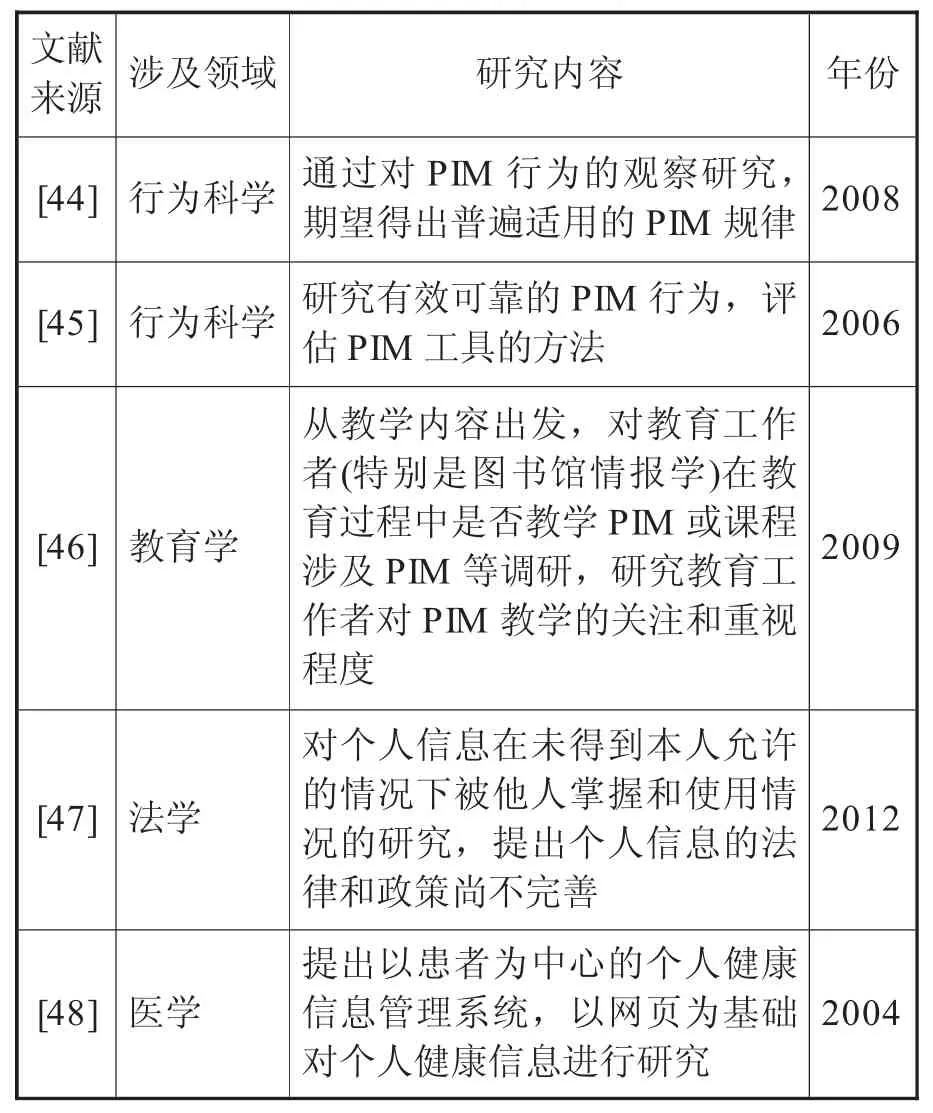
表2 PIM的跨领域研究
2.3 研究视角多样化
随着PIM研究对象转为普通个体,研究视角也逐渐多样化,如从时间、地点、活动、网络环境、设备等情景视角研究PIM。Gupta等从移动环境视角来探讨PIM[49];Komninos等将使用移动工具管理个人信息的一代人称为“游动的一代”(nomadic generation)[50];Majid等探讨在网络环境下大学生群体的信息安全和隐私问题,在对212位受访者的调研中发现超过三分之二对基于网络环境下的PIM中的信息安全和隐私较为重视,因此他们在网络中只存储非敏感性的个人信息[51];Catherine等从信息偶遇角度研究PIM[52],更多研究视角的内容见表3。
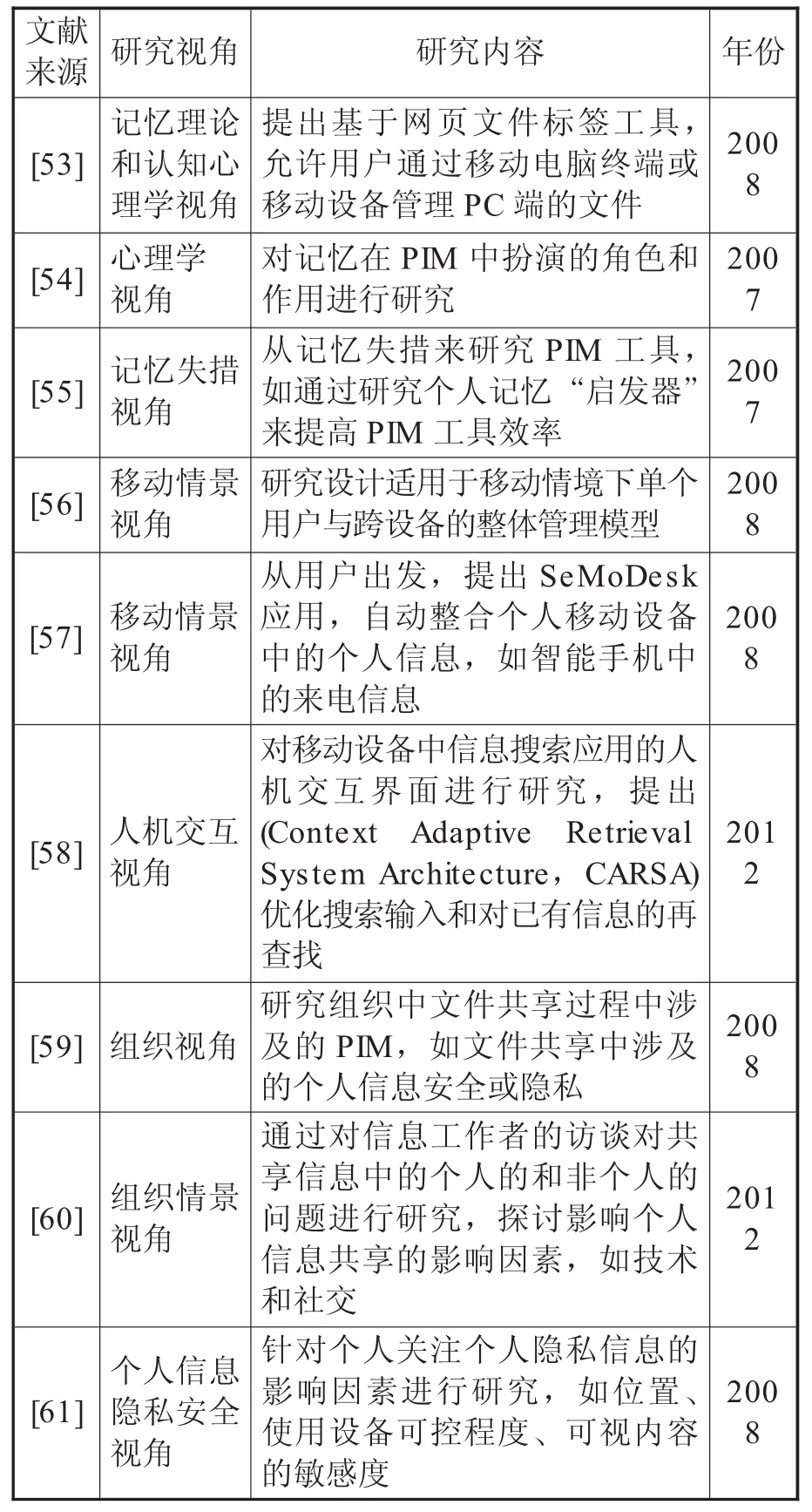
表3 多视角PIM研究
2.4 研究方法多样化
从PIM研究方法看,一般为定性与定量相结合。Zhang等通过调研和访谈法,探讨5位信息工作者对组织中个人信息共享的态度[62]。Elsweiler等利用马尔科夫链,通过可视化研究个人电子邮件的再查找行为[63]。Tungare等对个人面对多设备平台的PIM进行研究,通过主观精神负荷系数来分析PIM行为,利用NASATLX任务负荷指数指标对220位知识工作者的预调研,发现用户对跨设备获取管理个人信息表示失望,在此基础上,通过对18位志愿者在完成PIM任务时的精神负荷值进行评估和记录来研究[64]评估用户在多设备间PIM的心理负担。其他研究方法见表4。一个学科成熟的标志之一是拥有一套成熟的属于自身的规律准则和研究方法。PIM作为新兴研究领域,探索适用于PIM的规律和方法是未来PIM研究的重要方向。
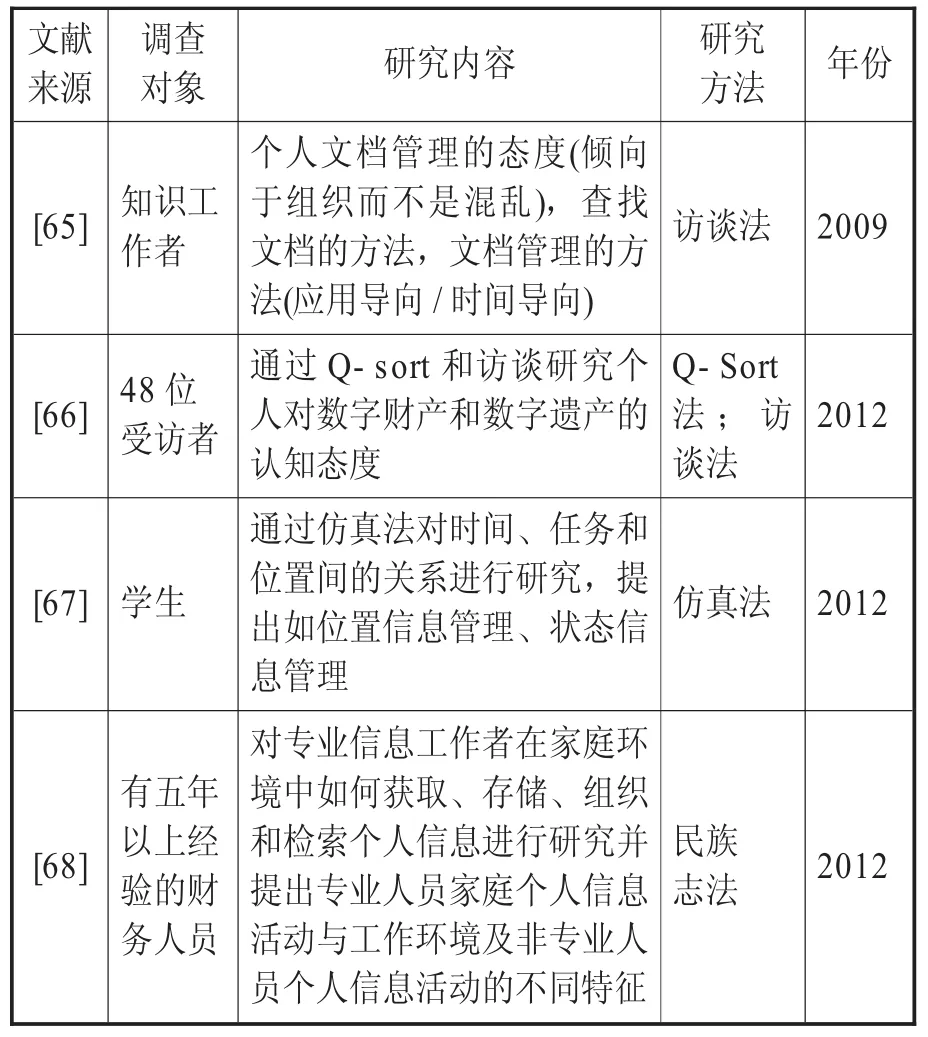
表4 PIM研究方法
2.5 注重整合管理
由于信息源的多样性和使用多种PIM工具及平台,个人信息在物理世界和虚拟世界出现碎片化现象,信息碎片是PIM中不能回避的问题。正如Jones等所言,无论是物理环境还是数字环境,不同终端或工具对同一信息处理的不同版本,即使在同一台电脑,信息也可能被“我的文档”、文件夹、电子邮件或书签所分离[69]。一些学者尝试通过整合方式来管理多种个人信息,如Kelly等通过对个人生活记录信息进行整合管理研究,个人生活记录(Personal life log archives)包括照片、手机短信、电子邮件、即时通讯信息、个人文本、网页浏览信息,均发生在个人生活、工作和学习的多个空间[70]。其他整合管理个人信息的研究见表5。
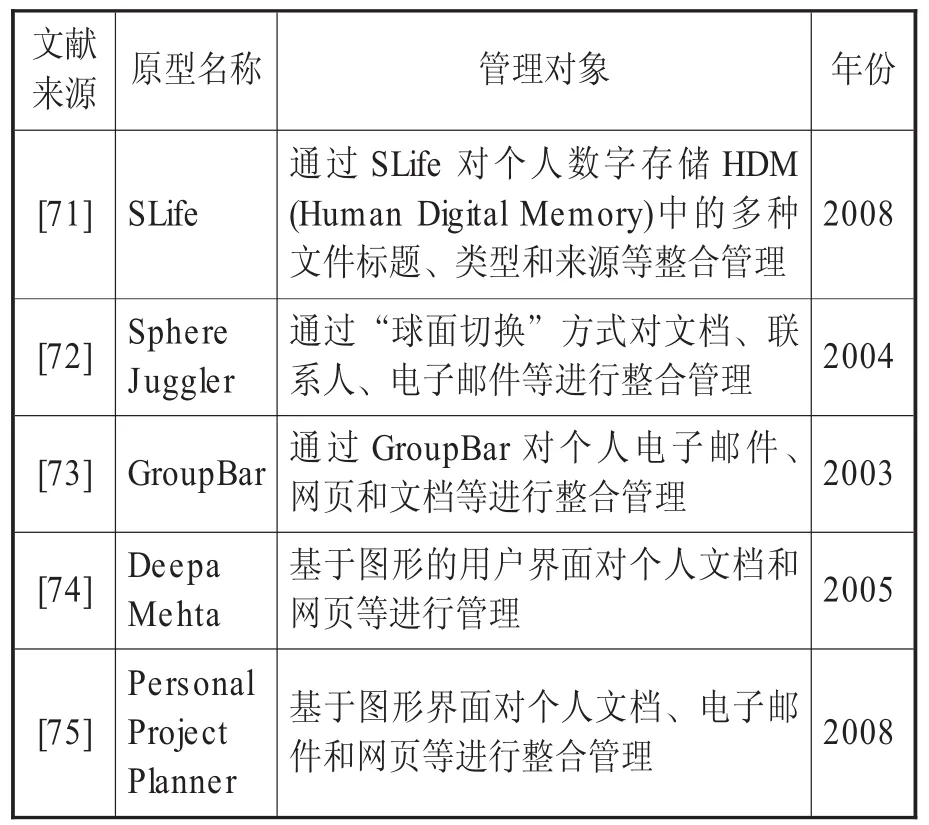
表5 个人信息整合研究
面向整合的PIM研究和工具的出现正是个人行为规律中最省力法则的体现。个人希望通过一种工具或统一的平台就能有效管理多种个人信息。因此,面向整合的PIM研究和工具越来越多,目前PIM工具的整合功能处于初级阶段,大多通过功能模块的添加和组合来完成整合管理个人信息。在未来PIM研究中,应通过以知识单元的有序化和数据库兼容等技术为个人提供一个跨平台及具有较强兼容性的整合管理工具。
2.6 PIM工具研究
随着个人信息的数量、类型、格式和载体增多,跨终端、跨平台导致个人信息碎片化,个人仅凭记忆很难优化管理个人信息,一些学者尝试通过PIM器即PIM工具来优化PIM。微软研究院Susan Dumais等针对个人信息检索和再利用开发Stuff I’ve Seen(SIS),通过两种方式来辅助个人信息再利用:系统提供一个统一的关于个人信息的索引,包括邮件、网页、文档;由于这些信息个人此前都了解,因此在搜索界面提供了丰富的情境线索[76]。其它PIM工具见表6。
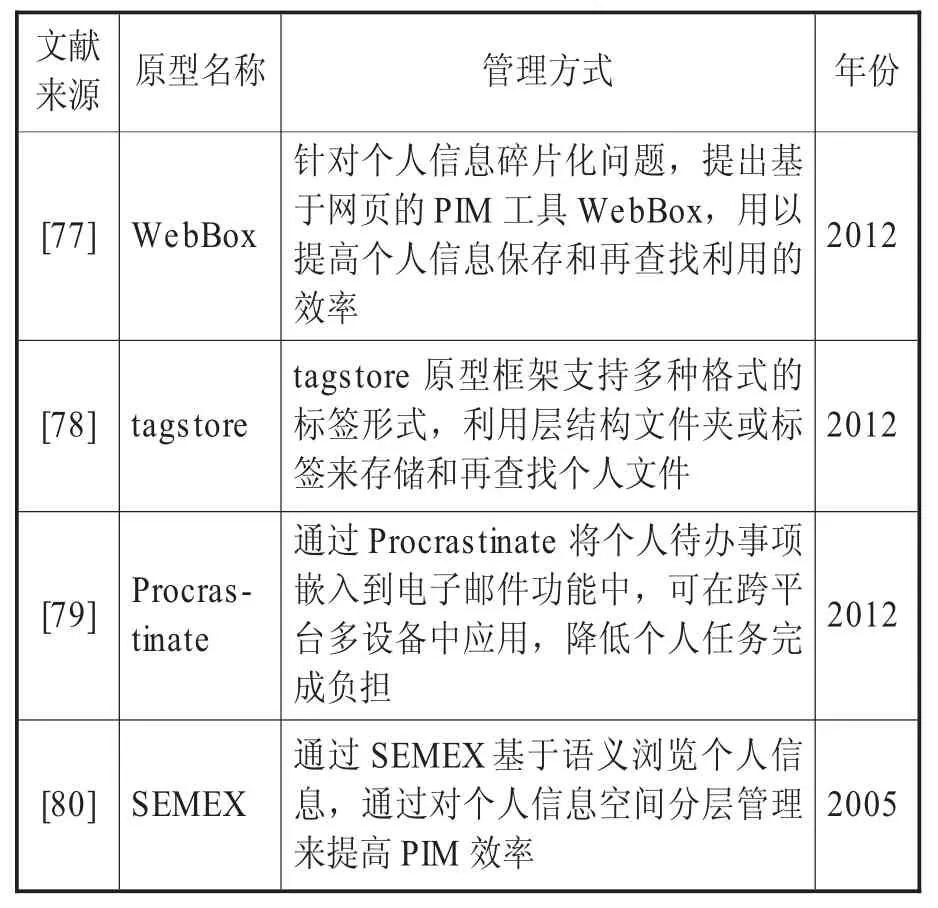
表6 PIM工具研究
3 结语
笔者在对国内一些用户进行PIM相关调查研究时发现,很多用户认为个人信息即是个人证件账号、密码等信息,认为PIM更应该是一个法律问题。随着社会的发展,个人信息数量、格式和涉及的内容、领域越来越多,个人自身作为信息工具的信息处理能力已很难满足PIM的需求,因此,除了用户自身外,学术界和产业界也应提高对PIM研究的重视,跳出“个人隐私”和“法律问题”的范围。庆幸的是,目前已有一些高校开展了PIM相关教学课程,通过对在校大学生进行系统的PIM方法和工具的学习,提高其PIM能力。
本文对国外PIM的现状和发展动态进行了研究,发现国外PIM的研究呈现出多视角、跨领域等特点,研究方法也不断多样。事实上,除了本文论述的PIM相关现状和发展动态,PIM还有很多尚待探讨的问题,如个人信息内容的界定、个人信息的分类探讨、元层次PIM活动研究、个人信息隐私和安全、PIM工具、PIM规律和方法等。期望本文对PIM的探讨能为国内PIM的研究提供一定的参考和借鉴。
[1]Bush.Vannevar.As we may think[J].Atlantic Monthly,1945(7):101-108.
[2]Engelbart D C.Special considerations of the individual as a user,generator,and retriever of information[J].American Documentation,1961,12(2):121-125.
[3]Nelson T H.Complex information processing:a file structure for the complex,the changing and the indeterminate[C]//Proceedings of the 1965 20th national conference.ACM,1965:84-100.
[4]Lansdale,M.W.The psychology of personal information management[J].Applied Ergonomics.,1988,19(1):55-66.
[5]Moon C.Computerized personal information systems for research scientists[J].International journal of information management,1988,8(4):265-273.
[6]Whittaker S,Sidner C.Email overload:exploring personal information management of email[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems.ACM,1996:276-283.
[7]Greenberg S,Boyle M,LaBerge J.PDAs and shared public displays:Making personal information public,and public information personal[J].Personal Technologies,1999,3(1-2):54-64.
[8]Bergman O,Boardman R,Gwizdka J,et al.Personal information management[C]//Chi'04 extended abstracts on human factors in computing systems.New York:ACM Press,2004:1598-1599.
[9][15][16]Spurgin K M.Everyday information organization practices in the pursuit of leisure:The information organization,management,and keeping activities of amateur art photographers[D].School of Library and Information Science,Univ.of North Carolina,Chapel Hill,2008.
[10]Lally,Elaine.Internet Research Annual.Volume 2[M]. Peter Lang Publishing Inc New York,2005:153-162.
[11][20]William Jones,Jaime Teevan,Personal Information Management[M].University of Washington Press,Seattle and London,2007.
[12]Richard Boardman Improving Tool Support for Personal Info rmation Management[D].University of London,2004:16.
[13]William Jones.How is information personal?[C]// Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[14]Jones W,Dumais S,Bruce H.Once found,what then?A study of“keeping”behaviors in the personal use of Web information[J].Proceedings of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2002,39(1):391-402.
[17]Madlock-Brown C,Chin S C,Eichmann D.InfoATV:enhancing PIM systemsto supportre-finding to(re)discovery[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[18]Erdelez S.Information encountering:It's more than just bumping into information[J].Bulletin of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,1999,25(3):26-29.
[19]Ducheneaut N,Bellotti V.E-mail as habitat:an exploration of embedded personal information management[J]. Interactions,2001,8(5):30-38.
[21]William Jones,Harry Bruce.A Report on the NSF Sponsored Workshop on Personal Information Management[C]//Report on the NSF PIM Workshop,Seattle,2005.
[22]Indratmo J,Vassileva J.A review of organizational structures of personal information management[J].Journal of digital information,2008,9(1):1-19.
[23]Whittaker S,Sidner C.Email overload:exploring personal information management of email[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems.ACM,1996:276-283.
[24]David Eichmann.Semantic Commonalities of Research Networking and PIM[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[25]Fernando Figueira Filho,Wendy Mackay,Paulo Lício de Geus.Using the web to explore scienti?c knowledge and extend the desktop information space[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[26]Lackey S.Integrating Place and Time with Tasks:Adding Transportation to PIM[C]//Personal Information Management Workshop,ASIST Vancouver2009.
[27]Dontcheva M,Drucker S M,Wade G,et al.Collecting and organizing web content[C]//Personal Information Management-Special Interest Group for Information Retrieval Workshop.2006:44-47.
[28]Yiu K S,Baecker R,Silver N,et al.A time-based interface for electronic mail and task management[J]. Advances in human factors ergonomics,1997,21:19-22.
[29]Whittaker S,Bellotti V,Gwizdka J.Email in personal information management[J].Communications of the ACM,2006,49(1):68-73.
[30]Melanie Kellar.An Overview of Web-Based Monitoring:Future Directions and Challenges[C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[31]Bellotti V,Thornton J D.Managing activities with TV-ACTA:Taskvista and activity-centered task assistant[C]//SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:8-12.
[32]CatarciT,Habegger B,Poggi A,et al.Intelligent user task oriented systems[C]//SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:20-23.
[33]Stumpf S,Herlocker J.Tasktracer:Enhancing personal information management through machine learning[C]// SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:105-107.
[34]Lepouras G,Dix A,Katifori A,et al.Ontopim:From personal information management to task information management[C]//SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:78-81.
[35]Shen X,Tan B,Zhai C.Exploiting Personal Search History to Improve Search Accuracy[C]//SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:94-97.
[36]Larsen JE,Luniewski M.Using mobile phone contextual information to facilitate managing image collections [C]//American Society for Information Science and Technology,2009:73-75.
[37]Sajedi A,Afzali SH,Zabardast Z.Can you retrieve a file on the computer in your first attempt?Think to anew file manager for multiple categorization of your personal information[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[38]Murakami H,Zheng N.Visualizing Family Trees:Development of a Dynamic Family Retrieval System [C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[39]Chaytor R,Brown E,Wareham T.Privacy advisors for personal information management[C]//SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:28-31.
[40]Maier D,Archner D,Delcambre L,et al.Personal Information Enhancement for Education[C]//SIGIR Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle,Washington.2006:86-89.
[41]Fourie I.Personal information management(PIM),reference management and mind maps:the way to creative librarians?[J].Library Hi Tech,2011,29(4):764-771.
[42]Fourie I.Librarians alert:how can we exploit what is happening with personal information management(PIM),reference management and related issues?[J]. Library Hi Tech,2011,29(3):550-556.
[43][54]Elsweiler D.Supporting human memory in personal information management[D].University of Strathclyde,2007.
[44]Deborah Barreau.From Novice to Expert:Personal Information Management Behaviors in Learning Contexts [C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[45]Kelly D.Evaluating personal information management behaviors and tools[J].Communications of the ACM,2006,49(1):84-86.
[46]Deborah Barreau,Laura O’Neill,Amanda Stevens. The Relationship Between Research and Practice:What Are We Learning About Teaching Personal Information Management?[C]//Personal Information Management Workshop,ASIST Vancouver2009.
[47]Tungare M.The Shoebox and the Safe:When Once-Personal Information Changes Hands[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[48]Kim E H,Wang M,Lau C,et al.Application and evaluation of personal health information management system[C]//Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,2004.IEMBS'04.26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE.IEEE,2004,2:3159-3162.
[49]Gupta G,Mahesh K.Secure Personal Information Management between Desktops and Handheld Devices [C]//Proceedings of the International Multi Conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists.2009.
[50]Komninos A,Baillie L,Barrie P.Holistic PIM:Managing personal information for a nomadic generation [C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[51]Majid S,San M M,Tun S T N,et al.Using Internet services for personal information management[M]// Technological Convergence and Social Networks in Information Management.Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2010:110-119.
[52]Catherine C.Marshall,Harry Bruce et al.Encountering,keeping and organizing information;maintaining an information collection[C]//Report on the NSF PIM Workshop,Seattle,2005.
[53]Chen C H,Lin I W,Hsieh J L,et al.A Web-based Tagging Tool for Organizing Personal Documents on PCs[C]//International Conference of Computer-Human Interaction 2008,CHI,2008.
[55]Elsweiler D,Ruthven I,Jones C.Towards memory supporting personal information management tools[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2007,58(7):924-946.
[56]Tungare M,Perez-Quinones M.Thinking outside the(beige)box:Personal information management beyond the desktop[C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[57]Woerndl W,Woehrl M.SeMoDesk:Towards a Mobile Semantic Desktop[C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[58]Nitsche M,Nü rnberger A,Bade K.An ergonomic user interface supporting information search and organization on a mobile device[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[59]Whalen T,Toms E,Blustein J.File sharing and group information management[C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI.2008.
[60]Zhang H,Twidale M.Mine,yours and ours:Using shared folders in personal information management[C]// Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[61]Kirstie Hawkey.A Model of Visual Privacy Concerns for PIM Systems[C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI. 2008.
[62]Zhang M T H,Twidale M.Mine,yours and ours:Using shared folders in personal information management [C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[63]Elsweiler D,Hacker M,Mandl S.Visualising pim behaviour with markov chains[C]//Personal Information Management Workshop,ASIST Vancouver2009.
[64]Tungare M,Pérez-Quinones M A.Mental Workload at Transitions between Multiple Devices in Personal Information Management[C]//Personal Information Management Workshop,ASIST Vancouver2009.
[65]Henderson S.Guidelines for the design of personal document management user interfaces[C]//Personal Information Management Workshop,ASIST Vancouver2009.
[66]Cushing AL.Exploring the potential for Q method in the study of personal information management[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[67]Lackey S.Improving Goal Completion:Tagging Locationsand Tasks[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[68]Thomson L.PIM in the professional home office:An ethnographic study[C]//Personal Information Management workshop at the Annual ACM Conference on Computer Supported Collaborative Work,Seattle,Washington.2012.
[69]Jones W,Karger D,Bergman O,et al.Towards a unification&integration of PIM support[C]//Report on the NSF PIM Workshop,Seattle,2005.
[70]Kelly L,Byrne D,Jones G J F.The role of places and spaces in lifelog retrieval[C]//Personal Information Management Workshop,ASIST Vancouver2009.
[71]Fuller M,Kelly L,Jones G J F.Applying contextual memory cues for retrieval from personal information archives[C]//Proceedings of PIM Workshop,CHI. 2008.
[72]Morteo R,González V M,Favela J,et al.Sphere Juggler:fast context retrieval in support of working spheres[C]//Proceedings of the Fifth Mexican International Conference in.IEEE,2004:361-367.
[73]Smith G,Baudisch P,Robertson G,et al.Groupbar:The task bar evolved[C]//ProceedingsofOZCHI.2003.
[74]Richter J,V?lkel M,Haller H.DeepaMehta-A Semantic Desktop[C]//Semantic Desktop Workshop. 2005.
[75]Jones W,Klasnja P,Civan A,et al.The personal project planner:planning to organize personal information[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.ACM,2008:681-684.
[76]Dumais S,Cutrell E,Cadiz JJ,et al.StuffI've seen:a system for personal information retrieval and re-use[C]// Proceedings of the 26th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in informaion retrieval.ACM,2003:72-79.
[77]Van Kleek M,Smith D A,Shadbolt N.A decentralized architecture for consolidating personal information ecosystems:The WebBox[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[78]Voit K,Andrews K,Slany W.Creating a comparative environment for pim evaluation[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[79]Hanrahan B V,Pé rez-Quinones M A.Procrastinate:How I Learned to Stop Worrying About Email and Love Procrastinating[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Personal Information Management,Seattle2012.
[80]Dong X L,Halevy A.A platform for personal information management and integration[C]//Proceedings of VLDB 2005 PhD Workshop.2005.
A Study of the Present Situation and the Development Trend of Personal Information Management Abroad
WANG Wen-tao,XIE Yang-qun,XIE Xiao
Based on the content analysis of overseas literature about personal information management(PIM)and papers from six international PIM conferences,this article discusses the present situation and the development trend of PIM study abroad.The present study involves how to understand the PIM,the content and classification of personal information,PIM activities,and the relationship among collection,environment and space of personal information.The development trend refers to the differentiation of research on the types of personal information;the diversification of research perspectives and research approaches;the interdisciplinary study of PIM;the integration management of personal information and the research on PIM tools.
personal information management;present situation;development trend
格式 王文韬,谢阳群,谢笑.国外个人信息管理现状及发展动态述评[J].图书馆论坛,2015(12):124-133.
王文韬(1986-),男,武汉大学信息管理学院2013级博士研究生;谢阳群(1962-),男,博士,淮北师范大学教授;谢笑(1987-),女,博士,安徽大学管理学院讲师。
2015-05-14
*本文系国家自然科学基金项目“差错文化、归因倾向和差错报告:作用机制和情境因素”(项目编号:71273109)研究成果之一

