贺氏火针温通法治疗肱骨外上髁炎临床观察
贺氏火针温通法治疗肱骨外上髁炎临床观察
薛立文1,王云峰2
(1.首都医科大学附属北京中医医院针灸科,北京100010;
2.北京卢沟桥社区卫生服务中心,北京100072)
[摘要]目的观察贺氏火针温通法对肱骨外上髁炎的疗效。方法收集2014年1月至2014年12月首都医科大学附属北京中医医院针灸科肱骨外上髁炎患者60例,按就诊顺序将患者分为治疗组和对照组,每组30例。对照组每日毫针刺肘髎、曲池、手三里、合谷穴,治疗组加用贺氏火针隔日点刺阿是穴,两组均连续治疗10 d。以疼痛视觉模拟量表(visual analogue scale,VAS)、Mayo肘关节功能评分表(mayo elbow performance score,MEPS)为观察指标,判定临床疗效。结果与治疗前比较,治疗后两组VAS评分均显著降低(P<0.05),MEPS评分均显著升高(P<0.05),治疗组VAS评分降低值和MEPS评分升高值均显著大于对照组(P<0.05)。结论贺氏火针温通法可有效缓解肱骨外上髁炎的疼痛程度,改善肘关节功能。
[关键词]肱骨外上髁炎;火针;温通法
[中图分类号]R681.7[DOI]10.3969/j.issn.2095-7246.2015.05.017
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2014CB543203)国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2014CB543203)
作者简介:薛立文(1970-),女,硕士,副主任医师
收稿日期:(2015-09-17;编辑:曹健)
肱骨外上髁炎(external humeral epicondylitis,EHE)俗称“网球肘”,是指由于急、慢性损伤造成的肱骨外上髁周围软组织创伤性炎症,表现为肘外侧--------------------
酸痛,肘关节功能活动受限,持物无力等。现又称作“肘外侧疼痛综合征”“前臂伸肌总腱炎”“桡侧伸腕短肌与环状韧带纤维组织炎”等,属中医学“伤筋”“筋痹”范畴。在英国、荷兰和斯堪的纳维亚发生率为0.4%~0.7%[1];在国内是针灸科、骨科常见病,好发于前臂劳动强度较大的中老年人及职业工人、运动员等[2]。目前中西医采用针灸、针刀、封闭、康复、口服药物、手术等治疗手段,虽取得一定疗效,但治疗期相对较长,患者常畏惧有创操作,担心药物毒性及不良反应,故寻找一种快速有效、安全经济、易于接受的治疗措施成为目前临床研究热点。笔者总结北京中医医院针灸科国医大师贺普仁临床经验,采用贺氏火针治疗该病,拟探讨温通法对EHE的治疗效果,进而为温通法治疗经筋病提供临床依据。
Effects of Acupuncture on Recovery of Gastrointestinal Function and Gastrointestinal Hormone Secretion after Abdominal Surgery
HUANGLong,YUQing-sheng,PANJin-fang,SHUAIJian-feng,LIANGJiu-yin,ZHANGQi,LIUJu-da,WANGZhen,ZHOUFu-hai
(1.DepartmentofGeneralSurgery,TheFirstHospitalAffiliatedtoAnhuiUniversityofChineseMedicine&InstituteofChineseTraditionalSurgery,AnhuiAcademyofChineseMedicine,AnhuiHefei230031,China)
Abstract[] ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of acupuncture on recovery of gastrointestinal function and gastrointestinal hormone secretion after abdominal surgery. MethodsOne hundred patients who received abdominal surgery were randomly and equally divided into acupuncture group and control group. Patients in both groups received conventional therapy, and patients in the acupuncture group received acupuncture therapy in addition. The treatment lasted for 7 days. The recovery of gastrointestinal function after treatment was observed in each group. Levels of serum gastrin, plasma somatostatin, and plasma motilin were determined using radioimmunoassay. ResultsCompared with the control group, the acupuncture group had significantly shortened postoperative time to first flatus, first defecation, first bowel sound, extubation, and first eating (P<0.05). Moreover, the acupuncture group had a significantly lower level of serum gastrin and significantly higher levels of plasma somatostatin and motilin compared with the control group (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidence of complications between the two groups (P>0.05). ConclusionThe impacts of acupuncture on recovery of gastrointestinal function after abdominal surgery are associated with the regulation of gastrointestinal hormone secretion.
[Key words]gastrin; somatostatin; motilin; gastric motility; gastrointestinal hormone
1 临床资料
1.1纳入标准①符合EHE中西医诊断标准,且疼痛发生在1个月内,未接受过针刀、手术及服用西药者;②疼痛视觉模拟量表(visual analogue scale,VAS)评分≥4分者;③年龄18~65岁者;④签署知情同意书,志愿受试,知情同意过程符合GCP的规定。
1.2排除标准①患有关节炎及其他免疫系统疾病者;②近1个月内接受过针灸治疗该病者;③合并有心血管、脑血管、肝、肾和造血系统等严重原发性疾病及精神病患者;④对针刺不能耐受或有晕针史者;⑤正在参加其他临床试验的患者。
1.3一般资料将60例合格门诊患者按接诊顺序分为治疗组(火针加常规针刺组)和对照组(常规针刺组)各30例。治疗组男13例,女17例;年龄23~56岁,平均年龄(41.11±9.12)岁;病程1~15 d,平均病程(5.72±3.86)d。对照组男12例,女18例;年龄25~59岁,平均年龄(42.72±9.01)岁;病程1~14 d,平均病程(5.40±3.60)d。两组患者性别、年龄、病程比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
2 方法
2.1治疗方法
2.1.1治疗组采用特制0.5 mm×23 mm贺氏细火针。选择压痛最明显处作为阿是穴,常规无菌操作皮肤,火针加热至通红,采用密刺法于阿是穴及旁开0.5 cm范围内快刺4~5针。再以0.35 mm×40 mm毫针,直刺患侧肘髎、曲池、手三里、合谷,留针30 min。火针隔日治疗1次,毫针每日治疗1次,连续治疗10 d。
2.1.2对照组采用0.35 mm×40 mm毫针,直刺患侧肘髎、曲池、手三里、合谷,留针30 min,每日治疗1次,连续治疗10 d。
2.2观察指标及方法治疗前后(即第0天和第11天)进行VAS及Mayo肘关节功能评分表(mayo elbow performance score,MEPS)[3]测评。
2.2.1VAS评分在纸上画一条长10 cm的线段,两端分别表示“无痛”(0分)和“想象中剧烈疼痛”(10分),共10分。患者根据自身对疼痛的感受程度,在线段上作记号以表示疼痛强度,从起点至记号之间的距离即为VAS评分。
2.2.2MEPS评分MEPS满分为100分,其中包括疼痛(疼痛程度、是否需服止疼药、疼痛是否影响关节活动)45分,运动功能(关节运动弧大小)20分,稳定性(内外翻是否稳定)10分,日常活动(梳头、吃饭、个人卫生、穿衬衣、穿鞋)25分。总分>90分为优,75~89分为良,60~74分为中,<60分为差。

3 结果
两组治疗前VAS和MEPS评分比较,差异均无统计学意义(P<0.05);与治疗前比较,治疗后两组VAS评分均显著降低(P<0.05),MEPS评分均显著升高(P<0.05),治疗组VAS评分降低值和MEPS评分升高值均显著大于对照组(P<0.05)。结果提示,两种疗法均可明显降低VAS评分和升高MEPS评分,但治疗组在降低VAS评分和升高MEPS评分方面明显优于对照组。见表1。
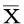
表1 两组患者VAS评分、MEPS评分比较( ± s)
注:与同组治疗前比较,*P<0.05;与对照组差值比较,#P<0.05。
4 讨论
EHE是由急性损伤或慢性劳损引起前臂伸肌群联合总腱在肱骨外上髁附着部出现牵拉、撕裂伤,局部出血、水肿,进而发生粘连,甚至出现纤维变性而致。本病属中医学“经筋病”或“伤筋病”范畴,多由风寒湿邪积聚肘关节,以致劳伤气血或敛缩脉道,筋经、脉络失和而发。《灵枢·经筋》认为经筋病和筋痛“治在燔针劫刺,以知为数,以痛为输”,说明EHE适宜以“燔针劫刺”“以痛为输”治则进行治疗。国医大师贺普仁经对火针疗法的挖掘整理,将其纳入“贺氏三通法”的温通法范畴,并开发出自制贺氏火针针具,用“燔针劫刺”治疗包括EHE在内的各种疾病。本病以阿是穴火针密刺法深达腱膜,通透深层筋脉,使局部血运通畅而病除;配以局部穴位肘髎、曲池、手三里疏通肘部气血,循经选取阳明经止痛要穴合谷通经活络、镇静止痛。
EHE的治疗除口服药物、封闭等常规手段外,国外最新研究围绕富血小板血浆疗法[4]及基因研究[5]展开,但价格昂贵、需忍受治疗带来的痛苦等问题将大部分患者拒之门外,且疗效未获得一致认可[6]。本研究应用贺普仁临床经验,以VAS和MEPS评分作为量化指标,结果显示两种疗法均有明显疗效,但治疗组在降低VAS评分和升高MEPS评分方面效果更突出,说明贺氏火针温通疗法治疗该病较普通毫针刺法具有更强的舒筋止痛作用。MEPS评分是一个综合性指标,EHE最主要的症状是疼痛,火针止痛效果突出,患者日常活动能力及运动功能随疼痛的减轻而逐渐恢复,后续研究可适当延长观察期,以期对MEPS评分的变化规律作进一步研究。
本研究证实贺氏火针温通法治疗EHE能有效减轻疼痛,改善肘关节功能,且操作简便,易被患者接受,是对名老中医宝贵临床经验的总结与传承。
参考文献:
[1]Buchbinder R, Green S,Struijs P. Tennis elbow[J].Am Fam Physician,2007,75(5):701-702.
[2]严隽陶.推拿学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003:227.
[3]戴闽,罗军.骨科运动康复[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:221-222.
[4]Mishra AK,Skrepnik NV,Edwards SG,et al. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of 230 patients [J]. Am J Sports Med, 2014, 42(2):463-471.
[5]Erduran M,Altinisik J,Meric G,et al. Is Sp1 binding site polymorphism withinCOL1A1gene associated with tennis elbow?[J].Gene,2014,537(2):308-311.
[6]de Vos RJ, Weir A, Brasher PM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: letters to the editor[J].Am J Sports Med,2014,42(1):NP3-5.
Clinical Effect of He’s Fire Needle and Warming Method in Treatment of External Humeral Epicondylitis
XUELi-wen1,WANGYun-feng2
(1.DepartmentofAcupunctureandMoxibustion,BeijingHospitalofTraditionalChineseMedicineAffiliatedtoCapitalUniversityofMedicalSciences,Beijing100010,China; 2.LugouqiaoCommunityHealthServiceCenter,Beijing100072,China)
Abstract[] ObjectiveTo observe the therapeutic effect of He’s fire needle and warming method in the treatment of external humeral epicondylitis. MethodsSixty patients with external humeral epicondylitis who were treated in Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Capital Medical University from January to December, 2014 were divided into treatment group (n=30) and control group (n=30) in the visiting order. The patients in the control group received routine acupuncture with filiform needle at Zhouliao, Quchi, Shousanli, and Hegu points; the patients in the treatment group received acupuncture with He’s fire needle at Ashi point every other day in addition to the therapy for the control group. Both groups received the treatment for 10 consecutive days. Pain Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS) were applied as indices for observation to determine the therapeutic effect. ResultsAfter treatment, both groups had significantly reduced VAS scores (P<0.05) and significantly increased MEPS scores (P<0.05); compared with the control group, the treatment group had significantly greater decrease in VAS score and increase in MEPS score (P<0.05). ConclusionHe’s fire needle and warming method can effectively relieve the pain in external humeral epicondylitis and improve elbow function.
[Key words] external humeral epicondylitis; fire needle; warming method

