Analysis of Quantitative Trait Loci for Pathogenic Strain Pi-1 of Resistance to Rice False Smut in Rice(Oryza sativa)
Yusheng LI, Juan YANG, Shengdeng HUANG
Institute of Food Crops, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences; Jiangsu High Quality Rice Research and Development Center,Nanjing 210014, China
Rice false smut is a kind of common fungal disease,which is a panicle disease caused by Ustilaginoidea virens (Cooke.) Takah.Rice false smut is widely distributed all over the major rice areas. Among them, rice false smutis the heaviest in Asia. Japan, China and Philippines have the most harmful diseases[1].Rice false smut occurs each year in the growth region of japonica rice in China, and has the characteristics of heavy incidence of the disease, wide range, high frequency, great loss and so on. Rice false smut has risen from the original secondary disease to the main disease at present, which is one of the important diseases seriously threaten rice. Since the 1980s, rice false smut becomes more serious and affects the quality and yield of rice with the extension of hybrid rice, the rapid promotion of high-yield varieties, and the increasing nitrogen application[2-6].Besides, false smut balls contain harmful toxin to both human and animal. Long-term consumption can significantly restrict the tubulin of animal[7-9]. Previous researches have shown that using rice with false smut as the feed for mice can cause tissue necrosis of liver, kidney, bladder and so on[2,10].
In-depth research has been carried out on the control and occurrence regularity of rice false smut. Bacteri-cide and regulating sowing time are usually used to avoid the disease epidemic period, so as to control the occurrence and spread of rice false smut[11-13]. However, these methods can not fundamentally prevent rice false smut; and large amount of bactericide use usually causes environmental pollution.At present,researches on the resistant mechanisms and disease resistance genetic research of rice false smut is still at its initial stage;and the research results have not been applied in practical production.Li et al.found out that rice false smut was controlled by two pairs of equivalent host genes + minor-polygene based on host gene+polygene mixed inheritance model[14]. Host disease resistance genes was genetically stable under different environments in different years[15-16].Xu Jian-long et al.detected two QTLs related to disease resistance by graphic genotypes overlap method[17].
Lagging of research on disease resistance genetic mechanism and disease resistance genes of rice false smut seriously restricted the development of rice breeding for disease resistance. Based on theses, molecular markers tightly linked to resistance genes were found out by locating new resistance genes, especially the disease resistance genes of a single pathogenic strain. Disease-resistant variety was selected by molecular marker assisted method; and new breeding way for rice false smut was found.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Daguandao was a local japonica rice variety in Tai Lake rice area. IR28 is an indica rice variety from Philippines-based International Rice Research Institute. Test materials for evaluation of disease resistance were 157 recombinant inbred lines (RILs)derived from an inter-subspecies cross of Daguandao/IR28. Artificial inoculation identification showed that Daguandao was susceptible to disease, while IR28 was resistance to disease. Molecular genetic map for analysis included 167 SSR molecular markers, which were evenly distributed in 12 chromosomes.The molecular mapping was 1846.6 cM in length and the average distance between markers was 11.1 cM.
Bacterium for inoculation was the hyphae-spore mixture of single pathogenic bacteria strain Pi-1. Spore concentration was 100-150 spores/vision under microscope with 100 times.
Methods
Material planting Two parents and 157 RILs caused by the strain Pi-1 of rice false smut were planted in special plants pool for disease identification in Nanjing City. Each RIL had 15 plants with two repetitions. The planting spacing was 12 cm 15 cm. Single seedling was planted; bactericide was not used during the whole growth period; and conventional cultivation management was adopted.
Pi-1 inoculation Artificial inoculation method of rice false smut was adopted[18-19]. One week before boot rupturing stage,inoculation fluid was injected to the side of ear buds by an injector on16:00. The inoculation amount was 1-2 ml/ear. A total of 10 plants were inoculated, with 3 ears for each plant.Besides, 5 rice plants were taken as the control. After inoculation, moisturizing spray was carried out according to the climate changes.
Evaluation of disease resistance
Three weeks after inoculation,lines without diseases resistance showed disease symptom. Incidence was investigated from this time; the diseased grain number on each ear was counted. With diseased grain number on ear with the most serious illness as the index, grading was carried out according to the standard of Tang Chun-sheng et al[20-21]. Grade 0 indicated no disease;grades Ⅰand Ⅱindicated one and two diseased grains on each ear;grade Ⅲand Ⅳwere 3-5 and 6-9 diseased grains on each ear; grade Ⅴwas more than 10 diseased grains on each ear. The diseased plant number and disease grade of two parents and RILs were obtained.Disease index was calculated by disease index equation; the result was converted to phenotypic value after arcsine transformation, so as to calculate QTL.
QTL analysis
QTL Cartographer2.5 software was adopted.QTL positioning and genetic parameter estimates were carried out by composite interval mapping. Test threshold LOD=2.5 was obtained[22]. QTL naming was carried out by the method of Mc Couch in 1997[23].
Results and Analysis
Resistance reaction of two parents to rice false smut
Parent IR28 had no or very slightly disease symptom in two years test,disease indexes of which were 0 and 0.002, respectively. According to resistance grade, the IR28 belonged to high resistance to rice false smut.Disease indexes of Daguandao in the two years were 76.3 and 79.4, which was highly susceptible(Table 1),
Resistance reaction of RIL population to rice false smut
In the two years, 157 RILs showed continuous distribution in both HR and HS. Population disease indexes were distributed in the ranges of 0.0-80.7 and 0.0-83.4,respectively(Fig.1). Distribution of population disease indexes showed continuous distribution in highly resistant,moderately resistant, moderately susceptible and highly susceptible lines, indicating that resistance of this population to rice false smut was controlled by host gene and minor modification genes.
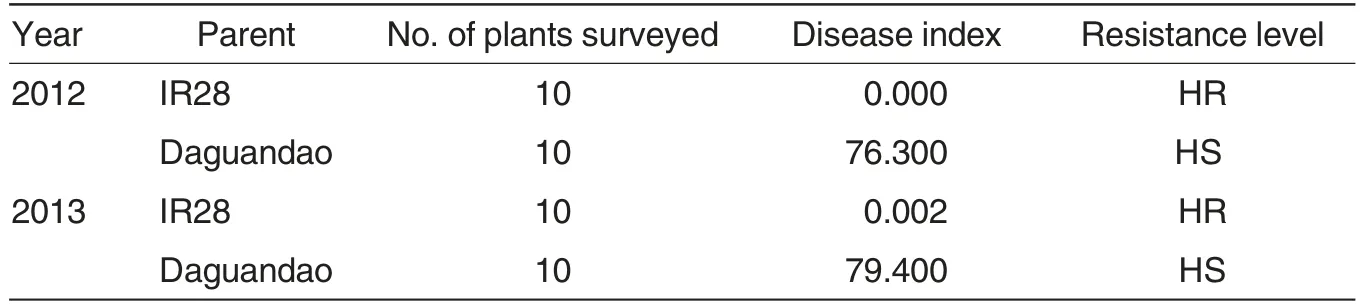
Table 1 Reaction of parents to rice false smut by artificial inoculation at booting stage
Rice false smut QTL detection and effects analysis
In 2012, four QTLs (qFsr2a, qFsr2b, qFsr8a, qFsr11)in Pi-1 strain of rice false smut were detected. Their LOD values were 5.8,3.6,3.2 and 9.6,respectively.The contribution rate was between 8.7% and 16.9% ; additiveeffect was within -9.9-7.6 (Table 2).The four QTLs were located on chromosomes 2,8 and 11 (Fig.2).qFsr2a,qFsr8a and qFsr11 were allelic genes from parent IR28; the additive values were -8.7, -6.7 and -9.9, respectively.The effects of actions reduced the disease index of population, the range of which was from -9.9 to -6.7. However, the rice resistance to rice false smut enhanced. As for qFsr2b from parent Daguandao,additive value was positive; disease index enhanced; effects of actions reduced the rice resistance to rice false smut.
In 2013, four QTLs (qFsr7, qFsr8b, qFsr11, qFsr12) were detected,which were located on chromosomes 7,8, 11 and 12 (Fig.2). Among them,additive value of qFsr7 was 7.1, which was the same as the qFsr2b detected in 2012. Both qFsr7 and qFsr2b were from the allelic genes of parent Daguandao. qFsr8b, qFsr11 and qFsr12 were all from the allelic genes of parent IR28. Their contribution rates were 8.5%-17.2%; and additive values were between -14.3 and -6.5(Table 2).
In the two years, seven QTLs of rice false smut were detected. Among them, qFsr11 was detected in both 2012 and 2013. In the RM26281 -RM3701 interval of chromosome 11,distance of molecular marker RM3701 was 0.16 cM. This locus had relatively high genetic stability in two years. The additive values of qFsr11 were -9.9 and -14.3 in 2012 and 2013, respectively. And the contribution rates were 13.5%and 17.2%(Table 2).
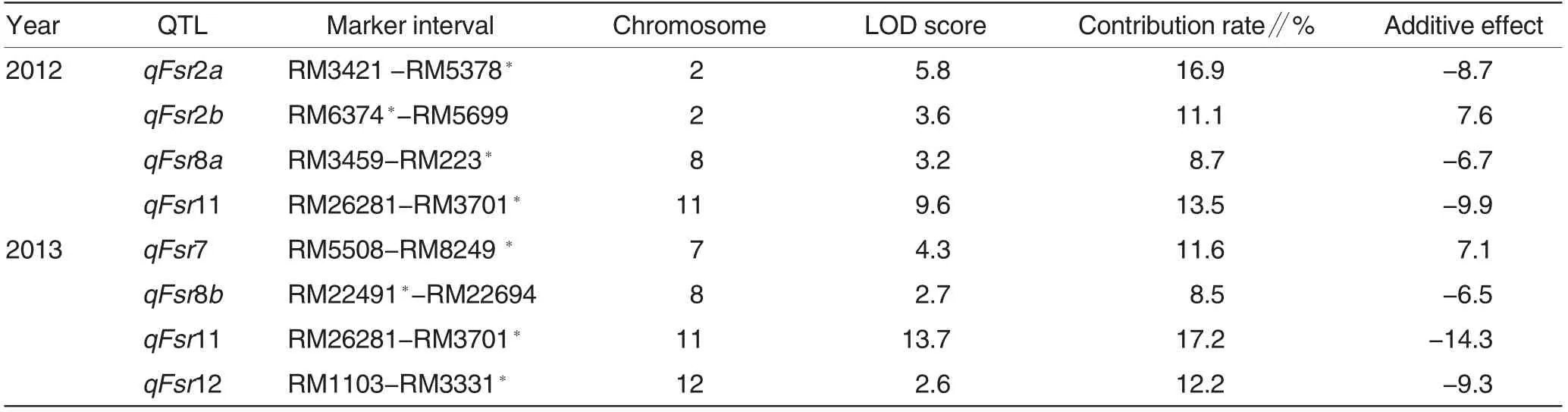
Table 2 Chromosome location and characteristics of QTLs for rice false smut resistance
Discussions
Occurrence of rice false smut was easily affected by the environment,especially that the changes of temperature and humidity had strong regulatory effects on the infection and spread of rice false smut. Therefore, it wasvery important to successfully induce the rice false smut and to select scientific method of resistance identification. In this research, artificial injection vaccination was adopted; the inoculation solution was hyphae-spore mixture liquid, which ensured the thoroughly exposed to Pi-1 strain and the fully infection. Zhang Jun-cheng et al.found out that this method had strong induced ability and good incidence efficiency[18].The maximum incidence rate reached 100% and disease index was 85.5. Therefore, this method had better effects than single conidium inoculation, which had only 11%-16% incidence rate[24]. At the same time, this method was more scientific and reliable than spray inoculation method[25],bacterium liquid coating inoculation method[12], natural infection in open field[26]and so on. In this research, the incidence rate of infected lines reached 90.6%;while the control showed no disease signs, showing that the disease was caused by inoculation.
There were anti-disease genes in disease-resistant variety, which was determined by genetic characteristics in variety itself. Few anti-disease genes were detected in susceptible varieties. Kunihiro Y[27]et al. found out that Jingxi 17 had resistance genes to sheath blight. Ding Xiu-lan et al. detected resistance genes to stripe leaf blight in Kinmaze. In this research,Daguandao was susceptible parent;the alleles resistance genes qFsr2b and qFsr7 were detected in its offspring. Thus, it could be concluded that due to the gene interaction in pure line cultivar, a few resistance genes could not be expressed. After genetic recombination, gene combination changed so that resistance of genes was expressed. The existence mode of this resistance gene would be a new research subject.
In this research, qFsr11 was detected in both 2012 and 201 on chromosome 11, showing that this locus had high genetic stability and could stably enhance the resistance of rice to diseases. Resistance stability of mixed strain of rice false smut was researched under different environments in different years. Results showed that there was genetic stability region in terminal chromosome 11 had,which had several disease-resistant QTLs[15-16]. The incidence rate and disease index of single pathogenic strain were lower than those of mixed strains, because of the cumulative effects of pathogenicity of various mixed strains, which formed relatively strong selection pressure and strengthened the effects of disease.
[1]OU S H. Rice Disease. Kew, Surrey,UK:CAB/CMI,1985.pp 307-311.
[2]NAKAMURA K I, IZUMIYAMA N. Lupiosis in rice caused by ustiloxin and crude extract of fungal culture of Ustilaginoidea virens. Proc Jpn Assoc Mycotoxicol,1992,35:41-43.
[3]DHINDSA H S,AULAKH K S,CHAHAL S S.Incidence and assessment of losses due to false smut of rice in Punjab.Indian Phytopathol,1991,44:120-121
[4]CHIB H S,TIKOO M L,KALHA C S.Effect of false smut on yield of rice.Indian J Mycol Plant Pathol, 1992, 22: 278-280.
[5]SINHA R K P, SINHA B B P, SINGH A P.Assessment of yield loss due to false smut disease of rice. J Appl Biol, 2003,13:35-37.
[6]JI JP(季宏平).Preliminary study on yield loss of rice damaged by rice false smut and chemical control to the disease (水稻稻曲病产量损失及药剂防治的初步研究). Heilongjiang Agricultural Science(黑龙江农业科学),2000,(4):18-19.
[7]IWASAKI S. Chemistry and biological activity of the mycotoxins interfering with tubulin function. Proc Jpn Assoc Mycotoxicol,1992,35:1-6.
[8]KOISO Y, LI Y, IWASAKI S, et al.Ustiloxins antimitotic cyclic peptides from false smut balls on rice panicles caused by Ustilaginoidea virens. J Antibiotics,1994,47:765-773.
[9]LI Y, KOSIO Y, HANAOKA K, YAEGASHI H. Ustiloxins new antimitotic cyclic peptides: interaction with porcine brain tubulin. Biochem Pharmacol,1995,49:1367-1372.
[10]NAKAMURA K I,IZUMIYAMA N,OHTSUBO K I. "Lupinosis"-like lesions in mice caused by ustiloxin, produced by Ustilaginoidea virens: a morphological study.Nat Toxins,1994,2:22-28.
[11]HUANG SW(黄世文),YU LQ(余柳青).Advances on studies about rice false smut in China (国内稻曲病的研究现状)).Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi (江西农业学报),2002,14(2):45-51.
[12]LI XJ(李小娟),LIU EM(刘二明), XIAO QM(肖启明),et al.Research progress of rice false smut (稻曲病研究进展).Agrochemicals Research & Application(农药研究与应用),2006,10(2):9-12.
[13]LIU YF (刘永锋),CHEN ZY (陈志谊),LU F (陆凡),et al.Study on controlling rice false smut (水稻稻曲病控制技术研究). Journal of Jinling Institute of Technology(金陵科技学院学报),2004,20(3):42-45.
[14]LI Y-S,ZHU Z,ZHANG Y-D,et al.Genetic analysis of rice false smut resistance using major gene plus polygene mixed genetic model. Acta Agron Sin,2008,34(10):1728-1733.
[15]LI YS (李余生),HUANG SD (黄胜东),YANG J(杨娟),et al.Analysis of quantitative trait loci for resistance to rice false smut (水稻抗稻曲病数量性状座位及效应分析).Acta Agronomica Sinica(作物学报),2011,37(5):778-783
[16]LI YS (李余生), HAN LH (韩丽华),YANG J(杨娟),et al.Analysis of quantitative trait loci for resistance to rice false smutunder different environmental conditions(不同环境下水稻稻曲病抗性位点检测). Journal of Jiangsu Agriculture (江苏农业学报), 2012, 28(5):933-937.
[17]XU JL(徐建龙),XUE QZ(薛庆中),LUO LJ(罗利军),et al.Preliminary report on quantitative trait loci mapping of false smut resistance using near-isogenic introgression lines in rice (近等基因导入定位水稻抗稻曲病数量性状位点的的研究初报),Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis(浙江农业学报),2002,14(1):14-19.
[18]ZHANG JC (张君成),CHEN ZY (陈志谊),ZHANG BX(张炳欣),et al.Preliminary study on inoculation method of rice false smut and its effect(稻曲病的接种方法及其效果初探). Chinese Journal of Rice Science (中国水稻科学),2003,17(4):390-392.
[19]ZHANG JC (张君成),CHEN ZY (陈志谊), ZHANG BX (张炳欣), et al. Research on inoculation technology of rice false smut (稻曲病的接种技术研究). Acta Phytopathologica Sinica (植物病理学报),2004,34(5):463-467.
[20]TANG CS(唐春生), GAO JZ(高家樟),CAO GP(曹国平),et al.Research and application of grading standard for rice false smut (稻曲病病情分级标准的研究和应用). Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (湖南农业大学学报),2000,26(2):122-125.
[21]TANG CS(唐春生),CAO GP(曹国平),GAO JZ (高家樟),et al.Research and application of grading standard for rice false smut (稻曲病病情分级标准的研究和应用). Plant protection (植物保护),2001,27(1):18-21
[22]COLLARD B C Y, JAHUFER M Z Z,BROUWER J B, et al. An introduction to markers,quantitative trait loci(QTL)mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: The basic concepts. Euphytica, 2005, 142: 169-196.
[23]MC COUCH S R,CHO Y G,YANO M,et al. Report on QTL nomenclature.Rice Genet Newsl,1997,14:11-13
[24]MIAO QM (缪巧明),WANG YH (王永华). Disease resistance identification technology of rice false smut in rice varieties (水稻品种对稻曲病的抗病性鉴定技术研究).Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences (西南农业学报),1994,7(2):67-70.
[25]DAI GH (代光辉),ZHAO J (赵杰),HE RM (何润梅),et al.preliminary observation of histochemistry and conidium infection way of different rice varieties with rice disease resistance(稻曲病不同抗性水稻品种的组织化学及分生孢子侵染途径的初步观察), Acta Phytopathologica Sinica (植物病理学报),2005,35(1):37-42
[26]ANSARIO M M, RAM T, SHAMA T.Yield loss assessment in promising rice cultures due to false smut. Oryza,1988,25(2):207-209.
[27]KUNIHIRO Y,QIAN Q,SATO H, et al.QTL analysis of sheath blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin,2002,29(1):50-55.
[28]DING XL(丁秀兰),JIANG L(江玲),LIU SJ(刘世家),et al.QTL analysis for rice stripe disease resistance gene using recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from crossing of Kinmaze and DV85 (利用重组自交系群体检测水稻条纹叶枯病抗性基因及QTL 分析),Journal of Genetics and Genomics(遗传学报),2004,31(3):287-292.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Research Advances in Gene Regulation and Genetic Improvement of Fish Feeding
- Instrucions for Authors
- Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)
- Overview of Pharmaceutical Research on the Poria with Hostwood of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
- Study on Relative Soil and Water Conservation Benefits of Ridge Tillage in Different Terrain Conditions in the Black Soil Area of Northeast China
