Breeding and Application of a Japonic Rice Cytoplasmic Male Sterility Line,E-Jing A
Qingsi ZENG, Aiqing YOU, Shiyuan ZHU, Bingliang WAN, Huaxiong QI, Desuo YIN, Hang CHENG, Zhenlian LI, Jianping WU, Deze XU, Liangjun LIU, Xiong CHEN
1. Food Crops Research Institute, Hubei Academy of Agricultural Science/Hubei Key Laboratory of Food Crop Germplasm and Genetic Improvement, Wuhan 430064, China;
2. Seed Administration Bureau of Hubei Povince, Wuhan 430070, China
In the early 1970s, Yuan longping first finished the breeding of wildabortive (WA) japonica rice“Jingyin 66” sterile line by nucleus substitution,and then different types of WA japonica rice sterile lines were bred taking wild-abortive cytoplasm as female parent in other provinces, but no one has been applied to field production until now[1]. At present, most hybrid japonica rice variety (combination) sterile lines are BT type or Dian type cytoplasmic sterile lines, belonging to gametophyte sterile type, and their andro gametes are aborted at a later period, with fertility easily influenced by the environment, especially by high temperature which enables fertility of partial pollen of sterile lines,resulting in influenced purity of produced seeds,which is one of the main reason restricting large-area popularization of hybrid Japonica rice in production. The region for cultivating twoline hybrid Japonica rice is relatively narrow,and the application area is difficult to be enlarged. Hubei Province even entire China has been in lack of new Japonica rice three-line combinations with high yield, good quality and high resistance. The successful breeding of E-jing A could solve this problem, and thus could facilitate the research on the utilization of three-line hybrid Japonica rice in our country as well as accelerate the development of Japonica rice industry, in order to adapt the change of domestic demand for food and satisfy domestic consumption demand for Japonica rice.
Breeding Process
A japonica maintainer line material with high stigma exsertion rate and early flowering time was bred through gathering good traits by mutual infiltrarion of indica and japonica and system breeding, and a japonica sterile line with high stigma exsertion rate and early flowering time was obtained by transfer breeding with it, to thereby improve seed production yield of hybrid japonica rice.
Cytoplasmic male sterile materialJing 5A (with a rate of typical abortive pollen of 30%, a plant type similar to indica rice) of Chaling wild rice was introduced from Hengyang Academy of Agricultural Science in April of 2006, which was used as female parent to conduct artificial hybridization with "648041" [(91315/R187)F6]. Until 2010, the pollen of the 5thgeneration by backcross was subjected to microscopic examination, showing a sterile plant percentage of 90%, and furthermore, one plant progeny row reached a sterile plant percentage of 100%.For the 6thgeneration by backcross in Lingshui County of Hainan Province in winter of 2010, microscopic examination of pollen showed a sterile plant percentage of 98%, whilst eight plant progeny rows had a sterile plant percentage of 100% . The sterile plant percentage of the 7thgeneration by backcross at Wuhan City in 2011 reached 100% under pollen microscopic examination. In the 7thgeneration, the plant progeny row 31081 had outstanding performance, and was designated as E-jing A, cytoplasmic japonica three-line sterile line for Chaling wide rice (Table 1). On September 15 in 2013, achievement appraisement was carried out by Science and Technology Department of Hubei Province, where the certifying commission agreed that the research achievement was in the leading domestic level.

Table 1 Breeding flow chart for E-jing A
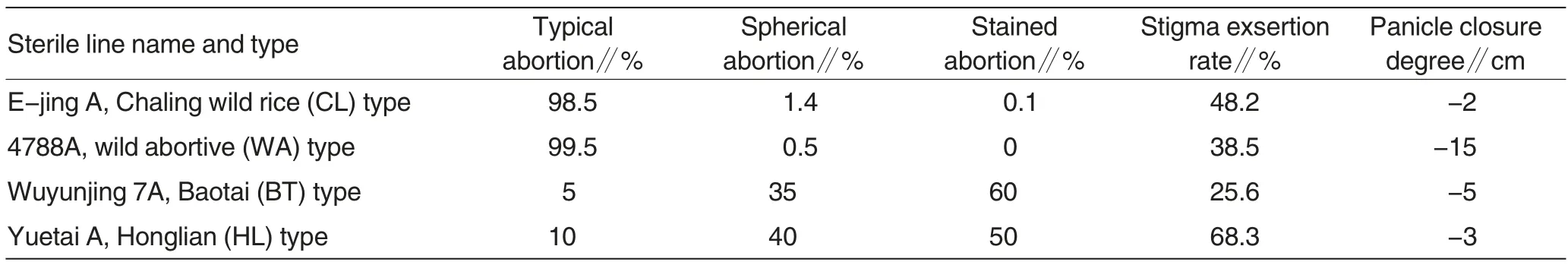
Table 2 Comparative table of pollen abortion,stigma exsertion rate and panicle closure degree for sterile lines
Main Characteristics
Morphological characteristics
E-jing A showed compact plant type and stiff flexible stem, and had good lodging resistance. There were 16.8 leaves in total, and the leaves were thick, straight, upright and dark green in color. The plant had a height of 85 cm, and large panicles, in an average length of 24.7 cm, carrying many grains, in specific, about 220 grains which were close to each other.The plant was endowed with strong tillering ability. Each individual plant had 12.7 effective panicles.The grains were elliptical, with lighter weight, and the kilo-grain weight was of 23 g. The plant has purple auricle, pulvinus and glume tip, and was moderate in threshability.
Fertility
E-jing A belongs to temperaturesensitive japonica rice. In Wuhan, Ejing A was sown during early May to mid June, and it took 78-90 d from sowing to initial heading date; and in Hainan,winter propagation began with sowing in early December, the seedling age was of 30 d,and heading began in mid March,taking 98-99 d.
Sterility and outcrossing characteristics
The sterile line had a sterile plant percentage of 100%,and a sterile degree of 99.8%. As to pollen abortion,typical abortion was dominant, accounting for 98%. By microscopic examination on 102 panicles on August 27 in 2013, in total 202 000 pollen grains,of which 198 970 were typically abortive(accounting for 98.5%),2 828 were spherically abortive (accounting for 1.4%), and 202 were of stained abortion type (accounting for 0.1%)(Table 2). The abortive morphologies of different types of sterile line pollen were shown in Fig.2. Meanwhile, the sterility of the sterile line was less susceptible to high temperature, and the fertility was stable, remarkably higher than Baotai (BT) Type and Honglian(HL) type sterile lines. One hundred twenty six self-crossed bagged panicles showed a self-fruitful rate of 0,reaching the fertility standard of threeline sterile line. The sterile line had a high stigma exsertion rate,and an outcrossing characteristic superior toBaotai (BT) type sterile line, resulting in high breeding and seed production yield.
Disease resistance
In field identification of disease resistance, rice blast and bacterial blight were not found.
Results of Combination Test
A trail test was carried out in 2009,and identification was performed in 2010 in Wuhan, obtaining a restoring degree only of 20%-50%. A combination test was carried out in the winter of Hainan in 2010, followed by identification in Wuhan in 2011, the restoring degrees of 3 combinations reached 80%-85%. The result satisfied the application level,and in specific, "31020", "31024" and "34022" had better performance. The combination test carried out in Wuhan in 2011 was followed by identification in Lingshui of Hainan in the winter of 2011, and the result showed that 5 combinations reached a setting rate above 85%,satisfying the level for production application, and D11509, D11511, D11515 and D11516 performed well. Thirty combinations were tested in the winter of 2011, and identification carried out in the summer of 2012 showed that 6 combinations reached a setting rate of 85%,satisfying the level for production application, and “234332”, “234318”,“234298”, “234302” and “234317”exhibited better performance. Among them, “234332”was sown on May 30,and began to head on September 5,taking 98 d. For “234332”, the plant height was of 118.2 cm;each individual plant had 7.8 effective panicles, the panicle length was of 24.4 cm, and each panicle carried 286 grains totally,258 of which were plump; the setting rate reached 90.21%; the kilo-weight was of 27.4 g; and the rice quality reached degrade 2 of national standard(Table 3).

Table 3 Performance of combinations of E-jing A series in 2012
Restoring and Maintaining Relationship of E-jing A
E-jing maintainer line was restorer for Baotai type and Honglian type sterile lines,i.e,it was different with Baotai and Honglian types; WA type 4788 maintainer line was maintainer for Ejing sterile line, i.e., they were the same;Chaling type restorer line 31112 was non-restoring to WA type 4788 sterile line, i.e., they were different[4];Chaling type restorer line 31112 was restoring to Baotai type Wuyunjing No.7;and Chaling type restorer line 31112 was half-restoring to Honglian type Yuetai sterile line.
Four combinations of CL type Ejing A with different restorer lines were cultivated, which were CL type 31112,BT type R254, HL type 9311 and WA type Minghui 63 respectively[5].Each combination included 50 individuals;on September 3, E-jing A/3112 was detected with a pollen sterility rate of 10%, with normal pollen release; the pollen sterility rate of E-jing A/R254 was of 30%, without pollen release;the pollen sterility rate of E-jing A/9311 was of 95%, without pollen release;the pollen sterility rate of E-jing A/Minghui 63 was of 1%, with normal pollen release;and E-jing A had the same restorer sources as WA type, while BT type had restorer sources different with that of HL type.
CL type E-jing A was combined with different maintainer lines, obtained four combinations to be planted,which were CL type (E-jing B), WA type (4788B), HL type (Honghan B)and BT type (Wuyunjin 7B) respectively. Each combination had 50 seedlings, and they were detected on September 3 as following: the pollensterility rate of E-jing A/E-jing B was of 98% , providing no seed; E-jing A/4788B showed a pollen sterility rate of 100%, giving no seed; and E-jing A/Honghan B showed a pollen sterility rate of 95%, giving no seed. WA type 4788 maintainer line was maintainer for E-jing sterile line,i.e.,they were the same.
Three combinations from CL type E-jing B and different sterile lines were cultivated,which were HL type (Yuetai A),HL type (Honghan A)and BT type(Wuyunjing 7A) respectively. Each combination was provided with 50 seedlings, and the detection carried out on September 3 showed that:Yuetai A/E-jing B had a pollen sterility rate of 50%, giving no seed; Honghan A/E-jing B had a pollen sterility rate of 30% , and seeded normally; and Wuyunjing 7A /E-jing B exhibited a pollen sterility rate of 70%,and seeded normally. E-jing B was restoring to Honghan A and Wuyunjing 7A, i.e.,they had different maintaining relationships.
By combining CL type restorer line 31112 with different sterile lines, 5 combinations, which were CL type (Ejing A), WA type (4788A), BT type(Wuyunjing 7A), HL type (Honghan A)and HL type (Yuetai A)were obtained and cultivated. Each combination was provided with 50 seedlings, and the detection carried out at September 3 showed that: E-jing A/31112 had a pollen sterility rate of 30%,and seeded normally; 4788A/31112 exhibited a pollen sterility rate of 2%, giving no seed; Wuyunjing 7A/31112 had a pollen sterility rate of 5%, and seeded normally;Honghan A/31112 presented a pollen sterility rate of 40% , and seeded normally; and Yuetai A/31112 showed a pollen sterility rate of 50%,resulting in a setting rate of 60%. CL type restorer line 31112 was restoring to E-jing A,Honghan A and Wuyunjing 7A, and non-restoring to WA 4788A,and further study was needed.
Discussion
The three-line hybrid sterile line E-jing A bred with Chaling wild rice cytoplasm had the advantages of stable sterility, lighter panicle closure degree and no restriction on geographical space, and it could effectively overcome the problem that the fertility of Baotai type and Dian type cytoplasmic sterile lines was easily affected by the environment, especially for the interference of high temperature causing partial fertility of pollen of sterile lines,thus influencing the purity of seed production and resulting in the weaknesses of relatively-narrow application region for two-line hybrid japonica rice and difficulties in enlarging application area. The sterile line also had the advantages of broad restorer sources,superiority in formed combinations,good quality and good resistance.
The emphasis for developing sterile lines is improving stigma exsertion rate, so japonica sterile lines with high stigma exsertion rate and early flowering time can be obtained by breeding japonica maintainer line materials with high stigma exsertion rate and early flowering time, to improve yield of hybrid japonica seed production.The improvement emphasis for restorer lines is improving exterior quality, setting rate and restoring degree. It is necessary to devote greater efforts to combination test to breed combinations with strong superiority.
[1]YANG J(杨军), ZHU XD (朱旭东). Research and breeding progress of WA type hybrid japonica rice(野败型杂交粳稻的研究及育种进展)[J].China Rice(中国稻米),2009(6):1-3.
[2]LI JJ (李金军),XU ML (徐美玲),LU JG(陆金根),et al.Breeding and application of three-line Japonica BT-type sterile line "Jia60"(粳稻BT 型三系不育系嘉60A 的选育及应用)[J].Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences(浙江农业科学),2004(1):19-21.
[3]XU HY (许红云),XU J (徐津),TAN XL(谭学林), et al. Breeding and Application of New Dian-type Japonica Hybrid Rice Combination Dianza 46(滇型杂交粳稻滇杂46 的选育与应用)[J].Seed(种子),2012,31(4):109-112.
[4]CHEN DZ(陈大洲), XIAO YQ(肖叶青),WU WC(邬文昌),et al.Breeding of WAtype Japonica Male Sterile Line 4788A(野败粳型雄性不育系4788A 选育) [J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi (江西农业学报),2007,19(3):6-7.
[5]XU DY (徐大勇), FANG ZW (方兆伟),FAN JW (樊纪伟),et al.Primary results for screening of restorer lines with wild abortive cytoplasm in japonica hybrid rice(野败型细胞质杂交粳稻恢复系筛选结果初报)[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences(江苏农业科学),2006(6):36-38.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Research Advances in Gene Regulation and Genetic Improvement of Fish Feeding
- Instrucions for Authors
- Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)
- Overview of Pharmaceutical Research on the Poria with Hostwood of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
- Study on Relative Soil and Water Conservation Benefits of Ridge Tillage in Different Terrain Conditions in the Black Soil Area of Northeast China
