Inhibition of Chlamydospore Germination and Mycelial Growth of Trichoderma spp.by Chemical Fungicides
Lin ZHANG, Xiliang JIANG*, Xiaoyan YANG, Mei LI*, Shuhua CHEN
1. Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Key Laboratory of Integrated Pest Management in Crops, Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing 100081, China;
2. National Biological Pesticides Quality Supervision and Inspection Center, Yanji 133000, China
Trichoderma spp. has antagonistic effect on many kinds of plant pathogenic fungi[1], especially on soil borne pathogenic fungi,and is one of biocontrol microorganisms which are widely studied and applied at home and abroad[2]. Common Trichoderma spp. preparation in production is mainly made of living conidiospore, which has the characteristics of strong selectivity, safety on human,animal and natural environment, not harming natural enemy and not easy generating resistance. Chlamydospore is the spore with thickened cell wall generated by Trichoderma spp. resisting adversity. Compared with conidiospore, chlamydospore has the advantages of tolerating dryness and low temperature, not sensitive to antimicrobial activity of soil, long survival period and biocontrol effect on pathogenic microorganism not easy to be affected by environment. There-fore, commercialization development of Trichoderma spp. chlamydospore preparation will become development trend of Trichoderma spp. preparation[3]. As extensive use of chemical fungicide for long term, pesticide residue and ecological destruction problems are increasingly prominent.It becomes important measure of chemical pesticide reduction and protecting agricultural sustainable development to use biological pesticide to replace or partially replace chemical pesticide, and combine biological pesticide with chemical pesticide[4].Because that various microorganisms have different sensitivities to different fungicides, application and residue of chemical fungicides will directly affect application effect of microbial pesticide.
T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 were two high efficient Trichoderma spp.strains separated by Key Laboratory of Integrated Pest Management in Crops, Ministry of Agriculture. Pot and field experiments displayed that the mixing chlamydospore preparation of the two Trichoderma spp. strains had stronger prevention and control effects on many kinds of plant diseases induced by Verticillium dahliae, Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium graminearum Schwabe.Preliminary study displayed that application method and residue of chemical pesticides in test field affected prevention and control effect of Trichoderma spp. chlamydospore preparation,thereby causing that prevention effect was unstable.To explore the influences of chemical fungicides on Trichoderma spp. biological pesticide,using chlamydospore of the above two Trichoderma spp. strains as the material, the influences of seven chemical fungicides on chlamydospore germination and mycelium growth of the above two Trichoderma spp. strains were determined in the room. The research aimed to provide the reference for field application of Trichoderma spp. chlamydospore preparation and its combined application with chemical pesticide.
Materials and Methods
Test time and site
The test was conducted by Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences during 2013-2014.
Test materials
Test strains T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 were separated and conserved by Biological Pesticide Research Room,Institute of Plant Protection,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Test fungicides 98% carbendazim active compound (Anhui Guangxin Agricultural Chemical Co., Ltd.), 95%metalaxyl active compound (Jiangsu Baoling Chemical Engineering Co.,Ltd.),95% difenoconazole active compound (Shanghai Shengnong Biochemical Product Co., Ltd.), 95% thiram active compound (Hebei Zanfeng Biological Engineering Co., Ltd.),96.2% tebuconazole active compound(Guangxi Tianyuan Biochemical Stock Limited Company), 98% carboxin active compound(Anhui Fengle Agricultural Chemical Co., Ltd.) and 70%pentachloronitrobenzene powder(Sichuan Guoguang Agricultural Chemical Co., Ltd.) were all provided by Pesticide Laboratory of Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.

Table 1 Fungicide concentration used in toxicity determination of T.longibrachiatum 758 chlamydospore germination μg/ml

Table 2 Fungicide concentration used in toxicity determination of T.harzianum 610 chlamydospore germination μg/ml
Test methods
Chlamydospore preparation of Trichoderma spp.strain T.harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 were inoculated in the sterilized chlamydospore fermentation medium of Trichoderma spp. strain[5], and they were fermented at 28 ℃and 200 r/min for 7 days. The fermentation liquid was filtered via two-layer etamine,and sterile water was used to repeatedly wash for three times, thereby obtaining Trichoderma spp.chlamydospore.
Toxicity determination of fungicide on chlamydospore germination of Trichoderma spp. strain Inhibition method of spore germination was used to determine. Fungicide was dissolved by 5% acetone, and Trichoderma spp.chlamydospore was made into spore suspension liquid in 2% glucose solution and 2%peptone solution[6].Fungicides at different concentrations were mixed with spore suspension liquid with the same volume, and it was appropriate when there were 30 -50 spores under each view by 10 ×20 times of lens. Final concentrations of different fungicides were shown as Table 1-Table 2. 20 μl spore suspension liquid was dropped on slide glass,and the slide glass was set in the sterilized culture dish by upside down.The culture dish was set in 28 ℃incubator with constant humidity, and germination amount of spore was detected after 9 hours. The standard of spore germination was that bud length exceeded the half of spore radius[7]. Calculation formulas of germination rate and inhabitation rate were shown as:
Germination rate= The germinated spore amount/Total spore amount×100% (1)
Inhibition rate=(Control germination rate-Treatment germination rate)/Control germination rate×100% (2)
Toxicity determination of fungicide on mycelium growth of Trichoderma spp. strain Velocity method of mycelium growth was used[8].The test-ed fungicide was dissolved by 25%acetone solution, and then was added into PDA medium. Final concentrations were shown as Table 3-Table 4.There were 3 repetitions, and 25%acetone solution was used as the control. Trichoderma spp. strain cake was taken by the punching bear with the diameter of 5 mm,and was inoculated on PDA plate center containing different fungicide concentrations.Under 28 ℃,when the culture dish would be filled with control strain (T. longibrachiatum 758 needed about 50 h,and T. harzianum 610 needed about 66 h), colony diameter was measured by cross method, and inhibition rate of fungicide on each strain growth was calculated.
Growth inhibition rate=(Colony diameter of control group-Colony diameter of treatment group)/(Colony diameter of control group-Strain cake diameter)×100% (3)

Table 3 Fungicide concentration used in toxicity determination of T.longibrachiatum 758 mycelium growth μg/ml

Table 4 Fungicide concentration used in toxicity determination of T.harzianum 610 mycelium growth μg/ml
Statistical analysis of data
Data were processed and calculated by SAS software. Inhibition rate of colony growth and inhibition rate of spore germination were respectively converted into probability value (y),and fungicide concentration was converted into concentration logarithm(x).According to regression method between concentration logarithm and probability value, linear regression equation y=a+bx was obtained. Using regression equation, effective medium concentration (EC50) of each fungicide on chlamydospore germination and mycelium growth of the two Trichoderma spp.strains, and correlation coefficient r between probability value and concentration logarithm were calculated.Inhibition effects of different fungicides on the two Trichoderma spp.strains were contrasted[9].
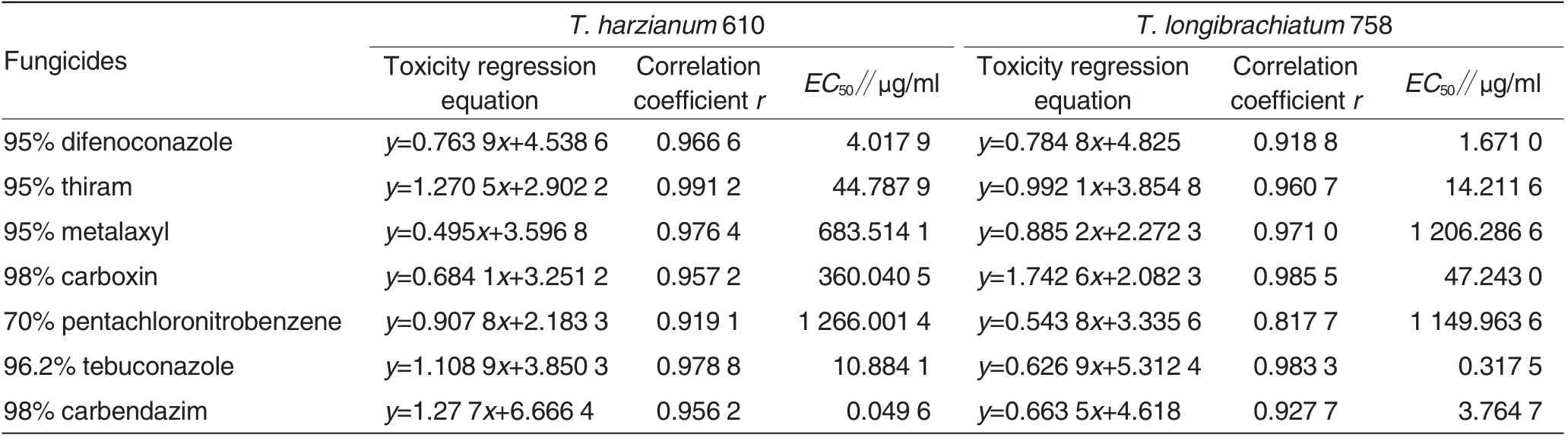
Table 6 Inhibition effects of different fungicides on mycelium growth of Trichoderma spp.strain
Results and Analysis
Inhibition effect of fungicide on chlamydospore germination of Trichoderma spp.strain
Inhibition effects of different fungicides on chlamydospore germination of Trichoderma spp.strain were shown as Table 5, and seven kinds of chemical fungicides all had inhibition effects at different extents on chlamydospore germination of the two Trichoderma spp. strains. The two Trichoderma spp. strains had different sensitivities to fungicide, and inhibition effects of seven fungicides on chlamydospore germination of T. harzianum610 were almost higher than that of T. longibrachiatum 758. The difference of metalaxyl was the most obvious. EC50of 95% metalaxyl inhibiting chlamydospore germination of T.harzianum 610 was 172.80 μg/ml,while EC50inhibiting chlamydospore germination of T. longibrachiatum 758 was 1 108.61 μg/ml,and the sensitivity differed by 6.4 times.
EC50values of different fungicides inhibiting chlamydospore germination of T. harzianum 610 were contrasted.Inhibition effect of 70%pentachloronitrobenzene was the weakest,and EC50was 681.82 μg/ml, followed by 255.48 μg/ml of 98% carboxin. The inhibition sequence of other fungicides from low to high was as below: 95% metalaxyl,95% thiram, 95% difenoconazole and 96.2% tebuconazole. The inhibition effect of 98% carbendazim was the strongest, and EC50was 1.64 μg/ml.EC50values of different fungicides inhibiting chlamydospore germination of T. longibrachiatum 758 were contrasted.Inhibition effect of 95% metalaxyl was the worst, followed by 70% pentachloronitrobenzene (EC50was 927.71 μg/ml).The inhibition sequence of other fungicides from low to high was as below: 95% thiram, 98% carboxin, 96.2% tebuconazole and 95%difenoconazole.The inhibition effect of 98% carbendazim was the strongest,and EC50was only 0.62 μg/ml.
Inhibition effect of fungicide on mycelium growth of Trichoderma spp.strain
The inhibition effects of different fungicides on mycelium growths of T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 were shown as Table 6. 7 kinds of chemical fungicides all had certain inhibition effects on mycelium growths of the two Trichoderma spp. strains, and mycelium growths of the two Trichoderma spp.strains had greater sensitivity difference to fungicide. Inhibition effects of metalaxyl and carbendazim on mycelium growth of T. harzianum 610 were higher than that of T. longibrachiatum 758, in which sensitivity difference of carbendazim was the maximum.EC50values of 98%carbendazim inhibiting mycelium growths of T.harzianum 610 and T.longibrachiatum 758 were respectively 0.05 and 3.76 μg/ml, and sensitivity differed by 75 times. Sensitivities of T. longibrachiatum 758 mycelium growth to thiram,carboxin,pentachloronitrobenzene, difenoconazole and tebuconazole were all higher than that of T. harzianum 610. EC50values of 96.2% tebuconazole inhibiting mycelium growths of T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 were respectively 10.88 and 0.32 μg/ml,and sensitivity differed by 34 times.
EC50values of different fungicides inhibiting mycelium growth of T. harzianum 610 were contrasted.Inhibition effect of 70% pentachloronitrobenzene on mycelium growth of T. harzianum 610 was the lowest,and EC50was 1 266.00 μg/ml, followed by 95% metalaxyl, 98% carboxin, 95%thiram, 96.2% tebuconazole and 95%difenoconazole.The inhibition effect of 98% carbendazim was the strongest,and EC50was 0.05 μg/ml. EC50values of different fungicides inhibiting mycelium growth of T.longibrachiatum 758 were contrasted. Inhibition activities of 70% pentachloronitrobenzene and 95% metalaxyl were the lowest,and EC50values were respectively 1 149.96 and 1 206.29 μg/ml. The inhibition sequence of other fungicides from low to high was as below: 98%carboxin, 95% thiram, 98% carbendazim and 95% difenoconazole, and the inhibition effect of tebuconazole was the strongest.
Conclusions
Chemical fungicide had inhibition effect on growth and germination of Trichoderma spp. strain chlamydospore. Different Trichoderma spp.strains, chlamydospore germination and mycelium growth had different sensitivities to various chemical fungicides. According to the research result, carbendazim, tebuconazole and difenoconazole had stronger inhibition effects on T. harzianum 610 and T.longibrachiatum 758, while inhibition effects of pentachloronitrobenzene and metalaxyl were weaker, and inhibition effects of thiram and carboxin were moderate. Compared with chlamydospore germination,mycelium growth period of Trichoderma spp.strain was more sensitive to fungicide.Chlamydospore germination of T.harzianum 610 was easier to be inhibited by chemical fungicide when compared with T.longibrachiatum 758,but tolerances of T. harzianum 610 mycelium growth on many kinds of chemical fungicides were higher than that of T. longibrachiatum 758. Compared with other six kinds of chemical fungicides, carbendazim had the strongest inhibition effect on chlamydospore germination and mycelium growth of T. harzianum 610, while inhibition effect of 70% pentachloronitrobenzene was the weakest.Carbendazim had the strongest inhibition effect on chlamydospore germination of T.longibrachiatum 758,and the inhibition effect of metalaxyl was the weakest. Inhibition effect of tebuconazole on mycelium growth of T. longibrachiatum 758 was the strongest,while the inhibition effect of metalaxyl was the weakest.
Discussion
Carbendazim is a kind of benzimidazole broad-spectrum internal absorption fungicide, which is widely applied, and its using concentration is between 500 and 1 000 μg/ml[10]. Niu Shanguang et al.obtained that EC50of carbendazim inhibiting mycelium growth of Trichoderma viride LTR-2 was 0.739 5 μg/g[11]. Li Guixiang et al.obtained that EC50of carbendazim inhibiting mycelium growth of wild Trichoderma spp.strain was 0.78 μg/g[12].According to the research result, carbendazim had stronger inhibition effects on chlamydospore germination and mycelium growths of the two Trichoderma spp.strains,and EC50range was 0.05-3.76 μg/ml,which was similar with the literature report.Therefore,biological prevention preparation of Trichoderma spp. strain can not be used simultaneously with carbendazim.When using Trichoderma spp.strain preparation in the soil with higher carbendazim residue concentration,biological prevention effect of Trichoderma spp. strain preparation will be seriously affected. There is report that Trichoderma spp. strain resisting carbendazim is obtained by physical,chemical and transgene methods[13-14],which provides new idea for Trichoderma spp.strain preventing and controlling plant soil borne disease.
Pentachloronitrobenzene belongs to organic nitrogen protective fungicide. It can be used on stem and leaf,and also soil and seed. Research found that tolerance of Trichoderma spp. strain on pentachloronitrobenzene was stronger, and its EC50range inhibiting chlamydospore germination and mycelium growths of the two Trichoderma spp. strains was 681.82-1 266.00 μg/ml. Niu Shanguang et al.measured that EC50of pentachloronitrobenzene inhibiting mycelium growth of Trichoderma viride LTR-2 was 204.26 μg/ml[11], which was lower than 1 266.00 and 1 149.96 μg/ml in the research. Maybe it was because that strain had different sensitive degrees to pentachloronitrobenzene. The usage concentration of pentachloronitrobenzene is 1 000 μg/ml[10]. Therefore,in actual application,according to the situation, it could be considered to combine chlamydospore preparation of Trichoderma spp. strain with pentachloronitrobenzene, to realize pesticide reduction and disease prevention effect improvement. Routine pesticide residue has small influence on Trichoderma spp.strain preparation[15].
Difenoconazole is a kind of sterol demethylation inhibitor. According to the research result, difenoconazole had stronger inhibition effect on mycelium growth of Trichoderma spp.strain, and its EC50range was 1.67-4.02 μg/ml. But its inhibition effect on chlamydospore germination was weaker, and EC50range was 104.38-143.33 μg/ml. Using concentration of difenoconazole is 15-125 μg/ml[10].But difenoconazole is easy to be digested,and its half life on soil and vegetable is 3-22 days[16-17]. Therefore, according to different disease types, it could be considered to combine difenoconazole with Trichoderma spp. strain preparation. As time goes by, inhibition effect of difenoconazole on Trichoderma spp. strain growth will decline or eliminate,thereby reaching the aim of using Trichoderma spp. strain preparation to prevent and control disease.
Metalaxyl is a kind of internal absorption substitutional benzene acyl amine fungicide,and has special killing ability on pathogenic bacteria of Oomycetes. Metalaxyl has weaker inhibition on Trichoderma spp. strain.EC50values of 95%metalaxyl inhibiting chlamydospore germination of T. longibrachiatum 758 and T. harzianum 610 were respectively 1 108.61 and 172.80 μg/ml, while EC50values inhibiting mycelium growth were respectively 1 206.29 and 683.51 μg/ml.Jiang Xingyin measured that EC50values of metalaxyl inhibiting mycelium growth and spore germination of Trichoderma spp. strain separated from soil were all higher than 1 000 μg/ml[18],which was partially consistent with our detection result. Using concentration of metalaxyl is between 250 and 1 000 μg/ml[10].It was clear that metalaxyl had smaller influence on T. longibrachiatum 758, but seriously inhibited chlamydospore germination of T. harzianum 610, and the influence on mycelium growth of T. harzianum 610 was smaller. Therefore, for sensitivities of different strains to metalaxyl, it can be used after spore of sensitive Trichoderma spp.strain germinates.
Tebuconazole is broad spectrum internal absorption triazole pesticide fungicide. EC50values of 96.2% tebuconazole inhibiting chlamydospore germination of T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 were respectively 93.12 and 146.91 μg/ml, while EC50values inhibiting mycelium growth were respectively 10.88 and 0.32 μg/ml. Using concentration of tebuconazole is between 50 and 100 μg/ml[10]. It has smaller influence on chlamydospore germination of Trichoderma spp.strain,but the inhibition effect on mycelium growth is extremely strong, especially on mycelium growth of T. longibrachiatum 758. Therefore,when using sensitive Trichoderma spp. strain, application and residue problems of tebuconazole also need considering[19].
Niu Fangsheng reported that EC50value of thiram inhibiting mycelium growth of T. harzianum was 1.780 μg/ml[20].According to the research result, EC50values of thiram inhibiting mycelium growths of the two Trichoderma spp. strains were respectively 14.21 and 44.79 μg/ml. Their tolerances on thiram were significantly higher than that of Trichoderma spp.strain reported by the literature. Routine using concentrations of thiram and carboxin are about 500-1 000 μg/ml[10],which are far higher than EC50values inhibiting chlamydospore germination and mycelium growth of T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 in the research. Therefore, in application process,we need considering if thiram or carboxin was used in the soil and their residue concentrations in soil[21].
Trichoderma spp. strain biopesticide is one of high-efficient, low-toxicity,low-residue and “harmless”pesticides vigorously promoting. When using Trichoderma spp. strain biopesticide, we must notice temperature, humidity, sunshine and rainwater. In actual production, it often needs considering the combined application with fungicide to comprehensively prevent and control soil born disease, and the influence of soil pesticide residue on disease prevention effect of Trichoderma spp. strain preparation. At present,there are fewer researches about the influences of difenoconazole,tebuconazole and carboxin on toxicity of Trichoderma spp. strain. Combining the sensitivities of T. harzianum 610 and T.longibrachiatum 758 to the seven kinds of fungicides and using concentrations of each fungicide in the research, when using T. harzianum 610 and T. longibrachiatum 758 chlamydospore preparations to prevent and control disease, they could not be used with carbendazim, tebuconazole, thiram and carboxin, and pesticide residue maybe affect the prevention effect of Trichoderma spp.strain preparation. They can be used with pentachloronitrobenzene and difenoconazole according to actual situation. T. longibrachiatum 758 can be used with metalaxyl, and T. harzianum 610 can be used with metalaxyl after spore germinating.Because that different Trichoderma spp. strains have different sensitivities to various fungicides, application techniques of pesticide and biopesticide are determined by comprehensively analyzing sensitivities of disease type,strain and different life stages to pesticide, using history and residue situation of soil pesticide, thereby reaching the aim of safe and high efficient disease prevention and control.
The influence of the combined application of fungicide and Trichoderma spp. strain on pathogenic microor-ganism is affected by mechanism of chemical fungicide, bacteria inhibition mechanism of Trichoderma spp.strain, environment condition and combined manner of chemical pesticide and Trichoderma spp. strain[22]. In the research, we determined indoor inhibition effect of fungicide on Trichoderma spp. strain, which could not directly reflect the inhibition effect on pathogenic bacteria after fungicide combining with Trichoderma spp.strain.Therefore,it needs studying not only toxicity measurement, but also their combined manner and relationship when studying the influence of combined application of fungicide and Trichoderma spp.strain on pathogenic bacteria. It needs further research to prevent and control plant disease by combined application of fungicide and Trichoderma spp.strain.
[1]WEINCLLING R. Trichoderma Iignorum as a parasite of other soil fungi[J].Phytopathology,1981,22(8):837-845.
[2]LI XL(李雪玲),LIU H(刘慧),ZHANG TY(张天宇).Some biological characteristics of three Trichoderma isolates 三株木霉生防菌的生物学特性研究[J].Journal of Shandong Agricultural University(山东农业大学学报: 自然科学版),2003,34(1):5-8.
[3]JI Y (冀颖). Colony and function of T.harzianum Th-33 ThChsC gene(哈茨木霉Th-33 ThChsC 基因的克隆及功能初步分析)[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(北京:中国农业科学院),2011:2-3.
[4]HWANG SF, CHANG KF, HOWAR RJ,et al. Decrease in incidence of Pythium damping-off of field pea by seed treatment with Bacillus spp.& metalaxyl[J].Journal of Plant Disease and Protection,1996,103(9):31-41.
[5]JIANG XL (蒋细良),SUN LZ (孙连壮),ZHU CX (朱昌雄), et al. The method generating chlamydospore by liquid submerged fermentation of Trichoderma spp.strain (木霉菌液体深层发酵生产厚垣孢子的方法)[P].China Patent(中国专利),10057339.0,2008-2-13.
[6]PAN W (潘玮).Comparisons of biological characteristics and biological prevention effects of Trichoderma viride chlamydospore and conidiospore (绿色木霉厚垣孢子与分生孢子生物学特性及生防效果比较研究)[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(北京:中国农业科学院),2006:26-28.
[7]GULIPIYA (古丽皮艳),HAN QM (韩青梅),WANG L (王兰),et al.Toxicity determination of different fungicides on Curvularia lunata (不同杀菌剂对玉米弯孢叶斑菌的毒力测定)[J]. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry(西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版),2005,33(S1):49-52.
[8]HUANG ZX (黄彰欣).Experiment guide of plant chemical protection(植物化学保护实验指导)[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press(北京:中国农业出版社),2009:56-58.
[9]SONG XC(宋修春).Indoor toxicity measurement of nine kinds of fungicides on shoot blight of Pinus sylvestris var. ongolica (9 种杀菌剂对樟子松枯梢病的室内毒力测定)[J].Jilin Agriculture(吉林农业),2012,39(12):38-39.
[10]LIU CL(刘长令).World pesticide(fungicide volume)(世界农药大全 (杀菌剂卷))[M].Beijing:industry press(北京:化学工业出版社),2008:152-307.
[11]NIU SG(牛赡光),ZHANG SJ(张淑静),WANG TM (王太明), et al. Selective toxicity of chemical fungicides to Verticillium dahliae causing cotton wilt disease and its biocontrol agents (化学农药对棉花黄萎病菌和生防菌的选择毒性)[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control(中国生物防治),2006,22(1):49-53.
[12]LI GX(李贵香).Screening and characteristic study of antagonistic Trichoderma spp.strain resisting carbendazim(拮抗性木霉耐多菌灵菌株的筛选及特性研究)[D].Tianjin:Hebei University of Technology (天津: 河北工业大学),2007:10-14.
[13]LI M(李敏),YANG Q(杨谦),YOU ZQ(尤子祺). Fixed point transformation of gene BenR from Neurospora crass(粗糙脉孢菌BenR 基因在哈茨木霉中的定点转化)[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science Edition)(西南师范大学学报),2008(33):58-59.
[14]LI H(李合),TANG W(唐文),LI JS(李纪顺),et al.Improvement of Trichoderma viride LTR-2 by ultraviolet mutation(绿色木霉LTR-2 菌株的紫外线诱变改良)[J].Chinese Journal of Biological Control(中国生物防治学报),2004,20(3):182-186.
[15]XUE JJ (薛津津),QIN X (秦旭),XU YM(徐应明), et al. Residue detection and digestion dynamics of pentachloronitrobenzene in watermelon and soil (土壤和西瓜中五氯硝基苯的残留检测与消解动态研究)[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment (安全与环境学报),2010,10(4):101-105.
[16]AN JJ(安晶晶),LIU XG(刘新刚),DONG FS(董丰收),et al.Dynamic analysis of difenoconazole residue in tomatoes and soil(苯醚甲环唑在番茄和土壤中的残留动态研究)[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences (环境科学研究),2009,22(7):868-872.
[17]LIU GH (刘纲华).Residue and degradation behavior of difenoconazole in several kinds of fruits and vegetables(苯醚甲环唑在几种果蔬中的残留降解行为研究)[D].Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University (长沙: 湖南农业大学),2012:71-72.
[18]JIANG XY(姜兴印).Biology of high efficient bio-prevention Trichoderma spp. strain and processing technique of its preparation(抗药木霉菌高效生防菌株生物学及其制剂加工技术)[D].Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University(泰安:山东农业大学),2006:44-46.
[19]SUN MN(孙明娜),DUAN JS(段劲生),WANG M(王梅), et al. Study on residues and dissipation of tebuconazole in grapes and soil (戊唑醇在葡萄和土壤中的残留和消解动态)[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science (农药学学报),2013,15(1):73-78.
[20]NIU FS(牛芳胜).Synergistic effect and mechanism of combined application of T. harzianum and five kinds of fungicides on Botrytis cinerea (哈茨木霉菌与5 种杀菌剂联合对番茄灰霉病菌的协同作用及增效机制研究)[D]. Baoding:Agricultural University of Hebei(保定:河北农业大学),2013:6-11.
[21]ZHANG Z(张造), WANG Y(王岩), LU ZB (逯忠斌), et al. The residual dynamics of carboxin and thiram in rice plants and soil(卫福(carboxin+thiram)在水稻苗及土壤上的残留动态)[J]. ,Journal of Jilin Agricultural University(吉林农业大学学报),2001,23 (4):64-68.
[22]NIU FS(牛芳胜),MA Z(马志),BI QY(毕秋艳).Toxicity measurement of different active mechanism fungicides to Trichoderma antagonistic strain against Botrytis cinerea (不同作用机制杀菌剂对番茄灰霉病菌拮抗木霉菌的毒力测定)[J].Agrochemicals(农药),2012(51):601-604.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年7期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年7期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Variation in Enzymes Activities of Rhizospheric Substrate and Influencing Factors during Nursing of Watermelon Seedlings
- Determination of Iprobenfos Residue in Rice by GC-FTD using Two-dim Ensional Purification
- Screening and Taxonomic Status of a Highly Efficient Antifungal Strain against Cytospora chrysosperma
- Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides in Yam Bulbils and Their Hypoglycemic Effect in Diabetic Mice
- Adsorption Kinetics of NH4+by Purple Soils with Different pH Values
- Effects of Slow-release Fertilizer and Balanced Fertilization on Nitrogen,Phosphorus and Potassium Uptake in Peppers
