模拟裂纹的弯曲弹簧模型比较
郭智刚, 陶海峰
(1.上海应用技术学院轨道交通学院,上海 201418;2.山东省济南市公路管理局,济南 250013)
模拟裂纹的弯曲弹簧模型比较
郭智刚1, 陶海峰2
(1.上海应用技术学院轨道交通学院,上海 201418;2.山东省济南市公路管理局,济南 250013)
合适的裂纹模型模拟能够真实反映梁裂纹的力学机理.首先分析了4种模拟裂纹的弯曲弹簧模型,然后以自由梁为例计算了4种弯曲弹簧模型下的固有频率值,并与实验结果进行对比.分析了4种弯曲弹簧模型模拟裂纹损伤的相对误差,结果表明,4种裂纹模型均可靠,能很好地模拟梁的裂纹损伤.弯曲弹簧模型III模拟裂纹的相对误差最小,建议采用此弹簧模型模拟裂纹损伤.
裂纹;弯曲弹簧模型;模拟;相对误差分析
梁是工程结构中最常使用的一类构件,在复杂的工作环境下可能会产生裂纹损伤,这些裂纹损伤对结构的正常工作相当不利.结构中裂纹的出现会引起局部刚度的改变,从而在一定程度上影响了结构整体的动力特性,导致结构参数如频响函数和模态参数等随之改变.利用完整梁结构的数学模型连同其振动试验数据作为识别梁裂纹的基准信息,与裂纹梁的动力参数进行比较从而识别裂纹的方法,是目前国内外研究的热点和难点.
国内外许多学者对裂纹梁、管道等结构的影响进行了研究[1-3].为了对裂纹梁、管道等结构进行动力分析和损伤识别研究,往往需要对裂纹进行模拟.合适的裂纹模型有助于真实反映梁裂纹的力学机理,正确反映裂纹梁的动力特性.到目前为止,多数学者采用无质量转动等效弹簧模拟裂纹,并对简支梁、悬臂梁等简单结构进行了理论分析和实验研究.然而,不同的学者提出了多种模拟梁裂纹的数学模型.Douka等[4-6]采用弯曲弹簧模型I,Bamnios等[7]采用弯曲弹簧模型II,Chondros等[8-10]采用弯曲弹簧模型III,Patil等[11-13]采用弯曲弹簧模型IV分别模拟裂纹,但没有人对这4种弹簧模型进行比较.本文首先介绍了这4种模拟梁裂纹的弯曲弹簧模型,然后分别采用这4种模型进行计算并通过比较得到最适合的弯曲弹簧模型.
1 弯曲弹簧模型
梁裂纹是由无质量弹簧来模拟,弯曲弹簧模型I~IV的4种弹簧刚度计算公式分别为:
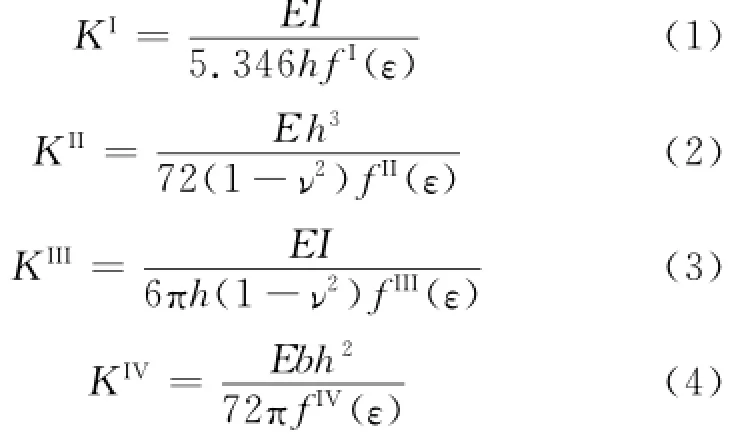
式中:

上述公式中:ε为损伤相对深度,ε=hd/h,hd为裂纹深度;h为梁的高度;b为梁的宽度;E为弹性模量;I为截面惯性矩;ν为泊松比;fI(ε)、fII(ε)、fIII(ε)、fIV(ε)依次为弯曲弹簧模型I、II、III、IV的无因次局部导纳函数.对4个弯曲弹簧模型进行分析,弹簧刚度随损伤深度变化曲线如图1所示.由图可见,模型I、III和IV的弹簧刚度基本上一致,而模型II的弹簧刚度偏差较大.
2 裂纹梁的固有频率
欧拉梁的自由振动方程为
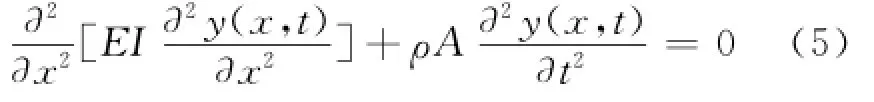
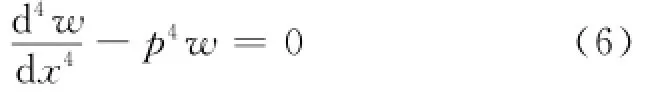
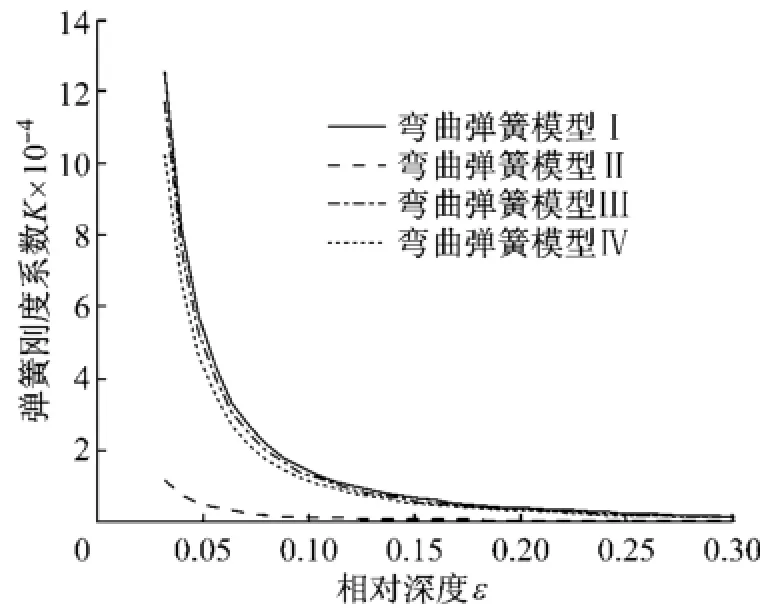
图1 弹簧刚度随损伤深度变化图Fig.1 The variation diagram of the damage depth of spring stiffness
式(6)的求解表达式为
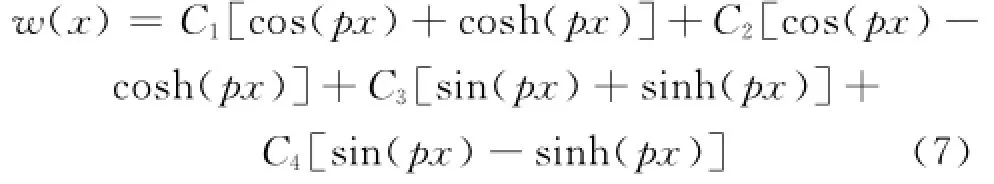
式中:

式(5)~(7)为完整欧拉梁振型表达式.现需求解裂纹梁的固有频率,故考虑梁有n个裂缝,如图2所示.
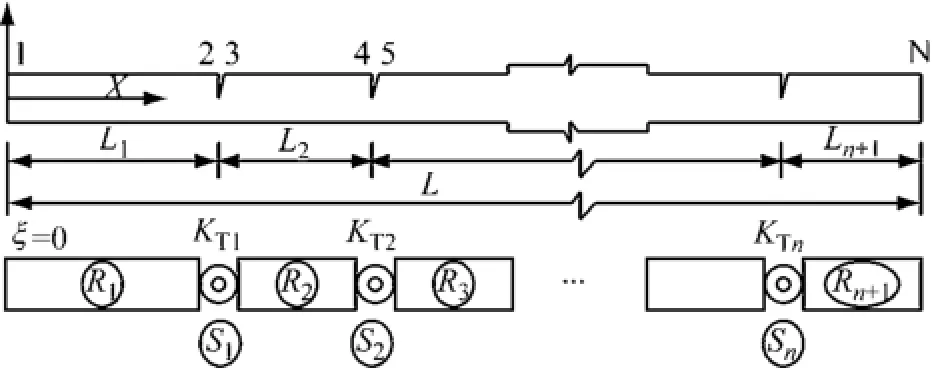
图2 多个裂缝的裂纹梁示意图Fig.2 The schematic diagram of cracked beam for more cracks
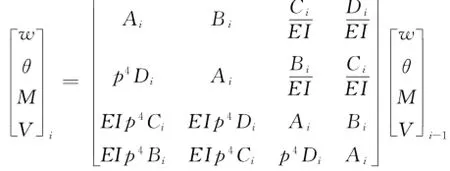
式中:Ri为i截段的传递矩阵;
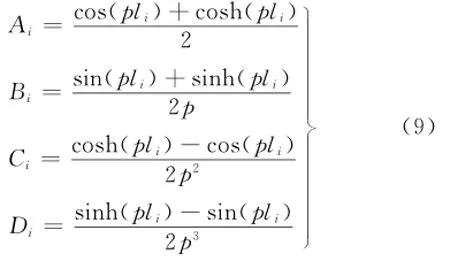
在裂缝位置处,裂缝两端的w、θ、M和V之间的关系如下:

或

式中:Si为传递矩阵;Ki为转动弹簧矩阵.
梁的总体传递矩阵
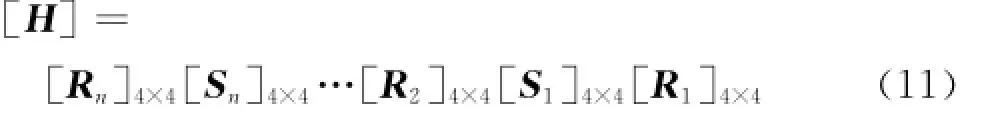
由式(11)可见,传递矩阵H为4×4的矩阵,对梁施加边界条件,则H变为2×2的矩阵.梁的振动方程为
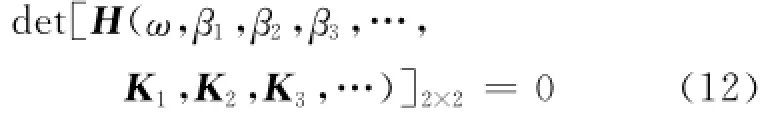
通过式(12)即可计算出梁的固有频率.
3 弯曲弹簧模型分析
为了验证上述裂纹模型,本文选择文献[14]中的实验数据进行分析.梁的参数见表1,裂纹梁的损伤工况见表2.弯曲弹簧模型I计算的固有频率和实验测得的固有频率见表3~4.由表可见,弯曲弹簧模型I模拟裂纹得到的固有频率与实验值很好吻合.同样,其他3种弯曲弹簧模型模拟裂纹得到的固有频率与实验值也很吻合,不再列出.表明这4种裂纹模型是可靠的,能很好地模拟梁的裂纹损伤.但4种模型模拟损伤的精度还无从得知,因此需进行误差分析.
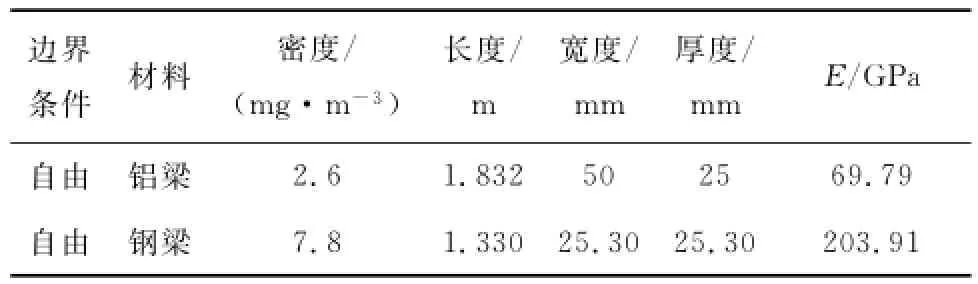
表1 裂纹梁的材料特性Tab.1 Material characteristic of cracked beam
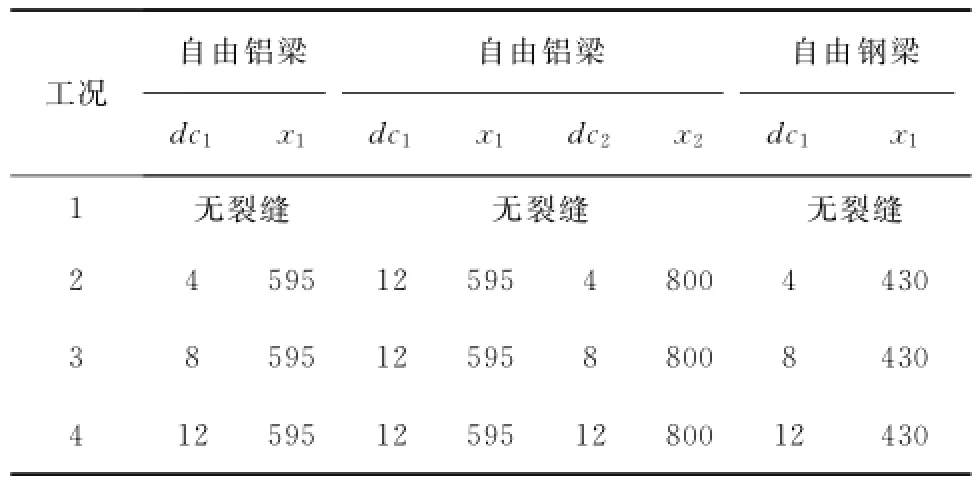
表2 裂纹梁损伤工况Tab.2 Damage case of cracked beammm

表3 弯曲弹簧模型I的1个及2个裂纹的自由铝梁损伤前后固有频率测量值和计算值Tab.3 The measured and computed natural frequencies of the aluminium free-free beam with one and two cracks for spring model I
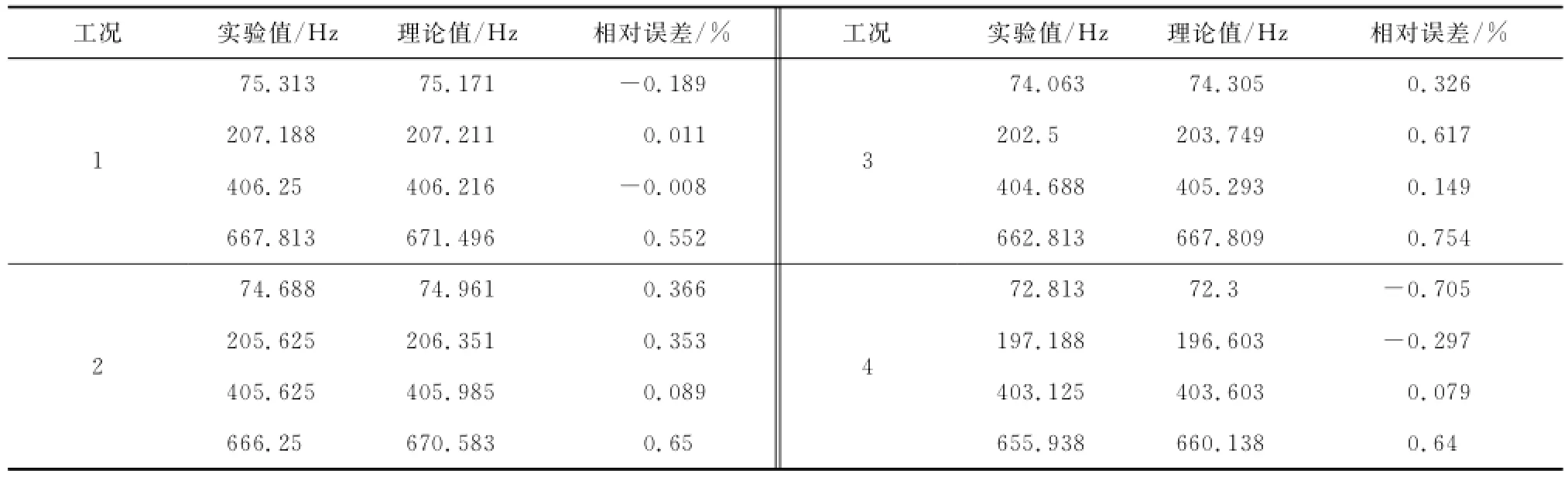
表4 弯曲弹簧模型I的一个裂纹的自由钢梁损伤前后固有频率测量值和计算值Tab.4 The measured and computed natural f requencies of the steel free-free beam with one crack for spring model I
图3~5分别对应表2中损伤工况的裂纹梁的相对误差分析图.由图3可见,模型II的相对误差比其他3种模型大,图3(a)、(b)中模型I相对误差最小,其次是模型III和IV,(c)中模型III相对误差最小,其次是模型IV和I.由图4可见,模型III的相对误差最小,其次是模型IV和I,模型II相对误差最大.由图5可见,图5(a)、(b)中模型IV的相对误差最小,其次是模型II和III,模型I误差最大,(c)中模型III误差最小,其次是模型II和I,模型IV误差最大.由图1、3~5综合考虑,模型III的相对误差最小,因此建议采用弯曲弹簧模型III模拟裂纹损伤.

图3 带单个裂纹的两端自由铝梁下模态频率误差分析图Fig.3 Model frequency error analysis for the aluminium free-free beam with one crack
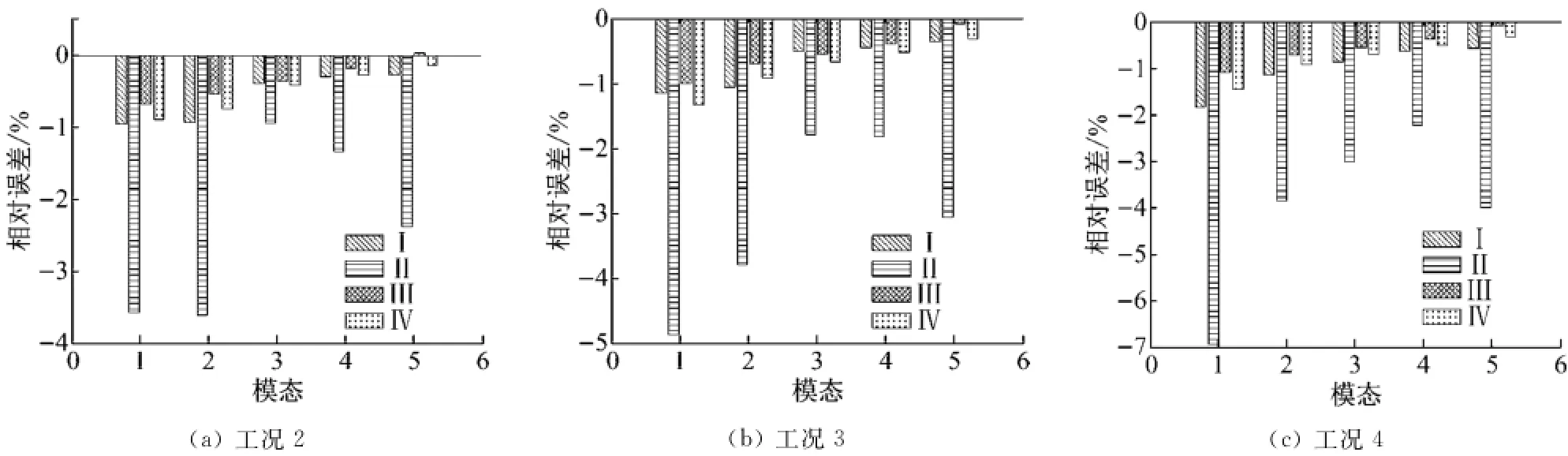
图4 带两个裂纹的两端自由铝梁下模态频率误差分析图Fig.4 Model frequency error analysis for the aluminium free-free beam with two cracks
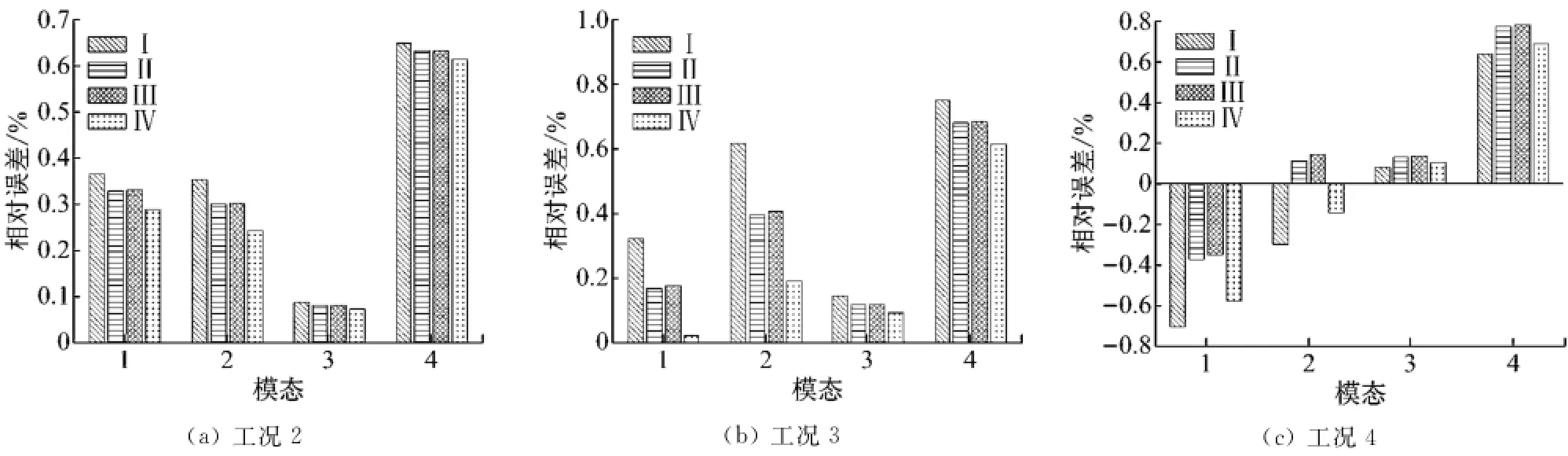
图5 带单个裂纹的两端自由钢梁下模态频率误差分析图Fig.5 Model frequency error analysis for the steel free-free beam with one crack
4 结 语
本文介绍了模拟裂纹损伤的4种弯曲弹簧模型,求解得到裂纹梁的固有频率值,并与实验得到的裂纹梁固有频率值进行比较,分析了4种弯曲弹簧模型模拟裂纹损伤的相对误差.结果表明,这4种裂纹模型是可靠的,能很好地模拟梁的裂纹损伤.弯曲弹簧模型III模拟裂纹的相对误差最小,因此建议采用弯曲弹簧模型III模拟裂纹损伤.
[1] Doebling S W,Farrar C R,Prime M B,et al.Damage identification and health monitoring of structural and mechanical systems from changes in their vibration characteristics:a literature review[R].United States:Los Alamos National Laboratory,1996.
[2] Friswell M I.Damage identification using inverse methods[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society London,Series A(Mathematical,Physical and Engineering Sciences),2007,365(1851):393-410.
[3] Sekhar A S.Multiple cracks effects and identification[J].Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2008,22(4):845-878.
[4] Douka E,Bamnios G,Trochidis A.A method for determining the location and depth of cracks in doublecracked beams[J].Applied Acoustics,2004,65(10):997-1008.
[5] Shifrin E I,Ruotolo R.Natural frequencies of a beam with an arbitrary number of cracks[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1999,222(3):409-423.
[6] Bamnios Y,Douka E,Trochidis A.Crack identification in beam structures using mechanical impedance[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2002,256(2):287-297.
[7] Bamnios G,Trochides A.Dynamic behaviour of a cracked cantilever beam[J].Applied Acoustics,1995,45(2):97.
[8] Chondros T G,Dimarogonas A D,Yao J.Continuous cracked beam vibration theory[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1998,215(1):17-34.
[9] Khiem N T,Lien T V.A simplified method for natural frequency analysis of a multiple cracked beam[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,2001,245(4):737-751.
[10] Zhang X Q,Han Q,Li F.Analytical approach for detection of multiple cracks in a beam[J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics-Asce,2010,136(3):345-357.
[11] Patil D P,Maiti S K.Detection of multiple cracks using frequency measurements[J].Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2003,70(12):1553-1572.
[12] Patil D P,Maiti S K.Experimental verification of a method of detection of multiple cracks in beams based on frequency measurements[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2005,281(1-2):439-451.
[13] Nandwana B P,Maiti S K.Detection of the location and size of a crack in stepped cantilever beams based on measurements of natural frequencies[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1997,203(3):435-446.
[14] Sinha J K,Friswell M I,Edwards S.Simplified models for the location of cracks in beam structures using measured vibration data[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2002,251(1):13-38.
(编辑 俞红卫)
The Comparison of Rotational Spring Model of Crack Simulation
GUO Zhigang1, TAO Haifeng2
(1.School of Railway Transportation,Shanghai Institute of Technology,Shanghai 201418,China;2.Jinan Road Administer Bureau,Jinan 250013,China)
Suitable crack model can reflect real mechanics mechanism of cracked beam.Four rotational spring models for simulating crack were analyzed.Natural frequencies of free-free cracked beams under four rotational spring models were calculated,which was compared with the experimental results. Meanwhile,the relative errors under four rotational spring models were analyzed.The results showed that the four cracked models could better simulate crack.The relative error of third rotational spring model was the smallest and was recommended to simulate the crack damage.
crack;rotational spring model;simulation;relative error analysis
O 327
A
1671-7333(2015)04-0362-05
10.3969/j.issn.1671-7333.2015.04.010
2014-10-20
铁道部科技研究开发计划资助项目(2012G003-E);上海应用技术学院引进人才基金资助项目(YJ2014-37)
郭智刚(1984-),男,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为结构健康监测方面的研究.E-mail:zhigangguo@sit.edu.cn

