双气囊电子小肠镜诊断小肠疾病价值分析
刘婉薇,沙卫红,王启仪,徐丽姝,马 娟
双气囊电子小肠镜诊断小肠疾病价值分析
刘婉薇,沙卫红,王启仪,徐丽姝,马娟
目的 探讨双气囊电子小肠镜诊断小肠疾病的价值。方法 收集2006年6月—2013年2月广东省人民医院接受双气囊电子小肠镜检查的患者116例,回顾性分析其小肠镜检查结果。结果 116例患者在异丙酚麻醉/镇静状态下共进行127例次小肠镜检查,包括经口检查68例,经肛门检查37例,双向入镜检查11例,检查成功率为99.2%(126/127)。小肠疾病阳性检出率为87.9%(102/116),位居前5位分别为克罗恩病(35例,30.2%)、小肠恶性肿瘤(23例,19.8%)、小肠糜烂溃疡性炎症(16例,13.8%)、小肠良性肿瘤(9例,7.8%)和小肠血管畸形(5例,4.3%)。少数患者于检查结束完全清醒后诉轻微的咽喉部不适、肛周不适或腹胀,均可自行缓解。结论 双气囊电子小肠镜检查成功率高,对小肠疾病阳性检出率高,相对安全可靠,对小肠疾病诊断价值高。
内窥镜检查,胃肠道;肠疾病;克罗恩病;肠肿瘤;诊断
刘婉薇,沙卫红,王启仪,等.双气囊电子小肠镜诊断小肠疾病价值分析[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(3):342-345.[www.chinagp.net]
Liu WW,Sha WH,Wang QY,et al.Diagnostic value of double-balloon enteroscopy in identifying small intestine diseases[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(3):342-345.
小肠是人体最长的器官,其疾病的临床确诊仍比较困难,双气囊电子小肠镜是近年发展起来的有效诊断小肠疾病的新方法。近年来,国内外在应用小肠镜诊断小肠疾病方面积累了一些经验,初步的临床应用表明,小肠镜对小肠疾病的总体诊断率达60% ~80%[1-3],并发症相对较低(0.72% ~1.70%)[4-7]。本研究收集行双气囊电子小肠镜检查的患者,回顾性分析了双气囊电子小肠镜诊断小肠疾病的临床实用性。
1 资料与方法
1.1临床资料 收集2006年6月—2013 年2月广东省人民医院接受双气囊电子小肠镜检查的患者116例为研究对象,其中男84例,女32例;年龄14~80岁,平均45.2岁。包括不明原因小肠出血43例,病程1 d~20年;不明原因腹痛31例,病程1个月~12年;小肠不全梗阻24例,病程1周~10年;慢性腹泻11例,病程2个月~10年;贫血4例,病程1周~10年;其他如发现癌胚抗原(CEA)升高1年、双下肢水肿2个月、体质量下降4个月各1例。患者均于小肠镜检查前进行了电子胃镜和结肠镜检查,均为临床怀疑有小肠疾病者,在麻醉或镇静状态下进行双气囊电子小肠镜检查。
1.2方法 患者均采用日本富士能EN-450/P5型双气囊电子小肠镜以及与之配套的活检钳、圈套器、注射针等配件。检查前常规术前准备,经口入镜者禁食12 h,口服5 ml硅油消泡剂;经肛入镜者口服复方聚乙二醇电解质溶液清洁肠道,待患者排出无渣淡黄色大便后进行小肠镜检查。同时根据麻醉科医师评估结果,给予异丙酚2 mg/kg静脉滴注进行麻醉,或者咪达唑仑静脉推注镇静,术中辅助盐酸哌替啶、盐酸屈他维林解痉止痛等,在吸氧、持续心电监护及严密观察生命体征的情况下进行双气囊电子小肠镜检查,均由经验丰富的高年资内镜医师完成,检查者根据患者的临床资料,包括胶囊内镜、CT/MRI检查结果判断疾病的大致部位。估计病变在中上段小肠者选择经口进镜,估计病变在远段小肠者选择经肛门进镜。经口检查超越幽门50 cm以上,经肛门检查超越回盲瓣50 cm以上,如果在小肠两端50 cm以内发现小肠疾病导致小肠狭窄,小肠镜无法通过而停止检查者,按检查成功计算。
2 结果
2.1双气囊电子小肠镜检查的完成情况
116例患者共接受了127次小肠镜检查(经口入镜68例、经肛门入镜37例、双向入镜11例),只有1例因十二指肠水平段扭曲狭窄,小肠镜未能通过,检查失败。其余患者经口检查均到达空肠下段或回肠上段,经肛门进镜可到达空回肠交界部或以上,总检查成功率为99.2% (126/127)。所有患者在异丙酚麻醉/镇静过程中生命体征平稳,无严重呼吸困难、心脏事件发生。操作过程中患者无明显不适、无胃肠穿孔和出血等其他严重并发症出现。少数患者于检查结束完全清醒后诉轻微的咽喉部不适、肛周不适或腹胀,均可自行缓解。
2.2双气囊电子小肠镜检查结果 116例患者接受小肠镜检查,102例检出不同小肠疾病,总阳性疾病检出率为87.9% 前3位阳性病变检出率为:慢性腹痛为主要临床表现的阳性疾病检出率为100.0%,小肠不全梗阻为主要临床表现的阳性疾病检出率为 91.7%,不明原因小肠出血为主要临床表现的阳性疾病检出率为83.7% (见表1)。前5位疾病分别为克罗恩病、小肠恶性肿瘤、小肠糜烂溃疡性炎症、小肠良性肿瘤、小肠血管畸形(见表2)。病变发生在回肠38例、空肠36例、空回肠14例、十二指肠12例、回盲瓣1例、输入袢1例。13例阴性患者中,1例接受外科手术,病理证实为小肠神经内分泌肿瘤。双气囊电子小肠镜检出阳性小肠疾病典型病例图片见图1。
3 讨论
双气囊电子小肠镜是小肠疾病检查手段的重要进展,理论上可以在不开腹的情况下进行全小肠直视检查,小肠镜对小肠黏膜的观察更直观、清晰,可以通过控制镜身对可疑部位反复观察,尤其对可疑病变可以通过活检获得病理学诊断,Almeida等[8]报道小肠镜能极大地提高小肠肿瘤的诊断水平,减少一些不必要的外科手术。经过近几年的临床初步应用实践,小肠镜对小肠疾病的诊断价值基本得到肯定,对小肠疾病的总阳性病变检出率可达到50% ~80%[1-3]。本研究结果表明,对于经胃镜、结肠镜检查而未发现出血灶的消化道出血患者,小肠镜阳性疾病检出率高达83.7%,慢性腹痛的阳性疾病检出率高达100.0%,小肠不全梗阻的阳性疾病检出率为91.7%,慢性腹泻的阳性疾病检出率高达81.8%,高于国内外文献报道的结果[9-11],这可能与病例选择和小肠镜检查适应证的把握有关。本研究结果显示,双气囊电子小肠镜对小肠疾病优越的诊断价值,不仅对小肠出血性疾病、小肠不全梗阻等,对于长期不明原因腹痛及腹泻的患者也有非常高的阳性检出率。
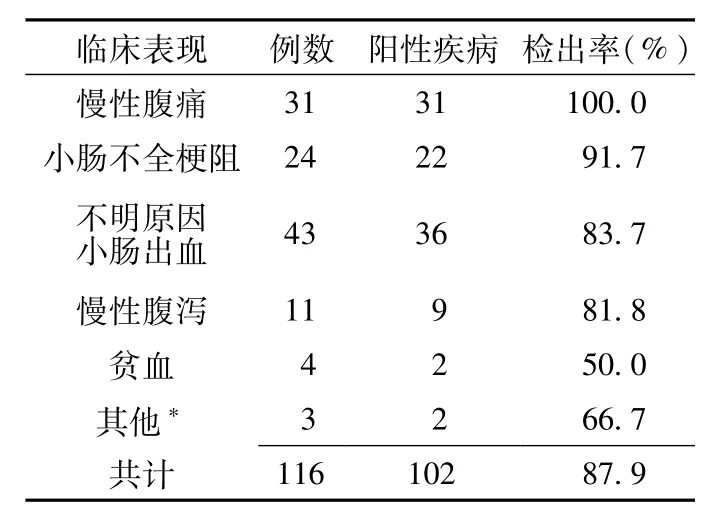
表1 双气囊电子小肠镜对可疑小肠疾病的阳性检出率Table 1 The positive detection rate of doubleballoon electronic enteroscopy for intestinal diseases

表2 双气囊电子小肠镜检出的主要小肠疾病及部位 (n=116)Table 2 The main intestine diseases and lesion location detected by double-balloon electronic enteroscopy
小肠镜检查操作有一定风险,尽管严重者可能导致小肠穿孔、出血、急性胰腺炎等有关,但风险总发生率极低,为0.72%~1.70%,其中急性胰腺炎的发生率为0.49%[4-7]。由于小肠镜检查时间相对较长,且检查所需耗材也相对昂贵,而且小肠疾病发病率相对较低,因此临床工作中仍应严格把握小肠镜检查适应证,尽量让患者先进行胃镜、结肠镜、腹部CT等检查,排除胃、十二指肠、大肠疾病及消化道以外的疾病,同时结合当地医疗条件,选择性进行口服法小肠造影、CT仿真肠镜或胶囊内镜等检查,若提示存在小肠疾病的情况,再针对性选择经口或经肛入镜行小肠镜检查。本研究小肠镜插入成功率达99.2%,患者均未发生小肠穿孔、出血、急性胰腺炎等并发症,仅有少部分患者存在咽部、肛门或腹部轻微不适,均可自行缓解,提示小肠镜临床使用安全性高。
双气囊电子小肠镜经口或肛门单侧进镜检查,很难完成对整个小肠的检查,由于检查费用较昂贵,临床上还不能常规从两侧进镜进行双向入镜检查。本组接受小肠镜检查的116例患者,仅9.5%(11/ 116)接受了双向入镜检查,但小肠疾病的阳性检出率仍令人满意,与国外报道经双向进镜的检查结果基本一致[9-11],所以入镜途径的选择对提高小肠镜的阳性检出率至关重要,通过详细询问病史,仔细查体,结合胃镜、结肠镜、消化道气钡造影、腹部CT及胶囊内镜等检查结果,估计小肠疾病的大概发病部位,对可能位于中上段小肠者,选择经口入镜;而对可能位于远段小肠者,选择经肛门入镜。高度怀疑存在小肠疾病,经一侧进镜检查未发现病变者,必须用墨水或亚甲蓝等标记后经双向进镜完成整个小肠的双向入镜检查,以免遗漏病变[12]。小肠胶囊内镜是一种无创检查小肠疾病的检查方法,有助于指导选择双气囊电子小肠镜检查的进镜方式[13]。相对胶囊内镜,双气囊电子小肠镜独特的优势是对发现的小肠阳性病变实施适宜内镜下活检及治疗,如内镜下止血、息肉切除、小肠狭窄的扩张治疗、小肠支架置放及取异物[14-17],显示了其重要的临床应用价值。本研究结果证明,双气囊电子小肠镜对小肠疾病的检出率较高,安全可靠,无严重并发症出现,显示了双气囊电子小肠镜在小肠疾病诊断中的独特优势和广阔的应用前景。
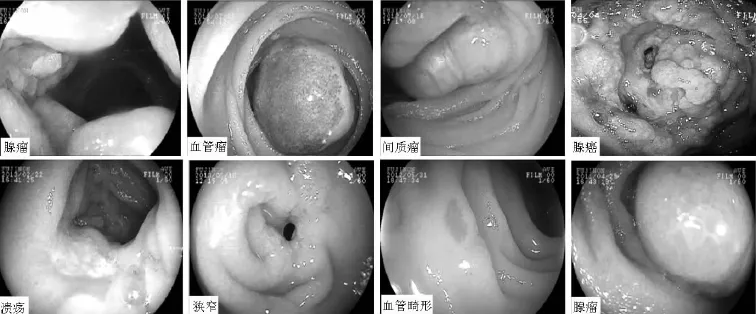
图1 双气囊电子小肠镜检出阳性小肠病变情况Figure 1 The positive intestinal diseases detected by double-balloon electronic enteroscopy
[1]Onal IK,Akadogan M,Arhan M,et al. Double balloon enteroscopy:a 3-year experience at a tertiary care center[J]. Hepatogastroenterology,2012,59(118):1851-1854.doi:10.5754/hge10828.
[2]Samaha E,Rahmi G,Landi B,et al. Long-term outcome of patients treated with double balloon enteroscopy for small bowel vascularlesions[J].AmJ Gastroenterology,2012,107(2):240-246.doi:10.1038/ajg.2011.325.
[3]Shi H,Ren J,Dong W.Double-balloon enteroscopy in the diagnosis and management ofsmall-boweldiseases[J]. Hepatogastroenterology,2011,58(106):477-486.
[4] XinL,LiaoZ,JiangYP,et al. Indications,detectability,positive findings,totalenteroscopy,and complicationsofdiagnosticdouble-balloon endoscopy:a systematic review of data over the first decade of use[J]. Gastrointest Endosc,2011,74(3):563-570.
[5]Di Caro S,May A,Heine DG,et al.The European experience with double-ballon enteroscopy:indications,methodology,safety, andclinicalimpact[J]. Gastrointest Endosc,2005,62(4):545 -550.
[6]Kopacova M,Tacheci I,Rejchrt S,et al. Doubleballonenteroscopyandacute pancreatitis[J].World J Gastroenterel,2010,16(19):2331-2340.
[7]黄适,唐少波,林寿宁,等.麻醉镇痛双气囊内镜检查在小肠疾病诊断中的应用[J].中华消化内镜杂志,2007,24 (3):224-225.
[8]Almeida N,Figueiredo P,Lopes S,et al. Double-ballon enteroscopy and small bowel tumors:a South European single-center experience[J].Dig Dis Sci,2009,54 (7):1520-1524.
[9]May A,Nachbar L,Ell C.Double-ballon enteroscopy(push-and-pull enterosopy)ofthesmallbowel: feasibilityand therapeutic yield in patients with suspected smallboweldisease[J].Gastrointest Endos,2005,62(1):62-67.
[10]Yamamoto H,Kita H,Sunada K,et al. Clinicaloutcomesofdouble-ballon endoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of small-intestinaldiseases[J].Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2004,2(11):1010-1016.
[11]Zhong J,Zhang CL,Zhang J,et al. Applicationofdouble-balloonpush enteroscopy in diagnosis of small bowel diseases[J].ChineseJournalof Digestive,2003,23(10):591-594. (in Chinese)钟捷,张晨莉,张吉,等.推进式双气囊电子小肠镜在小肠疾病诊断中的应用[J].中华消化杂志,2003,23(10):591-594.
[12]Liu J,Luo HS,Ding YJ,et al.Directive role of clinical symptoms in determining the route for double-balloon enteroscopy[J]. WorldChineseJournalofDigestology, 2009,17(6):623-626.(in Chinese)刘洁,罗和生,丁一娟,等.临床症状对双气囊小肠镜进镜方式选择的指导[J].世界华人消化杂志,2009,17 (6):623-626.
[13]Li XB,Chen HM,Dai J,et al.Guiding value of capsule endoscopy for access route ofdouble-balloonendoscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Digestive Endoscopy,2010,27(8):396-398.(in Chinese)李晓波,陈慧敏,戴军,等.胶囊内镜指导双气囊内镜进镜方式的临床研究[J].中华消化内镜杂志,2010,27 (8):396-398.
[14]MayA,NacharL,PohlJ,et al. Endoscopicinterventionsinthesmall bowel using double ballon enteroscopy:feasibility and limitations[J].Am J Gastroenterol,2007,102(3):527-535.
[15]Despott EJ,Gupta A,Burling D,et al. Effective dilation of small-bowel strictures by double-ballon enteroscopy in patients with symptomatic Crohn′s disease(with wideo)[J].Gastrointest Endosc,2009,70(5):1030-1036.
[16]Ross AS,Semarad C,Waxman I,et al. Enteral stent placement by double ballon enteroscopy for palliation of malignant small bowelobstruction[J].Gastrointest Endosc,2006,64(5):835-837.
[17]Mehdizadeh S,Lo SK.Treatment of smallbowel diaphragm disease by using doubleballonenteroscopy[J].Gastrointest Endosc,2006,64(6):1014-1017.
(本文编辑:陈素芳)
Diagnostic Value of Double-balloon Enteroscopy in Identifying Small Intestine Diseases
LIU Wan-wei,SHA Wei-hong,WANG Qi-yi,et al.Department of Gastroenterology,Guangdong General Hospital,Guangzhou 510080,China
Objective To investigate the diagnostic value of double-balloon enteroscopy in identifying small intestine diseases.Methods 116 cases who were examined using double-balloon enteroscopy in Guangdong General Hospital from July 2006 to February 2013,were selected as study subjects,the results of the enteroscopy examination were analysed retrospectively.Results Under propofol anesthesia/sedation,all patients received 127 times of double balloon enteroscopy examination,68 cases received examination through mouth,37 cases received examination through anus,11 cases received examination through both mouth and anus,the successful rate of examination was 99.2%(126/127).The detection rate of intestine diseases was 87.9%(102/116).Among the lesions detected by double-balloon enteroscopy,Crohn′s disease(35 cases,30.2%),intestinal malignancies(23 cases,19.8%),intestinal erosions and ulcers(16 cases,13.8%),intestinal benign tumors(9 cases,7.8%)and intestinal vascular malformation(5 cases,4.3%)were the most common lesions in order.After examination,a small number of cases had throat discomfort,crissum discomfort or abdominal distension,the symptoms were temporary,and could relieve itself.Conclusion The successful rate of double-balloon enteroscopy examination is high,the detection rate of intestine diseases is high,double-balloon enteroscopy is relatively safe,so it has high diagnostic value for detecting small intestine diseases.
Endoscopy,gastrointestinal;Intestinal diseases;Crohn disease;Intestinal neoplasms;Diagnosis
R 574.5
B
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.03.023
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81001112);广州市科技局珠江科技新星项目资助(2012J2200019)
510080广东省广州市,广东省人民医院(广东省医学科学院)消化科
马娟,510080广东省广州市,广东省人民医院(广东省医学科学院)消化科;E-mail:mjlqh@163.com
2014-06-21;
2014-11-25)

