司来吉兰对帕金森病模型大鼠黑质纹状体TH及GDNF表达的影响
吕超男,毛文静,马原源,刘斌,张晋霞,孙静,成晓华,李世英
司来吉兰对帕金森病模型大鼠黑质纹状体TH及GDNF表达的影响
吕超男,毛文静,马原源,刘斌△,张晋霞,孙静,成晓华,李世英
目的观察司来吉兰对帕金森病(PD)模型大鼠黑质纹状体内酪氨酸羟化酶(TH)及胶质细胞源性神经营养因子(GDNF)表达的影响,探讨司来吉兰对多巴胺能神经元的保护作用及机制。方法72只健康雄性SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组和司来吉兰组,每组均设4 d和8 d 2个亚组,各12只。模型组和司来吉兰组采用颈背部皮下注射鱼藤酮制备PD模型,对照组皮下注射等体积葵花油。之后司来吉兰组每日灌胃咪多吡0.5 mg/kg,模型组和对照组每日灌胃等体积生理盐水,4 d和8 d组分别连续灌胃4 d和8 d。采用免疫组化法和Western blotting法检测黑质纹状体TH和GDNF表达水平。结果免疫组化法和Western blotting法检测结果均显示,对照组大鼠黑质纹状体可见多量TH阳性细胞表达和少量GDNF阳性细胞表达,8 d和4 d组差异均无统计学意义。模型组TH和GDNF阳性细胞表达均明显低于对照组(均P<0.05),8 d和4 d组差异均无统计学意义。司来吉兰组TH阳性细胞表达低于对照组而高于模型组,GDNF阳性细胞表达高于对照组和模型组(均P<0.05),且8 d组均高于4 d组(均P<0.05)。结论司来吉兰可减轻PD模型大鼠黑质纹状体多巴胺能神经元的损伤,其作用机制可能与增加GDNF表达有关。
帕金森病;酪氨酸单氧化酶;胶质细胞源性神经营养因子;多巴胺;单胺氧化酶抑制剂;酪氨酸羟化酶;司来吉兰
帕金森病(Parkinson's disease,PD)是好发于中、老年人的慢性神经系统变性疾病[1],其主要病理变化是中脑黑质纹状体通路多巴胺能神经元变性死亡,导致纹状体内多巴胺(DA)水平不足。研究表明胶质细胞源性神经营养因子(glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor,GDNF)可明显改善多巴胺细胞和神经纤维的数量,恢复DA表达水平,运动症状也明显改善,提示GDNF可对黑质纹状体起保护和修复作用,并已成为治疗PD的新尝试[2]。单胺氧化酶B (MAO-B)抑制剂能够专一性抑制DA分解,维持脑内DA水平,延缓PD患者症状的发展,具有保护神经的作用[3-4]。司来吉兰作为一种选择性的单胺氧化酶B抑制剂,能保护黑质细胞免于各种神经毒素的侵害[5],但其作用机制还尚不清楚。本研究采用颈背部皮下注射鱼藤酮制备PD模型大鼠,观察司来吉兰对PD模型大鼠黑质纹状体内酪氨酸羟化酶(tyro⁃sine hydroxylase,TH)及GDNF表达的影响,探讨司来吉兰对多巴胺能神经元的保护作用及其机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
1.1.1实验动物清洁级健康雄性SD大鼠72只,体质量250~300 g,购自北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司,动物合格证编号11400500000020,设施许可证编号syxk(冀)2010-0038。在河北联合大学屏障环境动物实验室自由进食喂养,室温控制在(23±2)℃,自然光照,实验前适应喂养2周。
1.1.2主要试剂及仪器盐酸司来吉兰(咪多吡,Eldepryl,批准文号:H20040400),片剂,规格5 mg/片,产地:Orion Cor⁃poration Espoo,Finland;鱼藤酮(批号201212)、SP-0023免疫组化试剂盒(批号201302)、兔抗大鼠TH抗体和兔抗大鼠GDNF抗体均购自北京博奥森生物工程有限公司;DAB显色液购自北京中杉生物有限公司;SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳低分子质量标准蛋白购自华美生物公司;高速台式离心机购自上海安亭科学仪器厂。葵花油购自当地超市。
1.2方法
1.2.1动物分组采用随机数字表法将72只大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组和司来吉兰组,3组均分别设4 d和8 d 2个亚组,每个亚组12只(其中6只用于免疫组化检测,6只用于Western blotting检测)。
1.2.2动物模型制备与给药采用颈背部皮下注射鱼藤酮制备PD模型大鼠[6]。鱼藤酮以葵花油配制成乳液,充分震荡混匀后避光保存。模型组和司来吉兰组大鼠称质量后以鱼藤酮2 mg/kg体质量计算鱼藤酮葵花油乳液用量。捏起大鼠颈背部皮肤,用1 mL注射器皮下注射鱼藤酮葵花油乳液。对照组皮下注射等体积葵花油。行为学评分:1分,大鼠出现拒捕行为减弱、竖毛、毛色变黄变脏、弓背、主动活动减少;2分,有1分的表现,且主动活动减少明显、动作迟缓,并有震颤,或有步态不稳;4分,有2分的表现,且步态不稳,或不能直线行走、或行步时向一侧旋转;6分,向单侧斜卧,单侧前肢和(或)后肢瘫痪,行走困难、进食困难;8分,单侧,前肢和(或)后肢完全瘫痪,四肢拘挛,体质量大幅度减轻,不能进食;10分,濒死状态或死亡[7]。本实验选取2~6分大鼠入选PD模型。之后司来吉兰组每日灌胃咪多吡0.5 mg/kg,模型组和对照组每日灌胃等体积生理盐水,4 d和8 d 2个亚组分别连续灌胃4 d和8 d。
1.2.3标本制备 (1)免疫组化标本制备。用10%水合氯醛(4 mL/kg)腹腔麻醉动物,将动物后仰卧固定,然后开胸,左心室穿刺,剪开右心耳,快速灌注生理盐水100~200 mL(4℃)至肝脏完全变白,右心耳流出澄清液体后,继之灌入含4%多聚甲醛0.1 mol/L的PBS(pH 7.4,4℃)200~400 mL,先快后慢灌注,至大鼠肝脏变硬,肢体僵直,即固定完成,约1~2 h。然后完整取出鼠脑后再投入4%多聚甲醛0.1 mol/L的PBS(pH 7.4,4℃)过夜固定保存。然后依据大鼠脑解剖图谱在大鼠黑质纹状体取材,进行常规脱水、石蜡包埋。选择4 μm厚度连续切片,捞片后置60℃的烤箱中烘干备用。(2)Western blotting标本制备。用10%水合氯醛(0.3 mL/100 g)对大鼠进行深度麻醉。断头后于冰上开颅取脑,用冷的PBS漂洗残余血,立即分离出新鲜黑质纹状体,将黑质纹状体组织置于15 mL离心管中,组织匀浆机12 000 r/min匀浆15 s,加入4℃预冷的组织裂解液,振荡混匀,4℃作用30 min后,将细胞悬液置4℃低温离心12 000 r/min,离心10 min后取上清液4℃保存。经蛋白定量后分装,用4℃预冷的PBS调蛋白浓度到一致(750 mg/L),加入等体积的上样缓冲液,在沸水中至少煮5 min,置于4℃备用。
1.2.4检测方法 (1)免疫组化法。取各组制备好的黑质纹状体组织切片,加入正常羊血清封闭液中,分别滴加兔抗大鼠TH一抗(1∶200)、兔抗大鼠GDNF一抗(1∶200)4℃过夜,滴加二抗和适量辣根酶标记链霉卵白素工作液,进行DAB显色。按试剂说明书操作要求检测各组TH和GDNF蛋白表达。光镜下观察,胞浆呈棕黄色,核呈浅蓝色或紫蓝色为阳性细胞。高倍镜下随机分别观察各组大鼠黑质纹状体不重叠的6视野,进行TH和GDNF阳性细胞计数。(2)West⁃ern blotting法。取各组制备好的黑质纹状体组织20 μg,10%十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)电泳分离后,以湿转法电转移至聚偏二氟乙烯膜(polyvinylidene flu⁃oride,PVDF)膜上。转移缓冲液(甘氨酸5.8 g,Tris 2.9 g,SDS 0.37 g,800 mL重蒸馏水溶解后加入200 mL甲醇)。转移后的PVDF膜放入封闭液中封闭,然后分别加入稀释好的兔抗大鼠TH一抗(1∶500)、兔抗大鼠GDNF一抗(1∶500)4℃孵育过夜。PBS洗膜,加人相应稀释好的二抗(羊抗兔,1∶2 000),37℃反应1 h,洗膜,以ECL显色,胶片曝光显影,使用Image J软件进行平均灰度值测定。
1.3统计学方法采用SPSS 13.0统计软件进行统计处理,所得数据以±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间多重比较采用LSD-t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1各组TH和GDNF免疫组化检测结果对照组大鼠黑质纹状体可见多量TH阳性细胞表达和少量GDNF阳性细胞表达,8 d和4 d组比较差异均无统计学意义。模型组TH和GDNF阳性细胞表达均明显低于对照组(均P<0.05),8 d和4 d组比较差异均无统计学意义。司来吉兰组TH阳性细胞表达低于对照组而高于模型组,GDNF阳性细胞表达高于对照组和模型组(均P<0.05),且8 d组均高于4 d组(均P<0.05)。见表1,图1、2。
Tab.1 The number of the positive expression of TH,GDNF in substantia nigra and striatum in each group表1 各组黑质纹状体TH和GDNF阳性细胞数 (n=6,个/视野,±s)

Tab.1 The number of the positive expression of TH,GDNF in substantia nigra and striatum in each group表1 各组黑质纹状体TH和GDNF阳性细胞数 (n=6,个/视野,±s)
*P<0.05;a与对照组比较,b与模型组比较,P<0.05
组别对照组模型组司来吉兰组F TH t 4 d 79.66±2.80 50.83±5.03a66.83±5.07ab74.824*8 d 78.16±6.40 50.33±5.16a72.33±4.41ab44.525*0.526 0.170 2.262*组别对照组模型组司来吉兰组F GDNF 4 d 15.83±2.31 12.67±1.63a19.50±2.59ab14.287*t 8 d 16.67±2.16 11.67±2.16a22.50±3.01ab26.106*0.644 0.905 2.255*
2.2各组TH和GDNF蛋白Western blotting检测结果对照组大鼠黑质纹状体可见多量TH阳性细胞表达和少量GDNF阳性细胞表达,8 d和4 d组比较差异均无统计学意义。模型组TH和GDNF阳性细胞表达均明显低于对照组(均P<0.05),8 d和4 d组比较差异均无统计学意义。司来吉兰组TH阳性细胞表达低于对照组而高于模型组,GDNF阳性细胞表达高于对照组和模型组(均P<0.05),且8 d组均高于4 d组(均P<0.05)。见表2,图3、4。
Tab.2 The expression of TH and GDNF in substantia nigra and striatum in each group表2 各组大鼠黑质纹状体TH和GDNF蛋白表达量 (n=6,±s)
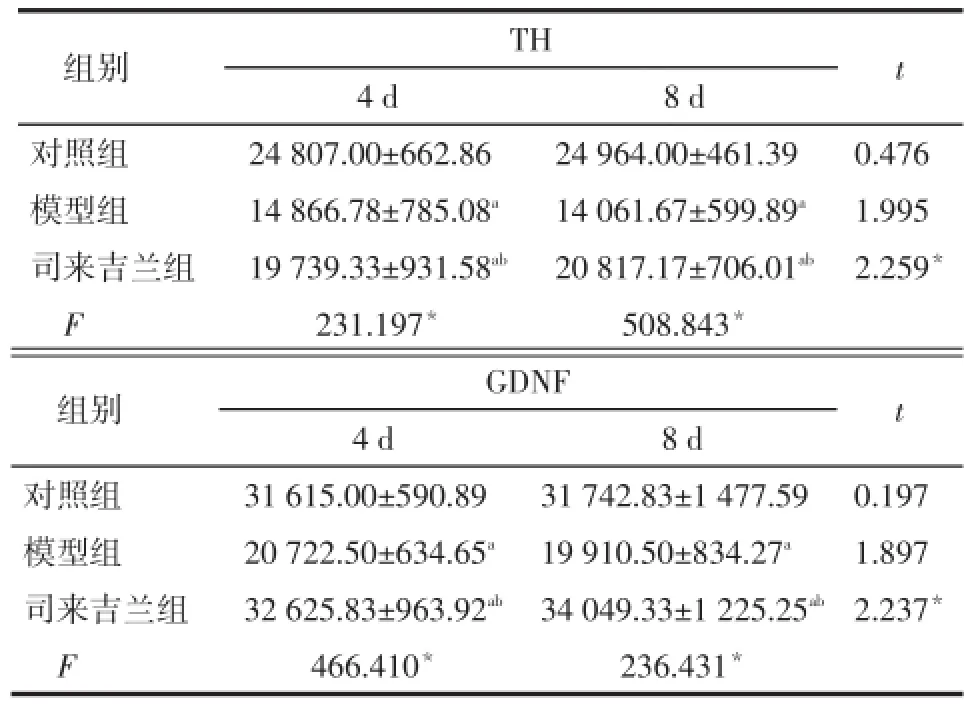
Tab.2 The expression of TH and GDNF in substantia nigra and striatum in each group表2 各组大鼠黑质纹状体TH和GDNF蛋白表达量 (n=6,±s)
*P<0.05;a与对照组比较,b与模型组比较,P<0.05
组别对照组模型组司来吉兰组F TH 4 d 24 807.00±662.86 14 866.78±785.08a19 739.33±931.58ab231.197*8 d 24 964.00±461.39 14 061.67±599.89a20 817.17±706.01ab508.843*t 0.476 1.995 2.259*组别对照组模型组司来吉兰组F GDNF 4 d 31 615.00±590.89 20 722.50±634.65a32 625.83±963.92ab466.410*8 d 31 742.83±1 477.59 19 910.50±834.27a34 049.33±1 225.25ab236.431*t 0.197 1.897 2.237*
3 讨论
采用颈背部皮下注射鱼藤酮的方法制备PD动物模型,能较好地模拟PD的慢性进行性病程和发病特点,已被广泛用于PD发病机制和治疗的研究[8]。本研究结果显示,造模后大鼠出现震颤、僵直、运动减少,活动迟缓,行步时向一侧旋转等行为学改变,大鼠黑质纹状体的TH显著减少,表明造模成功。
TH是脑内最重要的一条DA递质通路,即黑质-纹状体通路的起始步骤,在DA生物合成的调节中发挥重要作用[9]。已有研究显示,PD模型组动物TH阳性神经元较正常组动物显著减少[10]。本研究免疫组化法和Western blotting法检测结果均显示,模型组TH阳性细胞表达明显低于对照组,8 d组在数值上低于4 d组,但差异无统计学意义;司来吉兰组TH阳性细胞表达低于对照组,高于模型组,且8 d组高于4 d组,提示司来吉兰可以减轻PD模型大鼠黑质纹状体多巴胺能神经元的损伤,随着时间的延长,作用更明显。
神经营养因子在神经元的发育、分化、生存过程中的营养作用近年受到普遍重视[11]。GDNF是黑质纹状体通路中重要的靶源性神经营养因子,对多巴胺能神经元具有高效特异性营养活性,它通过增强细胞凋亡抑制基因的表达,并减少凋亡促进基因的表达,保护黑质多巴胺能神经元,并对其进行修复[12]。近来有研究表明GDNF可以通过激活PI3K/ Akt通路保护多巴胺能神经元[13]。既往研究显示用不同方式给予PD模型动物GDNF可以明显改善PD症状[1]。司来吉兰是一种选择性的单胺氧化酶B抑制剂,不仅能增加抗氧化酶的浓度、减轻细胞凋亡,还可以产生神经营养因子,如神经生长因子(NGF)、脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)、GDNF,阻止毒素的激活和自由基的形成,增强内源性和外源性DA的作用,延缓PD进展[14-15]。无论是用于早期PD患者的单药治疗,还是与其他PD治疗药物联合使用,均显示出较好的治疗效果[16]。本研究的免疫组化法和Western blotting法检测结果均显示,模型组GDNF阳性细胞表达明显低于对照组,8 d组在数值上低于4 d组,但差异无统计学意义,提示GDNF在PD的发病过程中发挥重要作用;司来吉兰组GDNF阳性细胞表达高于对照组和模型组,且8 d组高于4 d组,提示司来吉兰可以增加PD模型大鼠黑质纹状体GDNF阳性细胞表达,随着时间的延长,作用更明显。
综上所述,司来吉兰可减轻PD模型大鼠黑质纹状体多巴胺能神经元的损伤,其作用机制可能与增加GDNF表达有关。
(图1~4见插页)
[1]Wang Y,Wang WZ,Zhao ZX.Application and assessment of quality of life questionnaires in Parkinson's disease[J].Chin J Contemp Neurol Neurosurg,2014,14(4):286-290.[王雁,王文昭,赵忠新.帕金森病生活质量量表应用及评价[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2014,14(4):286-290].
[2]PatelNK,PaveseN,JavedS,etal.Benefits of putaminal GDNF infu⁃sioninParkinson disease are maintained after GDNF cessation[J]. Neurology,2013,81(13):1176-1178.doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a 55ea5.
[3]Zhao Q,Cai D,Bai Y.Selegiline rescues gait deficits and the loss of dopaminergic neurons in a subacute MPTP mouse model of Parkin⁃son's disease[J].Int J Mol Med,2013,32(4):883-891.doi:10.3892/ ijmm.2013.1450.
[4]Cesaro P,Defebvre L.Drug treatment of early-stage(de novo and "honeymoon")Parkinson disease[J].Rev Neurol(Paris),2014,170 (4):237-246.doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2013.10.015.
[5]Weinreb O,Amit T,Saqi Y,et al.Genomic and proteomic study to survey the mechanism of action of the anti-Parkinson's disease drug,rasagiline compared with selegiline,in the rat midbrain[J].J Neural Transm,2009,116(11):1457-1472.doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0225-x.
[6]Chang YT,Luo XG,Ren Y,et al.Behavior alteration and damage of dopaminergic neurons of substantia nigra caused by rotenone in rats [J].Progress of Anatomical Sciences,2011,17(1):60-62.[常宇涛,罗晓光,任艳,等.鱼藤酮损伤大鼠黑质至行为学及黑质多巴胺能神经元损伤[J].解剖科学进展,2011,17(1):60-62].
[7]Chen X,Zhang N,Zhao H,et al.Relations of pathological lesions of the substantia nigra and behavior in rats rotenone-induced with Par⁃kinson's disease[J].Chinese Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseas⁃es,2008,34(4):232-234.[陈忻,张楠,赵晖,等.鱼藤酮致帕金森病大鼠行为学与黑质病理损伤的关系[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2008,34(4):232-234].
[8]CarriereCH,KangNH,NilesLP.Neuroprotectionbyvalproicacidinan intrastriatal rotenone model of Parkinson's disease[J].Neuroscience,2014,267(16):114-121.doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.028.
[9]Zhang Y,Zhang ZJ,Yu XL,et al.Protective effects of the intracere⁃bral transfer of the lentiviral-mediated GDNF and TH bi-gene on the basis of improved Tet-on system in a rat model of Parkinson's disease[J].Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin,2011,27(2):234-239.[张阳,张志坚,俞晓岚,等.慢病毒介导的新型Tet-On系统大鼠GDNF和TH双基因脑内转移对帕金森病大鼠模型的保护作用[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(2):234-239].
[10]Ding YX,Hou LQ,Xiong KR.Effect of electroacupuncture on ex⁃pression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and glial fibrillary acid⁃ic protein in subventricular zone of Parkinson's disease rats[J]. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu(Acupunce Res,Chin),2012,37(4):286-290.
[11]Chen J,Jiao SS,Liang CR,et al.Inhibitory effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor on viability and neurite growth of mu⁃rine hippocampal neurons[J].Med J Chin PLA,2014,39(9):690-694.[陈甲,矫树生,梁春荣,等.脑源性神经营养因子前体对小鼠海马神经元存活和突起生长的抑制作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2014,39(9):690-694].
[12]Sterky FH,Pernold K,Harvey BK,et al.Glial cell line-derived neu⁃rotrophic factor partially ameliorates motor symptoms without slow⁃ing neurodegeneration in mice with respiratory chain-deficient do⁃pamine neurons[J].Cell Transplant,2013,22(9):1529-1539.doi: 10.3727/096368912X657693.
[13]Zuo T,Qin JY,Chen J,et al.Involvement of N-cadherin in the pro⁃tective effect of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on dopa⁃minergic neuron damage[J].Int J Mol Med,2013,31(3):561-568. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2013.1226.
[14]Naoi M,Maruyama W.Monoamine oxidase inhibitors as neuropro⁃tective agents in age-dependent neurodegenerative disorders[J]. Curr Pharm Des,2010,16(25):2799-2817.
[15]Kare P,Bhat J,Sobhia ME.Structure-based design and analysis of MAO-B inhibitors for Parkinson's disease:using in silico ap⁃proaches[J].Mol Divers,2013,17(1):111-122.doi:10.1007/ s11030-012-9420-z.
[16]Jiang YP,Jiang WW.The development of clinical trial and safety of Selegiline[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical Neurosciences,2012,20 (4):424-433.[蒋雨平,蒋雯巍.司来吉兰的临床研究进展及安全性[J].中国临床神经科学,2012,20(4):424-433].
(2014-03-13收稿2014-10-11修回)
(本文编辑陈丽洁)
Effects of Eldepryl on TH and GDNF expressions in substantia nigra and striatum in Parkinson's disease model in rat
LYU Chaonan,MAO Wenjing,MA Yuanyuan,LIU Bin△,ZHANG Jinxia,SUN Jing,CHENG Xiaohua,LI Shiying
First Department of Neurology,the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei United University,Tangshan 063000,China
△Corresponding AuthorE-mail:liubintsh@126.com
ObjectiveTo observe the effects of Eldepryl on expressions of tyrosine hydroxylase(TH)and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor(GDNF)in substantia nigra and striatum in Parkinson's disease(PD)and to explore the protective mechanism of Eldepryl on dopaminergic neuron.MethodsHealthy male Sprague-Dawley(SD)rats(n=72)were randomly divided into control group,model group and Eldepryl group(n=24 in each group).Each group was divided random⁃ly into 2 subgroups as 4 day treatment group and 8 day treatment group(n=12 in each subgrop).Pakinson's disease model was established by injecting rotenone subcutaneously back the neck,rats in the control group were injected with an equal vol⁃ume of sunflower oil subcutaneously at the same location.Rats in the Eldepryl group were then given Eldepryl 0.5 mg·kg-1in⁃tragastrically every day for 4 or 8 consecutive days and rats in model group and control group were given an equal volume of saline instead.The expression of TH and GDNF in substantia nigra and striatum were detected by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting.ResultsImmunohistochemistry and Western blotting showed that strong expression of TH positive cells with little expression of GDNF positive cells were seen in substantia nigra and striatum in rats of control group,and there was no significant difference between subgroup of 8 day treatment and 4 day treatment within control group.The expression of TH cells and GDNF were both significantly reduced in model group compared with those in control group(both P<0.05),and there was no significant difference between subgroup of 8 day treatment and 4 day treatment within each group.The ex⁃pression of TH positive cells were significantly reduced in Eldepryl group compared with those in control group,and were sig⁃nificantly increased compared with those in model group.The expression of GDNF positive cells were significantly increasedin Eldepryl group compared with those in control group and model group(all P<0.05).And there were significantly more ex⁃pression of TH positive cells and GDNF positive cells at subgroup of 8 day treatment compared with those at subgroup of 4 day treatment within Eldepryl group with(all P<0.05).ConclusionThese data suggest that Eldepryl can protect the dam⁃age of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra and striatum of PD rats.And its therapeutic mechanism may be associated with increased expression of GDNF.
Parkinson's disease;tyrosine 3-monooxygenase;glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor;dopamine;monoamine oxidase inhibitors;tyrosine hydroxylase;Eldepryl
R742.5
ADOI:10.11958/j.issn.0253-9896.2015.02.011
河北省医学科学研究重点课题(20130064)
河北联合大学附属医院神经内一科(邮编063000)
吕超男(1986),女,医师,硕士,主要从事神经变性疾病方面研究
△E-mail:liubintsh@126.com

