线粒体分裂在甲状腺鳞癌SW579细胞增殖、凋亡以及侵袭中的作用
申菲菲,郭睿,赵树鹏,齐凤杰△,孟翠丽
线粒体分裂在甲状腺鳞癌SW579细胞增殖、凋亡以及侵袭中的作用
申菲菲1,郭睿2,赵树鹏3,齐凤杰1△,孟翠丽1
目的研究线粒体动力学蛋白Mfn2和Drp1在甲状腺鳞癌SW579细胞中的表达和线粒体分裂抑制剂-1 (Mdivi-1)对SW579细胞增殖、凋亡及侵袭能力的影响。方法采用RT-PCR检测Mfn2和Drp1 mRNA,Western blot检测Mfn2和Drp1蛋白在Nthy-ori 3-1和SW579两种细胞中的表达;然后将SW579分为对照组(DMSO,0.1%)和Mdivi-1低、中、高剂量组(浓度分别为15、30、45 μmol/L),培养16 h,采用MTT法检测细胞增殖能力的变化,用荧光分光光度计检测线粒体膜电位的变化,用RT-PCR检测细胞色素C(Cyt C)和Caspase-3 mRNA的变化,Western blot检测Cyt C和Caspase-3蛋白的变化,用Transwell小室侵袭实验检测侵袭能力的变化。结果与Nthy-ori 3-1细胞系相比,SW579细胞系中Mfn2 mRNA和蛋白表达明显降低,Drp1 mRNA和蛋白表达明显升高(P<0.01);与对照组相比,Mdivi-1各组SW579细胞存活率和线粒体膜电位均明显降低,Cyt C和Caspase-3的mRNA及蛋白表达均明显增加,侵袭能力明显减弱(均P<0.01),并且呈药物浓度依赖性。结论甲状腺鳞癌SW579细胞中存在线粒体动力学异常,Mdivi-1可以抑制此细胞的增殖和侵袭,并能诱导其凋亡。
甲状腺肿瘤;癌,鳞状细胞;细胞增殖;细胞凋亡;线粒体动力学;Mdivi-1;Mfn2;Drp1
甲状腺癌是最常见内分泌系统恶性肿瘤[1],近年来,我国甲状腺癌发病率呈逐年上升趋势,而且其复发率和死亡率较高,这导致其治疗难度明显增加[2]。以前大量研究证实癌症中存在线粒体功能改变,针对恢复线粒体的功能或者促进线粒体诱导的细胞死亡等线粒体靶向治疗是提高癌症治疗效果的重要方法。最近越来越多的学者发现线粒体动力学在肿瘤生物学中也发挥着非常重要的作用[3-5]。线粒体动力学包括线粒体融合与分裂。在哺乳动物细胞中,Mfn1/2以及Opa1参与了线粒体外膜和内膜融合的调控,而Drp1和Fis1是控制线粒体外膜分裂的重要分子[6]。虽然已有研究证实在肺癌和乳腺癌存在着线粒体动力学变化[4,7],但目前尚鲜见有关线粒体动力学在甲状腺癌中的报道。本文旨在检测SW579细胞系中线粒体动力学蛋白变化以及不同浓度的线粒体分裂抑制剂-1(Mdivi-1)对其增殖能力、线粒体膜电位、凋亡相关蛋白表达及其侵袭能力的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1实验材料 (1)实验细胞。SV40大T抗原永生化人正常甲状腺细胞系Nthy-ori 3-1购自英国HPACC细胞中心,甲状腺鳞癌细胞系SW579,购于上海生命科学院细胞和生物化学研究所。(2)主要试剂。L15培养液(大连宝生物公司),RMPI 1640培养基(Hyclone公司),Mdivi-1(Sigma-Aldrich公司),二甲基亚砜(DMSO,Amresco公司),线粒体膜电位检测JC-1试剂盒(C2006)和RIPA裂解液(P0013B)均购自碧云天公司,Mfn2 Antibody(H-68),Drp1 Antibody(H-300),细胞色素C(Cyt C)Antibody(H-104),Caspase-3 Antibody(H-277),β-actin Antibody(C4),goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP均购自santa⁃cruz;PCR引物由上海生工生物工程股份有限公司合成,Trizol RNA提取试剂盒和Prime Script RT-PCR Kit(Cat No. DRR014A,大连宝生物公司)。(3)主要仪器。24孔Transwell小室(Corning,costar),Matrigel(BD公司),全自动酶标仪和电泳仪(Bio-Rad公司),高速冷冻离心机(Eppendorf公司),倒置显微镜(OLYMPUS公司),荧光分光光度计970CRT(上海分析仪器总厂),-80℃超低温冰箱(Thermo公司)。
1.2方法
1.2.1细胞培养及分组甲状腺鳞癌细胞系SW579置于含10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养基,饱和湿度、37℃、5%CO2的条件下进行传代培养。SV40大T抗原永生化人正常甲状腺细胞系Nthy-ori 3-1的培养条件与SW579细胞系相同。2种细胞系均2~3 d换液1次,3~5 d传代1次,当细胞处于对数生长期时以1×105个/mL浓度接种于25 cm2的培养瓶,24 h后待细胞贴壁后检测Mfn2、Drp1。选取贴壁后SW579细胞系,将其用胰酶消化、重悬后计数并分为对照组(DMSO,0.1%)和Mdivi-1组,其中Mdivi-1组再分为3个亚组:低剂量组(15 μmol/L)、中剂量组(30 μmol/L)和高剂量组(45 μmol/L),每组设6个复孔。先根据培养基体积算出各组所需的DMSO体积和Mdivi-1质量,然后将两者混合充分溶解,24 h后待细胞贴壁后,分别加入所配好的Mdivi-1溶液至培养基中,使Mdivi-1终浓度分别为0(对照组)、15、30、45 μmol/L,每组DMSO终浓度为0.1%,连续处理SW579细胞16h,然后进行相关检测。
1.2.2RT-PCR检测以1×105个/mL浓度接种于25 cm2的培养瓶,待24 h细胞贴壁后给药处理16 h,然后参照Trizol RNA提取试剂盒提取各组细胞总RNA,进行RNA含量测定。当A260/A280比值达1.9~2.1时可用于逆转录反应。参照Prime Script RT-PCR Kit说明书上的操作步骤进行逆转录合成cDNA及PCR扩增过程。引物序列见表1。取PCR产物10 μL进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳并拍照,应用EDAS290凝胶成像分析系统进行灰度测量,以每一样品与其内参GAPDH灰度比值表示目的基因mRNA表达水平。

Tab.1 RT-PCR primer sequences and the expected fragment sizes表1 RT-PCR引物序列及片段大小
1.2.3Western blot检测用RAPI裂解液提取各组细胞总蛋白,用BCA法测蛋白浓度后于10%或者15%SDS-PAGE上电泳分离,上样量为30 μg,然后转印至PVDF膜上;1% BSA室温封闭1 h,再分别用Mfn2一抗(1∶1 000)、Drp1一抗(1∶1 000)、Cyt-C一抗(1∶500),Caspase-3(1∶500)和β-actin一抗(1∶1 000)4℃孵育过夜;TBST 5 min×3次;然后用山羊抗兔IgG二抗(1∶2 000)室温孵育1 h;再TBST 5 min×3次;用增强型ECL化学液发光,凝胶成像系统曝光。用Image J软件求出Drp1、Mfn2、Cyt-C和β-actin的灰度值,并求出Drp1、Mfn2、Cyt-C与β-actin的比值,以反映Drp1、Mfn2、Cyt-C蛋白的相对表达水平。
1.2.4MTT法检测细胞存活率按每孔100 μL种于96孔板,每孔含1×104细胞,每组设6个复孔。待24 h细胞贴壁后给药处理16 h,每孔加入15 μL MTT,再继续培养4 h,然后弃孔中液体,每孔加入150 μL DMSO,37℃避光孵育30 min,用酶联免疫检测仪吸光度(A)值,根据A值计算出细胞存活率:细胞存活率(%)=(实验组A570-调零孔A570)/(对照组A570-调零孔A570)×100%。以上实验重复6次。
1.2.5线粒体膜电位检测参照线粒体膜电位检测试剂盒(JC-1)说明书中的悬浮细胞线粒体膜电位检测方法,用荧光分光光度计对各组线粒体膜电位进行检测。按每孔100 μL种于96孔板,每孔含1×105细胞,每组设6个复孔。待24 h细胞贴壁后给药处理16 h,然后将各组SW579细胞重悬于0.5 mL细胞培养液中,加入0.5 mL JC-1染色工作液,颠倒数次混匀。细胞培养箱中37℃孵育20 min。37℃孵育结束后,600×g 4℃离心4 min,沉淀细胞。用1 mL JC-1染色工作液重悬细胞,600×g 4℃离心4 min,沉淀细胞,弃上清,重复上述重悬洗涤过程一次。最后用适量JC-1染色工作液重悬并进行检测。
1.2.6Transwell小室侵袭实验将Transwell小室放入24孔板孔洞中,小室内为上室,24孔板孔洞为下室,中间有聚碳酸酯膜相隔,在聚碳酸酯膜上室侧铺盖基质胶(Matrigel)。待24 h细胞贴壁后给药处理16 h,然后从各组中取1×105个SW579细胞用100 μL无血清的RPMI 1640重悬后加入上室;下室放置500 μL含10%FBS的RPMI 1640,37℃,5%CO2及饱和湿度条件下培养24 h,当下室底部出现穿过Transwell上小孔的癌细胞时,对下室侧癌细胞进行HE染色。在光镜下计数穿过聚碳酸酯膜肿瘤细胞数,然后计算出侵袭率[8]。
1.3统计学方法采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析,所得数据均以均数±标准差(±s)表示,2组之间比较采用t检验;多组之间比较采用单因素方差分析,多重比较采用LSD-t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
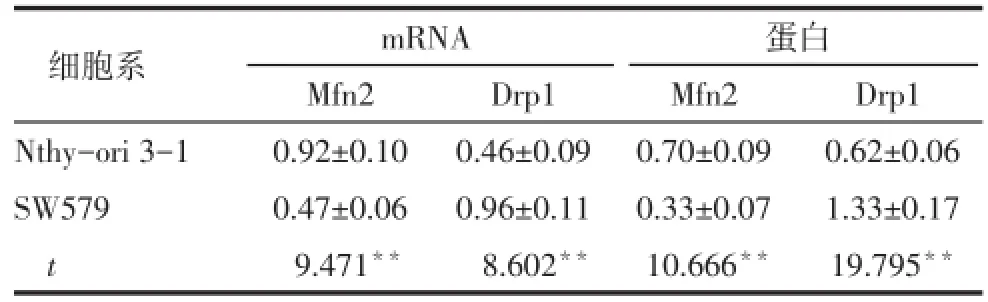
2.1SW579和Nthy-ori 3-1细胞Mfn2和Drp1表达水平比较与Nthy-ori 3-1细胞相比,SW579细胞中Mfn2 mRNA及蛋白明显降低,Drp1 mRNA及蛋白明显升高(均P<0.01),见图1、表2。
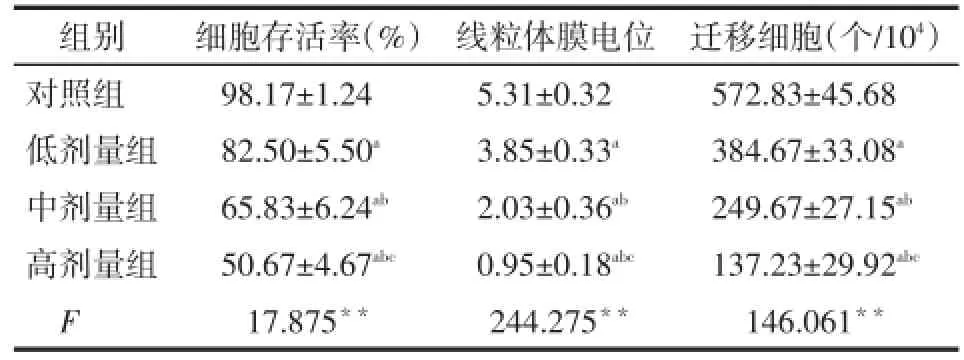
2.2Mdivi-1对SW579细胞系增殖能力、线粒体膜电位和侵袭能力的影响与对照组相比,Mdivi-1各组细胞存活率、线粒体膜电位均明显降低,侵袭率明显减弱(均P<0.01),且呈药物浓度依赖性,见表3。
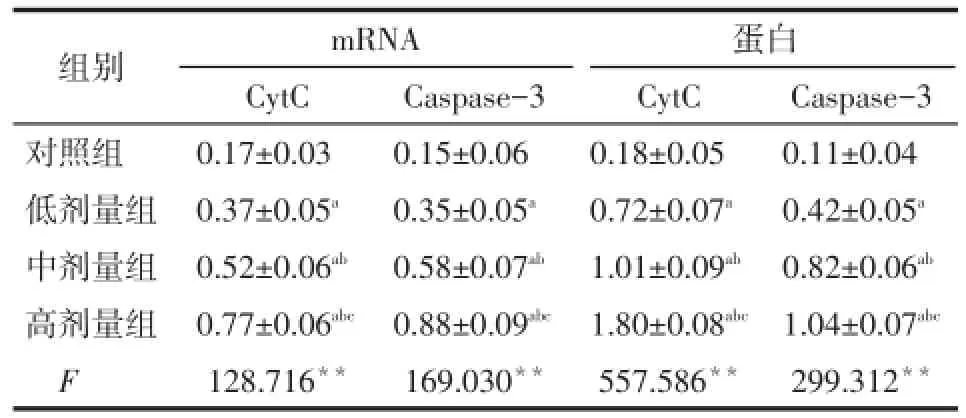
2.3Mdivi-1对SW579细胞系中CytC、Caspase-3表达水平的影响与对照组相比,Mdivi-1各组中CytC和Caspase-3的mRNA及蛋白表达明显升高(均P<0.01),且呈药物浓度依赖性,见图2、表4。
3 讨论
甲状腺癌是最常见的内分泌系统恶性肿瘤,占癌症死亡的0.20%,占所有恶性肿瘤的3.00%[9-10]。近年来,我国甲状腺癌的发病率呈逐年上升的趋势。目前大量研究证实线粒体动力学参与了癌症的调控,而且抑制线粒体分裂对癌症的增殖,侵袭转移有着明显的抑制作用[3-5,7]。虽然近年来对甲状腺癌分子发病机制有了深入的研究,但是目前尚鲜见有关线粒体动力学在甲状腺癌调控中的报道。
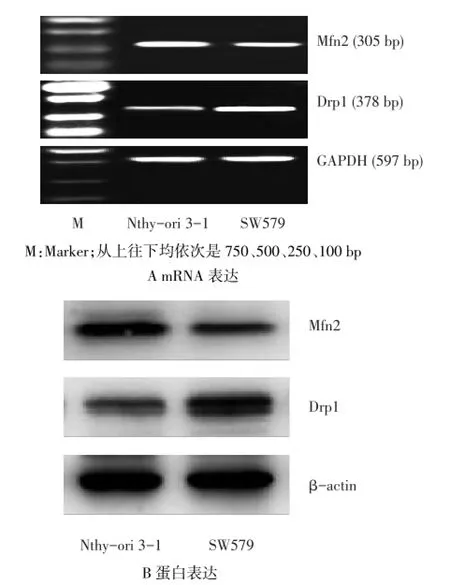
Fig.1 The transcription and expression levels of Mfn2,Drp1 mRNA (A)and protein(B)in SW579 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cell lines图1 SW579和Nthy-ori 3-1细胞中Mfn2、Drp1的mRNA及蛋白表达
Tab.2 The transcription and expression of Mfn2,Drp1 mRNA and protein in SW579 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cell lines表2 SW579和Nthy-ori 3-1细胞中Mfn2、Drp1的mRNA及蛋白表达水平 (n=6,±s)
Tab.2 The transcription and expression of Mfn2,Drp1 mRNA and protein in SW579 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cell lines表2 SW579和Nthy-ori 3-1细胞中Mfn2、Drp1的mRNA及蛋白表达水平 (n=6,±s)
**P<0.01
细胞系Nthy-ori 3-1 SW579 t mRNA Mfn2 0.92±0.10 0.47±0.06 9.471**Drp1 0.46±0.09 0.96±0.11 8.602**蛋白Mfn2 0.70±0.09 0.33±0.07 10.666**Drp1 0.62±0.06 1.33±0.17 19.795**
Tab.3 The effects of Mdivi-1 with different concentrations on proliferation,mitochondrial membrane potential and invasion rate in SW579 cell lines表3 不同浓度Mdivi-1对SW579细胞细胞存活率、线粒体膜电位和侵袭率的影响 (n=6,±s)
Tab.3 The effects of Mdivi-1 with different concentrations on proliferation,mitochondrial membrane potential and invasion rate in SW579 cell lines表3 不同浓度Mdivi-1对SW579细胞细胞存活率、线粒体膜电位和侵袭率的影响 (n=6,±s)
**P<0.01;a与对照组比较,b与低剂量组比较,c与中剂量组比较,P<0.01;表4同
组别对照组低剂量组中剂量组高剂量组F细胞存活率(%)98.17±1.24 82.50±5.50a65.83±6.24ab50.67±4.67abc17.875**线粒体膜电位5.31±0.32 3.85±0.33a2.03±0.36ab0.95±0.18abc244.275**迁移细胞(个/104)572.83±45.68 384.67±33.08a249.67±27.15ab137.23±29.92abc146.061**
线粒体是一个动态变化的细胞器,不断地进行移动,融合与分裂,这些过程统称线粒体动力学[11]。目前多数研究发现线粒体动力学失调与癌症之间存在明显的相关性[5]。Rehman等[4]在非小细胞肺癌细胞系A549中发现Mfn2明显降低和Drp1明显升高,与邻近的非癌组织相比,肺癌组织样本中Mfn2表达量明显降低,Drp1的总量和磷酸化水平明显升高,这些结果表明肺癌组织中线粒体呈分裂趋势。最重要的是,当他们把癌细胞中线粒体分裂情况逆转之后,体内和体外癌细胞的生长均受到明显地抑制。与之类似的是,Zhao等[7]研究表明Drp1介导的线粒体分裂参与了乳腺癌的侵袭和转移调节。

Fig.2 The effects of Mdivi-1 with different concentrations on the expression and transcription of CytC,Caspase-3 mRNA(B)and protein(B)in SW579 cell lines图2 不同浓度Mdivi-1对SW579细胞系中CytC、Caspase-3的mRNA及蛋白表达的影响
Tab.4 The effects of Mdivi-1 with different concentrations on the expression and transcription of CytC,Caspase-3 mRNA and protein in SW579 cell lines表4 不同浓度Mdivi-1对SW579细胞系中CytC、Caspase-3的mRNA及蛋白表达的影响 (n=6,±s)
Tab.4 The effects of Mdivi-1 with different concentrations on the expression and transcription of CytC,Caspase-3 mRNA and protein in SW579 cell lines表4 不同浓度Mdivi-1对SW579细胞系中CytC、Caspase-3的mRNA及蛋白表达的影响 (n=6,±s)
组别对照组低剂量组中剂量组高剂量组F mRNA CytC 0.17±0.03 0.37±0.05a0.52±0.06ab0.77±0.06abc128.716**Caspase-3 0.15±0.06 0.35±0.05a0.58±0.07ab0.88±0.09abc169.030**蛋白CytC 0.18±0.05 0.72±0.07a1.01±0.09ab1.80±0.08abc557.586**Caspase-3 0.11±0.04 0.42±0.05a0.82±0.06ab1.04±0.07abc299.312**
本研究发现SW579细胞系较Nthy-ori 3-1细胞系中Drp1核酸和蛋白水平均表达明显升高,Mfn2核酸和蛋白水平均表达显著降低,表明甲状腺鳞癌SW579细胞系中可能存在着线粒体分裂过度和线粒体融合受抑制现象,提示线粒体动力学异常可能在甲状腺癌发生及侵袭转移方面有重要作用[5],这支持了Inoue-Yamauchi[3]和Rehman等[4]的研究。
Mdivi-1是一种喹诺酮类衍生物,可以通过抑制Drp1的GTP酶活性来抑制线粒体分裂[12]。目前Mdivi-1被广泛用于多种疾病的治疗中,如急性肾损伤,心肌局部缺血/再灌注损伤和帕金森病等[12],但是在癌症治疗方面研究较少。Inoue-Yamauchi等[3]用siRNA抑制线粒体分裂蛋白Drp1后CytC表达量增多,大肠癌细胞凋亡明显增加。Rehman等[4]的体内试验发现Mdivi-1可以抑制肺癌细胞生长,这提示抑制癌细胞中线粒体分裂对癌症的治疗起到重要的作用。本研究发现Mdivi-1能浓度依赖性抑制SW579细胞增殖,这可能与抑制癌细胞线粒体分裂,进而抑制细胞G1/S过渡期后的顺利进行,最终抑制了细胞增殖[13];线粒体膜电位对线粒体正常功能维持是很重要的[14]。线粒体膜电位的降低是细胞凋亡级联反应过程中最早发生的事件[4]。本研究发现Mdivi-1能诱导SW579细胞系的线粒体膜电位降低,促进了CytC和Caspase-3核酸及蛋白水平的高表达,这表明Mdivi-1可能通过抑制线粒体过度分裂,降低线粒体膜电位,促进线粒体促凋亡因子CytC的表达,导致Caspase-3表达增多,最终促进了SW579癌细胞凋亡[3-4]。值得注意的是,本研究还显示Mdivi-1能浓度依赖性地抑制SW579细胞系的侵袭转移能力,这可能是由于Mdivi-1通过抑制癌细胞中线粒体分裂来减少线粒体数目,并且抑制线粒体重分布到细胞边缘,抑制细胞板状伪足的形成,最终对细胞的侵袭转移发挥抑制作用[15]。这些结果提示靶向抑制甲状腺癌组织中线粒体分裂蛋白Drp1可能是治疗甲状腺癌的一个新方法,但是抑制线粒体分裂是否对甲状腺癌动物模型也发挥着类似的作用有待进一步证实。
综上,Mdivi-1能浓度依赖性地抑制SW579细胞增殖及侵袭并诱导其凋亡,这提示线粒体分裂可能参与了甲状腺癌细胞增殖、凋亡及侵袭的调控,为甲状腺癌的机制及治疗研究提供一种新的思路。抑制甲状腺癌细胞中线粒体分裂有望成为治疗甲状腺癌的重要手段。
[1]Chen W,Zheng R,Zhang S,et al.Report of incidence and mortality in china cancer registries,2009[J].Chin J Cancer Res,2013,25(1): 10-21.
[2]Tuttle RM,Ball DW,Byrd D,et al.Thyroid carcinoma[J].J Natl Compr Canc Netw,2010,8(11):1228-1274.
[3]Inoue-Yamauchi A,Oda H.Depletion of mitochondrial fission fac⁃tor drp1 causes increased apoptosis in human colon cancer cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2012,421(1):81-85.
[4]Rehman J,Zhang HJ,Toth PT,et al.Inhibition of mitochondrial fis⁃sion prevents cell cycle progression in lung cancer[J].FASEB J,2012,26(5):2175-2186.
[5]Qian W,Wang J,Van Houten B.The role of dynamin-related pro⁃tein 1 in cancer growth:A promising therapeutic target[J]?Expert Opin Ther Targets,2013,17(9):997-1001.
[6]Chan DC.Mitochondrial fusion and fission in mammals[J].Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol,2006,22:79-99.
[7]Zhao J,Zhang J,Yu M,et al.Mitochondrial dynamics regulates mi⁃gration and invasion of breast cancer cells[J].Oncogene,2013,32 (40):4814-4824.
[8]Feng W,Jia S.Rapamycin inhibits the invasive ability of thyroid cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of vegf-c in vitro [J].Cell Biochem Funct,2012,30(6):487-491.
[9]Enewold L,Zhu K,Ron E,et al.Rising thyroid cancer incidence in the united states by demographic and tumor characteristics,1980-2005[J].Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev,2009,18(3):784-791.
[10]Siraj AK,Hussain AR,Al-Rasheed M,et al.Demethylation of tms1 gene sensitizes thyroid cancer cells to trail-induced apoptosis[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2011,96(1):E215-224.
[11]Westermann B.Mitochondrial fusion and fission in cell life and death[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2010,11(12):872-884.
[12]Lackner LL,Nunnari J.Small molecule inhibitors of mitochondrial division:Tools that translate basic biological research into medicine [J].Chem Biol,2010,17(6):578-583.
[13]Qian W,Choi S,Gibson GA,et al.Mitochondrial hyperfusion in⁃duced by loss of the fission protein drp1 causes atm-dependent g2/ m arrest and aneuploidy through DNA replication stress[J].J Cell Sci,2012,125(Pt 23):5745-5757.
[14]Brand MD,Nicholls DG.Assessing mitochondrial dysfunction in cells[J].Biochem J,2011,435(2):297-312.
[15]Yamaguchi H,Condeelis J.Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2007,1773(5):642-652.
(2014-08-24收稿2014-10-20修回)
(本文编辑李国琪)
Effects of mitochondrial fission in proliferation,apoptosis and invasion of thyroid squamous carcinoma cell line SW579
SHEN Feifei1,GUO Rui2,ZHAO Shupeng3,QI Fengjie1△,MENG Cuili1
1Department of Pathology,Liaoning Medical University,Liaoning 121001,China;2 Department of Pathology,the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University;3 Department of General Surgical,the First Affiliated Hospitals of Liaoning Medical University
△Corresponding AuthorE-mail:qifj2005@163.com
ObjectiveTo detect the expression of mitochondrial dynamics proteins(Mfn2 and Drp1)in thyroid squa⁃mous carcinoma cell line SW579 and the effects of Mitochondrial division inhibitor,Mdivi-1,on proliferation,apoptosis and invasion of SW579.MethodsIn SW579 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cell lines,the expression levels of Mfn2 and Drp1 were deter⁃mined by western blot while the transcription level of Mfn2 and Drp1 mRNA were measured by RT-PCR.Then,SW579 cells were divided into control group(DMSO,0.1%)and Mdivi-1 low,medium and high dose groups(Mdivi-1 of 15,30 and 45 μmol/L were incubated with cells for 16 hours respectively).Then the ability of cell proliferation was detected using MTT assay,the mitochondrial membrane potential was determined by fluorescence spectrophotometer,the expression levels of cy⁃tochrome C and Caspase-3 were quantified by Western blot and the transcription level of the Cyt C and Caspase-3 mRNA were determined by RT-PCR.The ability of invasion in each group was measured with Transwell assays.ResultsCom⁃pared with Nthy-ori 3-1,the mRNA transcription and protein expression levels of the Mfn2 was remarkably decreased,while the mRNA transcription and protein expression of the Drp1 was significantly increased in SW579 cells(P<0.01). Compared with control group,the cell survival rates and mitochondrial membrane potential of SW579 were decreased dramat⁃ically(P<0.01).The mRNA transcription and protein expression of the cytochrome C and Caspase-3 were increased dra⁃matically(P<0.01)and the capability of invasion was markedly decreased in all the Mdivi-1 groups in a dosage dependent manner compared with those in control groups(P<0.01).ConclusionAbnormal mitochondrial dynamics may be involved in thyroid squamous cell carcinoma SW579 cells;Mdivi-1 can inhibit the cell proliferation and invasion as well as induce apoptosis.
thyroid neoplasms;carcinoma,squamous cell;cell proliferation;apoptosis;mitochondrial dynamics;Mdivi-1;Mfn2;Drp1
R736.1
ADOI:10.11958/j.issn.0253-9896.2015.02.005

