一类双调和方程环绕解的存在性
蔡明建
(中南民族大学 数学与统计学学院,武汉430074)
一类双调和方程环绕解的存在性
蔡明建
(中南民族大学 数学与统计学学院,武汉430074)
在Steklov边值条件下,讨论了一类双调和方程, 当非线性项满足特定条件时,利用环绕定理,证明了该方程非平凡解的存在性.
双调和方程;环绕定理;非平凡解;Steklov特征值
1 主要问题及结果
本文考虑一类双调和方程:
(1)
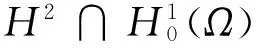
双调和方程的研究兴趣主要来源于两个方面.其一,在弹性力学中,该方程可以反映薄板的应力学分析,例如所谓的Kirchoff-Love模型[1]:
(2)
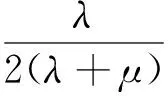
受上述文章的启发,本文拟考虑问题(1)满足下列条件时非平凡解的存在性.我们假设g满足如下条件:
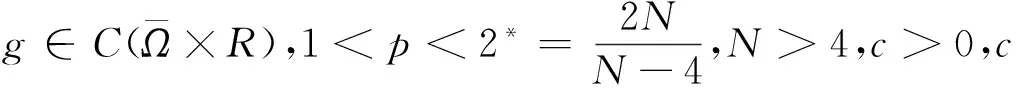
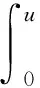
(iii) 当|u|→0时,g(x,u)=o(u),在Ω上一致成立.
本文的主要结果为定理1.
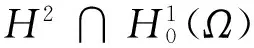
2 预备知识
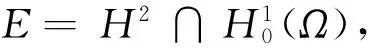
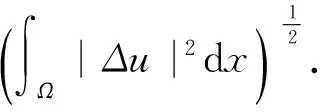
与方程组(1)所对应的能量泛函可以写为:
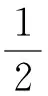
(3)
当u∈E满足:
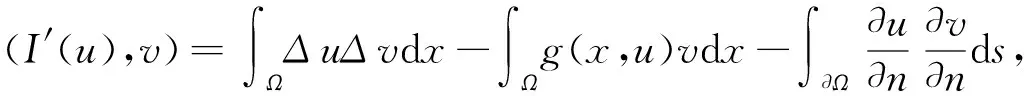
设E为一实的希尔伯特空间,泛函I∈C1(E,R).我们说{un}为I的P.S.序列:如果当n→∞时,有I(un)→c.泛函I在指标c∈R处满足P.S.条件是指,上述{un}存在一个收敛的子序列.若I(u)=c,I′(u)=0时,称u为I在E上的临界点,c为I的临界值.
设E为一Banach空间,S是E中的闭子集,Q是E中的子流形,记其边界为∂Q.若:
(1)S∩∂Q=∅,
(2) 任选h∈C0(E,E),当h|∂Q=id时,总有h(Q)∩S≠∅,则称S与∂Q环绕.
考虑当g(x,u)=0时,方程(1)的Steklov特征值问题,即此时若方程(1)有非零解,则称d为方程(1)的特征值,对应的解称为其特征函数.设:

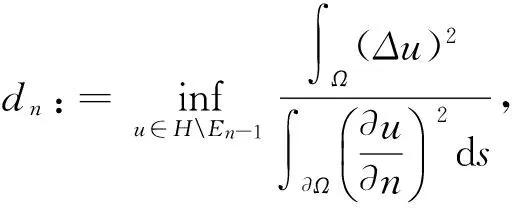
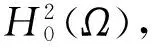
为了证明定理1,我们将用到文[16]中提出的环绕定理即引理1.
引理1 设E为一Banach空间,I∈C1(E,R)且I满足P.S.条件.设S是E中的闭子集,Q是E中的子流形,记其边界为∂Q,若:
(1)S与∂Q环绕.
令Γ={h∈C0(E,E);h|∂Q=id},
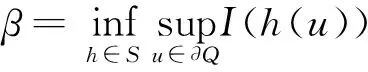
3 定理1的证明
引理2 假设条件(i)~(iii),(K)成立,则有I满足P.S.条件.
证明 (1)任取{un}⊂E满足I(un)→c并且I′(un)→0,那么{un}有界.
事实上
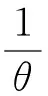
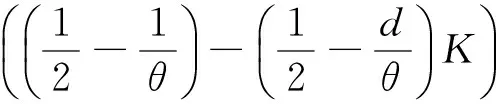
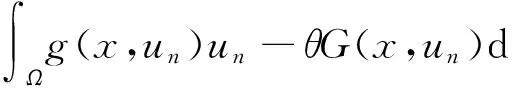
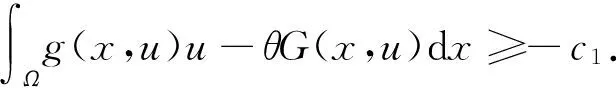
因此c(1+‖u‖)≥K(θ,d)‖u‖2-c1,可知{un}有界.

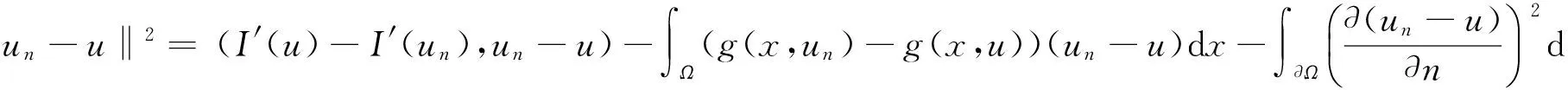
这里当n→∞,(I′(u)-I′(un),un-u)→0.
由(i),(iii)及Hölder不等式可知:
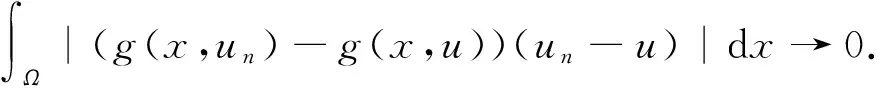
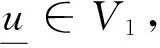
S={u∈V1;‖u‖=ρ},
0≤s≤R1,u2∈V2,‖u2‖≤R2},
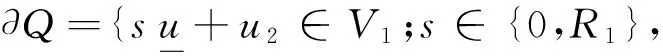
(1) S与∂Q环绕.
证明 结论(1)见文[16].下证结论(2).事实上,当u∈V2时,
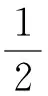
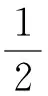
再由Sobolev嵌入定理可知:
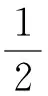
定理1的证明 定理1可直接由引理1~3得到.
[1] Kirchhoff G R. Uber das gleichgewicht und die bewegung einer elastischen scheibe[J]. J Reine Angew Math, 1850,40:51-88.
[2] Ferrero A, Gazzola F, Weth T. On a fourth order Steklov eigenvalue problem [J]. Anal,2005, 25: 315-332.
[3] Bucur D, Gazzola F. The first biharmonic Steklov eigenvalue:positive preserving and shape optimization [J]. Milan J Math,2011, 79(1):247-258.
[4] Edmunds D E, Fortunato D, Jannelli E. Critical exponents, critical dimensions and the biharmonic operator[J]. Arch Ration Mech Anal, 1990,112:269-289.
[5] Pucci P, Serrin J. Critical exponents and critical dimensions for polyharmonic operators[J]. J Math Pures Appl, 1990,69:55-83.
[6] Lin C S. A classification of solutions of a conformally invariant fourth order equation inRn[J]. Comment Math Helv, 1998,73:206-231.
[8] Zen X Z, Deng Y B. Existence of multiple solutions for a semilinear Biharmonic equation with critical exponent[J]. Acta Math Sci, 2000,20(4):547-554.
[9] Bernis F, García Azorero J, Peral I. Existence and multiplicity of nontrivial solutions in semilinear critical problems of fourth order[J]. Adv Differential Equations, 1996,1:219-240.
[10] Bahri A, Coron J M. On a nonlinear elliptic equation involving the critical Sobolev exponent: the effect of the topology of the domain[J]. Comm Pure Appl Math,1988,41:253-294.
[11] Zhou H S. An application of a Mountain Pass theorem [J]. Acta Math Scie, 2002, 18(1):27-36.
[12] Xu X. Uniqueness theorem for the entire positive solutions of biharmonic equations inRn[J]. Proc Roy Soc Edinburgh Sect A ,2000,130 (3): 651-670.
[13] Wang Y J, Shen Y T. Infinitely many sign-changing solutions for a class of biharmonic equation without symmetry[J]. Nonl Anal Theo,2009,71:967-977.
[14] Liu Y , Wang Z P. Biharmonic equations with asymptotically linear nonlinearities[J].Acta Math Sci,2007, 27 (3): 549-560.
[15] 彭超权.一类渐近线性方程非平凡解的存在性[J].中南民族大学学报:自然科学版,2010,29(4):118-120.
[16] Benci V, Rabinowitz P H. Critical point theorems for indefinite functionals[J]. Invent Math, 1979,52:241-273.
Existence of Linking Solutions for A Class of Biharmonic Equations
CaiMingjian
(College of Mathematics and Statistics,South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan 430074, China)
Under the Steklov boundary condition, this paper uses Linking Theorem to prove the existence of the nontrivial solutions to the biharmonic problems with some special nonlinearities.
biharmonic equations; Linking Theorem; nontrivial solutions;Steklov eigenvalues
2015-05-06
蔡明建(1981-),男,讲师,博士,研究方向:偏微分方程,E-mail: cmj9904@mail.scuec.edu.cn
中南民族大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(CZQ12014)
O175.25
A
1672-4321(2015)03-0126-03

