基于递归复杂网络的滚动轴承故障诊断*
孙 斌, 梁 超, 尚 达
(1.东北电力大学能源与动力工程学院 吉林,132012) (2.吉林省电力科学研究院有限公司 长春,130021)
基于递归复杂网络的滚动轴承故障诊断*
孙 斌1, 梁 超1, 尚 达2
(1.东北电力大学能源与动力工程学院 吉林,132012) (2.吉林省电力科学研究院有限公司 长春,130021)
针对滚动轴承振动信号的非线性、非平稳的特征,提出了一种基于递归复杂网络(recurrence complex network,简称RCN)的轴承故障诊断方法。首先,利用相空间重构的理论将一维时间序列扩展到高维相空间中,构建递归矩阵;然后,研究了基于递归思想的定量递归分析方法;最后,采用递归复杂网络的方法提取故障轴承振动信号的非线性特征参数,对轴承正常状态、内圈故障、滚动体故障和外圈故障振动信号进行分析。研究结果表明,RCN方法可以对滚动轴承故障进行较为准确的诊断,与传统方法相比具有较好的诊断效果。
递归复杂网络; 振动信号; 故障诊断; 波动模态
引 言
滚动轴承广泛应用于旋转机械中,轴承失效是机械产生故障的重要原因之一;因此,对其故障进行诊断识别具有重要的实际意义。滚动轴承包括内圈、外圈和滚动体,当其中的某一组件表面发生故障时,就会导致轴承与相邻组件发生共振频率,进而对旋转机械的正常运行产生一定的影响。滚动轴承的性能不仅与它的材料有关,日常的维护和及时的诊断也是其长期正常工作的有力保障[1-3]。目前,人们已经提出了多种轴承故障诊断的方法,如仪器检测和参数比较识别等方法。
复杂网络是一种天然的结构,代表了许多真实世界的系统[4]。近年来,复杂网络在医学、社会学等很多领域已经有了蓬勃的发展。复杂网络有着很好的灵活性和通用性,能代表所有的自然结构,包括那些发生动态变化的拓扑结构[5-8]。
轴承的振动信号更多呈现出的是非线性及非平稳的特性[9-10]。传统的统计特征量分析方法仅能进行粗略判断,如频谱分析法虽可以进行精确的故障诊断,但首先要了解诊断对象的故障机理。近年来,人们更多地将非线性时间序列分析方法应用于故障诊断[11]。例如,用基于递归定量分析(recurrence quantification analysis, 简称RQA)的方法对轴承的故障进行诊断分析,但RQA方法只能提取相空间中时间相关的特征,且当故障成分较为复杂时,诊断效果并不理想,对于这类问题用空间结构信息如递归复杂网络(recurrence complex network, 简称RCN)方法更为有效。笔者将递归复杂网络的方法应用于滚动轴承的故障诊断中,从应用的结果可以看出,RCN为滚动轴承故障诊断提供了一种有效可靠的方法。
1 递归图定量分析
1.1 递归图的算法及原理
递归性是很多动力系统最基本的特性,指系统的某些状态在特定的时间具有的相似性质[12]。Eckmannd等提出了递归图的概念,将一维时间序列扩展到二维相空间,能够更清楚地认识系统的递归性质。Maizel提出以像素点0和1的方式将一维空间扩展到二维平面空间,进而显示时间序列内部的结构特征。Zbilut等[13]提出了基于递归图的定量递归分析的方法,对非线性动力学系统的研究有积极的作用。
递归图采用Takens提出的相空间重构的思想,将一维时间序列重构到高维相空间中,具体算法如下。
1) 对于m维相空间的嵌入矢量从时间序列uk(k=1,2,…,N)以延迟时间τ重构得到的动力系统为
(1)
2) 计算重构相空间i和j两点的距离
(2)


3) 计算递归值
(3)


其中:H(·)为heaviside函数;‖·‖为范数(这里采用Euclidean范数);ε为参考阈值。
1.2 实验数据的采集
实验数据采用美国凯斯西储大学电气工程实验室[14]的轴承实验数据进行滚动轴承故障的特征提取和智能诊断。图1为滚动轴承振动实验台,用来模拟轴承的振动信号。实验所采用的滚动轴承型号为SKF6205,装置包括瑞恩电动机、加速度传感器、控制电子装置以及计算机等。轴承的状态为正常、内圈故障、滚动体故障和外圈故障4种,而轴承的故障损伤状况为单一损伤,是由电火花在轴承内圈、滚动体和外圈人为加工的,损伤的直径均为0.178 mm,深度为0.279 mm。测试轴承连接在电机上,电机的负荷为0~2.2 kW,额定转速为1 797 r/min。当传感器位置变化时轴承几种状态下的振动信号都随之变化,但都呈现出非线性非平稳的特性。因此,笔者在研究中将加速度传感器垂直固定于感应电机输出轴支撑轴承上方的壳上,这与水平方向放置有着相同的诊断结果。

图1 轴承振动实验台Fig.1 Experimental platform for the bearing
实验装置由电机带动输入轴,输出轴带动负载。为了获得最大负荷下的振动信号,故障信号在驱动端工作转速下进行采样。采样频率为12 kHz,每种故障信号采集10组数据,采样点数为10 000点。
2 振动信号复杂网络的拓扑性质
2.1 度及度的分布
度是复杂网络中单独节点属性中简单而又重要的性质。若v代表网络中的某一节点,kv表示节点v的度,网络的平均度对应于RQA中的递归度
(4)
网络的度分布可以表示为
(5)
其中:xv表示网络中度为k的节点的个数。
度的大小描述了各种振动模态之间的短程相关的关系,一个节点的度越大表明在实际中某种意义越重要。
2.2 聚类系数
聚类系数是刻画复杂网络结构统计特性的一个重要概念。局部的聚类系数是网络中各个节点的聚类系数,全局的聚类系数为网络中所有节点局部聚类系数的平均值
(6)
(7)
其中:Ev为与节点v相连的闭合三角形结构的数目;kv(kv-1)/2为与节点v相连的三元组的总数。
聚类系数反映网络顶点间的紧密程度,聚类系数越大说明振动信号之间的关系越紧密,反之则越稀疏。
2.3 平均最短路径
网络中两节点i和j之间的距离dij定义为连接这两个节点之间最短路径的边数,而网络中的平均最短路径则表示任意两节点之间距离的平均值
(8)
其中:N为网络中的顶点数;i和j分别为网络中的任意两个节点。
平均最短路径反应的是网络中一种振动信号向另一种振动信号变化时所经历的过程,平均最短路径越大,则变化的过程越复杂。
2.4 复杂网络的探索
网络中的模块度可定义为
(9)
其中:‖e2‖表示矩阵e2的各元素之和。
物理意义如下:网络中连接两种同类型节点的边的比例,减去同样社团结构下任意连接这两个节点的边的比例的期望值。若社团内部边的比例不大于任意连接时的期望值,则Q=0,而Q最大为1。通过定义可知,Q越大,所对应的网络越复杂,因此模块度Q可以作为衡量网络结构的有效标准。
3 故障特征分析
3.1 递归定量特性分析
笔者采取以下几种参数进行递归定量特征分析。
1) 递归率(recurrence rate)指递归图中递归点在图中所占有的比率
(10)
2) 确定率(determinism)指平行对角线线段数量与总的递归点数的比值
(11)
其中:l为平行对角线线段的长度;p(l)表示线段长度为l的频率,这里lmin取2。
3) 平均对角线长度指对角线方向线段长度的加权平均值
(12)
4) 递归熵(entropy)反应了递归图中对角线长度的熵分布
(13)
根据递归矩阵的定义,分别以i和j作为横、纵坐标绘出递归矩阵R所得到的图形即为递归图(RP图),该方法反映到图形上的实质就是采用黑白图形来刻画时间序列。图2为轴承在4种状态振动信号下的递归图。从RP图中可以看出,正常状态的RP图是均匀布满的,不存在与主对角线平行直线的点,表明振动信号是平稳随机的。几种故障图则存在不规则的图案,且存在与主对角线平行的点,这说明振动信号不是平稳的,系统存在不确定成分。
图3是轴承4种状态下的递归参数分布图。从图中可知,递归参数图中外圈的几个参数值都比较大,说明在递归图中沿对角线的线条纹理比较明显,系统的结构清晰完整,确定性较强,这与图2中的RP图是一致的。内圈和滚动体与正常的比变化较为复杂,整体表现为:内圈>正常>滚动体。几种递归参数都有不同趋势的变化,基于递归定量特性分析,仅仅从递归图中的线段分布情况量化轴承的动力学特性,只能对其故障进行大致的判别,但不能进行较为准确的故障分析,诊断效果不是很理想。

图2 轴承4种状态振动信号递归图Fig.2 Recurrence plot of vibration signal of four differential type bearings
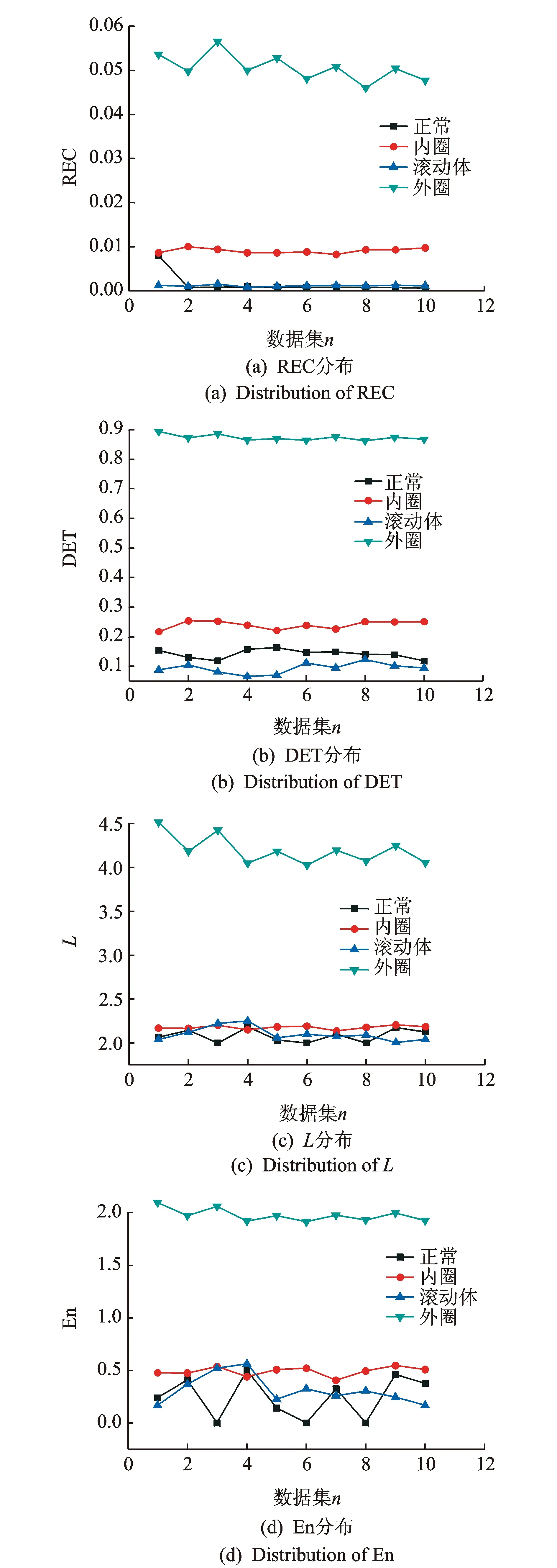
图3 轴承4种状态振动信号的递归参数分布图Fig.3 Recurrence parameter of vibration signal of four differential type bearings
3.2 网络特性的空间分布特征
邻接矩阵是复杂网络研究分析的基础,而从时间序列映射到复杂网络,构造出相应的邻接矩阵又是复杂网络应用于时间序列分析的关键。Donner等[15]研究发现,可直接将递归矩阵视为网络的邻接矩阵,提出了递归复杂网络的概念。其优点在于直接将时间序列定义为网络结构,且能从相空间中递归矩阵的空间角度量化动力学系统,克服了其他构造方法在概念上的限制,为动力系统中的非线性时间序列分析提供了统一的概念和实际框架。
图4为轴承4种状态下一组数据通过相空间重构得到的递归点所构建的复杂网络。从图中可看出,轴承不同状态所对应的复杂网络有着明显的不同。图中周围的数字表示递归矩阵的递归节点,复杂网络中一个节点与另一个节点间有连接,反映在振动信号中是一种振动模态向另一种振动模态的转变,即为振动信号的波动模态。不同的波动模态说明不同的振动特征,通过波动模态的转变,对轴承振动信号的变化有了更清晰的认识, 从而能够更好地对其故障进行诊断分析。如图4(a)中节点13指向节点33,表示轴承正常状态下这两个节点代表的波动模态之间的转换。不同状态下不同振动信号连接的紧密程度不同,反应出各种信号在网络中的强弱不同,从而造成网络的空间结构不同。从网络图中直接得到了相空间中轨迹递归的几何拓扑结构,为研究动力学系统提供了更加丰富的信息。
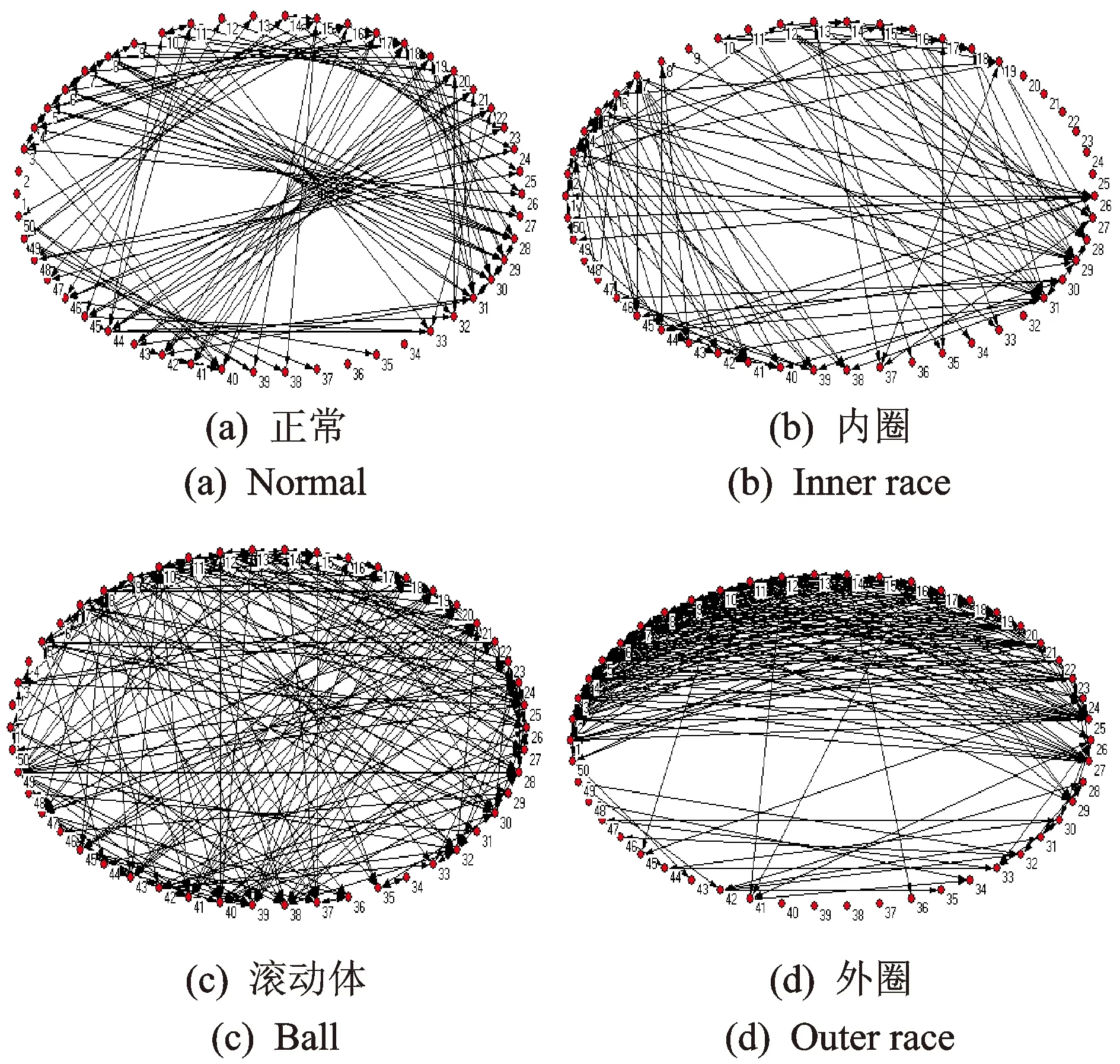
图4 轴承4种状态复杂网络Fig.4 Complex network of four differential type bearings
当轴承发生故障时,振动信号呈现非线性、非平稳的特性,对应的复杂网络也是不同的,而网络中的参数也呈现出不同的变化特征。表1~表4分别给出了轴承4种状态下,基于RCN参数平均度k、聚类系数C、平均最短路径L和模块度Q的诊断结果。
如表1所示,几种状态下振动信号呈现出不同的度值,整体表现为滚动体的度值相对较小,内圈和外圈故障也呈现出不同的变化,说明在轴承故障点撞击其他的部件时导致振动信号发生了变化。内圈故障中,度值比正常的略大,滚动体中度值略小,而外圈中度值则比较大。说明各个故障振动信号所对应的网络模态会出现一定概率的波动,网络中模态间有一定的相互转变(中间不需要经过其他模态的直接转变)。一种模态与另一种模态间的短程相关性越强,这种模态的度越大,则说明这种模态越重要,度小的波动模态较少发生。轴承不同的状态反映出的频发或不频发的振动模态种类是不同的。
表2是基于参数C的诊断结果,整体呈现的是正常状态的聚类系数大于故障状态。这是由于在正常状态下轴承具有较好的聚类性质。内圈的聚类系数较大,滚动体和外圈的则较小。在轴承旋转过程时,故障表面撞击轴承其他的部位,使得振动信号发生变化,从而对网络的聚类性质有一定的影响。
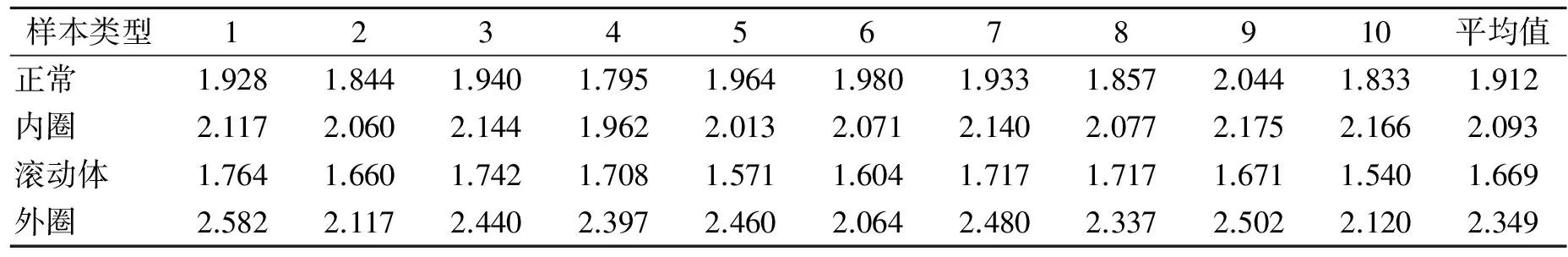
表1 基于参数k的诊断结果

表2 基于参数C的诊断结果
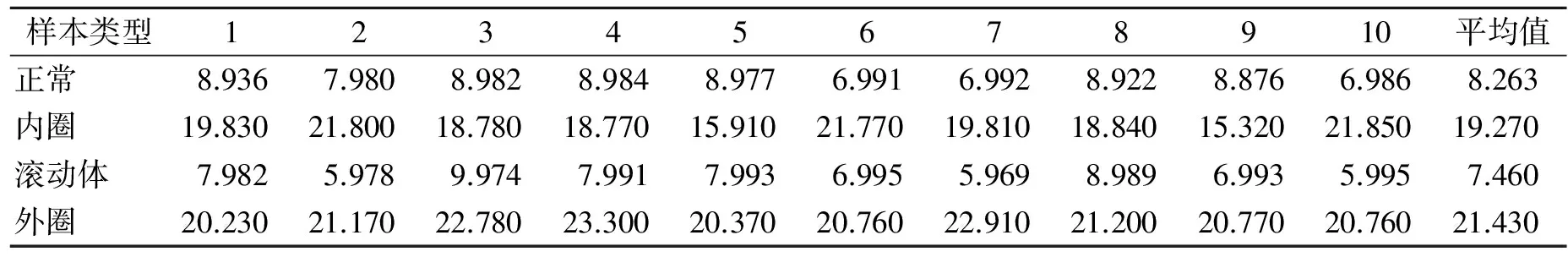
表3 基于参数L的诊断结果
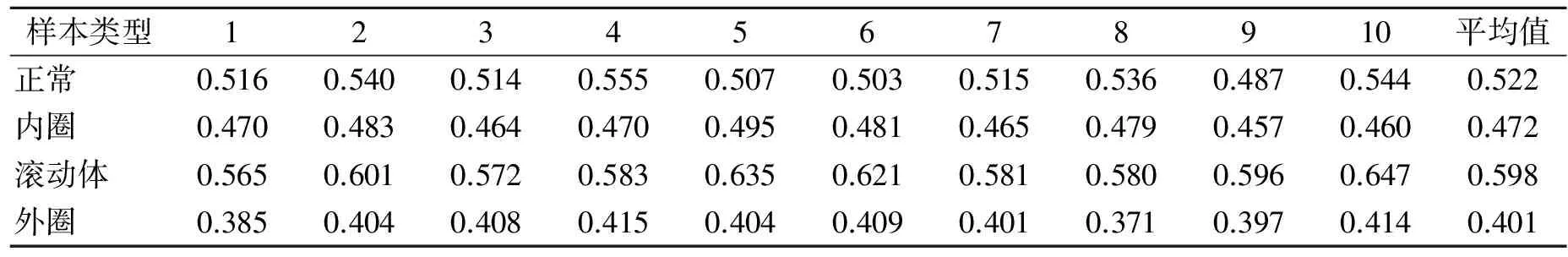
表4 基于参数Q的诊断结果
如表3所示,内圈和外圈的平均最短路径大于正常情况下的,说明内圈和外圈振动信号比较复杂,而滚动体的则整体小于正常情况,说明其振动信号所对应的波动网络的复杂性较小。平均最短路径体现了网络的任意两种模态之间转换所经历的时间,借此反映振动信号变化的复杂性。平均最短路径越大,说明网络中一种模态向另一种模态转换时所经过的中间模态越多,轴承振动信号变换越复杂。
由图5可知,几种故障所对应的网络累计节点度与度分布双对数关系较为复杂,整体表现为度值比较集中,度值较高和较低的比较少,且分布曲线能基本拟合为一条直线,即符合幂律分布。说明轴承的每种波动模态出现的次数在一个较长的时间段内遵循较多的模态出现的概率较少,而较小的模态出现的概率则较大。故障振动信号出现这种变化规律可能是由于所承受的载荷不均造成的,这又从侧面反映出轴承复杂的动力学特征,也反映出其网络模态随时间的变化是非线性的特征。每种故障网络中都有一定概率产生较大的波动模态,而这种波动模态对应着不同的故障典型振动变化信号。通过对不同故障典型振动信号的分析,量化轴承的动力学特征,从而对轴承故障进行准确的诊断。

图5 轴承故障网络累计节点度与度分布Fig.5 Degree distribution of the bearing fault complex network
表4为几种状态下网络的模块度,从表中可知,滚动体的模块度较大,外圈的较小,而模块度越大的对应的网络也越复杂,这与上文的复杂网络一致。通过模块度的变化对复杂网络社区进行较为精确的探索,对网络的社团结构进行准确的分析,从而对故障轴承进行较为准确的诊断识别。
4 讨 论
轴承内圈发生故障时,分布到故障点的静态载荷密度随内圈的旋转发生周期性的变化,内圈随着轴承的转动发生旋转,因此其损伤点有时位于载荷区内,有时位于载荷区外,振动信号变化较为复杂,对应网络中的平均最短路径、聚类系数较大,网络比较稀疏。滚动体故障中,损伤点与内圈接触时产生的脉冲力要通过滚动体及滚动体与外圈界面传播后才作用于外圈,在滚动体内及通过界面传播时的能量有损失,其振动信号的复杂性较小,对应于网络中聚类系数和平均最短路径较小,而网络较为复杂。外圈故障中,分布到故障点的静态载荷密度不变,聚类系数和模块度相应较小,网络较为稀疏,但由于传感器位于径向载荷密度最大的地方,振动信号比较复杂,因此其对应的平均最短路径比较大。从以上的网络参数分析中可以看出,轴承的振动信号表现出较小的平均节点度、较高的聚类系数和平均最短路径。随着度值的不同,聚类系数、平均最短路径和模块度变化比较复杂,度值大的聚类系数不一定大,而度值小的聚类系数可能较大,说明轴承网络特性既不是随机的,也不同于小世界网络。振动信号中的波动模态大多呈现出短程相关性,因此轴承振动信号的波动并不是无关联的随机过程,识别这些具有拓扑统计重要性的节点模态对于准确发现轴承的故障有积极的意义。
5 结束语
轴承的信号呈现的是非线性、非平稳的特性。笔者首先采用传统的递归定量特性分析的方法对轴承的故障进行诊断,但由于此方法是基于递归图上水平方向、垂直方向和对角线方向的递归性质的研究,因此诊断效果并不理想。与传统的诊断方法相比,采用递归复杂网络的方法,从网络的角度量化轴承的动力学特性,研究了几种状态下的振动信号间的变化规律,从空间的角度更好地解读系统的几何结构。结果表明,基于RCN的方法比基于RQA的方法更能揭示轴承的递归性质和空间拓扑结构,可对轴承振动故障进行较为准确的诊断分析。
[1] 苏连成,李兴林,李小俚,等.风电机组轴承的状态监测和故障诊断与运行维护[J].轴承,2012(1):47-53.
Su Lianchen, Li Xinglin, Li Xiaoli, et al. Condition monitoring and fault diagnosis and operating maintenance systems for wind turbine bearings[J]. Bearing, 2012(1):47-53. (in Chinese)
[2] Arabian-Hoseynabadi H, Oraee H, Tavner P J. Wind turbine productivity considering electrical subassembly reliability[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010,35(1):190-197.
[3] 范光辉,何加群.再论风电轴承的技术和市场[J].轴承,2012(3):56-59.
Fan Guanghui, He Jiaqun. Further discussion on technology and market of wind turbine bearings[J]. Bearing, 2012(3):56-59. (in Chinese)
[4] 周磊,龚志强,支蓉,等.基于复杂网络研究中国温度变化的区域特征[J].物理学报,2009,58(10):7351-7357.
Zhou Lei, Gong Zhiqiang, Zhi Rong, et al. Study on the regional characteristics of the temperature changes in China based oncomplex network[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009,58(10):7351-7357. (in Chinese)
[5] André R B, Dalcimar C, Odemir M B. Texture analysis and classification: a complex network-based approach[J]. Information Sciences, 2012,219:168-180.
[6] Mendes G A, da Silva L R, Herrmann H J. Traffic gridlock on complex networks[J]. Physica A, 2012,391(2):362-370.
[7] Wang Na, Li Dong, Wang Qiwen. Visibility graph analysis on quarterly macroeconomic series of China based on complex network theory[J]. Physica A, 2012,391(24):6543-6555.
[8] 孙斌,尚达.复杂网络在转子故障诊断中的应用[J].振动、测试与诊断,2012,32(6):1-6.
Sun Bin, Shang Da. The complex network in application of rotor fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2012,32(6):1-6. (in Chinese)
[9] 李辉,郑海起,唐立伟.基于阶次跟踪和变换时频谱的轴承故障诊断[J].振动、测试与诊断,2010,30(2):138-142.
Li Hui, Zheng Haiqi, Tang Liwie. Bearing fault diagnosis based on order tracking and Teager-Huang transform[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2010,30(2):138-142. (in Chinese)
[10]Andrew K, Anoop V. Analyzing bearing faults in wind turbines: a data-mining approach[J]. Renewable Energy, 2012,48:110-116.
[11]白宝丹,汪源源,杨翠微.基于递归复杂网络的房颤术后检测[J].仪器仪表学报,2012,33(4):809-815.
Bai Baodan, Wang Yuanyuan, Yang Cuiwei. Predicting recrudescence of atrial fibrillation based on recurrence complex network[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2012,33(4):809-815. (in Chinese)
[12]赵鹏,周云龙,孙斌.递归定量分析在离心泵故障诊断中的运用[J].振动、测试与诊断,2010,30(6):612-616.
Zhao Peng, Zhou Yunlong, Sun Bin. Application of recurrence quantification analysis to fault diagnosis of centrifugal pump[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2010,30(6):612-616. (in Chinese)
[13]Zbilut J P, Webber J, Charles L. Embeddings and delays as derived from quatification of recurrence plots[J]. Physics Letters A, 1992,171(3-4):199-203.
[14]The Case Western Reserve University Bearing Data Center. Bearing data center fault test data[EB/OL]. [2012-11-02]. http:∥www.eecs.cwru.edu/laboratory/bearing/.
[15]Donner R V, Zou Yong, Donges J F, et al. Recurrence networks a novel paradigm for nonlinear time series analysis[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2010,12(3):1-41.

Research on Dynamic Measurement Technology of Fiber Optic Sensors
and Their Development
ZhangXiaodong1,2,XieSiying2,NiuHang2,ZhangPing3,JiaBinghui4
(1.Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for Modern Design and Rotor-Bearing System,
Research on Design and Dynamics for Common Berthing Mechanism
ChenJinbao1,ChengMei2,NieHong3,YangMingbo2
(1 .College of Aeronautics Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
(2.Shanghai Institute of Satellite Engineering Shanghai, 201100, China)
(3.College of Aerospace Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract Based on international space station(ISS) mission requirements, this paper puts forward the development of a common berthing mechanism (CBM) with a large passageway. First, three typical docking mechanisms are surveyed and summarized. Second, by comparing it with the mechanism configuration of existing mechanisms, the configuration of the CBM′s main component is determined, a CAD model is presented, and the performance of the alignment guide and capture latch are analyzed. Third, a contact dynamics modeling is presented in detail as the key technological design aspect, and a virtual prototype of CBM is analyzed for the design of CBM. Finally, the modal analysis of CBM is studied, andthe natural frequencies and vibration modes are given. Through these analyses, this paper provides some scientific basis for reducing the structural vibration and improving the reliability of the CBM. This work has value for the design of CBMs and the development of China′s space berthing mechanism.
Keywords berthing mechanism; contact; dynamics; modal analysis
Method of Potential Fault Identification Based on the Projection Pursuit for
Rotary Equipment
ChengXiaohan,WangAiming,ChenYulin,LiWei,MengGuoying
(School of Mechanical Electronic & Information Engineering, China University of Mining
and Technology (Beijing) Beijing, 100083, China)
Abstract In order to solve the problems of a weak characteristic signal of the potential failure stage and the difficulty of extracting effective information, a method of potential fault identification for large equipment is put forward. Twenty-four characteristic indexes are calculated to describe the equipment running status. In order to avoid one-sidedness of disclosed information in a single projection direction, these 24 characteristic indexes of different states (including normal state and abnormal state) are projected into two-dimensional space under the best projection direction matrix, and an evaluation index system is established by virtue of distribution features of the projection value. By comparing the distribution of these 24 indexes under one status to be evaluated with the established evaluation index system, it can be judged whether the equipment state is abnormal or in the failure mode. Analysis of the test data shows that this method is feasible, reliable, and highly sensitive in capturing the early fault signal.
Keywords 24 characteristic indexes; the projection pursuit method; the best projection direction matrix; evaluation index system; status identification and early warning
Milling Vibration Suppression of Thin-Walled Structure Based on
Electromagnetic Induction
YangYiqing,GongJiwen
(School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Beihang University Beijing, 100191, China)
Abstract There are many thin-walled structures in aircraft. Due to the low flexibility of structures, workpiece deformation and deflection occur easily during the machining, which causes low precision and low surface quality. Therefore, much has been done to investigate the machining process, deflection prediction and control technology of thin-walled structure machining. However, real application in the industry is still a challenge. In this paper, a vibration suppression device for the thin-walled structure is investigated and designed based on electromagnetic induction. The workpiece vibration is utilized in order to cause a change in the magnetic flux through the closed circuit, so the resulting magnetic force can contribute to the suppression of workpiece vibration. The magnetic force resulting from the movement of the magnet inside the copper tube is formulated. It is shown to vary linearly with workpiece velocity in the opposite direction. Impact tests show that the device can sharply attenuate the oscillation time, and the chatter stability simulation shows that the stability limit of the thin-walled workpiece is increased from 0.4mm to 5.1mm. Cutting tests are carried out to verify the final vibration suppression effect.
Keywords thin-walled structure; electromagnetic induction; milling; vibration suppression
Fault Diagnosis of Service Robot Based on Multi-PCA Models
and SVM-DS Fusion Decision
YuanXianfeng1,SongMumin1,ZhouFengyu1,ChenZhumin2
(1.School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University Jinan, 250061, China)
(2.School of Computer Science and Technology, Shandong University Jinan, 250101, China)
Abstract To solve the fault diagnosis problem of the wheeled service robot driving system, a novel fault diagnosis method based on multi-principle component analysis (multi-PCA) models is proposed, which compounds with support vector machine (SVM) and Dempster-Shafer evidence theory(DS) . Multiple PCA models are established using sensor data sampled in the normal and fault states, respectively. The normal state PCA model is used to accomplish fault detection. During the fault isolation process, the multi-PCA models are used to carry out feature extraction from sensor data, and the processed data are taken as the input vectors of SVM classifiers, which achieves preliminary fault isolation. The global and local confidence values of the SVM classifiers are defined based on the confusion matrixes. To realize the effective combination of SVM and DS, the basic probability assignment (BPA) is appointed by the integration of the confidence values and the preliminary fault isolation results. Experimental results indicate that sensitive faults in the robot driving system can be detected, with an average fault isolation accuracy of 92.6%. Compared with the traditional single PCA model method, the proposed method has better performance in accuracy and stability.
Keywords service robot; fault diagnosis; principle component analysis(PCA); support vector machine(SVM); Dempster-Shafer evidence theory
Experimental and Analytical Study of Dynamic Response of Structure Controlled
by Active-Passive Hybrid Tune Mass Damper
LiuYanhui1,2,3,TanPing1,ZhouFulin1,2,YanWeiming2
(1.State Key Laboratory for Seismic Reduction /Control & Structural Safety (Cultivation),
Guangzhou University Guangzhou, 510405, China)
(2.College of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Beijing University of Technology Beijing, 100124, China)
(3.Department of Civil Engineering, University of Toronto Toronto, M5S1A4, Canada)
Abstract For the vibration control of structures under earthquake and wind excitation, the active-passive hybrid tune mass damper (HMD) is presented and the realization tactic of the control device is proposed, which adopts active mass damper (AMD) driven by linear motors, hollow rubber bearings as restoring force springs of the tune mass damper(TMD), and guide rails as supported structure. Then, the control effect and damping mechanism of the HMD for the dynamic response of the structure are analyzed under external excitations. Meanwhile, the influence of feedback response on control effect, control force and displacement AMD are discussed. Finally, the shaking table test of the structure controlled by HMD is carried out based on linear-quadratic-gaussian(LQG) and control algorithm. Simulation and experimental results show that HMD can effectively suppress the dynamic response of the structure and improve the performance of TMD. In order to solve the problem of AMD shifting, the displacement of AMD should be chosen as a control object and feedback vector when the AMD driven by linear motors is taken as the active control device. The control effect of the LQG control algorithm is better than that of thecontrol algorithm, and the feasibility of the HMD′s hardware system is experimentally proven, which supports the application of the HMD control system to pure engineering.
Keywords hybrid tune mass control; vibration control; active mass damper; tune mass damper; control algorithm
Experimental Study on the Vibration Fatigue Failure Confirmation Method
of the Structure Under Multi-axial Random Excitation
HeGuangzong1,2,ChenHuaihai1,HeXudong1
(1.College of Aerospace Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
(2.School of Transportation and Vehicle Engineering, Shandong University of Technology Zibo, 255049, China)
Abstract The fatigue failure characteristics of a structure under multi-axial random excitation presented in this paper have been researched, and two methods of determining the vibration-fatigue-life experiment are presented. A laser vibrometer and dynamic signal analyzer (35670A) are used to monitor the first order natural frequency, and the dynamic strain of the gap position on the structure is monitored using the dynamic strain measurement system in real time. Based on the investigation results, the relationship between the crack growth and the first order natural frequency as well as the strain variation are analyzed, two criteria for fatigue failure are determined, and the applicability of these two methods is discussed. This method lays the foundation for the multi-axial vibration fatigue experiment.
Keywords multi-axial random excitation; vibration fatigue; fatigue life; the first order natural frequency; dynamic strain
Characteristics Analysis and Extraction Method for Electrostatic
Monitoring Signal in Aero-engines Gas Path
WenZhenhua1,HouJunxing1,ZuoHongfu2
(1.School of Mechatronics Engineering, Zhengzhou Institute of Aeronautical Industry Management Zhengzhou, 450015, China)
(2.College of Civil Aviation, Nanjing University of Aerospace and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract The charge mechanism of aero-engine particles and the action mechanism between charged particles and the electrostatic sensor are analyzed, then the influence factors on the frequency property of the electrostatic monitoring signal are explored. Based on the difference in frequency spectrum caused by the flow features of particles, the energy distribution characteristics extraction from the frequency domain is proposed, and the wavelet analysis method is employed to calculate the energy distribution characteristics. The effectiveness of the characteristics is verified using simulated experiments and a turbo-shaft engine. The experimental results show that the electrostatic monitoring technology can detect the rapid change of aero-engine output power. The signals caused by continuous particles contain more high frequency content. The even distribution of energy can be applied to identify whether the particles are continuous or not, and the change in energy distribution can effectively reflect the small change in the output power of an engine. These results are helpful in promoting the airborne electrostatic technology and improving the ability to diagnose the work condition and track performance of parts in the aero-engines gas path.
Keywords aero-engines; electrostatic monitoring; characteristics extraction; electrostatic sensor
Self Adjusting Composite Cascade Morphology Filter
Algorithm and Its Application
ZhangPing1,2,ZhangXiaodong2DongXiaoni2,HeLile1,NiuHang2
(1.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Xi′an University of Architecture and Technology Xi′an, 710055, China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi′an Jiaotong University Xi′an, 710049, China)
Abstract In order to eliminate the pulse and random noise interference of the lubricant film thickness signal obtained by the optic fiber displacement sensor, a filtering algorithm based on self adjusting composite cascade mathematical morphology is proposed. The triangular and semi-circular structural elements are adopted in the filter. The composite cascade morphology filtering algorithm is built with cascading open-close and close-open combinational filters. The simulation results show that the algorithm improves the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Meanwhile, in order to avoid a low SNR, which is caused by the random selection of structural element parameters, a self adjusting method for the structural element parameters is proposed. Both experimental and simulation analysis results show that the filtering algorithm based on the self adjusting composite cascade mathematical morphology can effectively eliminate the pulse interference and random noise interference of the lubricant film thickness signal.
Keywords optical fiber; lubricant film; morphology filtering algorithm; structural element
Vibration Analysis of IC Trimming and Forming Mechanisms Based on
Rapid Chirplet Matching Pursuit
ChenZhong1,2,HuangMian1,2,ZhangXianmin1,2,ZhangQingchun3
(1.Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Precision Equipment Manufacturing Technology,
South China University of Technology Guangzhou, 510641, China)
(2.School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology Guangzhou, 510641, China)
(3.Dongguan Langcheng Microelectronic Equipment Co., Ltd Dongguan, 523945, China)
Abstract Aiming at the die-cutting precision of integrated circuit (IC) trimming and forming mechanisms, the rapid chirplet matching pursuit is used to analyze the vibration of a trimming and forming mechanism. Based on the fast matching pursuit of gaussian chirps, an algorithm is used to decompose the vibration signals of the key parts of the mechanism and obtain the chirp spectrograms. According to the characteristics of the atoms, the intrinsic frequency and other features can be identified from these spectrograms. The experiments indicate that the algorithm based on the fast matching pursuit of gaussian chirps, which has fine time-frequency resolution, can extract vibration characteristics from massive nonstationary signals, precisely reflect the work condition of the mechanisms, and lay a reliable basis for fault diagnosis.
Keywords chirplet; matching pursuit; trimming and forming; vibration analysis
Effect of Key Parameters on the Dynamic Performance
of the Multi-mesh Gear Systems
HuPeng,WangQibin,ZhangYimin
(School of Mechanical Engineering & Automation, Northeastern University Shenyang, 110819, China)
Abstract A nonlinear dynamic model and relative dimensionless equations focusing on time-varying stiffness and backlash are developed to study the steady state of the dynamic gear drive system of the computer numerical control (CNC) turret. The time-varying stiffness is obtained, considering the effect of the modification coefficient on stiffness values. The piecewise displacement functions caused by the backlash are simplified into an expression containing a hyperbolic tangent to avoid the complex judging in the iterative process. The equations are solved by employing the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method in Matlab programming. The influence of the alternating mesh stiffness amplitudes, transmitted static torque and backlash are investigated. Results show that smaller amplitudes of harmonic stiffness benefit the system′s stability. Stability is also improved under heavy loads, since working speed is smaller than critical speed, which increases due to the jumping phenomenon. Double-sided impact occurs more easily with small backlash and leads to noise.
Keywords time-varying mesh stiffness; gear backlash; nonlinear model; multi-mesh gear; jump phenomenon
Experimental Study of Caudal-Fin-Like Piezoelectric-Bimorph
Valveless Pump with Flexible-Rigid Structure
HuXiaoqi1,2,FangYamin1,ZhangRuihua1,YeXiaoping1,ChenXiaoyuan1,LüYongchang1
(1.College of Engineering and Design, Lishui University Lishui,323000,China)
(2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures,
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract Compared to the traditional valveless pump working principle based on structural asymmetry, unidirectional flow produced by swing vibration has the advantages of being easy to realize miniaturization, high efficiency, little flow pulsation, no back flow, etc. The key part of the pump is the flexible caudal-fin structure configured on the tip of the swing vibrator. First, the relationship between the pressure head and excitation frequency is obtained by the pressure head test method, in which the length of the flexible caudal-fin is within the range of 2~18 mm. Second, the vibration mode is scanned by laser doppler vabrimeter with the swing vibrator immersed in water, and the corresponding relation between the maximum pressure head and vibrator mode is established after comparison with the experiment. Finally, the relationship between the flexible caudal fin and main part is discussed, and the fluctuation phenomenon of the optimum working frequency is explained. The results show that the pressure head can be observed in the first three vibration modes when the vibrator works in the approximate infinite water domain. The pressure head reaches 55 mm when the length of the flexible caudal-fin is 4 mm or 6 mm. The optimum working frequencies of the series vibrator fluctuate around the second bending mode frequency of the main part, without the caudal fin.
Keywords piezoelectric-bimorph; caudal-fin structure; valve-less pump; weak coupling
A Gyromagnetic Piezo-cantilever Generator Used for RWMS
KanJunwu,LiShengjie,WangShuyun,LiYang,YanMengjia,ZengPing
(Institute of Precision Machinery, Zhejiang Normal University Jinhua, 321004, China)
Abstract A gyromagnetic piezo-cantilever generator (GPG) is presented to meet the demand of the railway wheelset monitoring system (RWMS) for self-power. The influence of the magnetic force and rotating speed on GPG energy generation, in terms of the number and configuration of the magnets, is experimentally investigated. The results show that there are 9 optimal rotating speeds for the GPG to achieve peak voltages in the speed range of 0~1 360 r/min. The increasing number of rotating magnets exerts no influence on optimal rotating speeds, but leads to increasing output voltage when the magnets on the piezo-cantilever are fixed. The peak voltages of GPG with 2, 4, 8, and 12 rotating magnets are 13.2, 16.6, 23.8, and 27.8V respectively at the rotating speed of 1 042.5 r/min. The optimal speeds decrease and the responding voltage rises with an increasing number of magnets fixed on the piezo-cantilever when the number of rotating magnets is constant. In the case of two rotating magnets, the 9thoptimal rotating speeds and the peak voltages of the GPG with 1, 3, 5, and 7 magnets fixed on the piezo-cantilever are 1 056.4, 861.8, 750.6, and 611.6 r/min and 13.2, 34.4, 48, and 64 V, respectively. Moreover, the generated energy in terms of the voltage and wave number produced by one excitation depends on the magnets′ rotating speed. The wave number generated at the lower rotating speed (264.1 r/min) and higher rotating speed (1 024.5 r/min) is 1 and 4, respectively.
Keywords piezoelectric; energy generation; rotating excitation; magnetic coupling
Research on Vibration Suppression for Magnetic Suspension Motor Based on
Repetitive Control Method
HanBangcheng1,2,LiuYang1,2,ZhengShiqiang1,2
(1.Science and Technology on Inertial Laboratory, Beihang University Beijing, 100191, China)
(2.Fundamental Science on Novel Inertial Instrument & Navigation System Technology Laboratory Beijing, 100191, China)
Abstract Aiming at the suppression of unbalance vibration in rotors suspended by magnetic bearings, a plug-in repetitive controller is presented. The model of the unbalance vibration is proposed with emphasis on its periodicity. The stability and the abilities of error tracking and disturbance elimination are analyzed with the repetitive controller. The experiment is conducted with a 4kW magnetic suspension motor at the rotating speed of 10 kr/min. The rotor′s peak-to-peak position is reduced by 33% in thex-direction and 37% in they-direction, and the maximum amplitude of vibration at the rotating frequency is reduced by 42.1% in thex-direction and 45.4% in they-direction. The results demonstrate that the repetitive controller has good effect on the suppression of the unbalance vibration, and the control precision and stability of the magnetic bearing system are effectively improved.
Keywords magnetic suspension motor; magnetic bearings; unbalance vibration; repetitive control
Distinguishing Spurious Modes Obtained from PRCE Based on
Modal Similarity Index
ZhangGuowen1,MaJinghua2,ChenZhuo3
(1.College of Life Information Science & Instrument Engineering, Hangzhou Dianzi University Hangzhou, 310018, China)
(2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission, Chongqing University Chongqing, 400044, China)
(3.State Key Laboratory of Bridge Structure Dynamics, Chongqing Communication
Research & Design Institute Chongqing, 400067, China)
Abstract A new method based on the modal similarity index is introduced to distinguish spurious modes. The method mainly focuses on the effect of spurious modes in the poly-reference complex exponential method on the results. First, two sets of results can be obtained by imposing different constraints on the coefficient matrix, in which the system poles appear at the same point, yet the mathematical poles are randomly distributed. Then, the mode similarity index (MSI) is proposed to measure the degree of similarity between the two sets of results. Spurious modes resulting from the noise or model redundancy can be removed according to the fact that the modal similarity index of physical modes is much larger than that of the spurious modes. Finally, parameter estimation of a linear time-invariant system of 3 degrees of freedom and the Chaotianmen bridge in Chongqing are presented. Results show that the proposed method can remove spurious modes effectively without losing physical modes.
Keywords modal analysis; polyreference complex exponential; spurious modes; stabilization diagram
Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on Generalized S-Transform
and Two-Directional 2DPCA
LiWeihua,LinLong,ShanWaiping
(School of Mechanical Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology Guangzhou, 510640, China)
Abstract The problem of bearing fault diagnosis can be solved by time-frequency image recognition. A two-directional, two-dimensional principal component analysis (TD-2DPCA) method is proposed to extract features from a time-frequency image matrix. First, features are extracted with TD-2DPCA using the generalized S-transform to transform fault signals into images in the time-frequency domain. The bearing fault experiments are carried out on a bearing test-bed, and vibration signals are collected under the normal condition, inner ring fault condition and outer ring fault condition. The proposed method is adopted to extract image features of three bearings from time-frequency spectrums, and the assembled matrix distance (AMD) is calculated for image classification. Experimental results show that TD-2DPCA combined with the generalized S-transform has good diagnostic performance and can effectively improve the computational speed.
Keywords generalized S-transform; two-dimensional principle component analysis(2DPCA); image recognition; feature extraction; fault diagnosis
Vibration Performance of the Cutter During Cutting Large Welded Cylinder
ChengYaonan,LiuLi,GongYa′nan,WuMingyang,QianJun,YanFugang
(The Key Laboratory of National and Local United Engineering for High-Efficiency Cutting & Tools,
Harbin University of Science and Technology Harbin, 150080, China)
Abstract The mechanism of cutting vibration is analyzed to research the dynamic characteristics of the cutter for cutting a large welded cylinder. The dynamic model of the cutting process of a large welded cylinder is established and solved. The cutting experiment is carried out under the real condition, and the vibration model is amended according to the changing of models. Thus, the feasibility and stability of the model in practical applications are verified. Finally, the critical condition of dynamically cutting a large welded cylinder is determined, which provides theoretical support to the further study of unstable vibration laws of large structure processing.
Keywords large welded cylinder; cutter vibration; dynamical model; numerical analysis
Compound Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on Dual-tree
Complex Wavelet Packet Transform and ICA
XuYonggangMengZhipengLuMing
(Beijing Engineering Research Center of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments,
Beijing University of Technology Beijing, 100124, China)
Abstract A new fault diagnosis method is proposed based on the dual-tree complex wavelet packet transform (DT-CWPT) and independent component analysis (ICA), aiming at separating fault information from the compound rolling bearing fault signal. First, the non-stationary and complex signal of the compound fault is decomposed into several different frequency band components through dual-tree complex wavelet packet decomposition. Then, ICA is used to separate the mixed signal consisting of each component to eliminate the frequency aliasing as much as possible. Finally, independent signal components separated from the mixed signal are processed by Hilbert demodulation. The results show that the fault feature of rolling bearing can be effectively separated and extracted, and the method′s feasibility and effectiveness are verified.
Keywords dual-tree complex wavelet packet transform (DT-CWPT); independent component analysis (ICA); blind source separation; frequency aliasing;compound fault
The Probability Imaging Algorithm of Composite T-joint Damage Monitoring
LiuBin1,2,QiuLei1,YuanShenfang1,ShaoHuixue1,ZhangHua1
(1.The State Key Lab of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures, Nanjing University of
Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
(2.Department of Air Force Military Transportation, Air Force Logistics College Xuzhou, 221006, China)
Abstract The T-joint is an important part of damage monitoring. However, it is difficult to accurately monitor T-joint′s damage with the PZT sensors array and Lamb wave based on structural health monitoring imaging methods because of its complex structures. The probability imaging algorithm independent of the signal propagation velocity, which is the base of traditional methods, is studied for engineering applications. The affected areas of each channel′s damage index (DI) are confirmed with the elliptical orbit method based on the DI of the piezoelectric excitation-sensor network. Then, the accurate monitoring of the T-joint damage is realized through the integration and imaging of all channels′ affected areas. The results are verified with the ultrasonic C-scan. The study reveals that the DI is able to monitor the T-joint of the composite material online and alert to the damage. Thus, damage locating can be implemented with the probability imaging algorithm.
Keywords composites; T-joint; structural health monitoring; damage index; probability imaging
Nonlinear Dynamics Characteristics of Dual-cylinder Opposed Compressor
Driven by Linear Motor
QinZhaoju1,2,GaoYuguo1,YuanYanpeng2,SongLiye2
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power Zhengzhou, 450045, China)
(2.School of Mechanical and Vehicular Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology Beijing, 100081, China)
Abstract A nonlinear dynamics model of the compressor is established based on thermodynamics equations and the electromagnetic force equation, in order to study the dynamics characteristics of the piston in a free-piston compressor driven by a linear motor. The approximate solution of the nonlinear model is solved by the energy equilibrium method based on the oscillation theory. The stability and frequency characteristics of the piston in the linear compressor are discussed in terms of the solution of the nonlinear model. The results show that the movement principle of the linear compressor is a single degree vibration system with self-excited force. The initial movement does not affect the final operation of the compressor, and the piston motion tends to be stable. Piston motion frequency is influenced by the compressor′s physical structure, the linear motor thrust and the intake pressure. The electromagnetism force determines the piston′s movement amplitude and has a serious impact on the piston′s vibration frequency. The piston motion frequency increases with intake pressure, and is mainly decided by the inlet pressure under larger load conditions.
Keywords dynamics; nonlinear model; frequency characteristics; linear compressor; piston
Investigation on Uncertain Factors Affecting the Joint Stiffness of
Some Rubber Isolator
ChenXueqian,ShenZhanpeng,LiuXin′en,WangYujun
(Institute of Systems Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics Mianyang, 621999, China)
Abstract Two types of modal tests are designed to separate the uncertain resources in some rubber isolation systems. Repeated multi-test cases are conducted in each type of test. According to the test results, the joint stiffness of the isolation system is identified based on the traditional finite element (FE) model updating. The probability density functions of the joint stiffness are established by combining the Bayesian method with the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC). Moreover, the effect of the uncertain resources on joint stiffness is quantified by the operation of random variables. Lastly, the uncertain model of the joint stiffness is validated with other validation tests. Results show that the effect of the assembling uncertainty on joint stiffness is only one tenth of that of the rubber material dispersion.
Keywords rubber isolator; uncertain resource; Bayesian method; uncertainty quantification
Localization of Delamination in Plate Structures Using
Natural Frequency Measurement
ChengXinlei1,2,XiaoGuanghong1,KennedyD2,ChengPeijiang3
(1.School of Civil and Architecture, Chongqing Jiaotong University Chongqing, 400074, China)
(2.School of Engineering, Cardiff University Cardiff, CF24 3AA, United Kingdom)
(3.Department of Civil Engineering, Logistic Engineering University Chongqing, 401311, China)
Abstract Delamination is regarded as one of the most serious defect in composite materials, which reduces the structural capacity and will spread to cause a catastrophic collapse. Based on the simplicity and high accuracy of measurement for natural frequency, a new type of non-destructive measurement is proposed to determine the delamination location in composite plate structures by using normalized natural frequencies. The predicted location by this method can be used before applying the quantitative detection, which can be considered as a preliminary work to improve the detection efficiency. The validity of this method is demonstrated by comparing the predicted location of a delaminated plate modelling with experimental data. The results show the procedure simplicity and accuracy of this method.
Keywords natural frequency; plate structure; delamination; location prediction
Self-Synchronous Theory of No-Swing Vibrating Machine Driven by Dual-motor
LiHe,LiuDan,ZhaoChunyu,WenBangchun
(School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Northeastern University Shenyang, 110819, China)
Abstract The self-synchronous theory of a no-swing vibrating machine driven by dual-motor is researched. The vibrating machine comprises an inner plastidium and an outer plastidium. The rotational centers of two eccentric rotors are in line with the inner plastidium′s center of mass along a vertical axis. Therefore, the moments generated by the inertial force of the eccentric rotors to the vertical axis are zero, thus eliminating the swing of the vibrating machine. First, the differential motion equations of the vibrating machine are established using the Lagrange equation, and the conditions of self-synchronization and motion stability are obtained. Moreover, numerical simulations are carried out to verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis. It can be shown that the capability of self-synchronization is positively correlated with the mass ratio of the two exciters and negatively related to the frequency ratio along the vertical direction, the angle of the resonant excitation, and the mass ratio between the material box and the vibrating system.
Keywords self-synchronous motion; vibrating mechanism; stability; vibratory synchronization transmission
Experimental Isolation Effect Analysis of Two-Stage Vibration Isolation System
SunYuhua1,DongDawei2,YanBing2,WangYuanwen2,WuJunda2
(1.College of Engineering and Technology, Southwest University Chongqing, 400715, China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University Chengdu, 610031, China)
Abstract Aiming at analyzing the isolation effect of a two-stage vibration isolation system that is used in exported internal combustion motor car, a ground platform experiment of the power train′s two-stage vibration isolation system is carried out according to the optimized two-stage vibration isolation system stiffness. By using the acceleration values of unit vibration intensity measuring points and each vibration isolator′s upper and lower measuring points, the isolation effect of the system is systematically analyzed from the unit vibration intensity, vibration level difference and dynamic dimpling force of each primary and secondary vibration isolator. The results show that the isolation effect of the system′s optimized stiffness is good, which can completely meet practical engineering needs.
Keywords two-stage vibration isolation system; vibration intensity;dynamic damping force; transmissibility
Analysis and Application of Deep Hole Drilling Straightness Error
Influenced by Cutting Fluid
ChenZhenya1,2,ShenXingquan1,2,XinZhijie1,2,PangJunzhong1,2,GuoTingting1
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering, North University of China Taiyuan, 030051, China)
(2.Shanxi Province Research Center of Deep-Hole Machining Engineering Technology Taiyuan, 03005l, China)
Abstract The equation for deep hole straightness error is established by using the cutting fluid Reynolds equation, bar bending deformation theory and drill bar angle equation, which reveals relationships between cutting fluid inlet pressure, drill rotation, whirl, squeezing feed and deep hole straightness. In the condition of cutting stability, deep hole straightness can be improved by reducing the cutting fluid inlet pressure, increasing the drill rotation speed or decreasing drill whirl speed and extrusion speed. A new type of multi-injection device is designed that can effectively reduce the deep hole straightness error through an additional shunt cavity and injection series to reduce the inlet pressure. Squeeze film dampers (SFD) are designed, and extruding whirl and extrusion of the deep hole drill pipe are decreased by using oil film resistance, which improves the deep hole straightness. Testing deep hole straightness error under the action of the multi-stage injection device and SFD, and drill in the lower cutting fluid inlet pressure and small whirl and extrusion have a better deep hole drilling straightness is verified. New ideas and a design scheme are given to control the deep hole processing straightness error.
Keywords deep hole drilling; straightness error; multi-injection device; squeeze film dampers(SFD)
Mixed-basis Superposition Method for Eigenvector Reanalysis
of Large Modified Structures
LiuZhijun,DengZhaoxiang
(The State Key Laboratory of Vehicle NVH and Safety Technology, China Automotive Engineering
Research Institute Chongqing, 400039, China)
Abstract In order to extend the application range of the structure reanalysis method based on the matrix perturbation theory in engineering practice, and to improve the calculation precision of reanalysis, an improved mixed-basis superposition method of dynamical reanalysis is proposed for large modified structures without complete modal space. The known modes are used to construct a new mixed-basis of the modal space, and the changes in the stiffness matrix and mass matrix reflecting the changes of structural physical parameters are represented as the incremental form of higher order. The present method is as simple and easy to operate as the classical perturbation method. The numerical results show that the presented method yields high precision for dynamical reanalysis of large modified structures.
Keywords structural dynamical reanalysis; large modifications of structures; matrix perturbation method; mixed-basis superposition method
Dynamic Characterization Analysis of Flexible Multibody Manipulator
with Joint Clearance
RenWu1,2,WuYunxin1,ZhangZhaowei1
(1.State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, Central South University Changsha, 410083, China)
(2.School of Biomedical Engineering , Xinxiang Medical University Xinxiang, 453003, China)
Abstract The long manipulator of ground machinery is typical multi-body system, the existing research on the kinematic relationship and dynamic characterization are generally concerned on the flexible booms with the ideal joint whereas the dynamics of joint clearance isn′t ignored. Firstly, a flexible multi-body boom model is established. Then, the first cylinder and boom joint clearance is considered. Next numerical simulation is done on the tip trajectory and vibration characteristic of ideal and clearance joint models. The simulation results show that the tip displacement of the flexible multi-body model with joint clearance is larger than that of ideal joint model. Meanwhile the hydraulic cylinder force also increases. And the first natural frequency is lower than that of ideal joint model. Finally an experiment is done on a flexible multi-body boom structure. The result provides a design reference for such machinery.
Keywords flexible multibody; manipulator; joint clearance; dynamic; natural frequency
Test Study on Adaptive Control Wavelet De-noising of the Semi-active
Air Suspension
WangRuochen,ChenXin,QianJingang,LiJiaojiao,ChenLong
(School of Automobile and Traffic Engineering, Jiangsu University Zhenjiang, 212013, China)
Abstract In order to eliminate the noise interference of the semi-active air suspension system caused by nonlinearity of the system, time-variation of parameters and uncertainty of the model, the working principle of wavelet de-noising of the semi-active air suspension is studied. In addition, the wavelet de-noising neuron adaptive controller of the semi-active air suspension is designed, the dynamic model of the semi-active air suspension is established based on wavelet de-noising, and the effectiveness of wavelet de-noising is analyzed using simulation and bench tests. The result shows that the semi-active air suspension based on wavelet de-noising neuron adaptive controller improves the centroid acceleration and pitching angular acceleration of the vehicle and ameliorates the comprehensive performance of the vehicle.
Keywords semi-active air suspension; adaptive control; wavelet de-noising; bench test
Conversion Method for Loss Factor of Unconstrained Damping Structures
ZhangAnfu1,YanXiaowei2,ShengMeiping1,WuQingqing1
(1.School of Marine Science and Technology, Northwestern Polytechnical University Xi′an, 710072, China)
(2.China State Shipbuilding Corporation Systems Engineering Research Institute Beijing, 100094, China)
Abstract Based on theoretical loss factor′s formula of damping structure, a conversion method for the loss factor of different unconstrained damping structures is proposed. The damping tests are carried out on a damping plate and damping shell. The experimental results are compared with the results from the conversion method in order to prove the effectiveness of the conversion process. The conversion coefficient change with thickness ratio and error amplification factor are both analyzed in the process of loss factor calculation. The simulation results show that the conversion coefficient change with height ratio is bigger for damping material with a small elastic modulus than for damping material with a large elastic modulus, and the conversion data is more accurate for damping material with a larger elastic modulus. In order to improve precision, the thickness of damping materials should be bigger than that of the target backing material, and the thickness of conversion backing should be smaller than twice thickness of target backing. The unmeasured loss factor of the structure can be obtained through the conversion method. It achieves the goal of acquiring the loss factor of the damping structure, which is difficult to be measured in practice. This method provides a referable solution to acquisition of the loss factor of large damping cylindrical shells and vibration suppression effect comparison of various damping layers on large damping cylindrical shells.
Keywords damping materials; loss factor; conversion method; error amplification factor
Rolling Bearings Fault Diagnosis Based on Recurrence Complex Network
SunBin1,LiangChao1,ShangDa2
(1.School of Energy and Power Engineering, Northeast Dianli University Jilin, 132012, China)
(2.Jilin Electric Power Research Institute Co.,Ltd Changchun, 130021, China)
Abstract In the case of the non-stationary and non-linear vibration signal of a rolling bearing with faults, a bearings fault diagnosis method based on the recurrence complex network (RCN) is put forward. First, a one dimension time series is extended to high dimension phase space by using the phase space reconstruction method, and a recurrence matrix is built. Then, recurrence quantification analysis (RQA) is discussed. Finally, the recurrence complex network (RCN) method is employed to extract nonlinear characteristic parameters of the vibration signals, which yield the feature vectors. The analysis results of the vibration signals acquired from the bearings with normal, outer track fault, ball fault and inner track fault, respectively, show that the RCN method has better diagnosis effect than the RQA method.
Keywords recurrence complex network; vibration signal; fault diagnosis; fluctuation modal
Xi′an Jiaotong University Xi′an, 710049, China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi′an Jiaotong University Xi′an, 710049, China)
(3.School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi′an University of Architecture and Technology Xi′an, 710055, China)
(4.School of Mechanical Engineering, Nanjing Institute of Technology Nanjing, 211100, China)
The fiber optic sensor is a new kind of measurement sensor that can detect various physical quantities, such as displacement, vibration, strain, and flow, by studying the modulating characteristic of the optical wave inside the fiber optic under the influence of the quantities to be measured. Based on fundamental theoretical knowledge of fiber optic measurement technology, the reflective displacement sensor and light-transmission fiber optic motion sensor are introduced as two typical transmission-type optical fiber sensors in order to elaborate the operational principle of the transmission-type optical fiber sensor and its applications in the dynamic measurement of lubricating oil film inside journal bearings, rotor vibration in rotating machinery, blade tip clearance in aircraft engines, fluid flow in aircraft engines and movement detection in the human body. Discussion on the innovative design of and the research on these measurement systems is presented. Then, another kind of fiber optic sensor, the functional-type optical fiber sensor, is discussed by introducing two typical sensors, the curvature optical fiber sensor and fiber Bragg grating sensor, as well as their measurement principles and applications in measuring casing deformation, and the measurement of dynamic stress on planet gear. Lastly, the development of this new technology is summarized and prospected.
fiber optic sensor; dynamic measurement technology; rotating machinery; engineering parameters
10.16450/j.cnki.issn.1004-6801.2015.03.030
2013-03-21;
2014-04-08
TH133.33
孙斌,男,1972年1月生,博士、教授。主要研究方向为非线性信号处理、故障诊断等。曾发表《基于等距特征映射和支持矢量机的转子故障诊断方法》(《机械工程学报》2012年第48卷第9期)等论文。 E-mail: sunbin@mail.nedu.edu.cn

