“失海”渔民养老保险衔接方案研究
赵青青
(河海大学公共管理学院,江苏 南京 210098)
“失海”渔民养老保险衔接方案研究
赵青青
(河海大学公共管理学院,江苏 南京 210098)
在吸取前人研究成果以及现行养老保障体系的基础上,借鉴日趋完善的被征地农民养老保险政策,参照过渡性、责任共担、相对生活水平不降低的原则,试图设计“失海”渔民养老保险与现有养老保险体系的衔接方案:根据年龄、性别的不同划分参保对象;由政府、项目业主、集体和个人四方共同筹集资金;借鉴被征地农民养老保险办法及不同参保对象对养老保险的需求设定缴费标准;参照现行社会养老保险政策确定给付方式及水平。以此将“失海”渔民纳入现有的养老保险体系中,以保障“失海”渔民的基本生活水平。
“失海”渔民;养老保险;政策衔接
近年来,随着我国城镇化的不断推进,近海海域和滩涂被大量占用,渔民“失海”现象日渐突出。然而,海域之于渔民,犹如土地之于农民,渔民“失海”犹如农民“失地”和工人“失业”[1],将会使许多渔民陷入“种地无田、养殖无海、转业无岗、社保无份”的困难境地,生活受到极大的影响。
目前我国学术界对“失海”渔民这一特殊群体缺乏系统的研究。在实践方面,多数地区在收回海域使用权后,对“失海”渔民重补偿轻安置,多采用一次性货币补偿的方式[2],并没有切实考虑渔民关注的养老等问题。仅有部分地区对“失海”渔民养老保险政策进行了实践,但也存在着政策供需不平衡、政策缺乏统一性和权威性、政策不成体系的弊端[3]。因此,笔者在吸收和借鉴前人研究成果以及现行养老保障体系的基础上,借鉴日趋完善的被征地农民养老保险政策,分析了“失海”渔民养老保险方案的设计依据和原则,从划定参保对象、资金筹集、确定缴费标准及缴费比例、给付方式及水平4个方面,设计了“失海”渔民养老保险与现有养老保险的衔接方案,通过一次性缴费的方式将“失海”渔民养老保险过渡到现有的社会保障体系中,以期为保障“失海”渔民的基本权益提供一定的借鉴。
1 设计原则
1.1 过渡性原则
长期以来,我国针对不同的人群采用不同的养老保险办法。现行社保制度已经具有逐渐走向碎片化的倾向[4],这不仅使得不同人群的养老待遇差异巨大,而且增加了管理上的难度。
随着养老保险体制改革的深入,解决“碎片化”问题、逐步走向统一是我国养老保险体制的发展趋势。然而,目前我国城乡存在很大的差异,不同群体之间采用的养老保险办法也不尽相同,要一次性建立覆盖所有群体的统一制度是不现实的,要将“失海”渔民直接纳入现有的养老保险体系中,在缴费标准、资金来源等方面存在很大的困难。在此前提下设计“失海”渔民养老保险方案,特别是建立可以转换、可以过渡的养老保险方案[5],在资金筹集模式、缴费机制与计发办法上做到统一[6],是进行养老保险方案设计的基本出发点。
1.2 责任共担原则
作为公民的一部分,“失海”渔民理应享受到与其他公民同等的待遇,因此在保障其他公民养老权益的同时,政府理应以公平的态度保障“失海”渔民的养老权益。另外,政府在收回海域使用之后,实际上间接剥夺了海域对于渔民的经济功能和保障功能,政府在给予一定的海域补偿费的同时,还要为渔民提供必要的经济和生活保障。
目前,“失海”渔民养老保险的缴费主体是个人,农村集体经济组织实际上并未承担相关责任与义务,使得“失海”渔民的缴费负担大,养老金难以提高,因此,必须强调农村集体的缴费责任。
另外,渔民由于项目业主用海而“失去”了海域使用权,项目的投入会给业主带来可观的经济收益,因此用海项目业主也应该为“失海”渔民养老保险负担一定的责任,缴纳一定的养老保险费。
综上所述,在与现有养老保险体系的衔接过程中,“失海”渔民养老保险的一次性缴费应该遵循以政府为主导的集体、业主及个人的责任共担原则,其中政府和集体代表着群众利益,应当担负主要责任。因此,可借鉴被征地农民养老保险的相关政策,将个人、村集体、项目业主、政府的缴费比例确定为2∶3∶2∶3。
1.3 相对生活水平不降低原则
《国务院办公厅转发劳动保障部关于做好被征地农民就业培训和社会保障工作指导意见的通知》(国办发[2006]29号)中指出,要确保被征地农民生活水平不因征地而降低。对于渔民而言,在被收回海域使用权后,理应享受到保障其生活水平不降低的权益。由此,各地政府在确定养老金水平时,多数以城市最低生活保障线为基准,使养老保险的待遇水平偏低,难以维持农民进城后的基本生活水平,并未真正达到保障其生活水平不降低的目标。此外,采用目前各地实行的此种养老保险方案,也难以与现有养老保险体系进行衔接。在确定养老金水平时,应该确保相对生活水平不降低的原则[7],使“失海”渔民在失去海域使用权后能够保障其相对的生活水平不降低。
2 方案设计
2.1 参保对象
根据年龄、性别的不同对养老保险需求的区别,对“失海”渔民进行了分类,见表1。
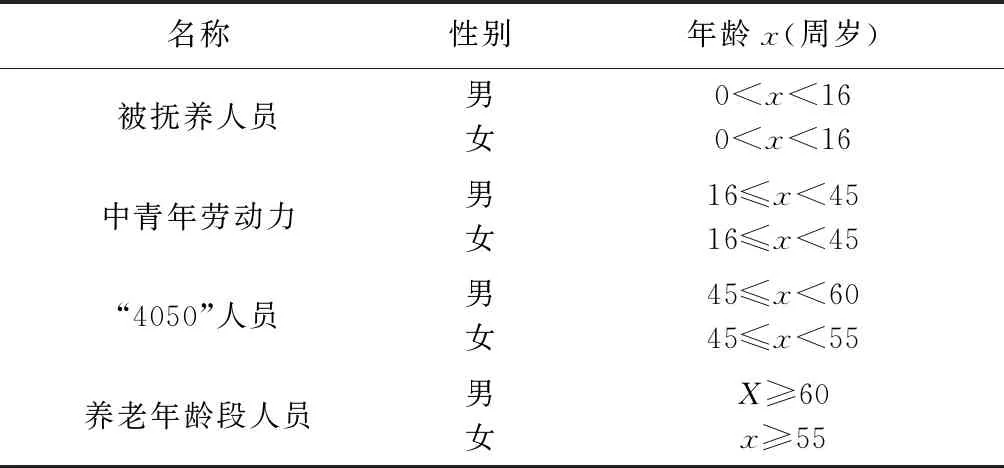
表1 “失海”渔民年龄分段
对于被抚养对象,可以直接给予一次性生活补助费,等其达到劳动年龄后,可以根据实际情况直接参与到城镇职工基本养老保险中。因此,这一部分人员可以不在“失海”渔民养老保险的参保对象中。
综上所述,参照目前已经日渐成熟的被征地农民养老保险的相关政策,“失海”渔民养老保险的参保对象可大概定义为由于直接或者间接原因失去海域作业权利后,家庭人均海域作业面积不足当地人均面积的30%,并且在征海协议签订时已年满16周岁的渔民。
2.2 资金筹集
笔者认为“失海”渔民应纳入现有的养老保险体系中,并且其养老保险缴费应该由政府、项目业主、集体和个人共同承担。资金主要来源于以下3个方面:①海域补偿费。海域补偿费不足失海渔民参加基本养老保险所需资金的50%,则由当地海洋行政主管部门负责补足。②地方政府海域使用金。地方政府按照当地的相关规定,把海域使用金按照一定的比例提留作养老保险费用,纳入社会统筹账户。③项目投资。项目的投入运营具有周期性,而“失海”渔民的安置补偿工作必须在前期落实,因此项目业主的资金在前期投资概算时就应列入,减轻“失海”渔民个人和集体的缴费负担。
2.3 缴费标准
对于中青年劳动力以及“4050”人员中能够实现再就业的人员,可借鉴被征地农民养老保险的相关规定,将“失海”渔民养老保险的缴费基数确定为全省上年度在岗职工月平均工资的60%,缴费比例为20%,个人、村集体、项目业主、政府的缴费比例为2∶3∶2∶3;对于养老年龄段人员以及“4050”人员中不能实现再就业的人员,缴费基数可定为现有城乡居民社会养老保险缴费标准中某一档次,具体档次可由参保人自行选择,缴费比例为100%,个人、村集体、项目业主、政府的缴费比例为2∶3∶2∶3。
缴费年限以收回海域使用权时“失海”渔民在海域上的劳动年限(最低年满16周岁起算),每满两年补缴一年的社会保障费(不满两年按两年计算),最高为15年。
在一次性缴费方面,按照每满2年补缴一年养老保险费的规则,具体办法如下:
2.3.1 中青年劳动力
该阶段人员为男、女均年满16周岁、不满45周岁。趸缴养老保险费的标准为:缴费基数×费率(20%)×本人应缴费年限,其中应缴年限是根据参保人参加劳动的年限确定,即上文所述的每满2年补缴一年养老保险费。本人应该缴费年限:年满17周岁不满18周岁补缴1年;年满19周岁不满20周岁补缴2年,以此类推,年满44周岁不满45周岁补缴14年;年满45周岁不满46周岁补缴15年;46周岁以上补缴15年。中青年劳动力人员一次性缴纳基本养老保险费的年限计算为城镇职工基本养老保险的缴费年限,缴费基数按1计算,并按规定补建个人账户。个人完成一次性缴费后,可以直接参加城镇职工养老保险,缴费的总年限至少为15年。

表2 MZW地区“失海”渔民参加城镇职工基本养老保险趸缴费用
2.3.2 “4050”人员
该阶段人员为男年满45周岁不满60周岁,女年满45周岁不满55周岁。根据上文计算,本阶段人员需要一次性补缴15年的养老保险费。
对于收回海域使用权后能够实现再就业的人员,趸缴养老保险费的标准为:缴费基数×费率(20%)×15。其一次性缴纳的基本养老保险费作为15年缴费年限,缴费基数按1计算,并补建个人账户。
对于收回海域使用权后不能实现再就业的人员,趸缴养老保险费的标准为:缴费基数×费率(100%)×15。缴费基数可由“失海”渔民自行选择当地城乡居民社会养老保险的某一档次进行缴费。
2.3.3 养老年龄段人员
该阶段人员为男年满60周岁、女年满55周岁。趸缴养老保险费的标准为:缴费基数×费率(100%)×15。缴费基数可由“失海”渔民自行选择当地城乡居民社会养老保险的某一档次进行缴费。
2.4 给付方式及水平
将“失海”渔民纳入现有的养老保险体系之后,在养老保险的给付上,可以按照城乡居民社会养老保险或者城镇职工基本养老保险的标准进行养老金给付,只需要调整统筹账户养老金的发放标准即可。
城乡居民基础养老金参照中央制定的最低标准,各地根据自身经济情况略有提高;个人账户养老金包括一次性缴费个人账户和参加城乡居民社会养老保险建立的个人账户,发放标准为本人基本养老保险个人账户累计储存额本息除以计发月数。
城镇职工基础养老金的发放基数为退休时上年度全省在岗职工月平均工资和本人指数化平均工资的平均值,缴费每满一年发给1%,上不封顶;而“失海”渔民无法计算本人指数化月平均工资。因此,基础养老金按照城镇企业退休人员最低基础养老金的标准按月发放,以保证“失海”渔民基本的养老需求。对于“4050”人员中能够实现再就业的人员,在其达到法定退休年龄前,继续缴纳城镇职工基本养老保险费不足5年的,从达到法定退休年龄的次月起,可领取养老金待遇=城镇企业退休人员最低养老金×(1+继续缴费月数×1%);继续缴纳城镇职工基本养老保险费5年以上的,按照城镇职工基本养老保险办法计发基础养老金。个人账户养老金包括一次性缴费个人账户和参加城镇职工基本养老保险建立的个人账户,发放标准为本人基本养老保险个人账户累计储存额本息除以计发月数。
3 可行性分析——以MZW地区为例
2012年MZW地区所在省在岗职工月平均工资为2 338元。根据本文设计的方案,“失海”渔民养老保险缴费基数为全省上年度在岗职工月平均工资的60%,则2012年MZW地区“失海”渔民养老保险的缴费基数为1 403元。根据本文设计的“失海”渔民养老保险方案,MZW地区不同年龄段“失海”渔民的一次性缴费标准如表2、表3所示。
根据收回海域使用权面积、影响人口及当地海域征收补偿办法计算所得,该项目的人均海域补偿费为4 025元,2012年MZW地区农民人均纯收入为9 967元。从上述表格可以看出,笔者设计的养老保险方案缴费标准较低,除“4050”人员中已经实现再就业人员的一次性缴纳费用略超过2012年农民人均纯收入外,其他年龄段的人员一次性缴纳的费用均低于2012年的农民人均纯收入。加之收回海域使用权后获得的海域补偿费,“失海”渔民个人缴费部分资金来源有所保障。

表3 MZW地区“失海”渔民参加城乡居民社会养老保险趸缴费用
根据MZW地区“失海”渔民的人员结构情况,该地区“失海”渔民养老保险费用需要政府出资约5 823.65万元,项目业主出资约3 731.08万元,见表4。
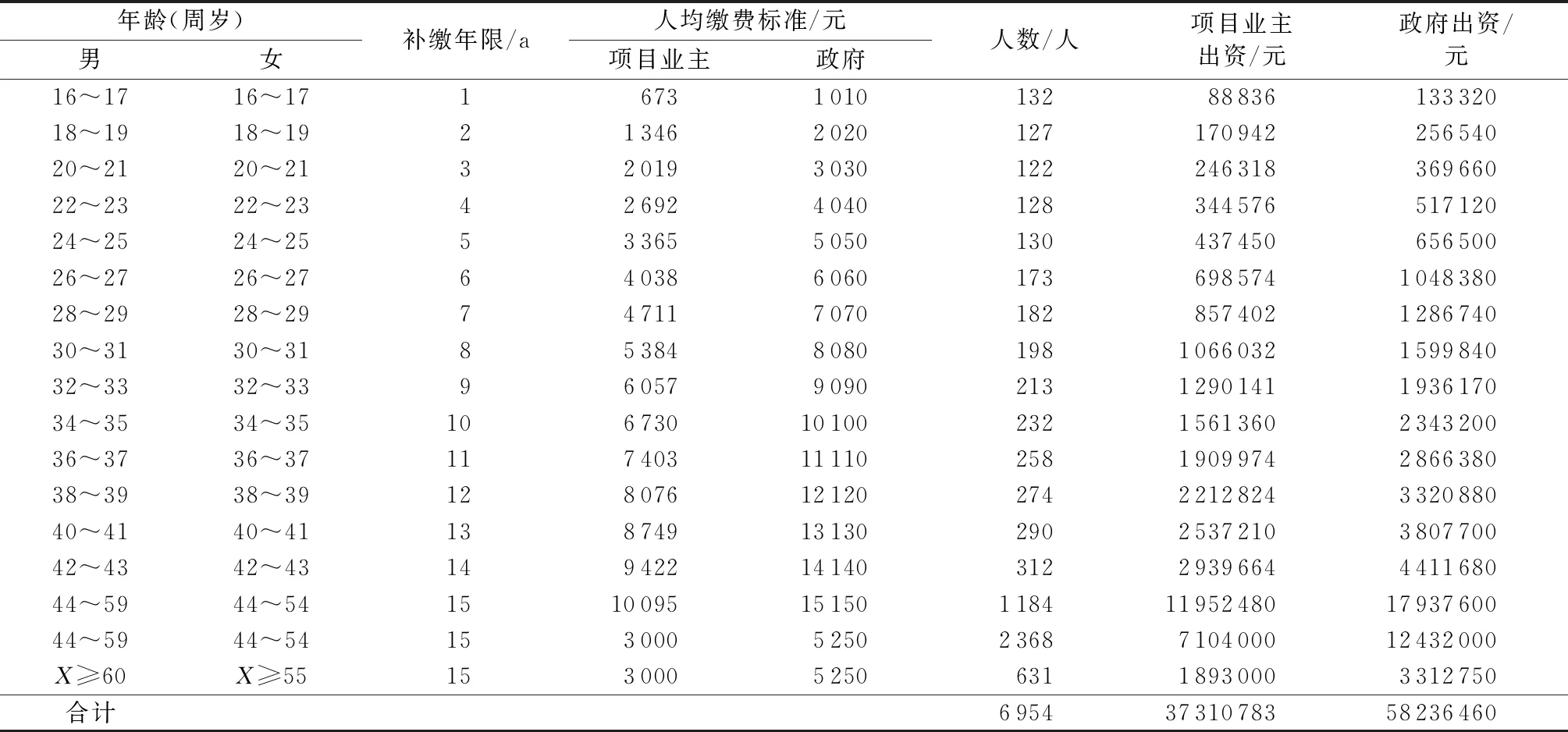
表4 MZW地区“失海”渔民养老保险政府、项目业主出资情况
MZW地区共收回海域面积约518.3 hm2,按照当地的海域使用金征收管理办法中海域使用金的征收规定,经计算可得当地政府海域使用金收入为13 993.2万元,足够支付“失海”渔民养老保险政府出资金额。
4 结 语
“失海”渔民的养老问题是保证城镇化发展进程、保障“失海”渔民长远生计的关键问题。然而,目前各地并未将“失海”渔民养老保险纳入现有的保障体系中,仅有的也只是参照被征地农民养老保险相关规定执行,保障水平偏低,不能满足“失海”渔民日益增长的消费成本。更为重要的是,目前实施的政策脱离了现有的养老保险体系,“碎片化”严重,不符合城乡一体化的发展趋势。因此,在城乡二元结构逐渐解体的大背景下,参照过渡性、责任共担、相对生活水平不降低的原则,根据年龄、性别的不同划分参保对象,由政府、项目业主、集体和个人四方共同筹集资金,借鉴被征地农民养老保险办法及不同参保对象对养老保险的需求设定缴费标准,参照现行社会养老保险政策确定给付方式及水平,以此将“失海”渔民纳入现有的养老保险体系中,将有助于保障“失海”渔民的基本生活水平,有利于社会和谐发展。
[1] 闵建,蔡平. 关于建立“失海”渔民保障机制的探讨[J]. 海洋开发与管理,2009,26(4): 64-67.
[2] 王建廷. 海域征收补偿制度研究[J]. 中国渔业经济,2008,26(4): 25-30.
[3] 同春芬,毛昕. “失海”渔民社会保障政策实践及体系构建[J]. 青岛农业大学学报,2012,24(4): 51-55.
[4] 刘迪,毛昕. 失地农民养老保险制度的路径依赖与城乡一体化[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报(社会科学版),2008 (5): 73-76.
[5] 刘竹艳. 沿海地区渔民社会养老保险制度构建研究:以舟山市为例[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2009.
[6] 刘丛丛. 当前我国失地农民养老保险模式比较分析[D]. 天津:天津财经大学,2013.
[7] 陈绍军,章戈武,彭玲玲. 南京市失地农民新型养老保障制度的构建[J]. 南京人口管理干部学院学报,2010,26(4):21-24,33.
Decoupling analysis of water resources and economic development in Jiangsu Province/YOU Haixia, et al (Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Based on the statistics of 13 cities in Jiangsu Province from 2000 to 2010, the relationship between water use and economic growth in various cities and the regional differences are described from four aspects of the whole industry, the primary industry, the secondary industry and the tertiary industry respectively bye using the decoupling methods ofIPATequation. The results show that the relationship between economic growth and water use is in a weak decoupling state in most of the years from 2000 to 2010. The development of the primary industry is roughly the same as that of Jiangsu Province. The relationship between economic growth and water use in the second industry has been gradually achieved a stable and strong decoupling state. While the relationship between economic growth and water use in the tertiary industry has been in a weak decoupling state. At the same time, the relationship between economic growth and water use has regional differences in 13 cities to some extent. In this regard, Jiangsu Province should actively adjust the industrial structure, increase efforts to protect water resources, give full play of regional synergy and achieve strong decoupling in the relationship between water use and economic growth steadily so as to promote the establishment of water-saving society.
Key words: water use; economic development; decoupling; Jiangsu Province
Economic critical point of protection and utilization of Gaoyou Lake/MENG Lingfang, et al (College of Hydrology and Water Resources, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: The economic critical point of protection and utilization of a lake is the maximum scale of development and utilization without excessive destruction of ecological service function. The standard of development and utilization is that the sum of the economic benefit and the ecological benefit compatible with the development projects must be greater than or equal to that of the ecological benefit incompatible or conditionally compatible with the development projects. The main exploitation mode of Gaoyou Lake is aquaculture. The ecosystem service which is basically incompatible with the aquaculture is water purification. The ecosystem service which is conditionally compatible with the aquaculture is water supply, water storage, flood drainage, maintenance of biodiversity and scientific culture and education. The ecosystem service which is fully compatible with the aquaculture is carbon fixation and oxygen release, and transpiration endothermic. The results show that, in 2009, the economic benefit of the aquaculture of Gaoyou Lake is 35 062 RMB yuan/(hm2·a), and the economic critical point of the aquaculture of Gaoyou Lake is -2 427 RMB yuan/(hm2·a), implying that the development and utilization of Gaoyou Lake exceeds the development and utilization of the economic criteria and is in the state of excessive development.
Key words: lake protection and utilization; ecological service function; economic critical point; Gaoyou Lake
Decision-making of concession period of hydropower station projects under government and social capital cooperation/WEI Xing, et al (Jiangsu Coastal Development and Protection Center, Nanjing 211100, China; Water Resources and Sustainable Development Research Center of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Under the satisfaction of requirements of the social capital investment returns, by setting the handover point as the origin, a new net present value-operating time coordinates for the government departments is established, and the choice range of transfer of the concession period simultaneously satisfies the government departments for the nonnegative net present value. It is applied to hydropower station PPP projects. Considering the influences of characteristics of hydropower projects and risk factors on the concession period, the cash flow statement of the projects is calculated. Under the circumstance of gaining both sides’ satisfaction, the choice range of the concession period is obtained so as to negotiate the concession transfer period of the projects.
Key words: PPP Mode; hydropower station project; concession period
Application of firefly algorithm-projection pursuit model in evaluation of flood disasters in Yunnan Province/DAO Haiya, et al (Yunnan Water Conservancy and Hydropower Survey and Design Institute, Kunming 650021, China)

Key words: flood disaster assessment; projection pursuit; firefly algorithm; Yunnan Province
Calculation of profit and loss ad benefit distribution mechanism of optimal scheduling of small cascade hydropower stations/YANG Fan, et al (Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Based on the analysis of benefit distribution and historical data of regional small hydropower station groups in Longyan, a model for calculating profit and loss and benefit distribution of hydropower station groups is proposed using the particle swarm optimization, and the partition coefficient is calculated. The results show that the distribution mechanism can drive stations to actively participate in joint scheduling so as to rationally use the water resources.
Key words: small cascade hydropower station; optimal scheduling; benefit distribution; calculation of profit and loss
Choice of development paths of water culture industry in China/LI Dan, et al (School of Public Administration, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: The “Planning outline for water culture construction (2011-2020)” issued by the Ministry of Water Resources of P. R. China suggests to vigorously promote water cultural undertakings and to actively cultivate the water culture industry, and the water culture industry as an important part of the cultural industry begins to enter people’s vision. On the basis of discussing the connotation of water culture industry, the predicament of the development of water culture industry in China is analyzed as follows: weak industry awareness, single water culture product, imperfect government support system and single industry body. The development path for the water culture industry is proposed from four aspects of strengthening propaganda, mining resources, strengthening government support and improving financing system so as to provide feasible methods for the development of water culture industry in China.
Key words: water culture industry; water culture product; industrial policy; development path
Multi-agent cooperation mechanism of water resource exploitation in Lancang River-Mekong River basin/HU Xingqiu, et al (Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China; International River Research Centre, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: The social and economic situations and the current cooperative foundation of water resource exploitation in Lancang River-Mekong River basin are analyzed. Based on the successful international experience, the multi-agent cooperation mechanism concerning water resource exploitation in Lancang River-Mekong River basin is proposed. It covers four levels: state, locality, society and market. It may provide a new way for the promotion of the cooperation of water resource exploitation in Mekong River basin.
Key words: Lancang River-Mekong River basin; water resource exploitation; multi-agent cooperation; cooperation mechanism
Primary researches on asset management of water scenic resources/XU Zengrang, et al (Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China)
Abstract: The asset management of water scenic resources is not only the effective adaption by water industry to the severe scarcity of natural resources and the growing demand for the ecological products, but also the positive response to the enhancing of production capability of ecological products initiated by the 18th National Congress of CPC. It aims to highlight the ecological and cultural superiority of water scenic parks and to realize the value of their material products, culture products and ecological products. The difficulty is to identify and display the ecosystem services of water scenic parks and to realize their value. The patterns of asset management of water scenic resources mainly include (1) development of environment-friendly agricultural products both in reservoir-based and irrigation system-based water scenic parks, (2) development of ecological tourism in river and lake-based water scenic parks, (3) ecological compensation in water and soil conservation-based water scenic parks, and (4) market transaction of water ecosystem services in the wetland-based water scenic parks. Different policy measures should be gradually improved with regard to different patterns of asset management of water scenic resources.
Key words: water scenic resource; water scenic park; ecosystem service; eco-compensation; ecological product
Support mechanism of scientific and technological innovation for construction of water ecological civilization/WU Zhaodan, et al (School of Business Administration, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, China; Jiangsu Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of World Water Valley and Water Ecological Civilization, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: The support mechanism of scientific and technological innovation for the construction of water ecological civilization is analyzed. It is systematically discussed from three aspects, that is, demand, condition and conduction path of the construction of water ecological civilization supported by the scientific and technological innovation. The results show that the support of fundamental science innovation, applied technology and method innovation, and scientific and technological practice innovation is necessary to the construction of water ecological civilization. The play of this support needs the premise of ecological science and technology, the internal motives such as interest driving, entrepreneurs’ innovation spirit and internal system as well as the external motives like demand-driving force, police-driving force, social cooperation, legal safeguard and cultural leading force. The support conduction paths include the soft power improvement of construction of water ecological civilization, the allocation optimization of water resources, the water saving management and the protection of water ecological environment.
Key words: scientific and technological innovation; construction of water ecological civilization; support mechanism; water saving; protection of water ecological environment
Establishment of incentive-constrained-supervised mechanism for industrial water environment regulation based on principal-agent relationship of regulatory subjects/ZHAO Shuang, et al (College of Economics and Management, Zhejiang Radio & Television University, Hangzhou 310030, China)
Abstract: The principal-agent relationship in stakeholders of industrial water environment in China is analyzed, and some principal-agent risks and the relevant reasons are gained. Then, the environmental administrative contract of industrial water environment regulation is proposed. Moreover, three mechanisms are established: the incentive mechanism by environmental subsidies, the constraint mechanism by supervision and law enforcement and administrative penalty, and the supervision mechanism by the central supervision and public participation. Furthermore, a model for the industrial water environment regulation is proposed to get the operating mechanism of the incentive-constrained-supervised mechanism. Finally, a regulatory contract implementation process is designed for promoting the efficient operation of industrial water environment regulation.
Key words: industrial water environment regulation; principal-agent; environmental administrative contract; incentive-constrained-supervised mechanism; implementation process
Dynamic relationship between industrial waste water pollution and process of urbanization China/MA Hailiang, et al (Institute for Low Carbon Economy of Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, China; Collaborative Innovation Center of World Water Valley and Water Ecological Civilization, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: By selecting five types of pollutants in industrial waste water in China from 2003 to 2012, Kuznets curve fitting for the relationship between the industrial waste water pollution and urbanization rate is conducted. On this basis, the cubic exponential smoothing method is used to forecast the emissions of industrial waste water pollutants. The results show that with the speeding up of urbanization construction, the emissions of petroleum and lead in the industrial waste water pollutants in China first decrease and then increase, but the chemical oxygen demand, ammonia nitrogen and volatile phenol do not conform to the shape of typical environmental Kuznets curve. By 2020, it is expected that the emissions of chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen will be reduced to negative values, but those of volatile phenol, petroleum and lead will increase sharply.
Key words: industrial waste water pollutant; urbanization; Kuznets curve; exponential smoothing method
Evaluation of sustainable utilization of water resources in China/TONG Jixin, et al (Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: By selecting the latest data from 31 provincial units, seven kinds (25 in total) of evaluation indexes of sustainable utilization of water resources are extracted. The principal component analysis and DEA are employed to evaluate the sustainable utilization of water resources in China. The research results show that the sustainable utilization capability of water resources of nearly 74.2% of China’s provinces is poor, and it is distributed like a ladder. The reason is mainly resulted from the non-coordination of sustainable use of water resources and socio-economy, water environment capacity, agricultural irrigation, urban development and ecological protection. However, there is still a large development potential.
Key words: water resource; sustainable utilization; DEA model; principal component analysis
Characteristics and suggestions of regional development of the seawater desalination industry in China/CHEN Aihui, et al (Institute of Seawater Desalination and Multipurpose Utilization, SOA (Tianjin), Tianjin 300192, China)
Abstract: Based on the current development of the desalination industry in China, the characteristics of desalination industry in the coastal regions of Bohai Rim Area, Yangtze River Delta and Pan-Pearl River Delta and the existing problems are analyzed. The factors such as regional distribution and industrial development are considered for the large-scale regional development. The relevant suggestions are put forward for the regional development of the seawater desalination industry in terms of the desalinated seawater to municipal water distribution system, brand establishment and island classification demonstration.
Key words: seawater desalination industry; unconventional water; regional development
Current situation and development trend of reuse of urban waste water in China/LI Yajuan, et al (Beijing Sinoriver Groundwater Protection and Utilization Institute, Beijing 100053, China)
Abstract: The current situation of reuse of waste water in China is summarized from the following aspects of reuse amount, policies and regulations and technology. The existing problems in the process of recycled water are put forward: immature institutional mechanism, deficient policies and regulations, short investment, difficult operation of enterprises, inadequate pipe networks, inadequate recognition of government, low public participation. The development trend of reuse of waste water in China are analyzed from five aspects, that is, market demand, price system, water quality before treatment, water quality after treatment, technical innovation and technological advance.
Key words: urban waste water; reuse; unconventional water; current situation; trend
Livelihood security assessment of rural reservoir resettlement in D County of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region/CHEN Mingyu, et al (National Research Center for Resettlement (NRCR), Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Based on the sustainable livelihood analytical framework and the reference pressure-state-response (PRS) model, an evaluation index system for the livelihood security of rural reservoir resettlement is established by taking D County in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. The comprehensive fuzzy hierarchy analysis method is employed to evaluate the livelihood security of resettlements in D County. The results show that the livelihood security of reservoir resettlements in D County is in a critical state. The reservoir construction has great impact on the resettlements. The implementation progress of regional resettlement development policy is very slow. The resettlements lack of their own ability, and the social forces on their livelihood recovery are short. Some suggestions are put forward: strengthening of resettlement agencies, improvement of social security system of landless resettlements and specification of livelihood recovery management operation.
Key words: rural reservoir resettlement; livelihood security; Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
Cohesion scheme for “sea-lost” fishermen’s endowment insurance/ZHAO Qingqing (School of Public Administration, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Based on the previous researches, the existing endowment insurance system and the gradually perfect policies of endowment insurance for landless farmers, the cohesion scheme for the “sea-lost” fishermen’s endowment insurance in accordance with the exiting endowment insurance system is designed referring to the principles of transition, shared responsibility and non-reduction of relative life. According to their different ages and genders, the insured “sea-lost” fishermen are divided. The government, the project owner, the collective and the individual jointly raise funds. The collecting standard is determined from the measures for landless farmers’ endowment insurance and the demands for different insured fishermen’ endowment. The payment mode and level are defined with reference to the existing policies for social endowment insurance. Accordingly, the “sea-lost” fishermen are included into the existing endowment insurance system so as to protect their basic living standards.
Key words: “sea-lost” fisherman; endowment insurance; policy cohesion
Based on the target of investment subjects (government, market investors and farmers) of rural drinking water safety projects, the relevant indexes are set, and a weighted multi-attribute grey target decision model is established. An example of the rural drinking water safety project in Huai’an is analyzed. The proposed model is used to evaluate whether the project is suitable for investment by a single subject. The results show that the project is not suitable for a single investor but for the joint investment by the government, market investors and farmers. Finally, some inspirations and suggestions are put forward for the investment of rural drinking water safety projects.
rural drinking water safety project; investment; subject selection
国家社会科学基金重大项目(13&ZD172)
赵青青(1989—),女,山东平度人,硕士研究生,从事土地经济与管理、征地拆迁与移民管理等研究。E-mail:794615885@qq.com
10.3880/j.issn.1003-9511.2015.06.017
F840.61
A
1003-9511(2015)06-0075-04
2015-06-17 编辑:方宇彤)
Journal of Economics of Water Resources
Selection of investment subjects of rural drinking water safety projects/FENG Jingchun, et al (Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China; Jiangsu Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of World Water Valley and Water Ecological Civilization, Nanjing 211100, China)

