以纳米炭纤维为模板浸渍制备V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂
吴 强, 赵 立, 武美霞, 姚伟峰
(1.上海电力学院环境工程与化学学院,上海 200090;2.山西大同大学化学与环境工程学院,山西大同 037009)
以纳米炭纤维为模板浸渍制备V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂
吴 强1, 赵 立1, 武美霞2, 姚伟峰1
(1.上海电力学院环境工程与化学学院,上海 200090;2.山西大同大学化学与环境工程学院,山西大同 037009)
以SiO2纤维为宏观基体材料,首先采用化学气相沉积法制备纳米炭纤维,然后以纳米炭纤维作模板将纳米多孔Al2O3固化在SiO2纤维上,以此得到Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体材料,最后采用浸渍法制得V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂。考察V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂对炭黑颗粒氧化反应的催化性能。结果表明,该类催化剂能明显降低炭黑颗粒的起燃温度,可以有效地降低柴油车尾气中炭黑颗粒的排放,具有潜在的实际应用前景。
SiO2纤维;纳米炭纤维;模板法;V2O5-K2SO4系催化剂;炭黑颗粒
Foundation item:National Natural Science Foundation of China(21107069,21103106);Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars,State Education Ministry (Z-2013-002); Shanghai Pujiang Program (12PJ1403800);Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission(14ZZ153);Open Project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Functional Materials(Z-2011-050);Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Scholars of Shanghai University of Electric Power(K-2011-004);085 Engineering Project of Smart Grid Energy Storage Technology of Shanghai University of Electric Power(C-8209-11-551).
Author introduction:WU Qiang,Ph.D.,Associate Professor,E-mail:qiangwu@shiep.edu.cn
1 前言
汽油机和柴油机是汽车最主要的动力源,而柴油机以其低油耗、高功率、高可靠性和耐久性的优势,逐渐成为车用动力的首选。但是,柴油车尾气排放的炭黑颗粒已引起严重的环境污染,因此控制和消除柴油车尾气炭黑颗粒的排放具有十分重要的意义[1-3]。采用氧化型催化剂将炭黑颗粒氧化成CO2是目前减少炭黑颗粒污染的最直接有效的排放后处理方法[4-6]。V2O5-K2SO4系催化剂具有低共熔点且易流动的特性,易于实现炭黑颗粒与催化剂紧密接触,因而具有优异的催化氧化炭黑颗粒的反应性能,并已受到广泛关注[7,8]。但这类催化剂难以大量并均匀地涂层负载在有序结构的宏观基体材料上如蛭石、水滑石、棒状纤维、蜂窝陶瓷体以及多孔阳极氧化铝膜(AAO)。因此,研发具有高质量和高性能催化剂的新工艺和新技术仍是研究重点。
近年来,模板法因其具有简便、经济、重复性高以及产品的形貌、结构、尺寸取向可控等诸多优点而广泛应用于纳米材料的制备工艺。纳米炭纤维是一种具有潜在应用前景的模板材料,它可以通过工艺简单、成本低廉的化学气相沉积(CVD)法来制备。纳米炭纤维不仅具有低密度、高比强度、高导电和导热性、强耐腐蚀和耐高温等性能,同时还兼具缺陷数量少、比表面积大和结构致密等优点,因而在催化剂和催化剂载体、高效吸附剂、复合材料以及新材料制备等领域具有广泛的应用前景[9-12]。近年来,利用纳米炭纤维模板可以制备出多种形貌可控的新型多孔功能复合材料,该类材料具有很强的吸附和催化性能[9-12]。
笔者采用纳米炭纤维模板技术先将纤维状纳米多孔Al2O3固化在有序结构的宏观基体材料SiO2纤维上得到复合材料,再将Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合材料作为载体涂层负载相应的活性组分 V2O5-K2SO4,进而得到V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂。通过优化制备条件,最终可以得到高质量有序结构宏观基体与微观颗粒复合的多孔材料,该类材料具有较强的吸附和催化性能,可以克服催化反应中使用传统纳米粉末催化剂所带来的各种弊端(如压力降和热传递问题、以及接触效率低和催化剂难于分离等),能更为有效地降低柴油车尾气中炭黑颗粒的排放,因而具有潜在的应用前景。
2 实验
2.1 SiO2纤维上制备纳米炭纤维
采用化学气相沉积法在有序结构的宏观基体材料上合成纳米炭纤维:以SiO2纤维作为有序结构宏观基体材料,采用Ni金属作催化剂活性组分(催化剂质量分数为基体材料的1%),CH4气体作为碳源,气体流量为20mL/min,反应温度为550℃,常压下反应2 h即得到固化在 SiO2纤维上的纳米炭纤维。
2.2 Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体的制备
采用纳米炭纤维模板法制备Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体:将上述得到的固化在SiO2纤维上的纳米炭纤维浸渍在浓度为0.3 mol/L Al(NO3)3前驱液中5min,然后抽滤以去除其表面过剩溶液,后经300℃干燥1h,重复上述浸渍和干燥过程3次;最后在空气中600℃下焙烧6h去除纳米炭纤维模板,得到Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体。
2.3 V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂的制备
在80℃水浴和搅拌条件下将一定量NH4VO3和草酸溶解于去离子水中,然后继续向溶液中缓慢地加入一定量的K2SO4,搅拌溶解后直至得到深蓝色溶液,其中NH4VO3∶草酸∶K2SO4∶去离子水的配比为3.2mol∶3.2 mol∶1.6 mol∶1 L;将Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体浸渍在上述所得的深蓝色溶液中1h,随后样品在烘箱中120℃ 条件下烘干5h,然后取出置于马弗炉中,马弗炉以10℃/min的升温速率由室温升至350℃焙烧24 h后冷却到室温得到V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂。
2.4 表征
采用X-射线衍射(XRD)测定样品结构形态,仪器为Rigaku D/Max-2500型X-射线衍射仪,Cu靶K α射线(λ=0.154 05 nm)。样品形貌由JSM-7400F(JEOL)型场发射扫描电镜(SEM)和Hitachi JEM-2000FX(JEOL)型透射电镜测试。BET比表面积由AUTOSORB-3仪器测定。催化性能测试采用热重-差热分析测试方式,所用仪器为 Rigaku Thermo Plus TG 8120热重分析仪,其中催化剂与炭黑颗粒保持质量比为1∶10,经混合研磨后放置于热重-差热分析仪的坩埚中,反应体系以10℃/min的升温速率由室温升至700℃观察热重曲线的变化,该过程中持续通入空气作为氧化剂,流量控制为30mL/min。另取相同质量比的α-Al2O3和炭黑颗粒混合物作对照实验,其他条件保持一致。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 SiO2纤维上纳米炭纤维的制备与表征
笔者前期研究结果表明,通过控制化学气相沉积反应的条件可以有效地调控纳米炭纤维的生成,并且反应温度为550℃,CH4气体流量为20mL/min,常压下反应2 h所制纳米炭纤维适宜作为模板材料[10-12],采用上述化学气相沉积反应的条件制备纳米炭纤维模板。图1(a)是化学气相沉积前SiO2纤维的SEM照片,可以看出SiO2纤维呈长棒状且表面较光滑,直径约5.0μm。图1(b)是化学气相沉积后SiO2纤维表面生成纳米炭纤维的SEM照片,可以看出纳米炭纤维(厚度约为4.0μm)均匀且大量负载在SiO2纤维上,具有纤维状结构并且互相交织。
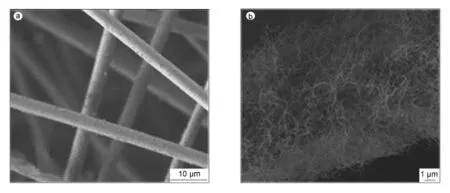
图1 (a)SiO2纤维及(b)SiO2纤维上生成纳米炭纤维的SEM照片Fig.1 SEM images of(a)pure silica fiber and(b)carbon nanofibers formed on silica fiber.
由图2可以看出,纳米炭纤维的直径为30-80nm,Ni粒子位于纳米炭纤维的顶部,这表明纳米炭纤维的生成机理遵循“顶端生长模式”[10]。
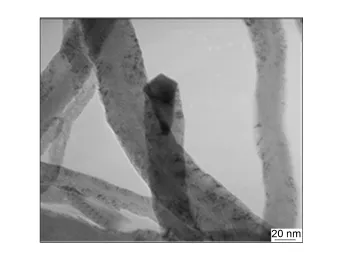
图2 纳米炭纤维的TEM照片Fig.2 TEM image of carbon nanofibers.
3.2 Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体的制备与表征
笔者前期研究结果表明,纳米炭纤维模板法可以实现快速且高效地在宏观基体材料上涂层附载大量的单金属或复合金属氧化物,并且在纳米炭纤维模板去除后,所生成的物质将具备与纳米炭纤维模板相似的形貌。考虑到这里所制V2O5-K2SO4复合载体催化剂主要用于炭黑氧化反应的催化性能的实验研究,因此不能直接采用纳米炭纤维模板法制备相应的V2O5-K2SO4复合载体催化剂,主要存在以下两点原因:一是采用空气中直接烧除纳米炭纤维模板时,其焙烧温度必须高于600℃;二是 V2O5-K2SO4系催化剂具有低共熔点,在制备过程中其焙烧温度不能高于400℃。因为当焙烧温高于上述400℃时,所制产物会不均匀并且出现大块聚结现象。而当焙烧温低于上述400℃时,纳米炭纤维模板不能被完全烧掉,它会明显影响后续的炭黑氧化反应的催化性能。
基于以上原因,本研究先采用纳米炭纤维模板法将纳米多孔 Al2O3固化在 SiO2纤维上得到Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体材料,再采用浸渍法制备V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂。图3是采用纳米炭纤维模板法所制Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体的 SEM照片。由图3可以看出,纳米多孔Al2O3可以大量并均匀的涂层附载在SiO2纤维上,其层厚约为2.5μm,并且保留了纳米炭纤维模板的形貌。
3.3 V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂的制备与表征
由图4可知,V2O5-K2SO4均匀地涂层附载在Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体上,其层厚约为3.5 μm。经计算,V2O5-K2SO4担载量(质量分数)为62.0%。BET比表面积测定V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂的比表面积为36.5 m2/g。可以推断,与表面光滑的SiO2纤维相比,Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体因其具备纤维状纳米多孔结构,因而可提供更多V2O5-K2SO4涂层附载的空间,制备出高质量有序结构宏观基体与微观颗粒复合的多孔材料。该类材料将具有较强的吸附和催化性能,可以克服催化反应中使用传统纳米粉末催化剂所带来的多种弊端,因而具有潜在的应用前景。
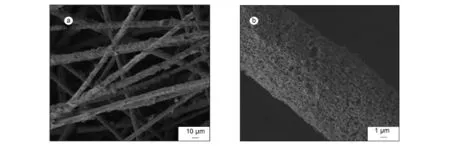
图3 纳米炭纤维模板法所制Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体SEM照片:(a)低分辨率下和(b)高分辨率下Fig.3 SEM images of Al2O3/silica fiber composites using carbon nanofibers template method:(a)low magnification and(b)high magnification.
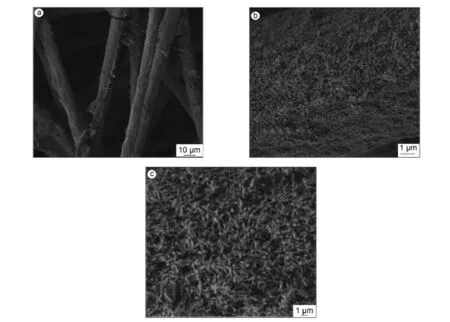
图4 V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂的SEM照片:(a)低分辨率下、(b)中分辨率下和(c)高分辨率下Fig.4 SEM images of V2O5-K2SO4supported over Al2O3/silica fiber composites by wet impregnation method:(a)low magnification,(b)mild magnification and(c)high magnification.
由图5中XRD谱图对比可知,采用浸渍法制得的V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂具有比较明显的V2O5特征吸收峰(15.1°、21.5°、26.0°),同时XRD谱图中出现了很强的K2SO4的特征吸收峰(24.0°、29.5°、31.0°、37.8°),与文献[13]报道结果一致。这表明K2SO4的添加能够提高 V2O5在 Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体上的分散度,使得V2O5在Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体上均匀分布,从而可提高催化活性相的有效比表面积。
3.4 催化性能测试分析
以炭黑颗粒催化燃烧反应作为探针考察所制复合催化剂的催化活性。图6是V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂催化燃烧炭黑颗粒的TG-DTA曲线。
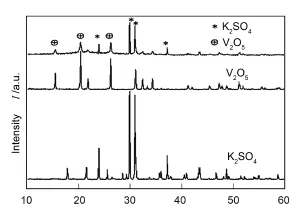
图5 V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂的XRD谱图Fig.5 XRD patterns of V2O5-K2SO4supported over Al2O3/silica fiber composites.
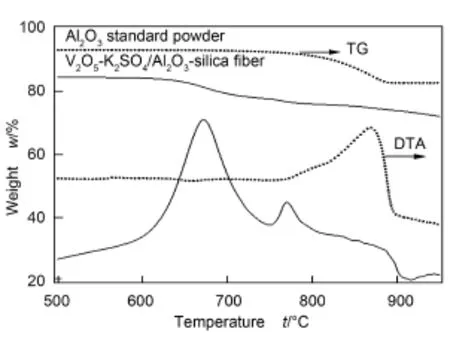
图6 V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂催化燃烧炭黑颗粒的TG-DTA曲线Fig.6 TG-DTA curves of V2O5-K2SO4supported over Al2O3-silica fiber composites mixed with carbon black.
另取用商品α-Al2O3粉末催化燃烧炭黑颗粒的实验作对比。商品α-Al2O3粉末催化燃烧炭黑颗粒时,其起燃温度约为500℃,达到50%转化率时为600℃。而对于V2O5-K2SO4/复合载体催化剂,其起燃温度约为350℃,达到50%转化率时为450℃,这证明了V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂能明显降低炭黑颗粒的起燃温度,可以有效地降低柴油车尾气中炭黑颗粒的排放,具有潜在的实际应用前景。关于其催化反应机理,对于V2O5-K2SO4/ Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂来说,K2SO4的作用主要是使V2O5在Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合载体上产生均匀分布,从而可提高催化活性相的有效比表面积。同时V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂是一种宏观基体与微观微粒相复合的多孔材料,并且在炭黑颗粒的催化氧化反应过程中,V2O5-K2SO4系催化剂具有低共熔点且易流动的特性,更易于实现炭黑颗粒与催化剂的紧密接触,因而具有优异的催化氧化炭黑颗粒的反应性能。
4 结论
以SiO2纤维为宏观基体材料,采用化学气相沉积法在其表面可制备出纳米炭纤维,提供一种有序结构定向催化生长纳米炭纤维的技术。采用纳米炭纤维模板法和浸渍法的复合方法,并优化实验条件可以得到 V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂。研究表明V2O5-K2SO4/Al2O3-SiO2纤维复合催化剂能明显降低炭黑颗粒的起燃温度,可以有效地降低柴油车尾气中炭黑颗粒的排放,具有潜在的实际应用前景。
[1] Van Stten B A A L,Makkee M,Moulijn J A.Science and technology of catalytic diesel particulate filters[J].Catal Re,2001, 43(4):489-564.
[2] Fino D,Specchia V.Open issues in oxidative catalysis for diesel particulate abatement[J].Powder Technol,2008,180(1-2): 64-73.
[3] Wei Y C,Liu J,Zhao Z,et al.The catalysts of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Ce1-xZrxO2-supported gold nanoparticles for soot combustion:The metal-support interaction[J]. J Catal,2012,287:13-29.
[4] Zhang G Z,Zhao Z,Xu J F,et al.Comparative study on the preparation,characterization and catalytic performances of 3DOM Ce-based materials for the combustion of diesel soot[J].Appl Catal B,2011,107(3-4):302-315.
[5] Ura B,Trawczynski J,Kotarba A,et al.Effect of potassium addition on catalytic activity of SrTiO3catalyst for diesel soot combustion[J].Appl Catal B,2011,101(3-4):169-175.
[6] Guihaume N,Bassou B,Bergeret G,et al.In situ investigation of Diesel soot combustion over an AgMnOx catalyst[J].Appl Catal B,2012,(119-120):287-296.
[7] Jelles S J,Van Setten B A A L,Makkee M,et al.Molten salts as promising catalysts for oxidation of diesel soot:importance of experimental conditions in testing procedures[J].Appl Catal B, 1999,21(1,3):35-49.
[8] Bentrup U,Martin A,Wolf G U.Comparative study of the thermal and redox behaviourof alkali-promoted V2O5catalysts[J]. Thermochim Acta,2003,398(1-2):131-143.
[9] Ogihara H,Sadakane M,Wu Q,et al.Immobilization of nanofibrous metal oxides on microfibers:macrostructured catalyst system functionalized with nanoscale fibrous metal oxides[J]. Chemical Communications,2007,39:4047-4049.
[10] Wu Q,Ogihara H,Uchida H,et al.Nano-scale hydroxyapatite coating on silica fiber by using carbon nanofibers as templates[J].Bull Chem Soc Jpn.2008,81(3):380-386.
[11] Wu Q,Sadakane M,Ogihara H,et al.Shape controlled synthesis of nanofibrous A-or B-site substituted LaMnO3perovskite-type oxides with carbon nanofibers templates[J].Materials Research Bulletin,2010,45(9):1330-1333.
[12] Wu Q,Sadakane M,Ogihara H,et al.Nano-scale hydroxyapatite formation with macroscopic shapes using different kinds of carbon nanofibers as templates[J].Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2010,10(8):5431-5436.
[13] Kaszonyi A,Hronec M,Delahay G,et al.Changes in properties of V2O5-K2SO4-SiO2catalysts in air,hydrogen and toluene vapors[J].Appl Catal A,1999,184(1):103-113.
Instructions to Authors
New Carbon Materials is a bimonthly journal published with the permission of the Ministry of Science and Technology and of the State News and Publication Agency.The journal is sponsored by the Institute of Coal Chemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences,and is published by Science Press.Aims and Scope
New Carbon Materials publishes research devoted to the physics,chemistry and technology of those organic substances that are precursors for producing aromatically or tetrahedrally bonded carbonaceous solids,and of the materials that may be produced from those organic precursors.These materials range from diamond and graphite through chars,semicokes,mesophase substances,carbons,carbon fibers,carbynes,fullerenes and carbon nanotubes,etc.Papers on the secondary production of new carbon and composites materials(for instance,carbon-carbon composites)from the above mentioned various carbons are also within the scope of the journal.Papers on organic substances will be considered if research has some relation to the resulting carbon materials.
Manuscript Requirements
1.New Carbon Materials accepts Research Paper,Short Communication and Review.The number of words in each Research Paper should be less than 6000 words.Short Communication<3500 words.There is no maxium of words for Review.
2.Manuscript including an abstract,graphical abstract,highlight,keywords,reference list,original figures and captions,tables.Manuscripts can be written both in Chinese and English.
3.Manuscript should be accompanied with key words placed after Abstract and a short resume of first author(name,academic degree,professional position)placed in the end of 1st page of text as foot-note.Corresponding author and his(her)E-mail address should also be mentioned.
4.All illustrations,photographs,figures and tables should be on separate sheets,figure captions should be typed separately,not included on the diagram.Authors are requested to submit original photographs,which should have good contrast and intensity.
5.References should be individually numbered in the order in which they are cited in the text,and listed in numerical sequence on separate sheets at the end of the paper,typed in double spacing.Remember that"unpublished works"are not references!In the reference list,periodicals[1],books[2],multi-author books with editors[3],proceedings[4],patents[5],and thesis[6]should be cited in accordance with the following examples:
[1] Mordkovich V Z,Baxendale M,Yoshimura S,et al.Intercalation into nanotubes.Carbon,1996,34(10):1301-1303.
[2] Lovell D R.Carbon and High-Performance Fibers Directory.5th ed.,London:Chapman&Hall,1991:66.
[3] Mochida I,Korai Y.Chemical characterization and preparation of the carbonaceous mesophase.In:Bacha J D,Newman J W,White J L, eds.Petroleum-Derived Carbons.Washington DC:ACS,1986,29-31.
[4] Su J,Li G,Hao Z.The research and application of copper impregnated coarse-grain graphite throat.23rd Int′l Biennial Conference on Carbon,Extended Abstract and Program,July 18-23,Pennsylvania 1997,256-258.
[5] Shigeki T,Jinichi M,Hiroshi H.Manufacture of mesocarbon microbeads.JP 61-222913,1986.
[6] Jones L E.The Effect of Boron on Carbon Fiber Microstructure and Reactivity.Ph.D.Thesis.Penn State University,University Partk, PA 1987.
Note:For the references with more than three authors,please give the first three and mark"et al".
6.Publication of papers in the journal is free of charge.Authors whose paper is published in the journal will receive 10 free offprints and 2 copy of this journal soon after its coming out.
7.Manuscript Submission:Online submission:http://xxtcl.sxicc.ac.cn/EN/volumn/home.shtml
Synthesis of Al2O3-silica fibers supported on a V2O5-K2SO4catalyst used for soot combustion
WU Qiang1, ZHAO Li1, WU Mei-xia2, YAO Wei-feng1
(1.College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering,Shanghai University of Electric Power,Shanghai200090,China; 2.College of Chemical and Environmental Engineering,Shanxi Datong University,Datong 037009,China)
An Al2O3-silica fiber support was prepared by first impregnating a Al(NO3)3solution on a silica fiber mat on which sacrificial carbon nanofibers had been formed by chemical-vapor deposition,followed by burning in air.The support was further impregnated with a solution containing NH4VO3and K2SO4to prepare the Al2O3-silica fiber supported V2O5-K2SO4catalyst.The catalyst can greatly decrease the combustion temperature of soot by around 200℃,which is promising for decreasing soot emission in diesel-powered vehicles.
Silica fiber;Carbon nanofibers;Template method;V2O5-K2SO4catalysts;Soot
O643.3
A
2015-03-15;
2015-08-15
国家自然科学基金(21107069,21103106);教育部留学回国人员科研启动基金(Z-2013-002);上海市浦江人才计划(12PJ1403800);上海市教育委员会科研创新项目(14ZZ153);稀土功能材料上海市重点实验室开放课题(Z-2011-050);上海电力学院海外引进人才科研启动项目(K-2011-004);上海电力学院085工程项目“智能电网储能技术”(C-8209-11-551).
吴 强,博士,副教授.E-mail:qiangwu@shiep.edu.cn
1007-8827(2015)05-0445-06

