两全同粒子在一维光晶格中的量子行走
张云波,王丽敏,王 利
山西大学理论物理研究所,太原 030006

【物理 / Physics】
两全同粒子在一维光晶格中的量子行走
张云波,王丽敏,王 利
山西大学理论物理研究所,太原 030006
基于满足周期性边界条件的一维光晶格模型,分别研究遵从玻色-爱因斯坦统计的玻色系统、遵从费米-狄拉克统计的费米系统以及硬核玻色系统下的两粒子关联、关联涨落、平均粒子数分布以及动力学演化等问题,计算量子统计性质和相互作用强度(排斥)对两粒子量子行走(独立行走和绑定行走)的影响.结果表明,在坐标空间中,随着时间的增大,粒子向晶格边缘移动,尤其当相互作用为零时,玻色系统的两粒子关联虽呈现聚束现象,却展示出一种与众不同的对称——输入输出对称,而费米(硬核玻色)系统的两粒子关联呈现类似环类的空间分布. 随着排斥相互作用的增大,3系统都会出现两粒子绑定行走行为,在强相互作用下,研究的物理量(粒子关联、关联涨落和平均粒子数分布)在3系统中几乎相同;在动量空间中,玻色系统呈典型的聚束现象,费米系统呈反聚束现象,硬核玻色系统呈聚束现象. 计算结果为实验上研究不同系统(玻色、费米和硬核玻色)的物理性质提供了依据,并佐证了实验上排斥相互作用下束缚态产生的实验结果.
凝聚态物理;光晶格模型;量子行走;量子统计;动力学演化;两粒子关联;关联涨落
量子行走是经典随机行走的量子力学推广[1],它不仅是量子传输中的一种基本现象,同时也是发展量子算法和实现量子计算的实用性工具.与经典随机行走相比,由于量子态的相干叠加特性,量子行走具有更快的扩展速度.近些年,随着研究的深入,研究者可以模拟许多实际生物和物理过程,如光合作用、蛋白质折叠[2]等.
迄今,单粒子的量子行走已在一些实验系统中实现[3-8].相比之下,多粒子的量子行走会有一些新奇的非经典关联特性,这将促进实用量子技术的发展.基于目前多粒子量子行走的研究,文献[9-10]发现两粒子的离散量子行走敏感地依赖于关联或纠缠,文献[10-12]研究了对于遵循不同量子统计的玻色(费米)系统在两粒子量子行走中所呈现的聚束(反聚束)现象,而文献[13-15]则在实验上实现了两粒子的量子行走.文献[16]研究了两粒子关联对统计性质和近邻相互作用(吸引)的依赖效应.本研究将这一模型扩展,考虑两粒子关联对次近邻相互作用(排斥)的依赖效应,期望通过改变相互作用模式和初态波函数,研究统计性质和次近邻相互作用对新系统下的量子行走的影响,同时为实验上观察到排斥相互作用背景下束缚态的产生[17]提供佐证.
1 理论模型和计算方法
本文研究周期性边界条件下一维光晶格中,考虑受非同一格点相互作用的两全同粒子(玻色子、费米子和硬核玻色子)的量子行走行为.系统哈密顿量可表示为

(1)
相应的周期边界条件为
a-L=aL+1
(2)
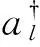
研究系统的希尔伯特空间可通过一系列的Fock态来构造,可表示为

(3)
则任意时刻的波函数为
(4)
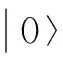
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)

(9)
(10)
2 量子行走关联效应结果分析
图1—图3依次给出玻色系统、费米系统和硬核玻色系统的两粒子量子行走关联效应,3列分别对应相互作用强度参数V取0、1 、4(以J为单位)的动力学演化过程.其中,第1行是时间t=0(以1/J为单位)时刻的关联图像,最后一行分别对应时间为Jt=4、4.5、7.5时的关联图像,这样的参数取值可使关联矩阵呈现出比较直观清晰的物理图像. 此外,为展示动力学演化过程,本研究给出中间时间参数的关联图像.

图1 坐标空间下玻色系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联效应随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.1 Time evolution of two-particle correlations of quantum walkers in position space for bosonic system(2L+1=21)
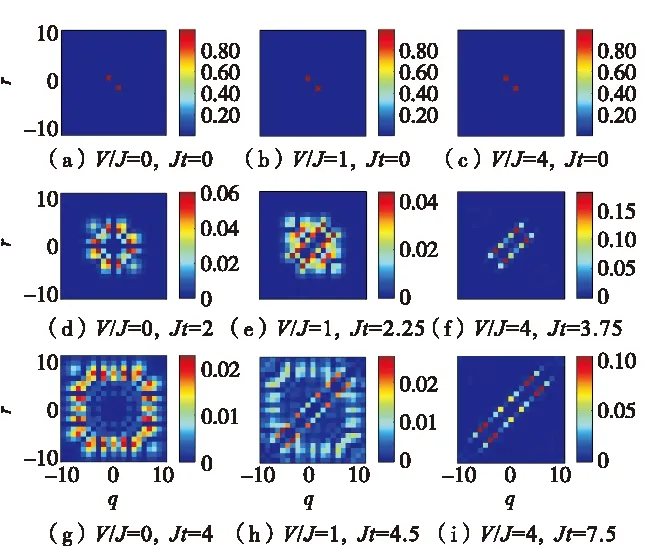
图2 坐标空间下费米系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联效应随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.2 Time evolution of two-particle correlations of quantum walkers in position space for fermionic system(2L+1=21)

图3 坐标空间下硬核玻色系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联效应随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.3 Time evolution of two-particle correlations of quantum walkers in position space for hard-core bosonic system(2L+1=21)
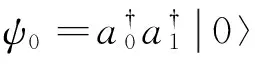
图4和图5分别给出在玻色系统和费米系统下粒子数密度随时间的变化情况.同样,在两系统中可发现随着时间的增长粒子向晶格边缘方向移动.尤其通过对图4(b)和(c),图5(b)和(c)的中间区域作比较,发现当V/J=4,Jt=3.75(格点(-1,1)密度分布值小于V/J=4,Jt=2.25的情况, 因为随着时间的增长粒子移向晶格的边缘)时,在格点(-1,1)处粒子的密度分布值明显大于V/J=1,Jt=2.25的情况.该现象违背人的直觉:排斥力促使粒子分离,吸引力有助于束缚粒子.这可理解为一种动力学稳态[18], 在强相互作用下,粒子的分离行为受到限制,似重新组合为一个复合粒子.

图4 玻色系统中粒子数密度随时间的变化Fig.4 Time evolution of particle density plotted against position for bosonic system

图5 费米系统中粒子数密度随时间的变化Fig.5 Time evolution of particle density plotted against position for fermionic system
图6—图8给出的是图1—图3相应参数下的3系统的关联涨落变化情况. 对于涨落,其描述的是物理量围绕自身统计平均值的微小的无规则偏离的现象.由图6—图8可见,考虑Jt≠0时刻,当相互作用为0时,关联矩阵呈现0值背景下的涨落正负对称现象;当相互作用取非零值时,涨落正负对称现象将会被打破,且随着相互作用的增大,这种涨落正负对称破坏的程度会越来越明显. 此外,费米系统和硬核玻色系统在关联涨落图像中存在明显的差异.

图6 坐标空间下玻色系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联涨落随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.6 Time evolution of two-particle correlation fluctuations of quantum walkers in position space for bosonic system(2L+1=21)
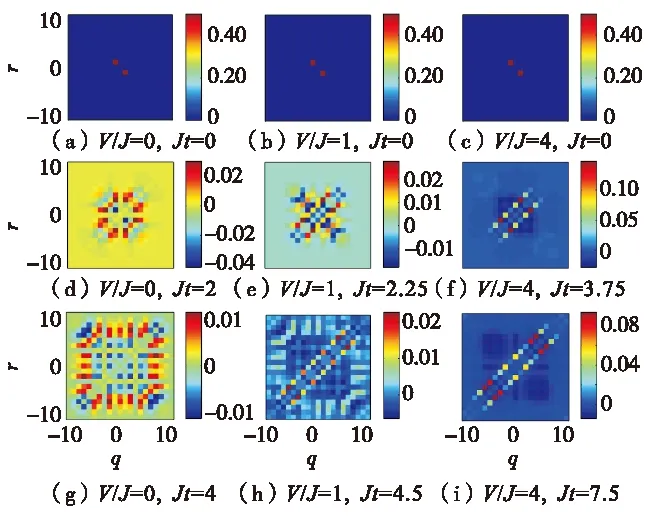
图7 坐标空间下费米系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联涨落随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.7 Time evolution of two-particle correlation fluctuations of quantum walkers in position space for fermionic system(2L+1=21)
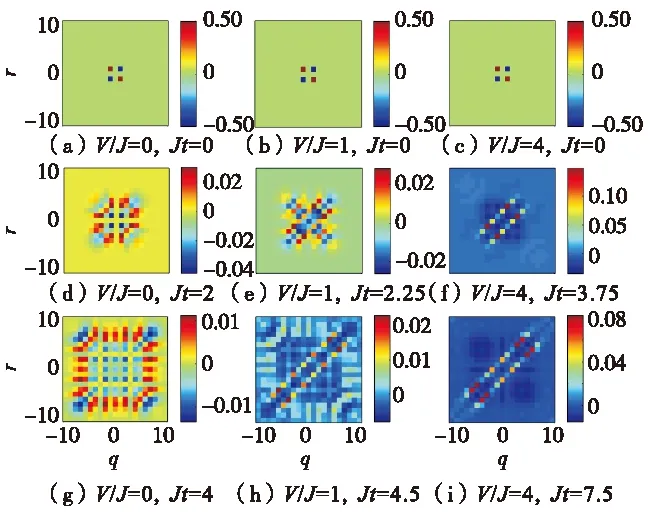
图8 坐标空间下硬核玻色系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联涨落随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.8 Time evolution of two-particle correlation fluctuations of quantum walkers in position space for hard-core bosonic system(2L+1=21)
图9为玻色系统和费米系统在强相互作用下两粒子的关联、关联涨落以及粒子数密度的分布情况.对于玻色、费米和硬核玻色3个系统,当次近邻相互作用增大到一定值时,哈密顿量中的动能项与相互作用项相比,前者可作为微扰来处理,且利用简并系统的二阶微扰理论,可解析获得有效单粒子哈密顿量为
(11)

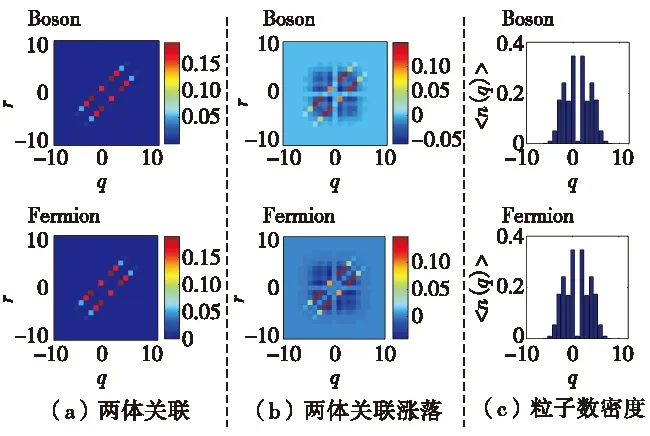
图9 坐标空间下两强相互作用粒子的量子行走 (V/J=60,Jt=55)Fig.9 Two strongly interacting walkers in position space(V/J=60,Jt=55)

图10 动量空间下玻色系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联效应随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.10 Time evolution of two-particle correlations of quantum walkers in momentum space for bosonic system(2L+1=21)
图10—图12描述了动量空间的两粒子关联函数随时间的变化情况. 由图10和图11可见,在相互作用为0时,玻色系统和费米系统的动力学演化过程并未被清楚地呈现,且玻色关联图像到费米关联图像是平移效果(具体操作可通过构建任意子模型[19]将两者联系起来). 当相互作用取非零值时,动力学演化过程呈现,且基于不同的量子统计性质,玻色系统呈现聚束行为,费米系统呈现反聚束行为,硬核玻色系统呈现聚束行为.

图11 动量空间下费米系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联效应随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.11 Time evolution of two-particle correlations of quantum walkers in momentum space for fermionic system(2L+1=21)
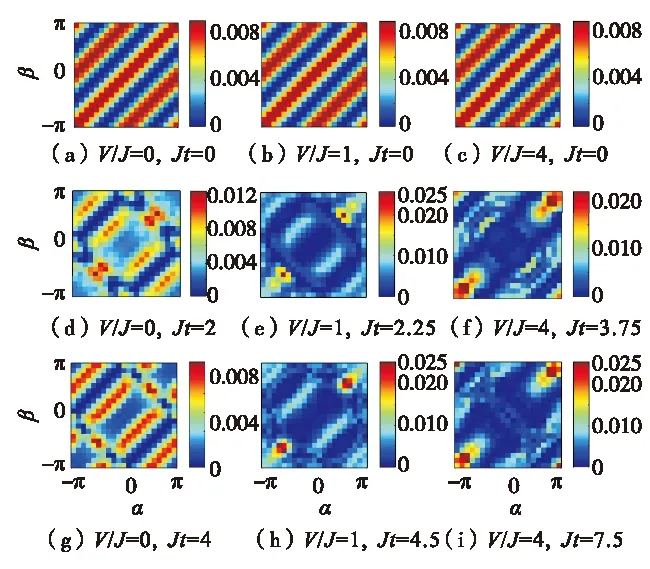
图12 动量空间下硬核玻色系统的两粒子量子行走的 关联效应随时间的变化(2L+1=21)Fig.12 Time evolution of two-particle correlations of quantum walkers in momentum space for hard-core bosonic system(2L+1=21)
结 语
研究了周期性边界条件下一维光晶格中两粒子量子行走对量子统计性质、相互作用强度和相互作用模式的依赖情况.结果显示,对于遵循不同量子统计性质的系统,其量子行走行为不同.但是,随着相互作用强度的增大,即使是排斥相互作用,系统中的两粒子也有较强的意愿待在粒子初始时刻置入晶格的位置,并随着时间的变化以某一共同速度等几率向晶格边缘反向移动.然而,两粒子绑定行走的形式则是初态波函数和相互作用模式联合作用的效果,这为研究玻色、费米和硬核玻色3系统提供了理论参考.同时,本研究具体选定排斥相互作用模式,也间接为排斥相互作用背景下束缚态的产生提供了依据.
/ References:
[1] Aharonov Y, Davidovich L, Zagury N.Quantum random walks[J].Physical Review A, 1993, 48(2):1687-1690.
[2] Mohseni M, Rebentrost P, Lloyd S, et al. Environment-assisted quantum walks in photosynthetic energy transfer[J].The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2008, 129(17):174106-1-174106-9.
[3] Du Jiangfeng, Li Hui, Xu Xiaodong, et al.Experimental implementation of the quantum random-walk algorithm[J].Physical Review A, 2003, 67(4):042316-1-042316-5.
[4] Schmitz H, Matjeschk R, Schneider Ch, et al.Quantum walk of a trapped ion in phase space[J].Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(9):090504-1-090504-4.

[6] Zähringer F,Kirchmair G,Gerritsma R,et al.Reali-zation of a quantum walk with one and two trapped ions[J].Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(10):100503-1-100503-4.
[7] Broome M A, Fedrizzi A, Lanyon B P, et al.Discrete single-photon quantum walks with tunable decoherence[J].Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(15):153602-1-153602-4.

[10] Pathak P K, Agarwal G S.Quantum random walk of two photons in separable and entangled states[J].Physical Review A, 2007, 75(3):032351-1-032351-13.
[11] Bromberg Y, Lahini Y, Morandotti R, et al.Quantum and classical correlations in waveguide lattices[J].Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(25):253904-1-253904-4.
[12] Lahini Y, Verbin M, Huber S D, et al.Quantum walk of two interacting bosons[J].Physical Review A, 2012, 86(1):011603-1-011603-5.
[13] Sansoni L, Sciarrino F, Vallone G, et al.Two-particle bosonic-fermionic quantum walk via integrated photonics[J].Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(1):010502-1-010502-5.
[14] Solntsev A S, Sukhorukov A A, Neshev D N, et al.Spontaneous parametric down-conversion and quantum walks in arrays of quadratic nonlinear waveguides[J].Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(2):023601-1-023601-5.
[15] Meinecke J D A, Poulios K, Politi A, et al.Coherent time evolution and boundary conditions of two-photon quantum walks in waveguide arrays[J].Physical Review A, 2013, 88(1):012308-1-012308-6.
[16] Qin Xizhou, Ke Yongguan, Guan Xiwen, et al.Statistics-dependent quantum co-walking of two particles in one-dimensional lattices with nearest-neighbor interactions[J].Physical Review A, 2014, 90(6):062301-1-062301-8.
[17] Winkler K, Thalhammer G, Lang F, et al.Repulsively bound atom pairs in an optical lattice[J].Nature, 2006, 441:853-856.
[18] Wang Li,Hao Yajiang,Chen Shu.Quantum dynamics of repulsively bound atom pairs in the Bose-Hubbard model [J].The European Physical Journal D,2008,48(2):229-234.
[19] Wang Limin, Wang Li, Zhang Yunbo. Quantum walks of two interacting anyons in 1D optical Lattices[J]. Physical Review A, 2014, 90(6):063618-1-063618-6.
【中文责编:英 子;英文责编:木 南】
Quantum walks of two identical particles in one-dimensional lattices
Zhang Yunbo†, Wang Limin, and Wang Li
Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, P.R.China
Based on one-dimensional lattices with periodic boundary conditions, we investigate the two-particle correlations, the correlation fluctuations, and the density distributions as well as the dynamic evolutions of the bosonic system governed by Bose-Einstein statistics, the fermionic system governed by Fermi-Dirac statistics, and the hard-core bosonic system, respectively. The dependences of independent walking and co-walking for two interacting particles on both quantum statistics and interaction strength are calculated. The results show that the particles move to the edge of the lattice with the increase of time in position space. Specifically, for zero interaction, bosonic correlations exhibit bunching but with a specific “in-out” correlation symmetry, while the fermionic correlations(hard-core bosonic correlations)are transformed into a ring-like pattern. However, two particles in the bosonic system and fermionic system (hard-core bosonic system) start to occupy adjacent lattice sites separated by one site and stick together when they are co-walking with increasing interaction. The correlations in the three systems are nearly the same under strong interactions and are the same with correlation fluctuations and density distributions. In momentum space, the quantum statistical natures for two bosonic (hard-core bosonic) walkers and two fermionic walkers result in the emergence of bunching and anti-bunching in two-particle quantum walks (QWs), respectively. In short, the results pave the way for exploring quantum statistics and can be used as evidences for the repulsively bound state observed experimentally.
condensed matter physics; lattice model; quantum walk; quantum statistics; dynamic evolution; two particle correlation; correlation fluctuation
:Zhang Yunbo,Wang Limin,Wang Li.Quantum walks of two identical particles in one-dimensional lattices[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 2015, 32(1): 1-7.(in Chinese)
O 469
A
10.3724/SP.J.1249.2015.01001
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11474189)
张云波(1969—),男(汉族),山西省黎城县人,山西大学教授.E-mail:ybzhang@sxu.edu.cn
Received:2014-10-29;Accepted:2014-12-13
Foundation:National Natural Science Foundation of China (11474189)
† Corresponding author:Professor Zhang Yunbo.E-mail:ybzhang@sxu.edu.cn
引 文:张云波,王丽敏,王 利. 两全同粒子在一维光晶格中的量子行走[J]. 深圳大学学报理工版,2015,32(1):1-7.

