A Study on the Effects of Oxygenation Irrigation on Some Growth Agronomic Traits of Super Rice Shenyou 9516
Licheng ZHANG,Bangsong YAO,Weihua XIAO,Xiaobo HUANG,Longbiao LIAO
College of Engineering,Hunan Agricultural University,Changsha 410128,China
Oxygenation irrigation could increase crop yield potentially,because the addition of oxygen into root zones of crop allows the root function to be in an optimal state which is beneficial to the activities of microorganisms in root zones and transportation of mineral substances,thereby improving plant growth and yield and increasing water utilization efficiency[1].Surya[2]found that oxygen around rootzonescould be discharged by soil water easily in rice growth process,especially for rice growing in heavy clay,resulting in oxygen deficit in root zones which influenced respiration and growth of roots.Meek[3-4]found that the respiration of roots was the driving force of metabolic activities of roots in 1990,while the growth of roots directly controlled the growth ofaboveground stem parts of plants.Zhang[5-6]deemed that oxygenation irrigation promoted the growth of tobacco roots in vigorous growing stage and squaring stage relative to conventional irrigation.Xiao[7]reckoned that oxygenation irrigation could increase single leaf area,total leaf area and total tobacco leaf quantity.It was found in the growth experiments of cucumber and oilseed rape that oxygenation irrigation could effectively change the distribution of root system,leading to plump oilseeds and increased cucumber number[8-10].All above studies have found that oxygenation irrigation had positive effect on crop growth.This study further investigated the effects of oxygenation irrigation on growth and yield of super rice on the basis of related studies by scholars.
Materials and Methods
General condition of experiment field
This experiment was conducted on Yunyuan test base of Agricultural University Of Hunan.The experimental site is a subtropical monsoon climate zone with an annual average temperature of 16-18℃and an annual average rainfall of about 1 200 mm.The experiment adopted a field experiment method under the conditions the same as ordinary field cultivation of rice.The soil is reddish clayey soil developed from quaternary red clay.
Experiment materials
The material was the super rice Shenyou 9516 provided by Longping Seed.
Experiment design
The experiment had 3 treatments,i.e.,mechanical oxygenation(A group),chemical oxygenation (B group),and conventional cultivation (CK group).The mechanical oxygenation adopted an air pump to supply gas to root parts of rice via PVC hoses(at a rate of 20 L/min).The chemical oxygenation adopted droppers to drop hydrogen peroxide via PVC hoses.The mechanical oxygenation was performed according to daytime and nighttime.The oxygenation method was shown in Table 1.
The chemical oxygenation was performed once every 15 d,on July 6,July 21 and August 6,respectively.The hydrogen peroxide had a concentration of 0.03%,and the amounts for B1,B2 and B3 were 10,20 and 30 ml,respectively.The control group was kept with a shallow water layer.
Experiment facility
The experiment began with seedling raising by sowing on June 18 in 2013,and performed transplanting to the experiment field on July 6.Each experiment plot had an area of 1.5 m×1 m,and were planted with 15 plants uniformly.The experiment field was divided into 6 mechanical oxygenation plots,3 chemical oxygenation plots and 1 control plot without treatment,which were separated mutually.Before transplanting each seedling into the field,7 tuck nets were buried in the field uniformly with a depth of 20 cm,to avoid in the destructive test later damage to roots which might result in error.The experiment was kept with a shallow water layer,and weeding and pest prevention were conducted according to rice cultivation in ordinary local field.
This experiment conducted study on root systems in seedling stage,tillering stage and heading stage.The rice growing vigorously in seedling stage has larger tiller number which determines panicle number which is the basis of yield.Therefore,study was performed on root system in the 3 stages.Four rice plants were pulled out from the field on July 14,and their roots were flushed with water to perform comparison.Fresh and dry root weights and crown weight were obtained with an electronic balance(Meitele)with a precision of 0.001 g,and root length and plant height were measured with a vernier caliper.Aeration time period and time interval were controlled with an L12 timer(Kerde).
Results and Analysis
With the conventional treatment CK group as control,comparison was performed on plant heights and some growth agronomic traits in super rice after mechanical oxygenation treatment and chemical oxygenation with those of the conventional treatment group in growth process of super rice.Statistics were performed with Excel and statisticalmethod.The major agronomic traits of the super rice in seedling stage,tillering stage and heading stage of growth process were shown in Table 2,in which the data were averages of various treatment groups.
It could be seen from Table 2 and Table 3 that the super rice of the oxygenation irrigation treatments had the plant heights,maximum root lengths,fresh root weights,dry root weights and dry plant weights all greater than those of the control group.The comparison of the major agronomic traits in the super rice in seedling stage,tillering stage and heading stage showed that:for the plant heights,from high to low sequentially,the mechanical oxygenation group showed the order of A4,A6,A2,A3,A1 and A5,and the chemical oxygenation group showed the order of B1,B2 and B3;for the maximum root lengths from high to low sequentially,the mechanical oxygenation group exhibited the order of A2,A6,A4,A3,A5 and A1,and the chemical oxygenation group exhibited the order of B2,B3 and B1;in the case of dry root weights from high to low sequentially,the mechanical oxygenation group showed the order of A2,A3,A4,A5,A6 and A1,and the chemical oxygenation group showed the order of B2,B3 and B1;the fresh root weight showed a trend in accordance with the dry root weight;and for the dry plant weights from high to low sequentially,the mechanicaloxygenation group showed the order of A4,A2,A5,A3,A6 and A1,and the chemical oxygenation group showed the order of B2,B1 and B3.From the comparison of major agronomic traits of various treatment groups,it could be seen that each group showed the characteristic of performing outstanding in a certain trait.That was because the comparison of data values could not completely reflect that one treatment had a remarkable promoting effecton the growth of super rice.For example,an agronomic trait of one treatment group shown as slightly higher than othertreatment groups might be due to some statistical error exiting in detection process.However,it could be reflected from above comparison that oxygenation irrigation was beneficial to the growth of super rice,overall.In the mechanical oxygenation groups,A2 group had the maximum root length and dry root weight greater than those of other treatment groups,and A4 group showed greater plant height and fresh root weight than other treatment groups.In the chemical oxygenation group,B2 showed greater agronomic traits than other treatment groups except plant height.

Table 1 Mechanical oxygenation of super rice
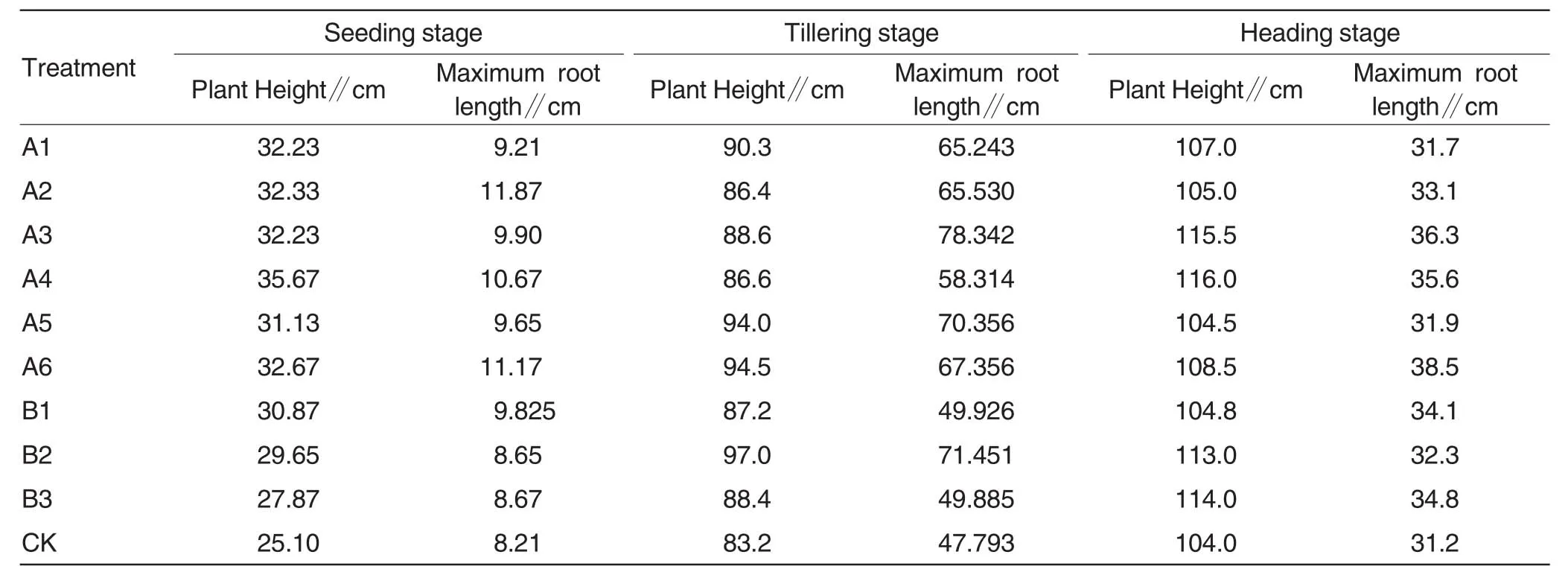
Table 2 The major agronomic traits of super rice

Table 3 The major agronomic traits of super rice
Effect of oxygenation irrigation on super rice in tillering stage
Tillering of rice is an important stage in growth and development of rice,and essentially refers to branching of stem[9].In ordinary growth environment,the tillering of rice mainly happens on the stem nodes near to the ground,which were called tillering nodes,and the rice stem where tillers located is known as mother stem of tillers.On the same mother stem,the node where the earliest tillering happens is called the lowest tillering node,and the uppermost tillering node is known as the highest tillering node[10].The total tiller numbers of the super rice in tillering stage in various treatment groups and the conventional group were listed in Table 4,in which the data values were averages of various treatment groups.
The oxygenation irrigation treatment A4 began tillering on August 2 at first in the growth process of the super rice,other oxygenation irrigation treatment groups began tillering successively gradually,while the conventional group without any treatment began tillering on August 6.The experiment indicated that oxygenation irrigation treatment could promote the super rice to enter tillering stage in advance.The tiller growing on the main stem of rice is the first tiller,and there have been studies indicating that the time when tillering happened obviously affected both the development and panicle formation of tiller[11].Generally,earlier tillering and lower tillering sites and times (from bottom upwards)lead to easier panicle formation as well as better panicle characters.On the contrary,later tillering and higher tillering sites and times lead to shorter vegetative growth period,less leaf number,less panicle formation possibility and less small panicles[12-15].The tillering of rice happened in advance by oxygenation treatment,thus improving the yield of rice indirectly.However,more tillers could not improve rice yield with less panicle formation rate certainly.In fact,some ineffective tillers would occur in late tillering stage.The ineffective tillers refers to tillers which tiller from the stems of rice without forming panicles.The situation of effective tillers and ineffective tillers of the super rice was analyzed with statistical charts below.The tiller number of each of the various treatment groups and conven-tional group was the average of corresponding group.
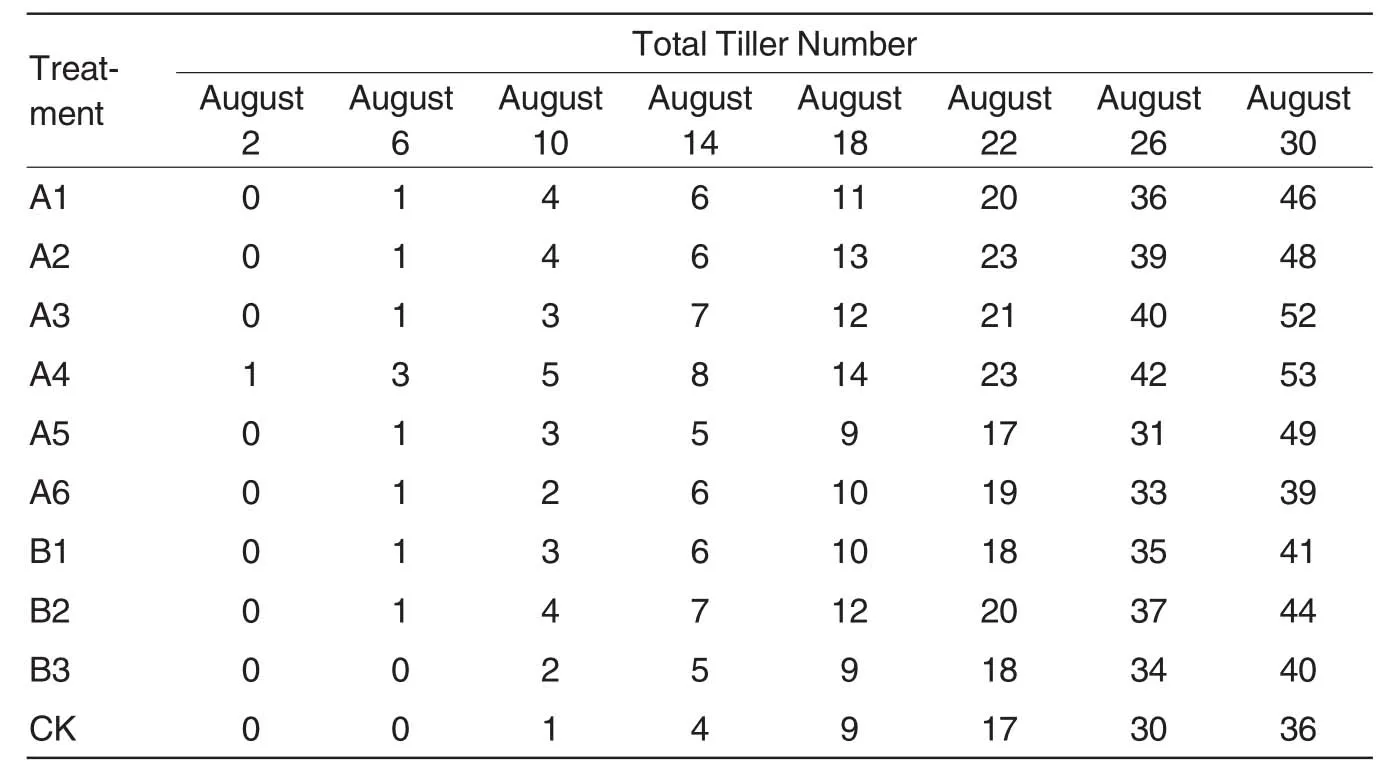
Table 4 The tiller number of super rice in growth process
The yield of each individual rice plant is decided by its panicle number and the number of filled grains per panicle,and rice has its panicle number increased by tillering continuously in growth process.As shown in Fig.1,the mechanical oxygenation treatment A4 had the highest effective tiller number,and furthermore,the effective tiller number of the oxygenation treatment groups were all higher than that of the conventionalcontrolgroup. Then comparison was conducted on the ratio of effective tiller number to total tiller number.It was found that the proportions of A1,A2,A3,A4,A5 and A6 groups were 87.0%,91.7%,88.5%,88.7%,85.7% and 84.6%,and proportions of B1,B2 and B3 groups were 90.2%,88.6% and 87.5%,and the proportion of CK group was 77.8%.Among them,the effective tillers of A2 groups accounted for the highest proportion of the total tiller number.
Effects of oxygenation irrigation on number of filled grains per panicle and kilo-grain weight of the super rice
Number of filled grains per panicle and kilo-grain weight are two component factors of overall yield of rice,i.e.,more panicles,larger grains and less empty hulls results in higher rice yield.Fig.2 and Fig.3 showed that oxygenation irrigation treatment A4 performed better in number of filled grains per panicle and kilo-grain weight obviously.From these two bar graphs,it was found that in the experiment the number of filled grains per panicle and kilograin weight of the super rice in various treatmentgroupsshowedfrom high to low the order of mechanical oxygenation treatment,chemical oxygenation treatment and conventional control.The increases in number of filled grains per panicle of A2 and A4 were related to the plant heights and maximum root lengths of the super rice higher than other treatment groups in growing period.It was to say that some growth agronomic traits of super rice affected its yield directly.
Conclusion and Discussion
Some previous studies have been reported on crop oxygenation irrigation.This study analyzed the effects of mechanical oxygenation and chemical oxygenationonmultipleagronomic traits in rice growth,and found that oxygenation irrigation achieved different results on different plants.Previous studies found by oxygenation irrigation to tobacco that chemical oxy-genation couldbetterpromote the growth of root system,plant and tobacco leaf than mechanical oxygenation in seedling stage of tobacco,while this study found that in the growth process of rice subjected to oxygenation irrigation,mechanical irrigation showed higher indexes of several growth agronomic traits in rice than chemical oxygenation.This might be due to the fact that rice is a paddy field crop,while tobacco is a dry land crop,i.e.,their root systemsgrow in differentenvironments.In the experiment,it was found that mechanical oxygenation treatment A4 group subjected to oxygenation once daily only,showed higher values of several agronomic traits than other treatment groups,indicating that too high or too low times of aeration was not ideal.High oxygenation times is not beneficial to the stability of root systems due to disturbance to soil.Low oxygenation times results in low oxygen content which could not satisfy the demand of roots for oxygen.In addition,higher indexes of the multiple agronomic traits in the super rice were in correspondence with higher kilograin weight and number of filled grains per panicle.This might be because that oxygenation irrigation promotes the growth of root systems,and strong root system could improve the absorption to nutrient elements and nutrients desired by super rice,which ensures vigorous growth of aboveground parts of super rice,resulting in correspondingly-increased number of filled grains per panicle and kilo-grain weight.Further study is required on the promotion mechanism of oxygenation on growth of root system.The absorption of root systems to microelements in soil or the effect of oxygenation on growth of microorganisms could be studied in future,to determine whether the activities of microorganisms promote the growth of root systems.Furthermore,all the oxygenation time in the study was designed according to the experience of previous studies,and thus whether the time period of aerobic respiration in rice roots accords with other crops should be verified by experiments,as well as its aerobic respiration law should be studied.Performing oxygenation in an proper amount at proper time according to aerobic respiration law could lead to better effect of oxygenation irrigation.
[1]CHEN XM(陈新明),JAY D,SURYA B.Impact of oxygation on soil respiration and crop physiological characteristics in pineapple(加氧灌溉对菠萝根区土壤呼吸和生理特性的影响等)[J].Drainage and Irrigation Machinery(排灌机械工程学报),2011,28(6):543-547.
[2]SURYA PB,SU NH,DAVID JM.Oxygation unlocks yield potentials of crops in oxygen-limited soil environments[J].Advancesin Agronomy,2005(88):314-377.
[3]SU NH.Generalisation of various hydrolohical and environmental transpornt models using the forker-planckequation[J].Environ Model&Software,2004(19):345-356.
[4]SU NH,MIDMORE DJ.Two-phase flow of water and air during aerated subsurface drip irrigation[J].Journal of Hydrology,2006,30(4):330-765.
[5]YAO BS(姚帮松).The effect of regulated deficit irrigation on the growth,physiological-zoology and yield of Brazil upland rice IAPAR9(调亏灌溉对巴西陆稻IAPAR9生长、生理生态及产量的影响)[D].Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University,2006.
[6]ZHANG WP(张文萍),YAO BS(姚帮松),XIAO WH(肖卫华),et al.Study on agronomic traits of tobacco under aerobic irrigation(增氧滴灌对烟草农艺性状的影响研究)[J].Journal of Irrigation and Drainage(灌溉排水学报),2013,32(1):142-144.
[7]XIAO WH(肖卫华),YAO BS(姚帮松),ZHANG WP(张文萍),et al.Research on the influence of tobacco growth by oxygation(加氧灌溉对烟草生长影响规律的研究)[J].China Rural Water and Hydropower(中国农村水利水电),2014,2:30-32.
[8]XU HH(徐欢欢),YAO BS(姚帮松),et al.Effect of gas irrigation on the main agronomic traits of autumn cucumber in greenhouse(输气灌溉对大棚秋黄瓜主要农艺性状的影响)[J].Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power(华北水利水电学院学报),2011,32(4):32-35.
[9]LIU DD(刘朵朵),YAO BS(姚帮松),ZHANG WP(张文萍),et al.Effect of root zone oxygen supply on the growth characteristic of stagnant water rape(根区供氧对滞水油菜生长特性的影响研究)[J].Journal of Irrigation and Drainage(灌溉排水学报),2013,32(3):128-130.
[10]SHAN TB(单提波),WEI HG(魏宏国),WANG AD(王安东),et al.Effect of rice straw return plus nitrogen fertilizer on growth and development,yield and quality in rice(稻草还田配施化学氮肥对水稻生长发育、产量和品质的影响)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报),2010,32(2):265-270.
[11]DAI GJ(代贵金),HUA ZT(华泽田),et al.Comparison of root systems of hybrid Japonica rice,conventional Japonica rice,early rice and Indica rice(早稻及籼稻根系特征比较)[J].Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University(沈阳农业大学学报),2008,39(5):515-519.
[12]LIAO YC(廖迎春),WANG MH(王辉明),FAN HB(樊后保),et al.Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on growth,yield and photosynthesis of rice(Oryza sativaL.)(模拟氮沉降对水稻生长、产量及光合特性的影响)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报),2012,34(1):10-15.
[13]XIONG YJ(熊元基),YAO BS(姚帮松),SU NH,et al.Effects of different oxygation treatments on the germination and agronomic characters of young seedlings of super rice(不同加氧处理对超级稻种子萌发和幼苗农艺性状的影响)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报),2014,36(2):256-260.
[14]WANG XJ(王雪君),YAO BS(姚帮松),LUO L(罗琳),et al.Effect of water content in soil on germination and agronomic traits of seedlings ofTriarrhena lutarioripariaseeds(土壤含水量对南荻种子萌发及幼苗农艺性状的影响)[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences(江苏农业科学),2014,42(4):287-289.
[15]LIU TJ(刘桃菊),TANG JJ(唐建军),QI CH(戚昌瀚).A Study on the fractal characters and the visual simulation of rice morphology(水稻形态的分形特征及其可视化模拟研究)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报),2002,24(5):583-586.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年12期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年12期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Study on Engineering Characteristics and Application of Sticky Rice
- Periodical Development Trend of Vertical Greening
- Advances in Microbial Remediation on the Application of Heavy Metal Pollution in Agricultural Water Resources
- Analysis on Status quo and Future Development of Fruit and Vegetable Protreatment
- Effect of Three Treatment Measures on Harmless Seedling Raising of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Litv.
- Discussions and Recommendations for Supervision of Vegetable Quality and Safety in Miyun County
