The Breeding and Application of a New Super High-yield Mini Watermelon Variety‘Jinmi 2’
Xinhua LIU,Lin LIU,Chunxin CAO,Pu ZHU,Qin ZHOU,Xiaoping CAO,Haidong JIANG
1.Jinhua Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Jinhua 321017,China;
2.Zhejiang Kedefeng Seed Co.Ltd,Jinhua 322399,China;
3.College of Agronomy,Nanjing Agricultural University,Nanjing 210095,China
Responsible editor:Lingyang MENG Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
China is a large watermelonproducing country of watermelon and muskmelon,with sowing areas exceeding 2 million hm2[1].In China,watermelon is an important industrial crop for Zhejiang Province,which is list as one of dominant and characteristic crops[2].With improvement of living standard,small watermelon becomes popular in market thanks for excellent quality,high economic benefits and convenience.According to statistics,the cultivation area of small watermelon maintains 10 hm2[3]and large-scale production bases of small watermelon develop fast in East China,represented by Jiangsu,Zhejiang and Shanghai.Currently,small watermelon cultivated in greenhouses is dominated by Citrullus lanatus and Nabite watermelon[4-6].Specifically,Citrullus lanatus is a precocious species introduced from Japan,whose fruit weight tends to be volatile in the range of 1.0-1.5 kg,and it is a variety with sweet flesh,containing high content of soluble solids[7].Nabite watermelon is also a smallscale watermelon,characterized by early ripening,high sugar and good quality[8].What’s more,both of the two varieties are lighter in terms of single fruit,low in yield per unit area and hardly to be stored[9-10],with high costs.Based on the problems,Jinhua Academy of Agricultural Sciences proposed to cultivate moderate-sized,early ripening and easy-cultivation fruits with the same quality of fruits available,and the yield increasing by 20% compared with Nabite watermelon.
Breeding Process
Parent breeding
Breeding and characters of female parent J52J52 is a female parent,generation F1,developed based on Jingxin No.1 and Citrullus lanatus and a self-bred line by orientation cultivation with generations during 4 years.The growth proves exuberant and matures early.Total growth period lasts for 89 d,and fruit development continues for 28 d.The fruit is high and round,with deep and green stripes on rinds,and the red flesh taste sweet and crisp.What’s more,it has 12.3%soluble solids,and few seeds,but the crack resistance performs poorly.
Breeding and characters of male parent X712X712 is a male parent and self-bred line developed with 7 generations within 4 years based on watermelon Xiuli.The growth stage totals 80 d and fruit development stage lasts for 25 d.It is a large,oblong fruit and has a light green rind with jagged dark green stripes.The flesh is red and tastes crisp and delicious.In addition to that,it contains sugar at 13.1%and commonly produces fruit at 2.5 kg.
Breeding
According to breeding goals,selfbred lines X712 and J52 were obtained based on oriented breeding with self-selected materials in terms of quality,yielding,early-ripeness,and disease-resistance.Specifically,X712 is bred on basis of self-fertilization of 7 generations of Xiuli and J52 was a hybrid of Jingxin No.1 and Citrullus lanatus.In 2008,5 treatments were set with the two varieties as male and female parents,which were carried out in a test region during 2009-2010 in order to select the optimal treatment in terms of early-ripeness,yielding,crack-resistance,and tastes and the results showed that the treatment of X712×J52 performed the best,which was named Jinmi No.2.Subsequently,Jinmi No.2 was used for regional test in Zhejiang Province during 2011 -2012 and production test in Zhejiang Province in 2013.Because of excellent performance,Jinmi No.2 was approved by Zhejiang Crop Committee in 2014 and numbered Zhe approved melon 2014002.
Results and Analysis
Regional test
Jinmi No.2 took part in a facilitywatermelon regional test in Zhejiang during 2011-2012,with a plot control,and the test plot was 12-16 m2,with three repetitions,as per random arrangement.In 2013,Jinmi No.2 took part in a production test,with a field control group,and the agricultural field was 250-300 m2,without repetitions,as per random arrangement.As shown in Table1,the regional yield of Jinmi No.2 in 2011 reached 35 026.5 kg/hm2,increasing by 45.0% compared with control,and showing extremely significant differences.In 2012,regional yield reached 27 882.0 kg/hm2,increasing by 22.7%,with extremely significant differences.In general,average yield of the two years reached 31 455 kg/hm2,which grew by 34.2% compared with control group.From weight of single fruit,Jinmi No.2 averaged 2.4 kg,which increased by 0.5 kg compared with Nabite watermelon in control group.It can be concluded from Table1 that the first pistillate flower of Jinmi No.2 had 7.1 nodes and of Nabite watermelon had 8.4 nodes in control group.These indicated that the developmental period of Jinmi No.2 was 31.4 d,and total growth stage was 108.3 d,which were shorter compared with control group.
Quality character
The evaluation on watermelon quality characters in the regional test includes rind thickness,flesh color,texture,and tastes.Compared with Nabite watermelon in control group,Jinmi No.2 was smaller,but fruit uniformity maintained well.Furthermore,fruit shape index averaged 1.3; the fruit was oblong; it has a light green rind with jagged dark green stripes.In addition to that,the flesh is red and juicy,containing soluble solids at 11.0%in center and at 7.8%in margin(Tabel 2).
Disease tolerance
Appraised by the Institute of Plant Protection and Microbiology,Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences in 2011 and 2012,the disease rate of Jinmmi No.2 was 60.85% in seedling stage after artificial inoculation of fusarium wilt(Table3).
Characteristics of the Varieties
Jinmi No.2 is a hybrid small watermelon,and it takes about 108 d from planting to harvest,of which the developmental stage lasts for about 31 d.It grows moderately and bears more fruits; it has 7.1 nodes of the 1st pistillate flower which grows with 6 intervals.The melon averagely weighs 2.4 kg and constitutes a moderate-size melon,with a yield of 31 455 kg/hm2.The fruit is oblong and fruit shape index is 1.3.What’s more,it has a light green rind with jagged dark green stripes.Additionally,the flesh is red and juicy,containing soluble solids at 11.0%in center and at 7.8%in margin.
Key Points in Cultivation
Planting time
The variety is suitable to be plant-ed in greenhouses in Zhejiang with early-ripening facilities.In spring,the seedlings are commonly cultivated in greenhouses in middle January and planted in middle February.
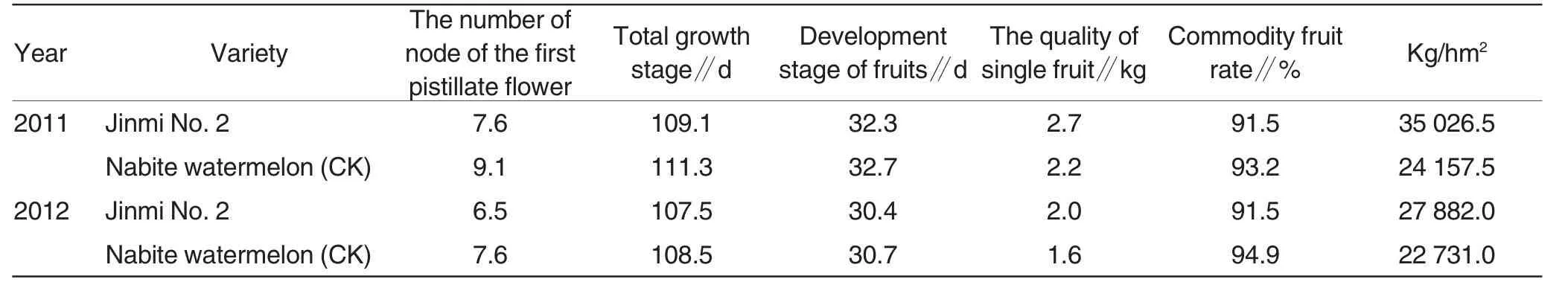
Table1 Regional test of Jinmi No.2
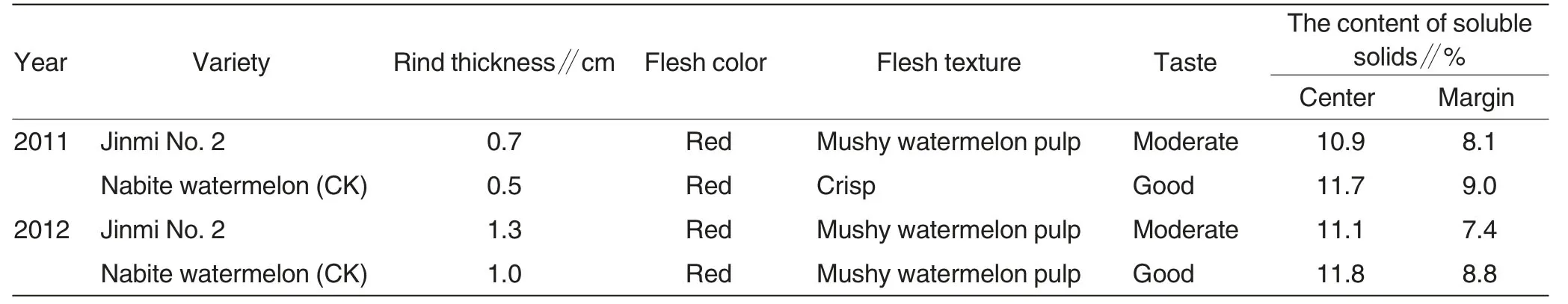
Table2 Quality characters of Jinmi No.2

Table3 Identification of disease resistance to Fusarium wilt in Jinmi 2 at the seeding stage
Planting density
The planting density generally keeps at 7 500 plants per hm2for creeping cultivation and 15 000 plants per hm2for vertical-cultivation.
Reinforcement of base fertilizers and timely application of additional fertilizer
In order to fully exploit the advantage of large fruit and improve tastes,it is recommended to reinforce base fertilizer before transplanting.Specifically,base fertilizer is dominated by organic fertilizer,including 20-30 t/hm2for row replacement,700-900 kg/hm2for cake fertilizer and 750 kg N,P and K fertilizers.In young fruit stage,N,P and K fertilizers should be applied at 700-900 kg/hm2to promote fruit growth; monopotassium phosphate should be then twice fertilized on leaves at 0.3% every 7 days,to prevent premature senility of melon vine.What’s more,after harvest of the first batch of watermelon,N,P and K fertilizers should be applied again at 750 kg/hm2to avoid following melon expansion.
Disease prevention
Jinmi No.2 performs poorly in disease tolerance.In growth stage,it is usually hit by wilt,anthracnose and gummy stem blight,and it is recommended to conduct crop rotation over three years with rice,wheat,maize,and rapeseed or plant watermelon by grafting technique.Specifically,wilt should be prevented before transplanting or direct seeding in the continuous cropping field,as follows:Before transplanting or sowing,70%Genfulin (wettable powder×1 000),a drug preventing root rotting,can be spread on farmlands and 70% thiophanate-methyl (×800) can be spread once or twice in seedling stage.For anthracnose,43% folicur (×7 500) solution or 70% antracol (×600) can be spread for multiple times.To prevent gummy stem blight,before flowering,80%Ludasheng (wettable powder),a drug,or 70% antracol (×600) added with 10%difenoconazole(×1 500)can be spread.After flowering,43% folicur(×10 000) added with 70% antracol(×600)should be spread.
[1]Productions of dominant watermelongproducing regions in China(全国西瓜主要优势产区生产现状)(一)[J].China Vegetables(中国蔬菜),2011,(13):5-9.
[2]PAN HF (潘慧锋),HU MH (胡美华),ZHAO JY (赵建阳).Status quo and development countermeasreus of small watermelons in Zhejiang Province(浙江省西甜瓜产业现状及发展对策)[J].Journal of Changjiang Vegetables(长江蔬菜),2008,19:1-5.
[3]DENG DC(邓大成),SUN XW(孙小武),MO XP (莫小平),et al.Status quo,problem and development of small watermelon in China(我国小西瓜生产的现状、问题与发展) [J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables (中国瓜菜),2006,(2):44-45.
[4]HU MH (胡美华),WANG RB (王仁杯),ZHU GR(朱国荣),et al.Application and development potential of small watermelon in Zhejiang Province (浙江省西甜瓜品种应用现状及潜力品种推荐)[J].Journal of Changjiang Vegetables(长江蔬菜),2009,9:5-8.
[5]ZHOU ZH (周正红),LIU DJ (刘德俊),ZHOU LJ (周六斤),et al.Breeding of a small fruit watermelon variety Yingchun(小果型西瓜新品种迎春的选育) [J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables (中国瓜菜),2010,3:25-27.
[6]SUN DX(孙德玺),DENG Y(邓云),ZHU YC (朱迎春),et al.A new mini watermelon varieyt "Zhongxinghong" No.1(小果型西瓜新品种中兴红1号的选育)[J].China Cucurbits and Vegetables(中国瓜菜),2013,6:27-30.
[7]SHEN MJ(沈海金).Citrullus lanatus No.8424,a small watermelon ariety (小型西瓜优良品种早春红玉和8424) [J].Northwest Horticulture (西北园艺 (蔬菜)),2011,2:46-47.
[8]WENG XZ(翁雄壮),FENG XJ(冯新军).Cultivation keys of Nabite watermelon(拿比特小西瓜栽培技术要点)[J].China Watermelon and Muskmelon(中国西瓜甜瓜),2002,3:33-34.
[9]CAO GH (曹国华),XU WM (徐炜民),SHEN H (沈华).A compararive test of mini-watermelons cultured in greenhouses(大棚礼品西瓜品种比较试验)[J].Shanghai Vegetables (上海蔬菜),2005,1:30-31.
[10]JIAO XB(焦小波).A compartive test of mini-watermelon varieties in spring(春季小西瓜品种比较试验)[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis(浙江农业科学),2010,2:278-279.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年1期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年1期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Nutrient Solution pH on the Growth of Seedlings of Sugarcane
- Effects of Soaking Seeds with Different Solutions on the Growth and Yield of Rice
- Effects of Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine on the Structure of Duodenal Mucosa of Chickens under Heat Stress
- Optimization of Microwave Extraction of Flavonoids from Water Chestnut Skin Dregs with Response Surface Method
- Establishmentand Comparison of Two TaqMan Real-time PCR Methods for PCV2
- Characteristics and High-yielding Cultivation Technology of HuaimaiNo.29
