Design of two-layer switching rule for stabilization of switched linear systems with mismatched switching
Dan MA
State Key Laboratory of Synthetical Automation for Process Industries,and College of Information Science and Engineering,Northeastern University,Shenyang,110819,China
Design of two-layer switching rule for stabilization of switched linear systems with mismatched switching
Dan MA
State Key Laboratory of Synthetical Automation for Process Industries,and College of Information Science and Engineering,Northeastern University,Shenyang,110819,China
A two-layer switching architecture and a two-layer switching rule for stabilization of switched linear control systems are proposed,under which the mismatched switching between switched systems and their candidate hybrid controllers can be allowed.In the low layer,a state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint to exponentially stabilize switched linear systems is given;in the high layer,supervisory conditions on the mismatched switching frequency and the mismatched switching ratio are presented,under which the closed-loop switched system is still exponentially stable in case of the candidate controller switches delay with respect to the subsystems.Different from the traditional switching rule,the two-layer switching architecture and switching rule have robustness,which in some extend permit mismatched switching between switched subsystems and their candidate controllers.
Two-layer switching rule;Mismatched switching;Switched linear systems
1 Introduction
As a special class of hybrid systems,a switched system is a dynamical system that consists of a finite number of continuous variable subsystems and a rule that orchestrates switching between them[1–21].It is widely used to model dynamical systems that exhibit mode switching due to jumping system parameters or changing environmental factors,such as the slippage of a legged robot and the gear switch of a car.Meanwhile,there are a great variety of applications on switched systems in other fields,including manufacturing systems,auto-pilot design and chemical processes.Unlike nonswitched systems,switched systems will exhibit different performance for different choice of the switching rule.Switched systems might be unstable even if eachsubsystem is stablizable under its candidate controller provided that the switching rule is not designed properly.Such examples are given in reference[3].On the other hand,switched systems may be(asymptotically)stable under some switching rule even if each subsystem is destabilized by its candidate controller.Thus,in order to obtain the performance of switched systems,such as stability,we need to co-design the switching rule and the continuous control algorithms.
There are many works concerning analysis and synthesis methods of switched systems,such as the common Lyapunov function method which deals with stability under an arbitrary switching,the multiple Lyapunov functions(MLFs)method which no need the stability of each individual subsystem,but to find a switching law,the average dwell-time(ADT)approach[20]and the piecewise quadratic Lyapunov function method are also employed to study the stability and stabilization of switched systems.However,to the best of the author’s knowledge,all the above proposed switching rules have not robustness,which means switched systems can be destabilized once switching is not in time or the switching rule is not satisfied.This motives our work.
Recently,networked switched systems and multiagent systems have attracted much attention.See[1,22,23]and the references therein.For networked switched systems,the switched plant enables one to capture many processes encountered in practice,which allows one to incorporate scenarios where the controller is remotely located or how much the network-induced delay is permitted.However,once the data from sensors and actuators exchanged by networks,networkinduced delays and packet dropout often occur since the network bandwidth is limited.Since switched systems arise from the interaction between a discrete switching rule and continuous control algorithms in dynamical systems,networks will be taken into account in designing the switching rule and continuous control algorithms.Specifically,network-induced delays of the switching signal might cause the candidate controller switches delay with respect to its subsystem.In this case,the performance of switched systems(such as stability)may be degraded;even the system is unstable.Therefore,it is urgent to present a new switching rule to maintain the performance of switched systems.As for the multiagent systems,the cooperative control objective under the switching topology might fail once switching is not in time.Thus,in order to deal with the switching delay proposed above,we study a two-layer switching architecture and a two-layer switching rule.If the actuator inertia or switching delay happens,wegive the instruction to the system in the high layer and decide how to switch in the low layer.The proposed two-layer switching architecture and the two-layer switching rule have strong robustness,which permitthe mismatched switching between the subsystems and their candidate controllers.The high layer switching rule gives us conditions on the mismatched switching frequency and the mismatched switching ratio.The low layer switching rule is the statedependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint.If the mismatched switching interval is zero,we only use the low layer switching rule to stabilize the system.
Intuitively,if the system is still stable under the proposed switching rule when the candidate controller switches delay,then we say the switching rule is robust to the delay.Similar to the robust control,the switching rule is robust if it can still stabilize the system for the given admissible upper bound.As we all known,the state-dependent switching rule usually does not guarantee any minimal dwell time.However,in many cases we need to reduce discontinuities in system operations,such as the passengers in the airplane demand a dwell time to maintain the smooth and comfortable ride if they are caught in the bumpy.Moreover,if the candidate hybrid controller switches delay with respect to its subsystem,the proposed state-dependent switching rule and the continuous feedback controllers in the low layer need still stabilize the system.Thus,if the statedependent switching rule can obey a dwell time and the switching delay in each active interval is no more than the dwell time,then wemight maintain the performance of the system.Inspired by the state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint technique in[24],we propose a two-layer architecture and a two-layer switching rule to deal with the mismatched switching problem.
First,we formulate the problem of mismatched switching based on the analysis of the switched linear control system.If the candidate controller switches delay with respect to the subsystem,then the closed-loop system can be described by two types of switched systems.One is matched system between subsystems and their candidate controllers,and the other is mismatched one.Third,we give two-layer switching conditions to exponentially stabilize the system if the mismatched switching occurs.Finally,we give the conclusions.
NotationsRndenotes the n dimentional Euclidean space.P>0 denotes a symmetric positive definite matrix.λmax(P)(λmin(P))denotes the maximal(minimal)eigenvalue of P.In a matrix,the term of symmetry is stated by the asterisk∗.
2 Problem formulation
The system to be controlled is a switched linear control system
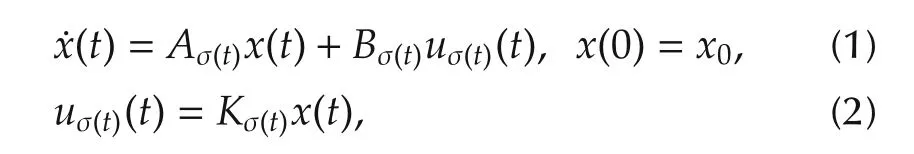
where x(t)∈Rnis the system state,u(t)∈Rmis the system control input,{Ap,Bp:p∈Υ}is a collection of matrix pairs defining the individual subsystems(“modes”)of the switched system,Kp,p∈Υ is the feedback control gain of the hybrid controller up(t),Υ is a finite index set,and σ(t):is a right-continuous,piecewise constant function called the switching signal which specifies the active mode at each time.The system switches between m linear subsystems.
The switching signal σ(t)of the switched plant can be characterized by the following switching sequence:
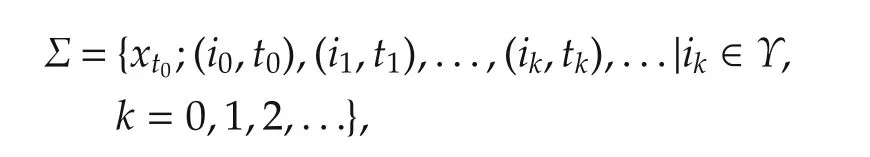
in which xt0is the initial state,t0is the initial time.We assume that none of subsystem can be stabilized by its candidate controller,that is to say Ap+BpKpfor any p∈Υ is not Hurwitz.
One of the objectives is to co-design the feedback control gain Kp,p ∈ Υ and the switching signal σ(t),under which switched system(1)is exponentially stable.However,due to the actuator inertia or the networkinduced imperfect factors,the exponential stability conditions under the proposed hybrid controller may be broken.For example,the candidate feedback controller switches asynchronously with respect to the subsystem,which might degrade the performance of the system or destabilize the system.In this case,a new switching rule needs to be given in the high layer to maintain the performance of switched systems.Thus,the other objective is to find a class of switching rule in the high layer to exponentially stabilize the system if the mismatched switching occurs.
Denote τk(tk)is the actuator inertia-induced delay or network-induced delay at each switching,which can be different at each instant tkand is satisfied with τk(tk)< tk+1− tk.That means each candidate controller switches delay τk(tk)with respect to the subsystem in each active interval.Usingˆσ(t)to denote the switching signal of the candidate controllers,whose switching sequence can be given as follows:
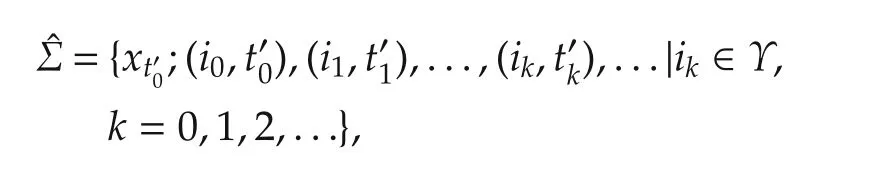
For τk(tk)in each switching interval[tk,tk+1),k=0,1,2,...,we use the following updating logic to denote the switching of hybrid controllers
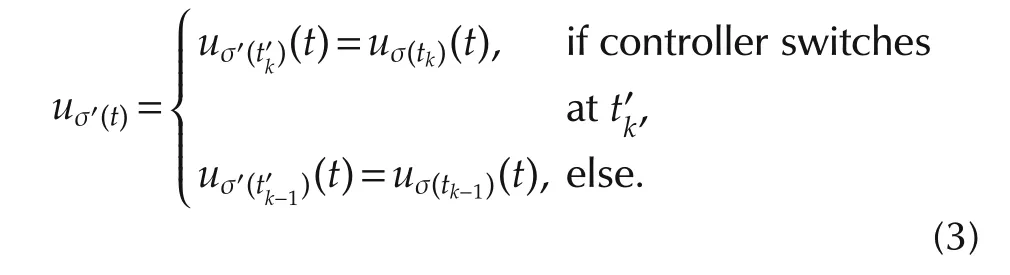
From the above updating logic,we know that the candidate controller switches delay one step with respect to its subsystem.Thus,system(1)is controlled by the following switching controllers with the updating logic(3):

Introduce the following two sets:
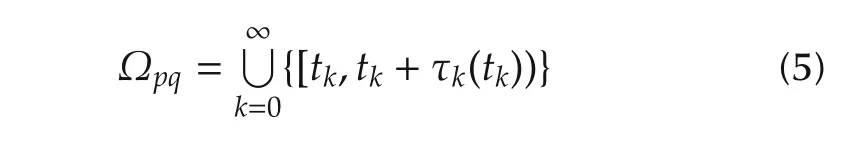
and
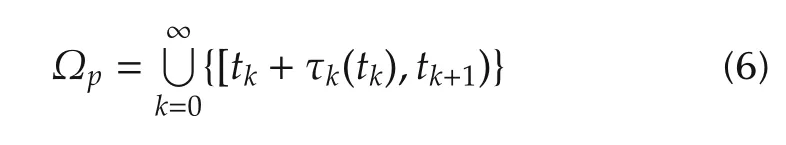
to describe the mismatched transmission intervals and the matched transmission intervals,respectively.Tp(t0,t)and Tpq(t0,t)are the length of Ωpand Ωpq,respectively.
For t∈[tk,tk+1),k=0,1,2,...,without loss of generality,letting σ(tk)=p,σ(tk−1)=q,and then we havewhich means the candidate controller Kpof the pth subsystem is active in the time tk+τk(tk)if the pth subsystem is active in the time tk.Combining(5)and(6),for any t∈[tk,tk+1),k=0,1,2,...,we use the following two classes of switched systems to describe system(1)under the mismatched and matched controller with the update logic(3):
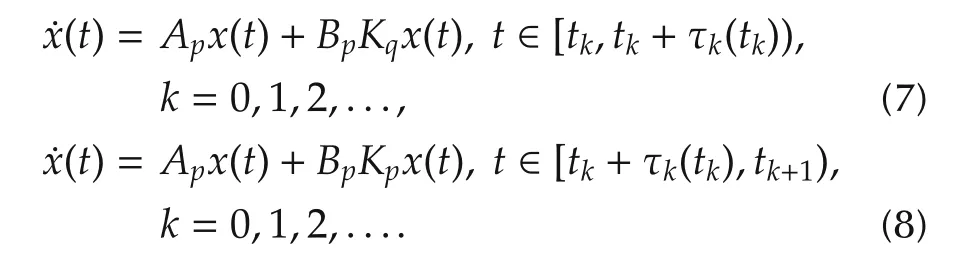
Remark 1Systems(7)and(8)can be regarded as switched linear systems controlled by two classes of hybrid controllers in turn.One class is matched switching controllers with their switched plant,and the other one is mismatched switching controllers with the plant.
In what follows,we will design a two-layer switching architecture and a two-layer switching rule based on the update logic to exponentially stabilize the switched linear systems even if the mismatched switching occurs.In the low layer,we will design the state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint to stabilize switched system(1).Once the switching delay occursin the candidate controller,we will combine the high layer switching rule with the low layer one to maintain the system performance.Therefore,we say the proposed two-layer switching architecture is robust to the switching delay between the subsystem and its candidate controller.Before presenting the main result,we give the following definition.
De finition 1For any t>0,Tp(t0,t)and Tpq(t0,t)are the total asynchronous switching time interval and synchronous switching time interval,respectively.We callasynchronous switching ratio by denoting ρ(t0,t).
De finition 2The equilibrium x∗=0 of a switched system is said to be exponentially stable under switching signal σ(t),if the solution to system(1)satisfies

for some constants Γ > 1 and γ > 0,where ‖·‖denotes the Euclidean norm.
3 Design of two-layer switching rules for Exponential stabilization of switched systems
In this section,we will design a two-layer switching rule to exponentially stabilize system(1)with(4).In the low layer,we consider the case that none of subsystems can be stabilized by its candidate controller,but can be stabilized by combining a state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint.Once the candidate controller mismatches its subsystem due to the switching delay,we try to find a switching rule in the high layer.In this case,we can regard the system as two classes of switched systems,one is mismatched subsystems with their candidate hybrid controllers,and the other is matched systems with their candidate hybrid controllers.
3.1 Co-Design of controllers and switching law in the low layer
Lemma 1For given constants αp> 0,βp,q> 0,p,q ∈if there exist positive definite matrices Ppand with such that the following matrix inequalities:
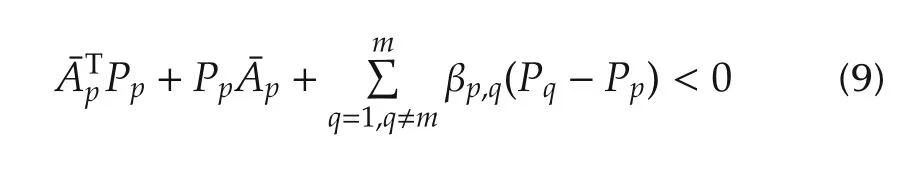
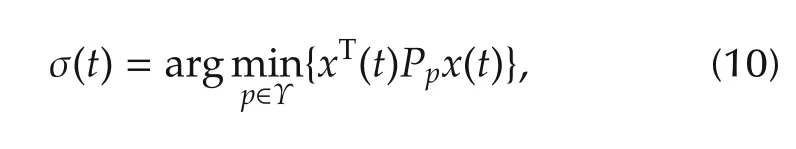
system(1)and(2)is exponentially stable with the decay rate αp/2.
ProofFor system(1)and(2),consider a piecewise Lyapunov-like function candidate as follows:
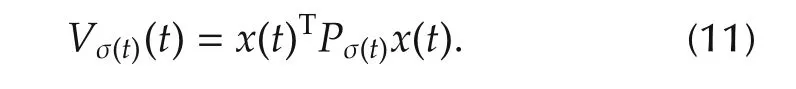
Pσ(t)are positive matrices.Forσ(t)=p,p∈ Υ,the derivative of Vp(x)along system(1)and(2)becomes
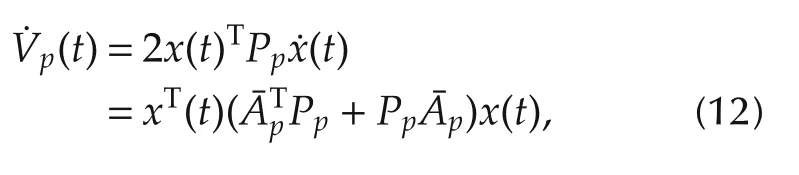
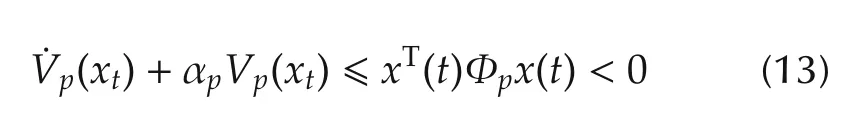
hold,where
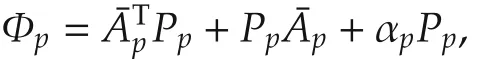
which means system(1)is exponentially stable under the controller(2)and the switching rule(10)with the decay rate αp/2.The proof is completed.
The following corollary can be used to co-design the switching rule and the state feedback control gain Kp,p∈Υ.
Corollary 1For given constants αp> 0,βp,q> 0,p,q∈Υ,p≠q,if there exist positive definite matrices Fpand and positive definite matrices Mpsuch that the following matrix inequalities:
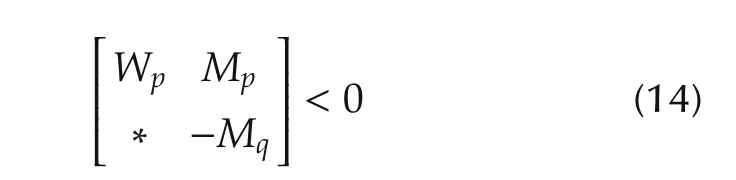
hold for any p∈Υ,then under the following switching rule:
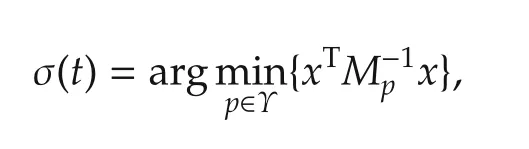
system(1)and(2)is exponentially stable with the decay rate αp/2.The continuous feedback control gain is Kp=FpMp,where
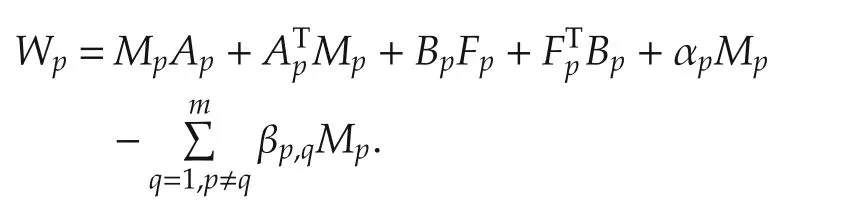
ProofIn order to co-solve the controller gains Kp,p∈Υ and positive definite matrices Pp,p∈Υ in Lemma1,we just need to pre-multiply and post-multiply(9)byandrespectively.Setting,from Schur complement Lemma,we can transfer(9)into LMIs(14)and then use the LMI Toolbox to solve the controller gains Kp=FpMpand positive definite matrices Mp,p∈Υ.
Sincethe controller switches delay with respect to the subsystem,we hope to find the conditions based on the upper bound of the delay,Furthermore,we hope to use the state-dependent switching rule proposed in Lemma1 to stabilize the system.Therefore,in what follows,we will derive the sufficient conditions to guarantee the exponential stability under the state-dependent switching rule with dwell time T constraint,even if each controller switches delay τk< T For simplicity and without loss of generality,we assume that τ is the upper bound of each τk.
3.2 Design of two-layer switching rule
We first introduce the following Lemma to give the conditions and the switching rule to obtain asymptotically stabilization with a dwell time constraint.
Lemma 2(Theorem 2[24])Givensystem (1)switched at t=tkto σ(tk)=p and assume there exist a collection of positive definite matrices Pp,l,p=1,2,...,m,l=0,1,...,L in Rn×n,and a set of scalars βp,q≥ 0,p=1,2,...,m,q∈Qpsuch that
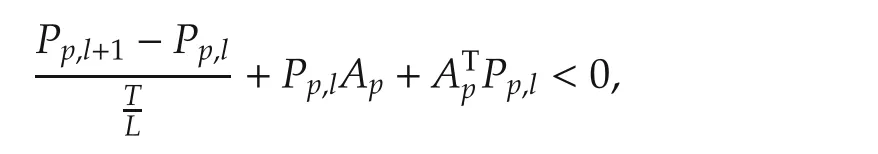
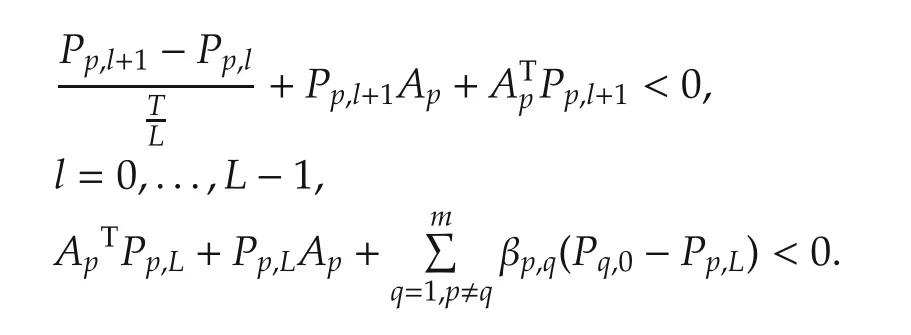
Then,the following law for the next switching at t=tk+1
σ(t)=p,∀t∈ [τk,τk+T),
σ(t)=p,∀t> τk+T,
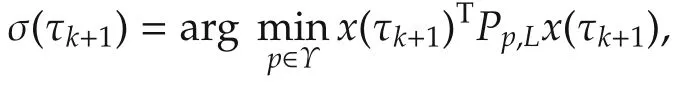
Remark 2In Lemma 2,T>0 is the dwell time,L is a specific integer,which leads to less conservatism in the conditions.Qpis the set of Υ except p.As an extreme case with T=0,L=1 which exactly implies that the constraint on the switching times is almost eliminated and the resulting switching can be state-dependent switching as in Lemma 1 with αp=0.
In order to avoid the mismatched switching effect on the system stability,we will try to find the conditions including time delays,under which the system is still exponentially stable for the proposed state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint.
For the closed-loop system,the candidate controller switches delay with respect to the subsystem,which might destabilize the subsystem and leads to the Lyapunov function increase.However,if we can find the conditions on the relationship between the matched and mismatched subsystem,the whole switched system can still be stabilized under some switching rule.Here we say the proposed state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint is the low layer switching rule,and the additional supervisory conditions on the mismatched switching frequency and the mismatched switching ratio is the high layer switching conditions.The two-layer switching architecture and the two-layer switching rule show the robustness.The following theorem gives us two-layer switching conditions to guarantee switched system(1)is still exponentially stable even if the mismatched switching controller(5)is instead.
Theorem 1Given system(1)switched to σ(tk)=p at t=tkand the candidate controller switched toand constants αp> 0,αpq> 0,a set of scalars βp,q≥ 0,p,q ∈ Υ,p ≠ q,pq ∈ Υ′,if there exist a collection of positive definite matrices Ppq,l,Pp,l,pq ∈ Υ′,p ∈ Υ,l=0,...,L in Rn×nsuch that
Condition 1

Condition 2
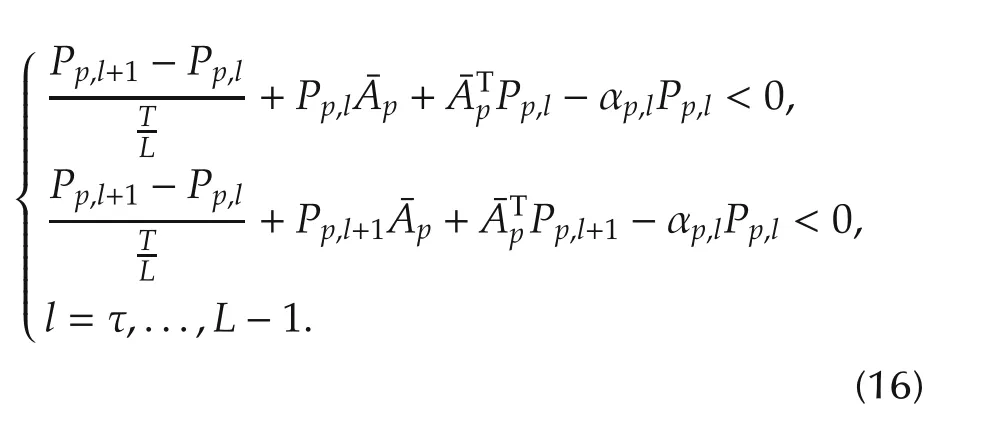
Condition 3There exists μ >1 satisfying
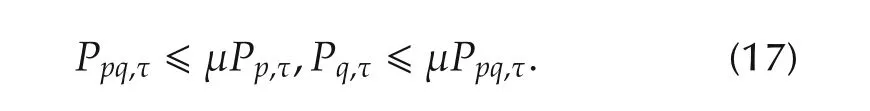
Condition 4The mismatched switching frequency satisfying

Condition 5The mismatched switching ratio satisfying
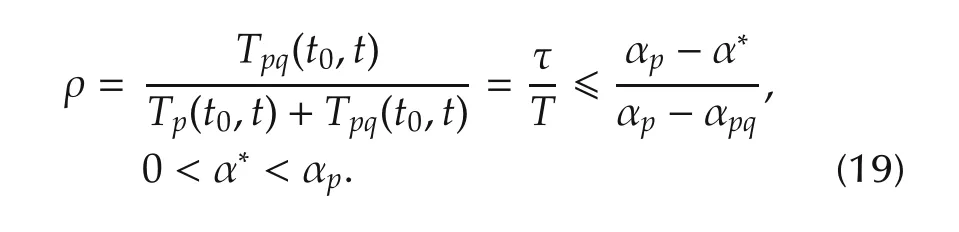
Condition 6
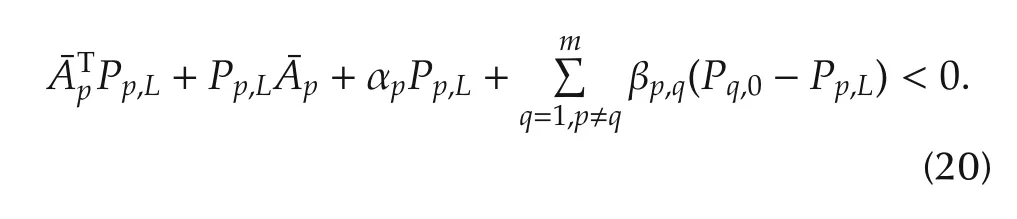
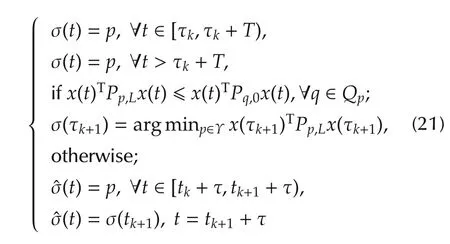
exponentially stabilizes system(1)even if the candidate controller switches delay with respect to the subsystem at each switching.Moreover,an estimate of state decay is given by

where
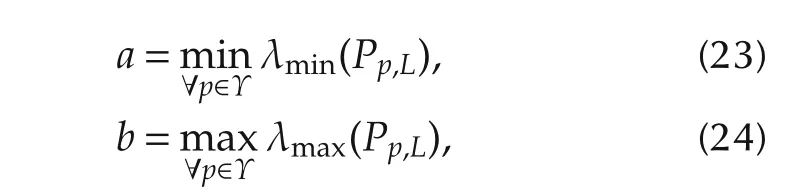
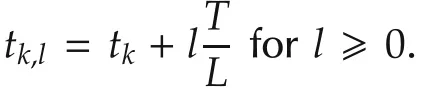

where
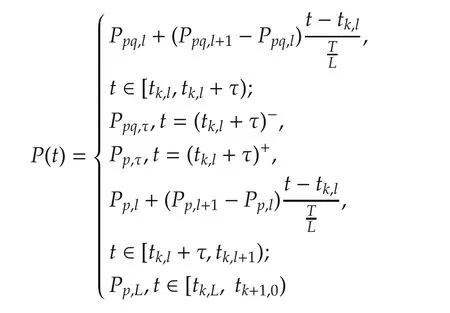
for k=0,1,....The subscript pq is the index of the pth subsystem and the qth controller which is active at time t.And p is the index of the pth subsystem and its candidate controller that is active at time t.Due to the actuator inertia,the controller switches delay with respect to the switched subsystems,which might yield a destabilized switched systems.
In t∈ [tk,l,tk,l+τ),k=0,1,...,from(15),we know that the state of(7)is permitted to grow with the upper rate
From(16),we know that for any t∈ [tk+τ,tk+T),k=0,1,...,the state of(8)is decreasing with the upper bound αp/2.
For[t0,t),the switched linear systems can be regarded as a switched system with two classes of switching signal σ(t)andˆσ(t).In order to find an immergence switching signal σ′(t)which combine σ(t)andˆσ(t)such that the closed-loop system are exponentially stable,we try to find the asynchronous switching time ratio and the asynchronous switching frequency based on the performance of the two classes switched systems.In what follows,we will give an asynchronous switching rule in the high layer to force the trajectory of systems(7)and(8)to exponentially converge to the equilibrium point.
Therefore,from(15)and(16),we know that
For t∈ [tk,tk+τ),t∈ [tk+τ,tk+T),k=0,1,...,and t∈ [tk+T,tk+1),weuseVpq,l(t),l=0,...,τ−1,Vp,l(t),l=τ,...,L−1andto denote V(x),respectively.
For t∈ [tk,tk+τ),k=0,1,...,l=0,...,τ−1 considering systems(7)and(8)and combining(15)–(17)and(21),we have
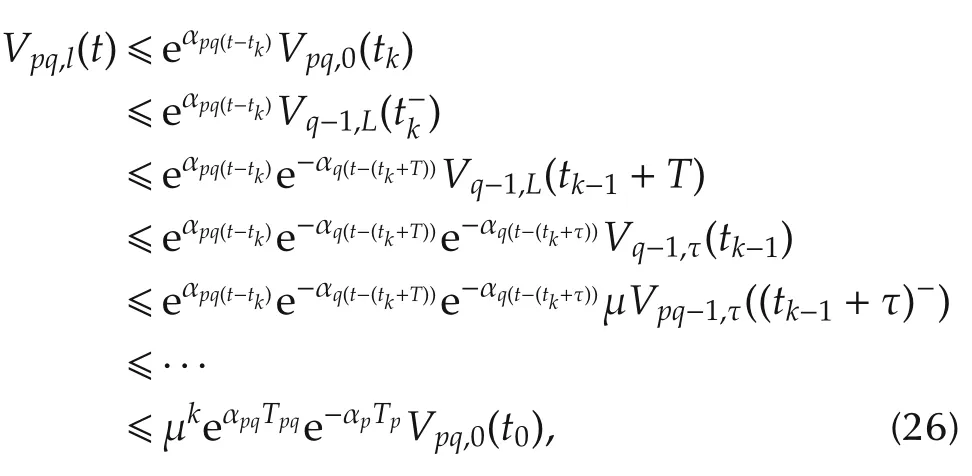
If t∈ [tk+τ,tk+T),k=0,1,...,l= τ,...,L−1 we know that
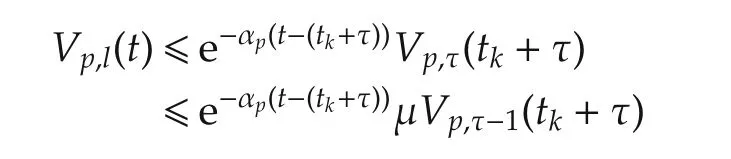
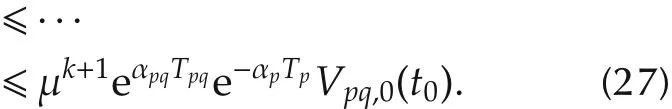
Denote the number of asynchronous switching on an interval[t0,t)by Nσ′(t)(t0,t),where Np(t0,t)=k+1 and Npq(t0,t)=k.From(26)and(27),we can get
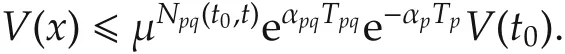
Combining(18)and(19),we obtain
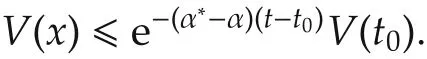
Since α‖x(t)‖2≤ V(x)and V(x0)≤ b‖xt0‖2,we infer that
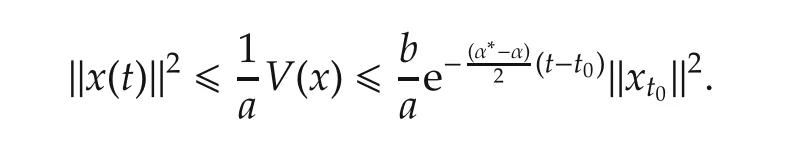
Therefore,we conclude that the trajectory of systems(7)and(8)exponentially converges to zero as t tends to infinite,which means system(1)is still exponentially stable if the candidate controllers switch with delay τ.This completes the proof.
Remark3Theorem 1 gives two-layer switching conditions to guarantee system(1)is still exponentially stable if the candidate controller is subject to the delayed switching.The proposed switching rule(20)combined with conditions(15)and(16)can make the system state trajectory increase or decrease in turn,if the mismatched switching occurs at each switching interval.However,whether the switched system under the mismatched switching is still exponentially stable is up to the high layer conditions(17)–(19),which give us the mismatched switching time ratio and the mismatched switching frequency.In fact,besides the hybrid state feedback controller to stabilize the system,we can also design other controllers,such as LQR and H∞controller to pursuit the other performance of the systems.
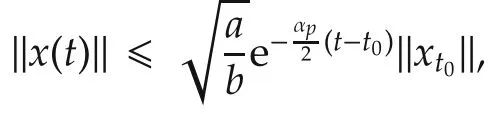
4 Conclusions
In this paper,we studied the stabilization problem for switched linear systems under mismatched switching through a two-layer switching architecture and a two-layer switching rule.The switched subsystems are allowed to be destabilized by their candidate state feedback controllers.The system can be stabilized by the state-dependent switching rule with a dwell time constraint in the low layer.Once switching delay occurs,we can detect it and then check the switching conditions in the high layer,under which switched systems are still exponentially stabilized.The conditions tell us the switched system is exponentially stable provided that both the upper bound of the mismatched switching time ratio and the mismatched switching frequency are bounded.The two-layer switching architecture can be used in the switched nonlinear systems and networked switched systems,which is our future work.
[1] L.Hetel,J.Daafouz,C.Iung.Stabilization ofarbitrary switched linear systems with unknown time-varying delays.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,2006,51(10):1668–1674.
[2] Y.E.Wang,J.Zhao,B.Jiang.Stabilization of a class of switched linear neutral systems under asynchronous switching.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,58(8):2114–2119.
[3]D.Liberzon.Switchingin Systemsand Control.Boston:Birkhauser,2003.
[4]G.Zhai,B.H.K.Yasuda,A.N.Michel.Stability analysis of switched systems with stable and unstable subsystems:an average dwell time approach.International Journal of System Science,2001,32(8):1055–1061.
[5] X.Sun,G.Liu,D.Rees,et al.Stability of systems with controller failure and time-varying delay.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,2008,53(10):2391–2396.
[6]W.Zhang,L.Yu.Stabilization of sampled-data control systems with control inputs missing.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,2010,55(2):2391–2396.
[7] L.Zhang,P.Shi.Stability,L2-gain and asynchronous H∞control of discrete-time switched systems with average dwell time.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,2009,54(9):2193–2200.
[8]M.C.F.Donkers,L.Hetel,W.P.M.H.Heemels,et al.Stability analysis of networked control systems using a switched linear systems approach.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,2011,56(9):2101–2115.
[9] H.Lin,P.J.Antsaklis.Stability and stabilizability of switched linear systems:a survey of recent results.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2009,54(2):308–322.
[10]J.Zhao,D.J.Hill.Dissipativity theory for switched systems.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2008,53(4):941–953.
[11]G.Xie,L.Wang.Stabilization of switched linear systems with time-delay in detection of switching signal.Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,2005,305(1):277–290.
[12]D.Xie,Q.Wang,Y.Wu.Average dwell-time approach to L2gain control synthesis of switched linear systems with time delay in detection of switching signal.IET Control Theory and Applications,2009,3(6):763–771.
[13]L.Vu,M.A.Kristi.Stability of time-delay feedback switched linear systems.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2010,55(10):2385–2389.
[14]A.G.Aghdam,E.J.Davison.Pseudo-decentralized switching control.Automatica,2003,39(2):317–324.
[15]K.S.Narendra,J.Balakrishnan.Improving transient response of adaptive control systems using multiple models and switching.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,1994,39(9):1861–1866.
[16]H.Yang,V.Cocquempot,B.Jiang.On stabilization of switched nonlinear systems with unstable modes.Systems&Control Letters,2009,58(10/11):703–708.
[17]Z.Xiang,R.Wang.Robust control for uncertain switched nonlinear systems with time delay under asynchronous switching.IET Control Theory and Applications,2009,3(8):1041–1050.
[18]S.Zahirazami,I.Karuei,A.G.Aghdam.Multi-layer switching structure with periodic feedback control.Proceedings of the American Control Conference.Minneapolis,MN:IEEE,2006:5425–5431.
[19]I.Karuei,N.Meskin,A.G.Aghdam.Multi-layer switching control.Proceedings of the American Control Conference.Portland:IEEE,2005:4772–4777.
[20]J.P.Hespanha,A.S.Morse.Stability of switched systems with average dwell-time.Proceedings of the 38th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control.Phoenix,AZ:IEEE,1999:2655–2660.
[21]A.S.Morse.Supervisory control of families of linear setpoint controllers–Part 1:exact matching.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,1996,41(10):1413–1431.
[22]D.Ma,J.Liu.Robust Exponential stabilization for networkbased switched control systems.International Journal of Control,Automation,and Systems,2010,8(1):67–72.
[23]D.Ma.Asynchronous Switching network protocol design for networked linear switched systems.Proceedings of the 30th Chinese Control Conference.Yantai:IEEE,2011:4670–4675.
[24]L.I Allerhand,U.Shaked.Robust state-dependent switching of linear systems with dwell time.IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control,2013,58(4):994–1001.

[18]and[19]propose a switching control architecture for improving the transient response of the switching control system by reducing the number of switching to destabilizing controllers,and also give the multi-layer switching algorithm.Different from the literatures,we focus on design of two-layer switching architecture and the two-layer switching rule to maintain the performance of switched systems.The proposed switching architecture permits the mismatched switching or switching delays in some extend.“Switching with delays”here wemean that the actuated switching from the subsystems to the candidate controllers mismatch due to the actuator inertia or the transmission by imperfect networks.Our aim is to present a two-layer switching architecture for switched linear systems,under which the two-layer mismatched hybrid controllers designed can exponentially stabilize a switched linear system subjected to the mismatched switching.Here “hybrid”means that the controller in the low layer is finite continuous state feedback control law and a state-dependent rule that orchestrates switching between them.However,how to maintain the control performance when the mismatched switching occurs is up to the mismatched switching ratio and the mismatched switching frequency conditions in the high layer.
29 June 2014;revised 10 July 2014;accepted 10 July 2014
DOI10.1007/s11768-014-4093-z
E-mail:madan@mail.neu.edu.cn.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.61233002)and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(No.N120404019).
©2014 South China University of Technology,Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science,CAS,and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
Dan MAreceived her M.S.and Ph.D.degrees from Shenyang University of Technology and Northeastern University,Shenyang,China,in 2004 and 2007,respectively.Between March 2012 and September 2012,she was a Guest Professor of University of Notre Dame,U.S.A.She is currently an Associate Professor of Northeastern University,China.Her research interests include networked control and hybrid dynamical systems.E-mail:madan@mail.neu.edu.cn.
 Control Theory and Technology2014年3期
Control Theory and Technology2014年3期
- Control Theory and Technology的其它文章
- Progressive events in supervisory control and compositional verification
- Passivity-based consensus for linear multi-agent systems under switching topologies
- Introducing robustness in model predictive control with multiple models and switching
- On the ℓ2-stability of time-varying linear and nonlinear discrete-time MIMO systems
- A noninteracting control strategy for the robust output synchronization of linear heterogeneous networks
- A learning-based synthesis approach to decentralized supervisory control of discrete event systems with unknown plants
