基于Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso研究
张吐辉,张海
(西北大学数学系,陕西 西安 710069)
基于Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso研究
张吐辉,张海
(西北大学数学系,陕西 西安 710069)
基于稀疏group lasso的思想和adaptive lasso的优点,提出更具一般性的Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso,并对其高维统计性质进行了研究.通过对正则子、损失函数的性质和正则参数的选择的分析,最终得到基于Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso非渐近误差界估计.
稀疏group lasso;限制强凸;可分解性;adaptive lasso
1 前言
一般线性回归问题
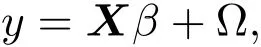
其中 y是 n×1响应变量,X=(X1,X2,···,Xn)T是 n×d矩阵,Xi=(xi1,···,xid), i=1,···,n,β=(β1,···,βd)为d×1未知参数.Ω是噪声向量且服从高斯分布Ω∼N(0,σ2I).若真实模型系数为β∗=(,,···,)且q 一般地,具有组结构线性模型可表示为: 其中y是n×1响应变量,Ω∼N(0,σ2I),Xl是n×ml矩阵,表示第l个因子,βl是第l个因子对应系数,大小为ml,l=1,···,L.若记X=(X1,X2,···,XL),β=(β1,β2,···,βL)′,进而上述线性回归问题可写为y=Xβ+Ω.针对变量之间具有组结构的问题,文献[4]提出了以组的形式进行变量选择的group lasso,其模型为: 该方法对lasso进行了改进,为高维结构化海量数据分析提供了一种新方法,并能从中选择出重要因子.随后,不同研究者开始了各种变形的group lasso方法研究[5-6].但group lasso只在组间具有稀疏性,而组内没有稀疏性,也就是说,在一个组内,因子将被同时选择或删除,然而在许多实际问题中,组内变量影响往往有所差异,这一缺点限制了它的应用.文献[7]提出p=2的稀疏group lasso组内组间都具有稀疏性,模型为: 此时,当 λ1=0时是大家熟知的lasso;当λ2=0时是group lasso. 显然,稀疏group lasso具有lasso的优良性质,可以选择出相关重要因子,但是lasso方法具有不一致性,详见文献[8-11].文献[12]提出的adaptive lasso,只要选择出合适权重就能解决lasso的缺点,从而稀疏group lasso也继承了lasso的缺点.基于此,本文研究更一般的Lp(p≥2)正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso,模型为: 其中ωl>0.由于p≥2时,正则化模型具有优良性质[13-14].本文关注于参数d大于样本数n时Lp(p≥2)正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso的非渐近误差界估计. 注 1.1Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso三项都是关于β的凸函数,因此求解模型是对应于一个凸优化问题的求解. 一般地,正则化问题都可以写成如下形式: 其中L(β;X,y)是损失函数,r(β)是正则函数,λn≥0是正则参数.在高维统计情形下,通过估计值βλn与真实值β∗之间的误差界来度量一个算法的好坏[15-17]. 首先引入相应定义.正则子r可分是指正则子关于Rd的两个子空间A⊆B,满足 损失函数满足限制强凸是指给定的集合 上,下式成立: 其中参数kL>0. 引理 2.1[17]平方损失函数满足限制强凸性即就是损失函数满足限制特征值.如果设计矩阵的每行向量服从分布正态分布,即其中是协方差矩阵,则损失函数限制强凸性以较大概率成立. 引理 2.2[17]如果损失函数L是凸函数、可微函数且满足限制强凸性,同时正则子满足可分性,正则参数时,有 下面利用上述两引理研究Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso理论性质.假设具有组结构的线性模型组的划分为: 即i=1时组的大小为1. 则Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso在平方损失下的模型可写为: 定理Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso模型(2.1),当正则参数 证明首先证明模型(2.1)满足引理2.2的条件.对于任意的 由此可知Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso正则子r(β)满足可分性. 由于此模型的损失函数是平方损失函数,由引理2.1知限制强凸性满足.除限制强凸性外,对于给定大小为m的组G,令XG:→,算子范数 对所有的l=1,2,···,ni.当i=1时,即每组的大小是1,有 使正则参数λn满足定理中的条件,即就是使参数成立.由对偶范数的定义,有 其中b=min{Ωl},l=1,···,d.而,即 由对偶范数的定义知: 为 ∥u∥1的对偶范数,由列标准化和高斯条件,有 而 对于高斯过程 由Sudakov-Fernique[18],有 由此可知, 由(2.2)式误差界可知,当损失函数满足限制强凸性和正则函数满足可分性且选择适当正则参数时,对基于Lp正则化的自适应稀疏 group lasso的误差界估计有准确的描述.可以看到Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso误差界不仅与正则参数λn和限制强凸常量kL有关,而且还与罚函数范数的选择有关. 变量选择问题是统计学基本问题.本文主要研究具有组结构的变量选择问题,针对经典group lasso的缺点,研究了更一般的Lp正则化的自适应稀疏group lasso,在对损失函数加限制强凸性条件以及罚函数满足可分性时,选择适当的参数,给出了估计值与真实值之间的非渐近界估计. 本文研究罚函数是凸罚函数的情形.对于目前流行的非凸罚函数情况[2,10,19-21],其高维统计性质是否成立尚没有研究.另外如果损失函数是非凸损失函数,研究具有组结构的变量选择问题也是有意义的工作之一. [1]Efron B,Hastie T Johnstone.Least angle regression[J].The Annals of Statistics,2004,32,407-499. [2]Xu Z.B,Zhang H,Wang Y.Lregularizer[J].Science in China(Information Sciences),2010,53:1159-1169. [3]Tibshirani R.Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B,1996,5:267-288. [4]Yuan M,Lin Y.Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables[J].Journal of the Royal Statistics Society B,2006,68(1):49-67. [5]Vogt J E,Roth V.A Complete Analysis of the lpGroup Lasso[C].Edinburgh:International Conference on Machine Learning,2012. [6]Meier L,Geer S,Buhlmann P.The group lasso for logistic regression[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series B,2008,70(1):53-71. [7]Friedman J,Hastie T,Tibshirani R.A note on the group lasso and a sparse group lasso[J].Mathmatical Statistics,arXiv:1001.0736vl,2010. [8]Meinshausen N,Buhlmann P.High dimensional graphs and variable selection with the lasso[J].The Annals of Statistics,2006,34:1436-1462. [9]Zhao P,Yu B.On model seletion consistency of lasso[J].Journal of Machine Learning Reseach,2006,7:2541-2567. [10]Fan J,Li R.Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association,2001,96:1348-1360. [11]Fan J,Peng H.Nonconcave penalized likelihood with diverging nunmber of parameters[J].The Annals of Statistics,2004,32:928-961. [12]Zou H.The adaptive lasso and its oracle properties[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2006,101:1418-1429. [13]Vogt J E,Roth V.The group lasso:l(1,∞)regularization versus l(1,2)regularization[J].In Department of Computer Science,2010(9):252-261. [14]Zhao P,Rocha G,Yu B.The composite absolute penalties family for grouped and hierarchical variable selection Source[J].The Annals of Statistics,2009,37(6A):3468-3497. [15]曹怀火,张永,王勇.种群扩散系数互译系统解的一致有界性[J].纯粹数学与应用数学,2011,27(3):38-41. [16]Raskutti G,wainwright M,Yu B.Minimax rates of estimation for high-dimentional linear regression over lq-ball[J].IEEE Transactiions on Information Theory,2011,57(10):6976-6994. [17]Negahban S,Ravikumar P,Wainwright M,Yu B.A unifed framework for high-dimensional analysis of M-estimators with decomposable regularizers[J].Statistical Science,2012,27(4):538-557. [18]Ledoux M,Talagrand M.Probability in Banach Spaces:Isoperimetry and Processes[M].New York: Springer-Verlag,1991. [19]Breheny P,Huang J.Coordinate descent algorithms for nonconvex penalized regression with appications to biological feature seletion[J].Annals of Applied Statistics,2011,5(1):232-253. [20]Zhang C H.Nearly unbiased variable seletion under minimax concave penalty[J].Annals of Statistics, 2012,38(2):894-942. [21]Zhang C H,Zhang T.A general theory of concave regularization for high-dimentional sparse estimation problems[J].Statistical Science,2012,27(4):576-593. The analysis of adaptive sparse group lasso based on the Lpregularizer Zhang Tuhui,Zhang Hai In this paper we propose adaptive sparse group lasso based on the Lpregularizer,we studied the high-dimensional statistical properties of our method by analysising properties of loss function and regularizer and choosing appropriate regularization paramete.Finally we obtained the nonasymptotic error bound. sparse group lasso,restricted strong convexity,decomposability,adaptive lasso O236,O213 A 1008-5513(2014)02-0178-08 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5513.2014.02.009 2013-11-10. 国家自然科学基金(60975036,11171272). 张吐辉(1988-),硕士生,研究方向:机器学习. 2010 MSC:62B10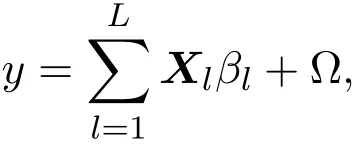
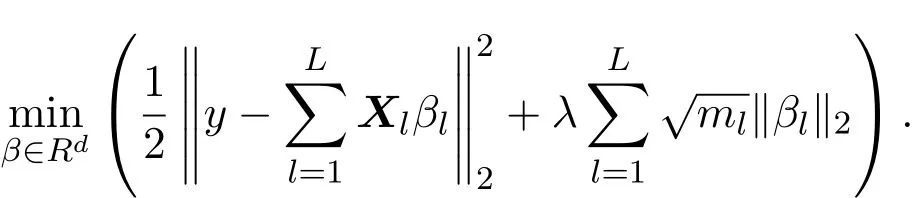
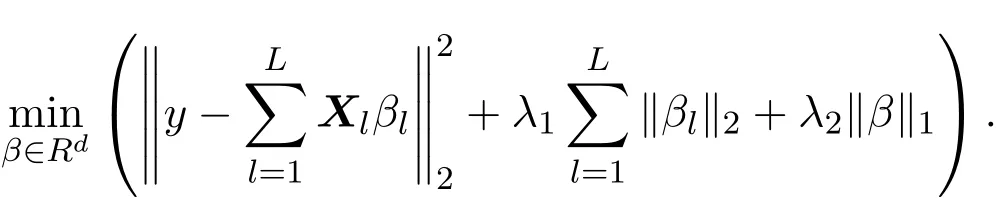
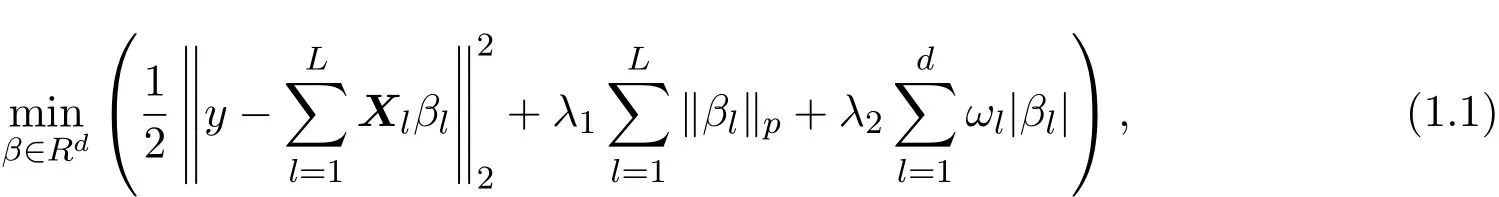
2 理论分析
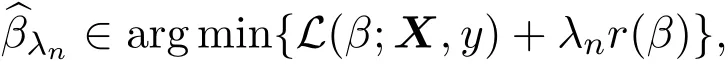
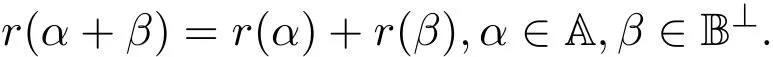
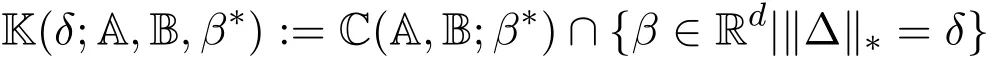
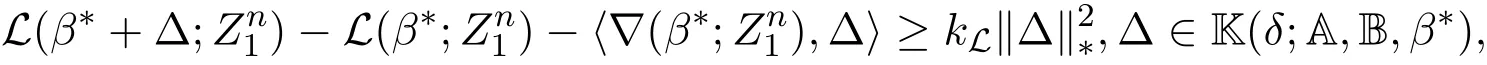
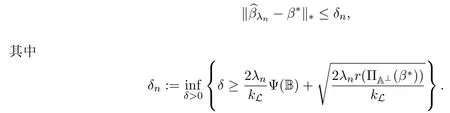
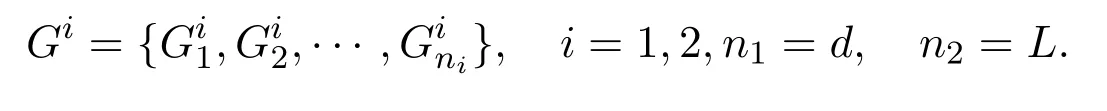
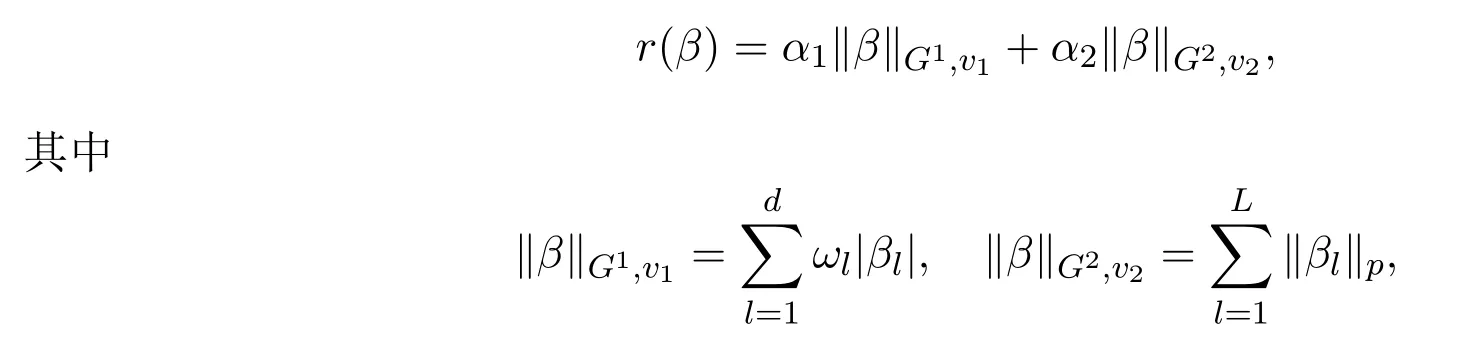
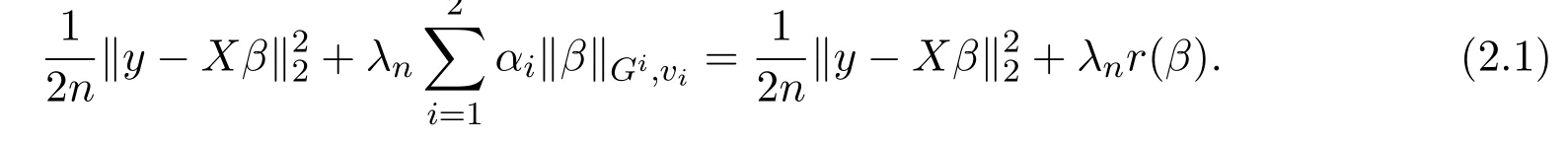

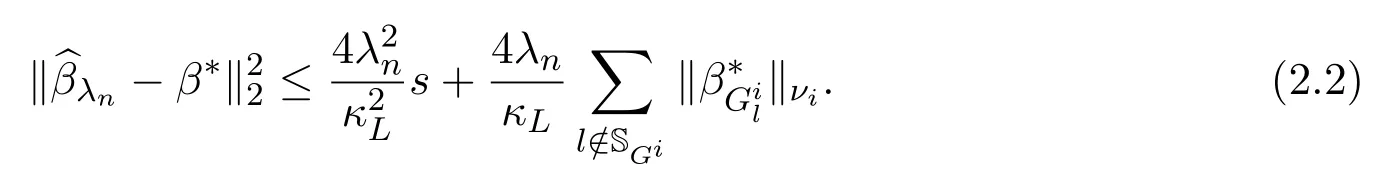
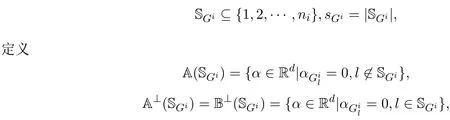
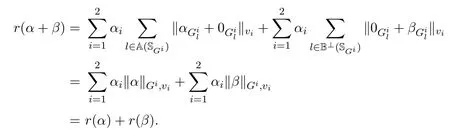

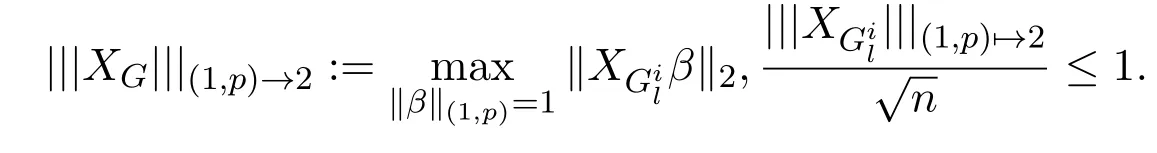
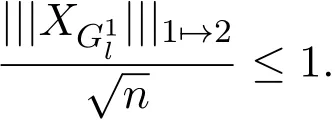
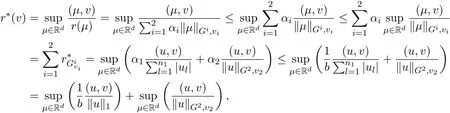
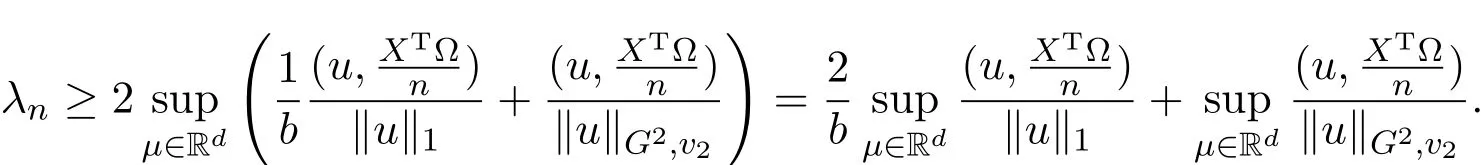
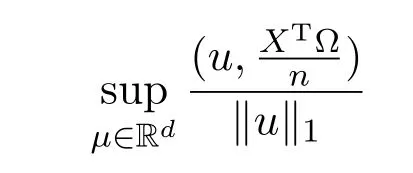

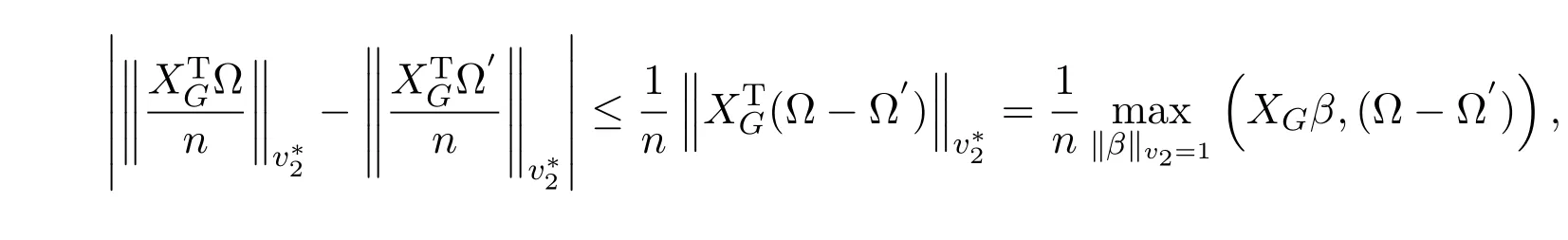
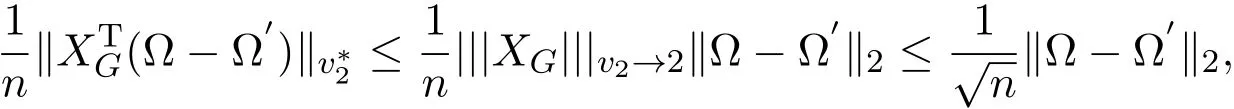
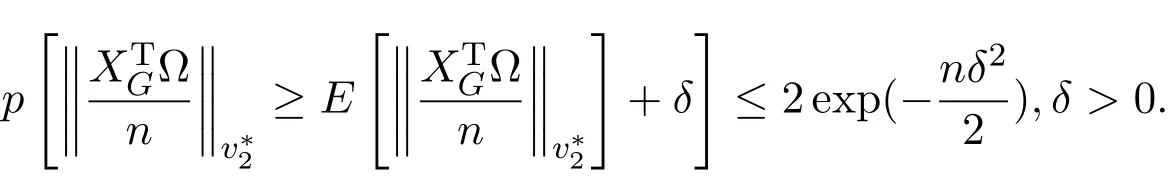
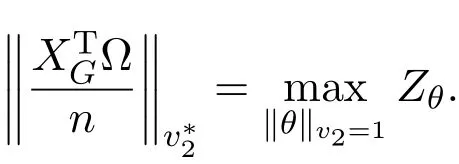
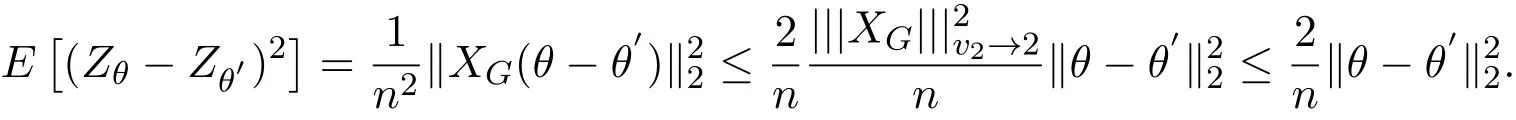




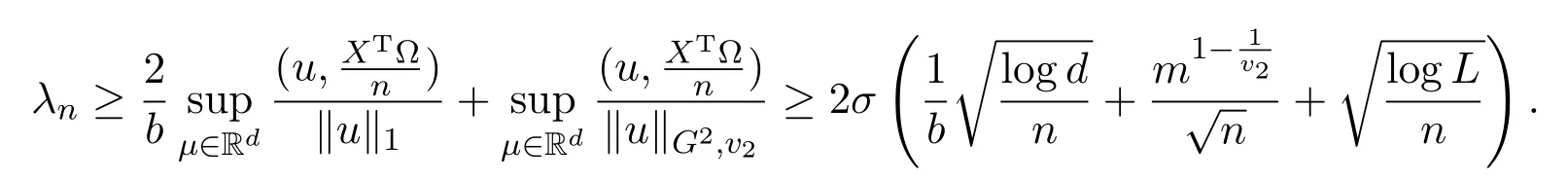
3 结论
(Department of Mathematics,Northwest University,Xi′an 710069,China)

