Ki67、EGFR在三阴性及非三阴性乳腺癌中的表达与相关性分析
张 淼,任 力,胡 蓉,褚晓雨,朱广卿
Ki67、EGFR在三阴性及非三阴性乳腺癌中的表达与相关性分析
张 淼,任 力,胡 蓉,褚晓雨,朱广卿
目的 对比Ki67、EGFR在三阴性乳腺癌(triple-negative breast cancer,TNBC)及非三阴性乳腺癌(non triple-negative breast cancer,NTNBC)中的表达,探讨Ki67与EGFR基因表达的相关性。方法 免疫组织化学法检测513例乳腺癌标本中Ki67及EGFR的表达,对比两者在TNBC和NTNBC中的区别,应用Spearman法分析Ki67与EGFR基因表达的相关性。结果 TNBC组织中Ki67 阳性表达率(94.32%)明显高于NTNBC(80.47%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) 。TNBC组织中EGFR表达率(68.18%)明显高于NTNBC(11.76%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 Ki67和EGFR在TNBC中均表达升高,但两者无相关性,两者均对乳腺癌预后判断有重要意义。
三阴性乳腺癌;Ki67;表皮生长因子受体
乳腺癌是女性常见恶性肿瘤,其中三阴性乳腺癌(triple-negative breast cancer,TNBC)是指雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone receptor,PR)、表皮生长因子2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2,HER-2)表达均为阴性的乳腺癌[1]。目前,TNBC无内分泌治疗、靶向药物治疗指征,主要依靠化学药物治疗,表现为增殖速度快、容易局部复发、远处转移率高、病死率高、预后较差[2],故成为临床研究热点之一。TNBC的发生、发展与细胞的异常增殖有关,而Ki67是评估肿瘤细胞增殖活性的重要标记物,对乳腺癌预后判断有重要意义[3]。表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)也在细胞增殖过程中起重要作用,EGFR过度表达可促进乳腺恶性肿瘤细胞增殖、加快转移、抑制凋亡[4]。本研究旨在分析TNBC与NTNBC中Ki67、EGFR表达的差异,探讨Ki67与EGFR的相关性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取我院2008-01-01至2013-06-01共513例乳腺癌患者资料,均为女性。手术方式: 根治术3例,改良根治术453例,保乳术57例。均有病理结果,其中浸润性导管癌359例,浸润性小叶癌67例,其他类型87例(包括黏液腺癌9例,髓样癌9例,大汗腺癌1例,导管内癌26例,硬癌4例,派杰氏病13例,脂质癌3例,单纯癌14例,类癌2例,鳞癌3例,腺癌3例) 。
1.2 方法 肿瘤标本经4%甲醛固定,石蜡4 mm厚切片,HE染色,光镜观察。免疫组化采用EnVision二部法,试剂盒购自福州迈新生物技术有限公司。ER、PR 结果判断: ER或PR≥10%肿瘤细胞核棕黄色染色为阳性表达;<10%肿瘤细胞染色为阴性。 HER2结果判断:0或( + ) 者被判定为HER2 阴性,(++) 及( +++) 者被判定为HER2阳性。如ER、PR、HER2 均阴性即定义为TNBC,有任何一个阳性者即定义为NTNBC。其中TNBC 88例,年龄29~81岁,中位年龄49.8岁;NTNBC 425例,年龄26~89岁,中位年龄54.2岁。
1.3 Ki67、EGFR结果判断 Ki67阳性细胞为细胞核棕黄色着色,光镜下观察,5个高倍镜视野计数200个细胞,计算阳性细胞所占的细胞总数百分比。阳性细胞数≤5%为阴性(-),6%~25%为弱阳性(+),26%~50%为阳性(++),>50%为强阳性(+++)。EGFR阳性细胞为膜着色,不着色为阴性(-),着色阳性细胞数<25%为(+),25%~50%为(++),>50%为(+++) 。TNBC和NTNBC组均检测Ki67和EGFR,对比两组的阴性、弱阳性、阳性、强阳性表达率及相关性。
1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS17.0 统计软件进行数据处理,计数资料采用χ2检验,应用Spearman法分析Ki67与EGFR基因表达的相关性,P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 Ki67和EGFR在两组乳腺癌组织中的表达 TNBC组织中Ki67、EGFR阳性表达率均明显高于NTNBC,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。EGFR和Ki67在乳腺癌组织中表达的免疫组化结果见图1。

表1 Ki67在TNBC和NTNBC中的表达 (n;%)
注:与NTNBC组比较,①P<0.05

图1 EGFR和Ki67在乳腺癌组织中表达(SP,×400)
2.2 Ki67和EGFR在TNBC组织中的相关性 88 例TNBC患者中,Ki67阳性率为94.32%(83/88),EGFR阳性率为68.18%(60/88),Ki67与EGFR无明显相关性(χ2=0.193,P>0.05,表2)。
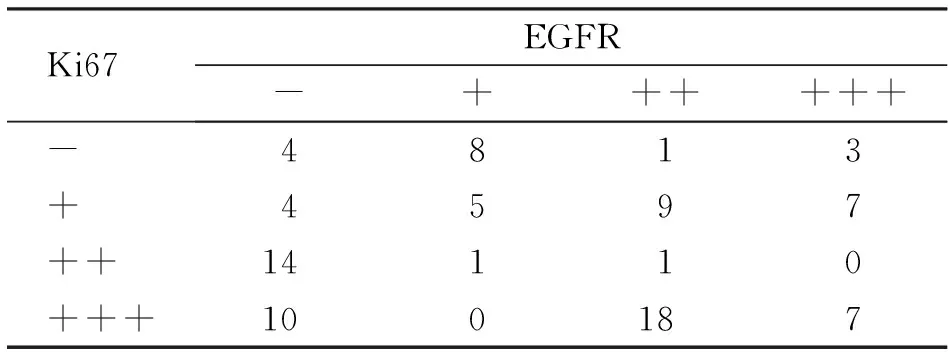
表2 Ki67和EGFR在TNBC中的表达
3 讨 论
分子生物学技术的发展使乳腺癌的分子病理学研究不断深入,ER、PR 和HER-2已成为乳腺癌病理学常规检查项目,内分泌治疗和靶向治疗已让大多数乳腺癌患者受益。TNBC作为乳腺癌中的特殊类型,占全部乳腺癌的10%~17%[5],只能依赖传统的放化疗,且疗效欠佳[6]。
Ki67是一种增殖细胞内的核抗原,功能与细胞周期密切相关,半衰期为1 h或更短[7,8]。Ki67抗原是当前较为肯定的核增殖标志物,因其半衰期短,脱离细胞周期后迅速降解,因此成为评估肿瘤细胞增殖活性的重要标记物[9]。Bauer等[10]研究表明,多种恶性实体肿瘤中Ki67的表达率远高于正常组织,与多种恶性肿瘤的发展、转移、预后有关。乳腺癌也是如此,Ki67高表达与原发肿瘤较大、腋窝淋巴结转移数目较多、分期较晚有关。本研究表明,Ki67在TNBC组织中的阳性表达率明显高于NTNBC(P<0.05),提示Ki67强阳性表达很可能是TNBC预后差的一个重要原因。
EGFR是酪氨酸激酶受体家族,多种肿瘤的发生发展与EGFR的异常表达有关,其与乳腺癌的增殖及生长也有密切相关。有研究表明,乳腺肿瘤患者中27%~30%有EGFR过表达[11],TNBC中高表达概率更高达45%~70%[12]。本研究显示,TNBC中约68.18%表达EGFR,明显高于其在NTNBC中(11.76%)的表达,考虑与肿瘤增殖速度快有关。
另外,本研究发现,TNBC中Ki67和EGFR均为高表达,但两者无相关性,与有关文献报道不同,考虑与样本量小及样本构成不同有关。EGFR的高表达可能在TNBC的增殖发展中起重要作用,可以作为靶向药物治疗TNBC的重要突破口。但目前这些实验入组例数较少,而且酪氨酸激酶抑制药仅对EGFR基因突变的非小细胞肺癌有效,而并非针对EFGR高表达的肺癌[14],故在乳腺癌患者中也需寻找酪氨酸激酶抑制药的疗效预测指标。EGFR基因扩增与过表达的关系,仍是今后研究的重点方向。
[1] 赵卫红,徐兵河,李 青,等.70 岁以上老年女性乳腺癌患者的特点和预后分析[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2006,28(2):385-388.
[2] Morris G J, Naidu S, Topham A K,etal. Differences in breast carcinoma characteristics in newly diagnosed African- American and Caucasian patients: a single -institution compilation comparedwith the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance,Epidemiology,and End Results database [J]. Cancer, 2007, 110(4):876-884.
[3] Tan P H ,Bay B H,Yip G,etal.Immunohistochemical detection of Ki67 in breast cancer correlates with transcriptional regu-Lation of genes related to apoptosis and cell death[J].Mod Pathol,2005,18(3):374-381.
[4] Nalwoga H, Arnes J B, Wabinga H,etal. Expression of EGFR and ckit is associated with the basal-like phenotype in breast carcinomas of African women [J].APMIS,2008,116(6):515-525.
[5] Dent R,Trudeau M,Pritchard K J,etal. Triple negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2007,13(5):4429-4434.
[6] Reis-Filho J S, Tutt A N. Triple negative tumours: a critical review[J]. Histopathology, 2008, 52(1):108-118.
[7] Ciulla M M, Acquistapace G, Toffetti L,etal. Ki67 cytop lasmic expression: observations in norm a l tissue from heart atr ia l appendages of healthy rats [J]. Cell Cycle, 2009,8(13):2125.
[8] Preusser M, Heinzl H, Gelpi E,etal. Ki67 index in intracran ia l ependymom a: a prom is ing h istopa tho log ical cand idate biom arke r[J]. Histopathology, 2008, 53(1):39-47.
[9] K m D K, Kim D W, Kim S W,etal. Ki67 antigen as a predictive factor for prognosis of sinonasa lmucosal melanoma[J].Clin Exp Otorhino laryngol,2008,1(4):206-210.
[10] Bauer K R,Brown M,Cress R D.Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor(ER)-negative,progesterone receptor(PR)-negative, andHER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple -negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California Cancer Registry[J].Cancer,2007,109:1721-1728.
[11] Montemurro F, Valabrega G, Aglietta M. Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER-2 tyrosine kinase activity[J].Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2007,7(2):257-268.
[12] Burness M L, Grushko T A, Olopade O I. Epidermal growth factor receptor in triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer: promising clinical target or only a marker? [J]. Cancer J,2010,16(1):23-32.
[13] Kim H G, Kassis J, Souto J C,etal. EGF receptor signaling in prostste morphogenesis and tumorigenesis [J]. Histol Histopathol, 1999, 14(4):1175-1182.
[14] Pal S K, Childs B H, Pegram M. Triple negative breast cancer:unmet medical needs [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat,2011,125(3):627-636.
(2014-07-18收稿 2014-09-06修回)
(责任编辑 尤伟杰)
Expression of Ki67,EGFR in triple negative breast cancer and correlation analysis
ZHANG Miao,REN Li, HU Rong,CHU Xiaoyu,and ZHU Guangqing.
Department of Oncology, Air Force General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100142,China
Objective To study Ki67, EGFR in non-triple negative and triple negative expression in breast cancer, and to explore the correlation between Ki67 and EGFR gene expression. Methods Immune histochemical method was used to detect Ki67 in specimens of 513 cases of breast cancer and the expression of EGFR, comparing both in triple negative and none triple negative breast cancer, and the correlation was analyzed by chi square and Spearman method. Results Ki67 positive expression rate in triple negative breast cancer tissues (94.32%) was significantly higher than that in triple negative breast cancer (80.47%) (P<0.05). Triple negative rate of EGFR expression in breast cancer tissue (68.18%) was significantly higher than that of non-triple negative breast cancer (11.76%) (P<0.05). Conclusions Ki67 and EGFR expression in triple negative breast cancer increases,but no correlation between both,has important significance in breast cancer prognosis judgement.
triple negative breast cancer;Ki67;EGFR
张 淼,本科学历,主治医师,E-mail:kjzhangmiao@sina.cn
100142北京,空军总医院肿瘤内科
朱广卿,E-mail: kjzhugq@sina.com
R737.9

