强相干干扰下基于二阶锥规划的圆弧阵宽带二维成像
黄 聪 孙大军 张殿伦 滕婷婷
强相干干扰下基于二阶锥规划的圆弧阵宽带二维成像
黄 聪 孙大军*张殿伦 滕婷婷
(哈尔滨工程大学水声技术重点实验室 哈尔滨 150001)(哈尔滨工程大学水声工程学院 哈尔滨 150001)
该文针对水下目标2维成像在强相干干扰情况下,目标亮点容易被淹没的问题,以及圆弧阵波束的高旁瓣给图像检测带来较多虚警的缺陷,提出基于二阶锥规划的宽带2维成像优化方法。该方法在对相干干扰抑制的同时,很好地控制了波束的旁瓣。分析了2维成像算法流程中由于时域滑窗导致阵列的接收信号矢量与阵列流形不同,造成二阶锥规划设计的权值与阵列的接收信号矢量失配,旁瓣控制和零陷设计无法满足设计的要求。针对该问题提出利用计算出的滑窗理论阵列的接收信号矢量代替阵列流形来进行二阶锥权值设计的方法,通过改进的二阶锥权值,将波束优化与圆弧阵的2维成像优化相结合。计算机仿真和水池实验都验证了该方法的有效性。
声呐;2维成像;二阶锥规划;旁瓣控制;干扰抑制
1 引言
水下目标定位[1,2]是水下探测、海岸防御、轨迹导航、目标打击的重要技术之一,目标定位的精准性很大程度上决定了算法和设备的性能。2维成像技术属于成像声呐[3,4]的一种,是利用1维阵列实现对目标距离和方位的2维分辨。通过实时有效的声学图像可以直接对目标进行探测识别。存在强相干干扰时,声学图像上目标亮度将被强干扰源的旁瓣所淹没,且圆弧阵成像高旁瓣的特性给图像检测造成更多的虚警。
很多旁瓣抑制算法对阵列模型有要求,无法直接利用在圆弧阵上,而近场模型的旁瓣控制就更加困难。虚拟线阵技术[5]利用均匀圆阵的相位模式激励理论,转化为虚拟的均匀线阵,再利用较成熟的线阵旁瓣控制算法,但该方法不适用于圆弧阵及其他阵形中。文献[6-9]提出了增加虚拟干扰源来计算权值的方法,该方法使用自适应迭代方式,适用于非均匀阵形,但迭代的收敛性和波束输出的稳健性都不能得到保证。文献[10]利用最小均方准则自适应设计法使设计的波束按最小方差准则逼近期望响应,但由于迭代的步长选取困难,导致设计结果出现误差。
2 基于二阶锥规划的圆弧阵波束优化
契比雪夫加权是一种经典的波束旁瓣控制方法,但其限制条件是只能用于远场条件下的均匀线阵。基于二阶锥规划的波束设计思想与契比雪夫加权方法的极大极小准则相同。由于该约束方法对阵列模型没有要求,故可适用于任意阵型中,可看作是契比雪夫加权在任意阵形上的拓展。
2.1 波束的旁瓣设计
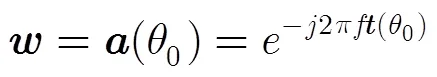
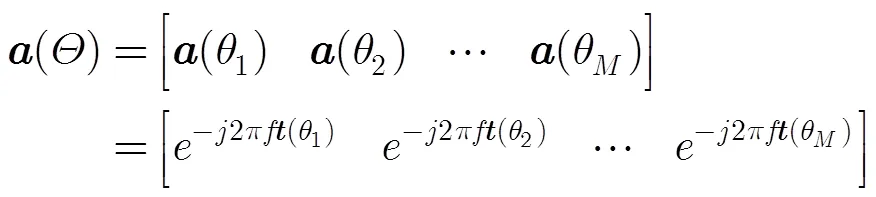
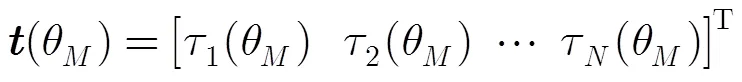

若对波束进行优化设计,在波束主瓣不失真的情况下,对波束的旁瓣级和零陷深度进行规划,其约束优化问题可以写为
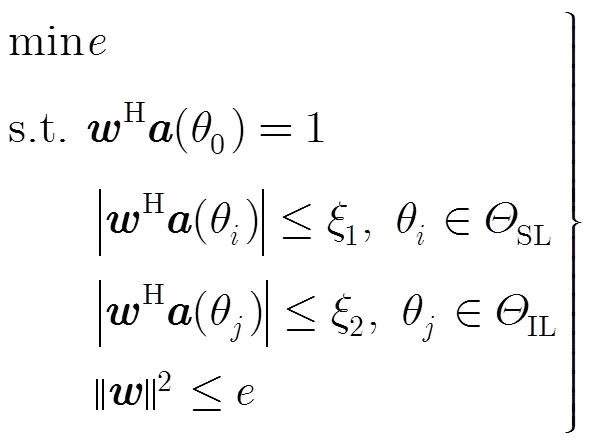

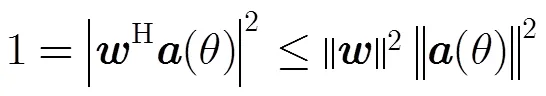

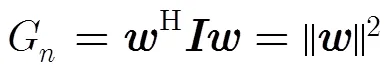
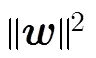

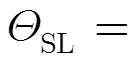
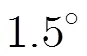
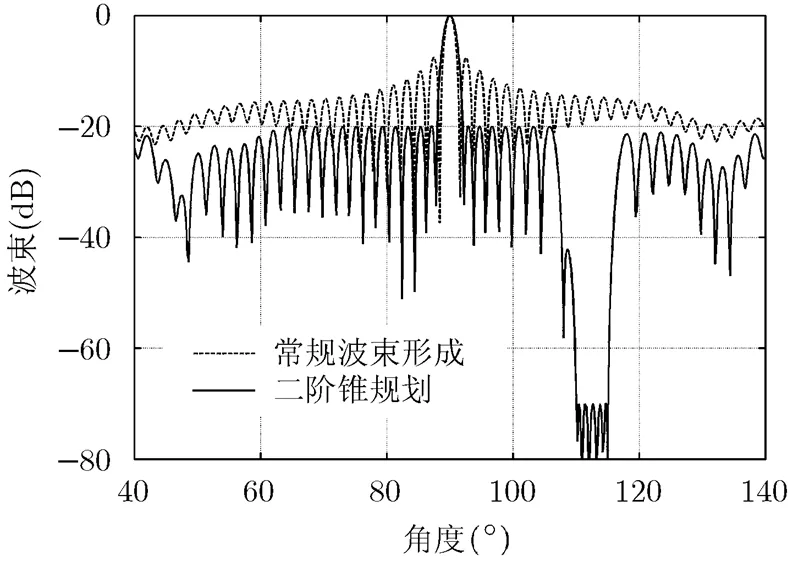
图1 理想情况下圆弧阵波束图
2.2 方位谱和波束图的联系
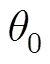
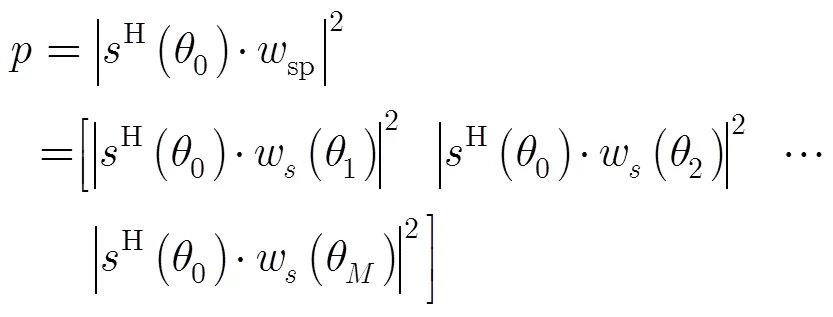
3 圆弧阵宽带2维成像优化
3.1 圆弧阵宽带2维成像算法流程
宽带2维成像先根据扫描位置对脉冲压缩后的信号在时域上进行滑窗处理,再对滑窗内截取的信号进行频域波束形成,得到距离和方位的2维图像处理结果,其流程图如图2所示。具体步骤如下:

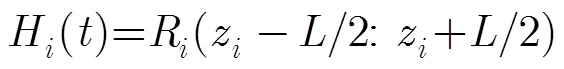

最后,进行宽带频域波束形成,得到距离和方位的2维成像结果。
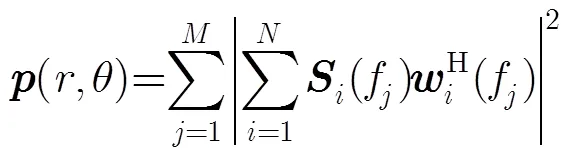
3.2 滑窗对二阶锥加权方位谱的影响
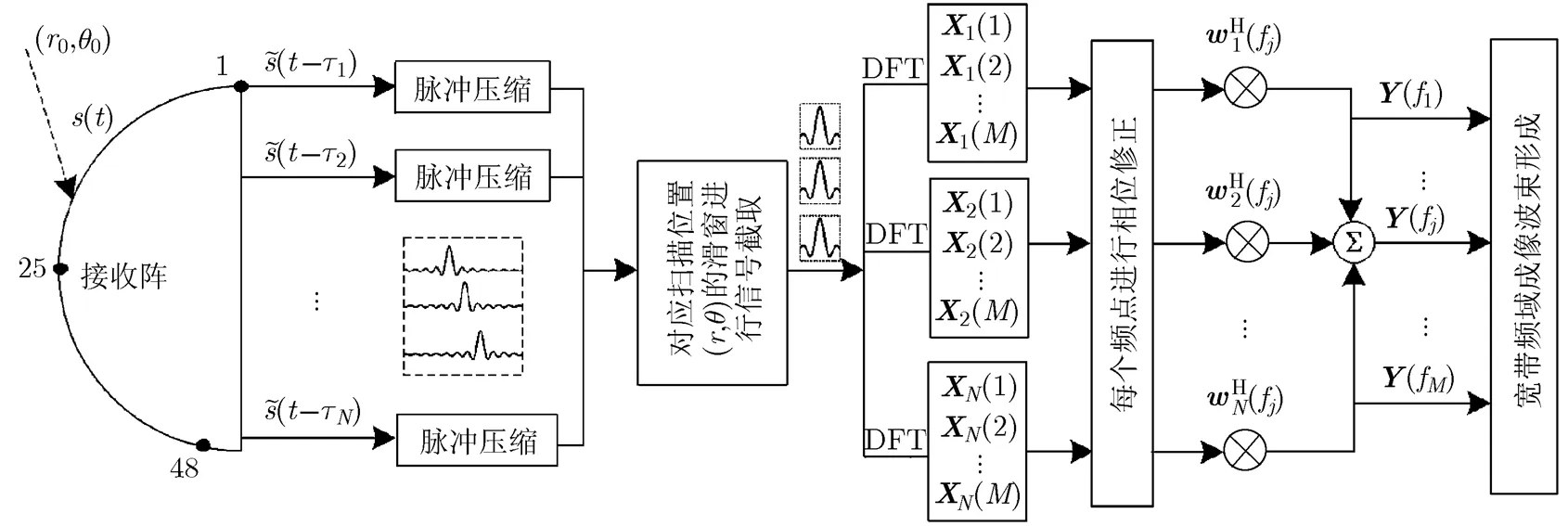
图2 宽带2维成像流程图

3.3 改进的二阶锥权值
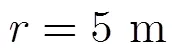
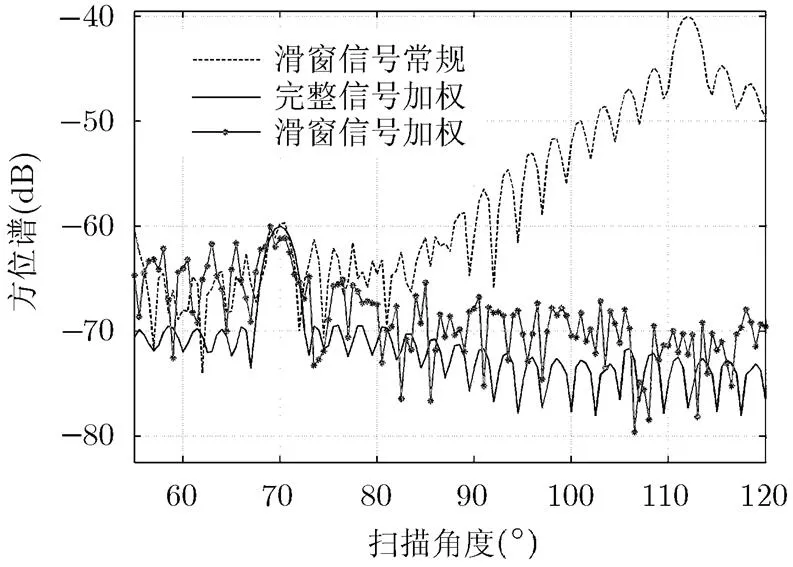
图.3 理想情况下的5 m处的方位谱

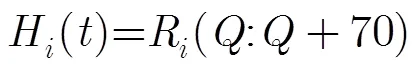
图4 固定距离滑窗方式
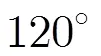

4 2维成像优化仿真及水池验证
4.1 2维成像计算机仿真
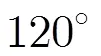
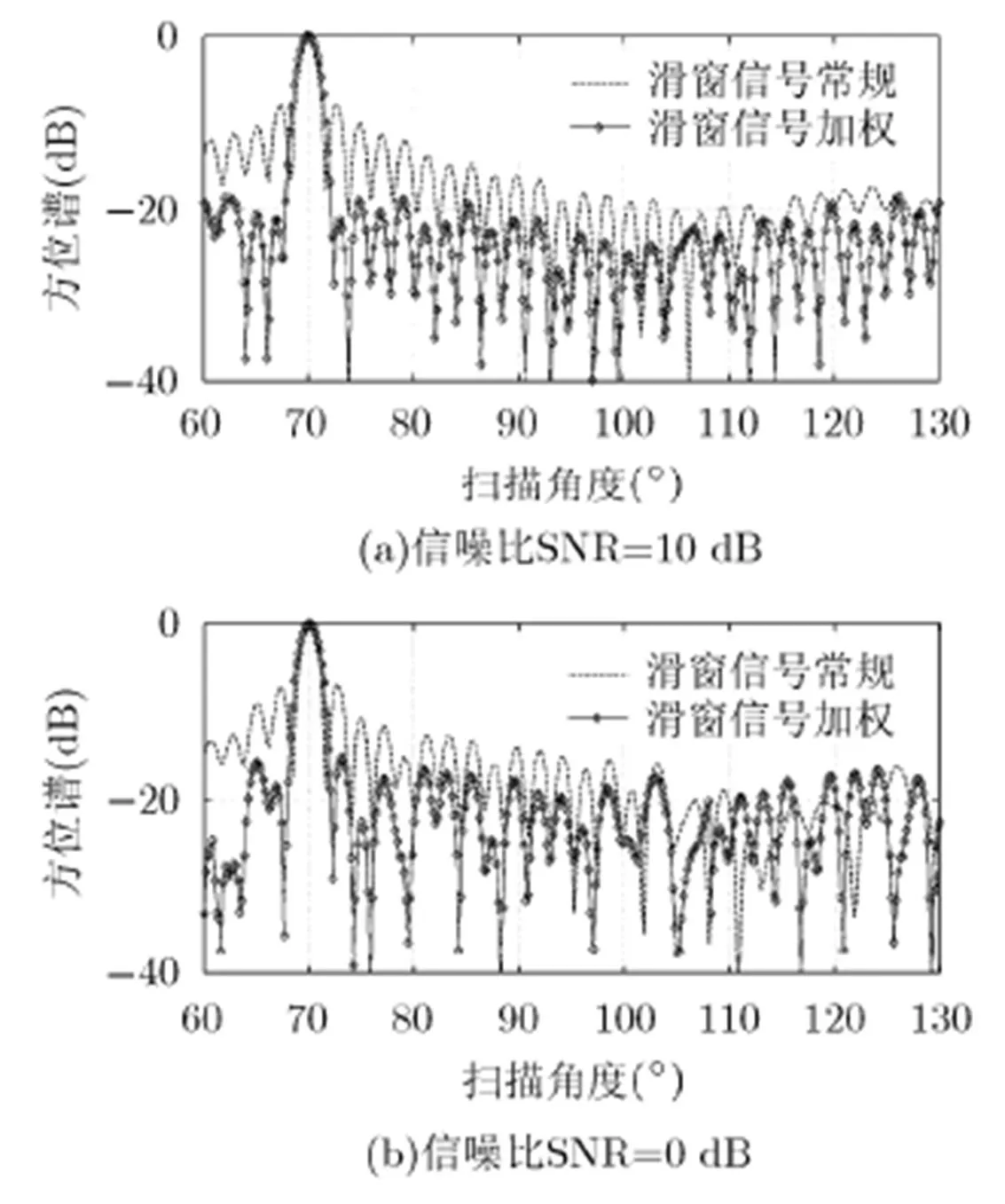
图5 无干扰下5 m处的方位谱
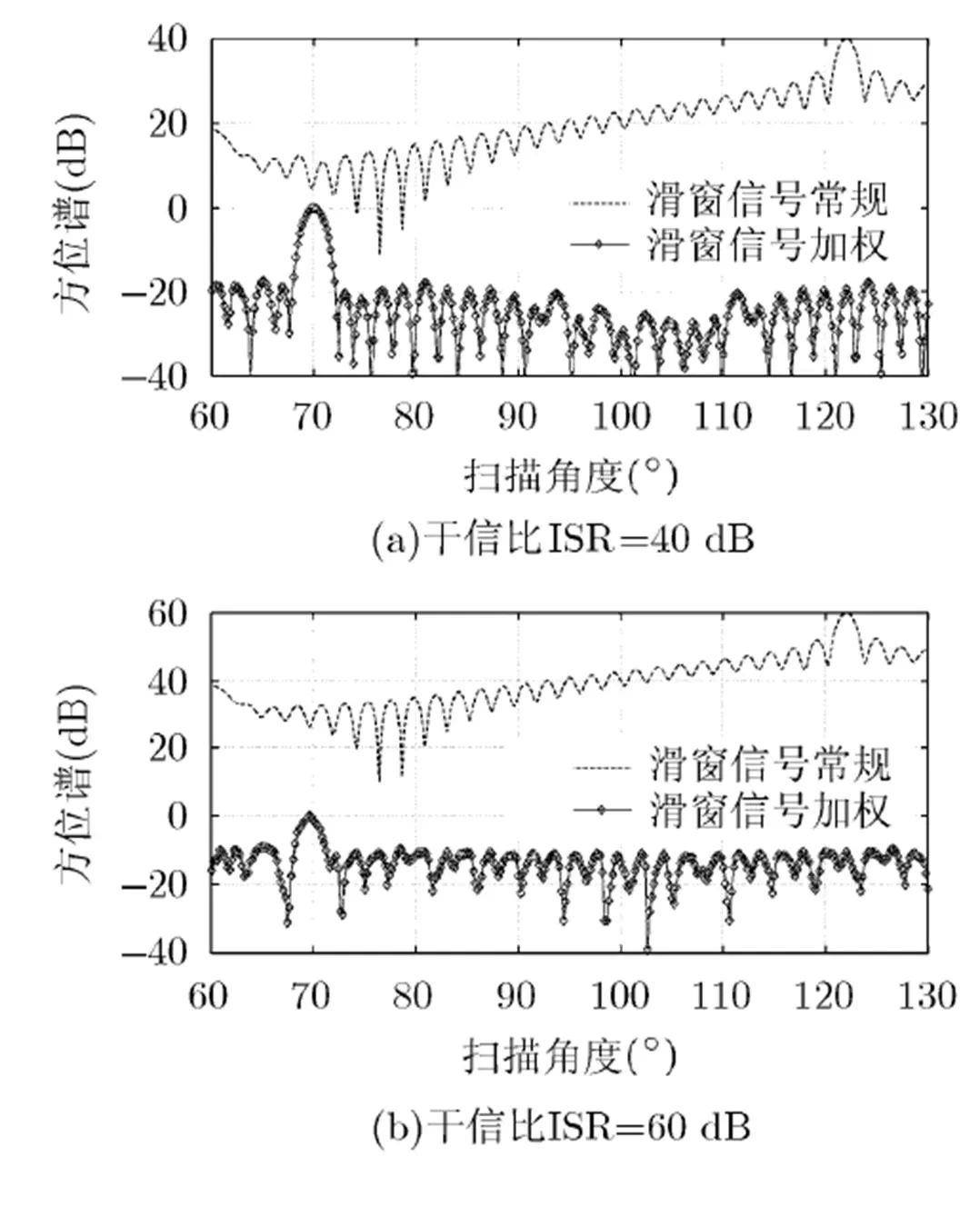
图6 有干扰下5 m处的方位谱

图.7 无干扰下的双目标2 维成像

从图8(a)可以看出加入强相干干扰后,常规成像只能估计出强相干干扰的位置,将图8(a)调整colorbar后得到图8(b),可以看出5 m处的目标已经完全淹没在相干干扰的旁瓣中,5.8 m处的目标还可以分辨,但也受到相干干扰距离旁瓣的影响。图8(c)为二阶锥加权成像结果,可以看出二阶锥加权在控制旁瓣的同时,对相干干扰进行了有效的抑制。
4.2 水池验证
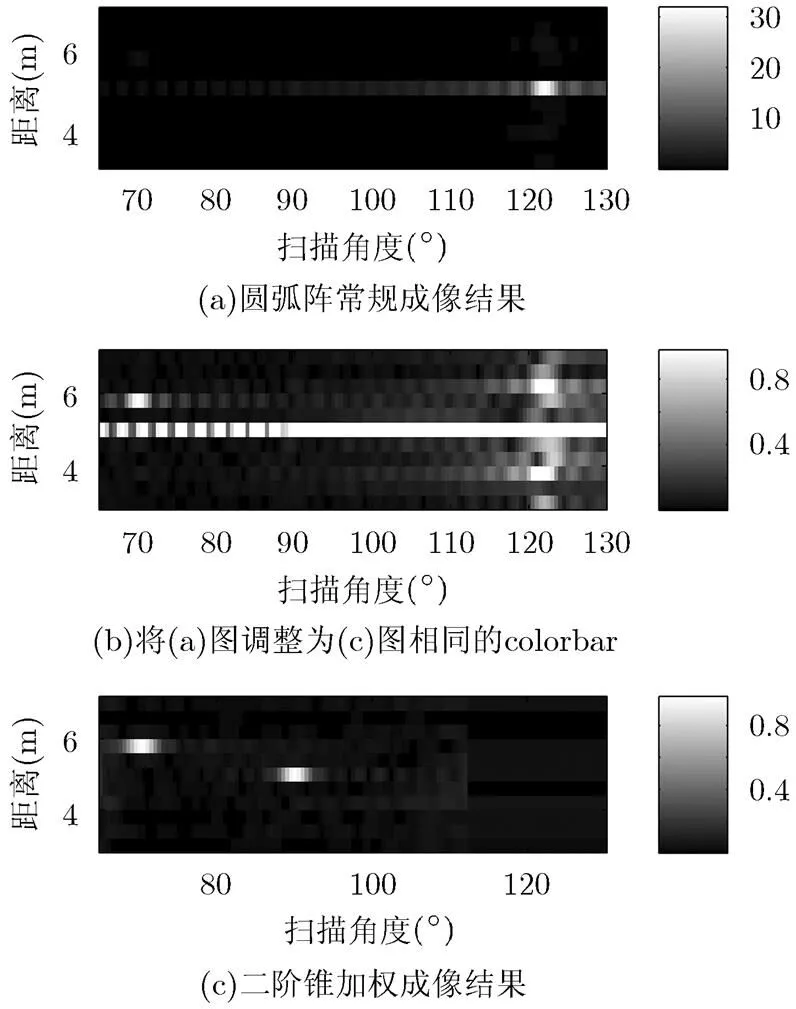
图8 干信比为30 dB时的2维成像
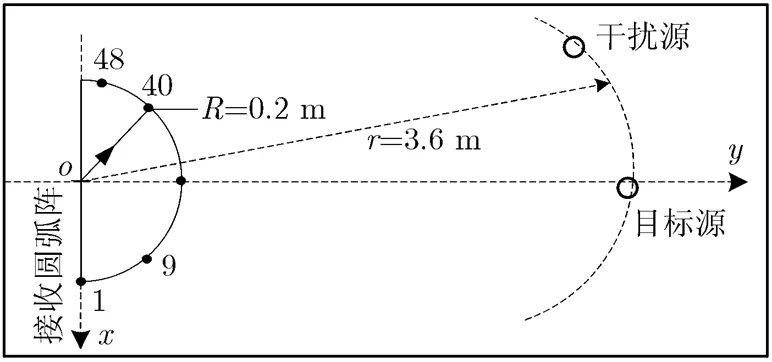
图9 水池实验配置图

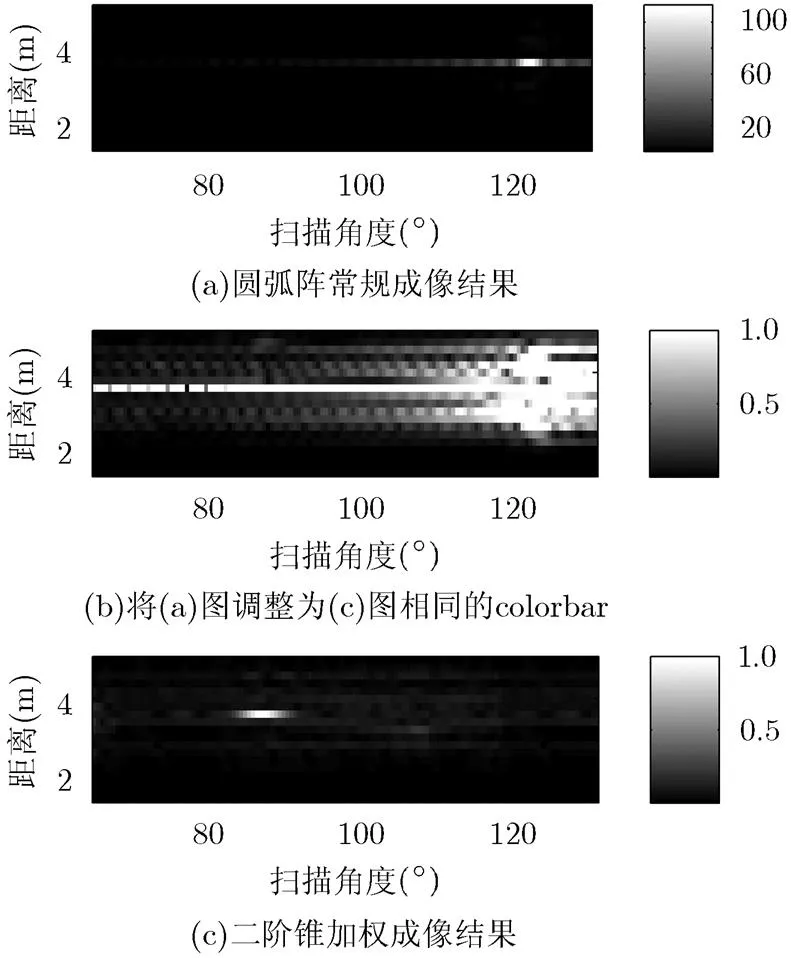
图10 2.维成像结果

图11 3.6 m 处的方位谱
5 结论
本文利用二阶锥规划方式对圆弧阵进行波束优化,在波束上进行旁瓣控制和零陷设计,并将波束优化的思想与方位谱相相结合,对2维成像进行优化。由于2维成像中对脉冲压缩信号的滑窗处理,方位谱旁瓣区域内的滑窗无法截取到完整的信号相关峰,阵列的接收信号矢量与利用阵列流形设计的二阶锥权值失配,最终导致输出的方位谱无法满足波束的旁瓣和零陷设计要求。本文通过仿真模拟出宽带2维成像在不同距离上的滑窗过程,将窗内截取的理论阵列的接收信号矢量代替阵列流形来进行二阶锥的权值设计,解决了2维成像滑窗带来的二阶锥权值不匹配的问题,将二阶锥加权方式成功应用于2维成像的优化中。在对相干干扰抑制的同时很好地控制了目标成像的旁瓣,改善了后续目标的图像检测和识别的性能。
[1] Hansen R K, Castellani U, Murino V,.. Mosaicing of 3D sonar data setstechniques and applications[C]. IEEE Oceans Marine Technology Society, Washington DC, 2005: 2006-2011.
[2] Becker K. A general approach to TMA observability from angle and frequency measurements[J]., 1996, 32(1): 487-496.
[3] 勇俊. 基于二维成像声呐的水下运动目标定位技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2012.
Jun Yong. Research on positioning techniques of the underwater moving target track based on two-dimensional imaging sonar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2012.
[4] Wang F, Balakrishnan V, and Zhou P Y. Optimal array pattern synthesis using semidefinite programming[J]., 2003, 51(5): 1172-1183.
[5] 邹吉武. 多基地声呐关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2012.
Zou Ji-wu. Study on multistatic sonar key technologies[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2012.
[6] 杨益新. 声波束形成与波束域高分辨方位估计技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西北工业大学, 2002.
Yang Yi-xin. Studies on beamforming and beamspace high resolution bearing estimation techniques in sonar systems[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2002.
[7] Olen C A and Compton R T. A numerical pattern synthesis algorithm for arrays[J]., 1990, 38(10): 1666-1676.
[8] Ng B P, Er M H, and Kot C. Linear array geometry synthesis with minimum sidelobe level and null control[J]., 1994, 141(3): 162-166.
[9] Palmese M and Trucco A. An efficient digital CZT beamforming design for near-field 3-D sonar imaging[J]., 2010, 35(3): 584-594.
[10] Palmese M and Trucco A. Acoustic imaging of underwater embedded objects: signal simulation for three-dimensional sonar instrumentation[J]., 2006, 55(4): 1339-1347.
[11] 鄢社锋, 马远良. 二阶锥规划方法对于时空域滤波器的优化设计与验证[J].中国科学E辑信息科学, 2006, 36(2): 153-171.
Yan She-feng and Ma Yuan-liang. Second-order cone programming method for the optimization of spatial filter design and validation[J]., (), 2006, 36(2): 153-171.
[12] 杨益新, 孙超, 鄢社锋. 圆阵宽带恒定束宽波束形成的实验研究[J].声学学报, 2003, 28(6): 504-508.
Yang Yi-xin, Sun Chao, and Yan She-feng. Experimental studies on broadband constant beamwidth beamforming for circular arrays[J]., 2003, 28(6): 504-508.
[13] 鄢社锋, 马远良. 基于二阶锥规划的任意传感器阵列时域恒定束宽波束形成[J].声学学报, 2005, 30(4): 309-315.
Yan She-feng and Ma Yuan-liang. Broadband constant beamwidth beamforming for arbitrary sensor arrays in time domain via second-order cone programming[J]., 2005, 30(4): 309-315.
[14] 鄢社锋, 马晓川. 宽带波束形成器的设计与实现[J].声学学报, 2008, 33(4): 316-319.
Yan She-feng and Ma Xiao-chuan. Designs and implementations of broadband beamformers[J]., 2008, 33(4): 309-315.
[15] 梁国龙, 马巍, 范展. 矢量声呐高速运动目标稳健高分辨方位估计[J].物理学报, 2013, 62(14): 144302-144306.
Liang Guo-long, Ma Wei, and Fan Zhan. A high resolution robust localization approach of high speed target based on vector sonar[J]., 2013, 62(4): 144302-144306.
[16] 杨涛, 苏涛, 何学辉. 基于波束域导向矢量估计的稳健自适应波束形成方法[J].电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(11): 2758-2763.
Yang Tao, Su Tao, and He Xue-hui. Robust adaptive beamforming based on beamspace steering vector estimation[J].&, 2013, 35(11): 2758-2763.
[17] 徐晓男, 马启明, 杜栓平. 波束空间能量约束的稳健自适应波束形成[J].声学学报, 2013, 38(3): 258-261.
Xu Xiao-nan, Ma Qi-ming, and Du Shuan-ping. Robust adaptive beamforming based on beam space power constraint[J]., 2013, 38(3): 258-261.
[18] 范展, 梁国龙, 王逸林. 一种零陷展宽鲁棒自适应波束形成算法[J].电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(11): 2764-2770.
Fan Zhan, Liang Guo-long, and Wang Yi-lin. Robust adaptive beamforming with null widening[J].&, 2013, 35(11): 2764-2770.
黄 聪: 男,1988年生,博士生,研究方向为水下阵列信号处理.
孙大军: 男,1972年生,教授,研究方向为水下信道与声呐环境、水下目标探测与定位.
张殿伦: 男,1967年生,教授,研究方向为水声定位与导航.
滕婷婷: 女,1982年生,讲师,研究方向为水下目标定位成像.
Wideband Two-dimensional Imaging with Arc Array Based on Second-order Cone Programming under Strong Coherent Interference
Huang Cong Sun Da-jun Zhang Dian-lun Teng Ting-ting
(,,150001,)(,,150001,)
To solve the problem that in two-dimensional imaging the target under water is easily hidden by the strong coherent interference, and high side lobe of arc array beam pattern causes more false alarm, an optimized two-dimensional imaging method based on second-order cone programming is proposed. Not only the strong coherent interference is suppressed, but also the side lobe is controlled well with the method. The issue that the sliding window in time domain leads to the difference between the steering vector and array manifold is analyzed, which causes the mismatch between the weights computed by the second-order cone programming and steering vector, and the failure to satisfy the side lobe control and null design requirement. To solve the issue, the method using the theoretical steering vector calculated by the sliding window in time domain instead of the array manifold to design the second-order cone programming weights is proposed, and the optimizations of the beam pattern and the arc array two-dimensional imaging are combined by the improved second-order cone programming weights .The validity of the proposed method is demonstrated by computer simulation and the pool experiment.
Sonar; Two-dimensional imaging; Second-order cone programming; Side lobe control; Interference suppression
U666.72; TN911.7
A
1009-5896(2014)11-2633-07
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01796
孙大军 sundajun@hrbeu.edu.cn
2013-11-14收到,2014-07-03改回
国家重点实验室基金(9140C200406110C2001),国家部委基金和国家863计划项目(2012AA090901-4)资助课题

