沉默信息调节因子1小干扰RNA抑制前列腺癌细胞DU145的迁移
王翠瑶,王忠利
辽宁医学院,辽宁锦州 121001 1生物化学与分子生物学教研室;2附属一院普外科
沉默信息调节因子1小干扰RNA抑制前列腺癌细胞DU145的迁移
王翠瑶1,王忠利2
辽宁医学院,辽宁锦州 1210011生物化学与分子生物学教研室;2附属一院普外科
目的观察沉默信息调节因子1(silent information regulator 1,SIRT1)小干扰RNA(siRNA)对前列腺癌DU145细胞迁移和基质金属蛋白酶中MMP2和MMP9表达变化的影响。方法体外培养DU145细胞,实验分Scramble siRNA组和SIRT1 siRNA组;利用脂质体介导转染技术转染前列腺癌DU145细胞,Western blot方法检测DU145细胞中SIRT1的干涉效能;划痕实验、平板克隆实验和Transwell迁移实验研究SIRT1对其体外迁移运动能力的影响;Western blot方法检测DU145细胞中MMP2和MMP9的蛋白表达。结果与Scramble siRNA组比较,SIRT1 siRNA组SIRT1的蛋白表达水平降低,明显抑制DU145细胞的迁移,降低MMP2和MMP9蛋白。结论下调SIRT1的表达可以抑制前列腺癌细胞DU145的迁移,其机制可能与改变基质金属蛋白酶中MMP2和MMP9的表达相关。
沉默信息调节因子1;siRNA;前列腺癌;DU145
2 细胞培养 人前列腺癌细胞DU145购自上海生命科学院细胞和生物化学研究所,生长于含10%已灭活胎牛血清的DMEM培养基中(含100 U/ml青霉素和50 U/ml链霉素),37℃、5% CO2饱和湿度的温箱中培养,每两天换液1次,0.25%胰蛋白酶消化传代。
3 SIRT1小干扰RNA(small interfering RNA,siRNA)的合成和转染 针对人SIRT1(GenBank No.NM_012 238)的RNAi靶点序列:正义链5'-GAAGUUGACCU CCUCAUUGUdTdT-3',反义链5'-ACAAUGAGGAG GUCAACUUCdTdT-3',由上海吉玛公司纯化合成[6]。DU145细胞接种于6孔细胞培养板中,细胞转染按照Invitrogen公司的Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂说明书进行。实验分Scramble siRNA组和SIRT1 siRNA组。20 μmol/L Scramble siRNA或 SIRT1 siRNA转染细胞48 h后收集细胞进行后续实验。
4 划痕试验 将生长至融合度达90%的DU145细胞,用黄色枪头进行划痕;PBS清洗3次;利用倒置显微镜标尺,测量划痕宽度,摄像纪录;细胞转染后不同时间点监测划痕宽度变化,并照相。
5 平板克隆形成实验 取对数生长期的细胞,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化并吹打成单个细胞,将细胞悬液作梯度倍数稀释,以适当的细胞密度接种于培养皿中。静置培养10 d左右,培养皿中出现肉眼可见的克隆时,终止培养。弃去上清液,用PBS小心浸洗2次。加纯甲醇或1∶3醋酸/甲醇5 ml,固定15 min。然后去固定液,加适量Giemsa应用染色液染10 ~ 30 min,然后缓慢洗去染色液,空气干燥。将平皿倒置并叠加一张带网格的透明胶片,用肉眼直接计数克隆,或在显微镜(低倍镜)计数>10个细胞的克隆数。最后计算克隆形成率。
6 Transwell实验 对数生长期细胞撤血清饥饿12 ~24 h,细胞转染后调整细胞浓度,收集消化后细胞,用无菌PBS洗2遍,无血清培养基悬浮后调整细胞密度至6×105/ml。取细胞悬液100 μl加入Transwell小室(24孔板),下室一般加入500 μl含胎牛血清的DMEM培养基培养细胞,常规培养24 h后用0.1%结晶紫染色,PBS洗去浮色,摄像记录。33%醋酸脱色,将结晶紫完全洗脱,在酶标仪上用波长595 nm测其OD值。
7 Western blot方法检测SIRT1、MMP2和MMP9的蛋白表达 蛋白裂解液提取收集细胞的总蛋白,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,加入5×SDS样品缓冲液煮沸5 min,离心后上样,10% SDS-PAGE电泳分离,然后将蛋白转至硝酸纤维素膜上,用含5%脱脂奶粉的TBS(pH 7.4)封闭滤膜,再分别与SIRT1、MMP2和MMP9抗体(稀释比为1∶1 000)及β-actin抗体(稀释比为1∶1 000) 4℃温育过夜。TTBS洗膜3次,HRP偶联的IgG作为二抗(稀释比为1∶5 000)室温温育2 h,重复洗膜3次,ECL发光法显色。
8 统计学分析 应用Graphpad prism 5统计软件进行数据统计与分析,各组数据以±s表示,多样本均数检验采用方差分析。P<0.01为差异有统计学意义。
结果
1 转染SIRT1 siRNA能够干涉SIRT1基因在DU145细胞中的表达 转染SIRT1 siRNA或Scramble siRNA入DU145细胞后,与Scramble siRNA组比较,SIRT1 siRNA明显抑制内源性SIRT1的蛋白表达。见图1。

图 1 Western blot检测DU145细胞转染SIRT1 siRNA后SIRT1蛋白表达水平Fig.1 Expression levels of SIRT1 protein in DU145 cells transfected with SIRT1 siRNA Lane 1: Mock group; Lane 2: scramble siRNA group; Lane 3: SIRT1 siRNA group
2 干涉SIRT1基因表达能够抑制DU145细胞迁移转染48 h后,转染SIRT1 siRNA组细胞迁移的数量较Scramble siRNA组小,距离相对较远。两组细胞48 h愈合率分别为14.80%±1.9%和98.50%± 3.8%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01,图2)。说明转染SIRT1 siRNA能够显著抑制DU145细胞迁移。
3 干涉SIRT1基因表达能够抑制DU145细胞克隆形成 克隆平板实验显示,与转染Scramble siRNA组相比,SIRT1 siRNA细胞转染组克隆形成数目减少,两组细胞克隆形成数分别为234%±4.9%和88%±3.8%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。见图3。
4 干涉SIRT1基因表达能够抑制DU145细胞侵袭

图 2 划痕实验检测转染SIRT1 siRNA后DU145细胞的迁移情况Fig.2 Effect of SIRT1 siRNA on DU145 cell migration determined by wound healing assays
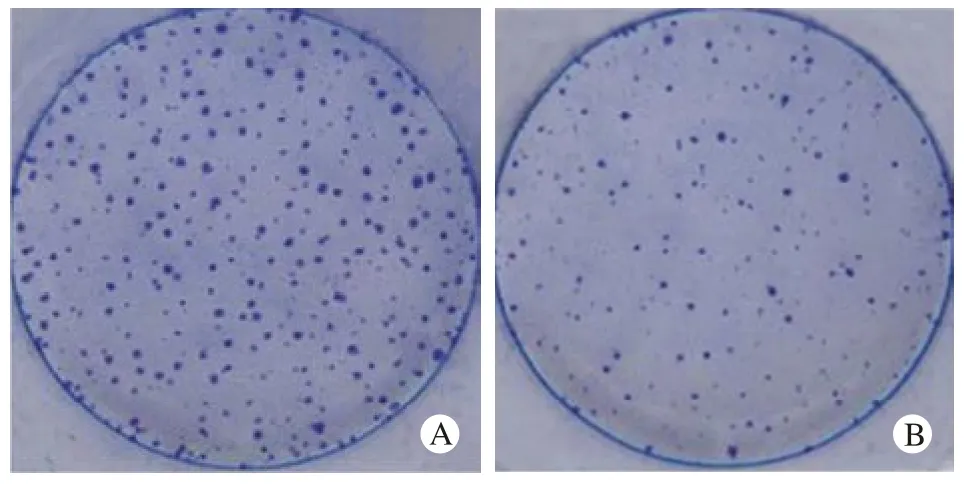
图 3 平板克隆实验检测转染SIRT1 siRNA DU145细胞的迁移情况Fig.3 Effect of SIRT1 siRNA on DU145 cell migration determined by colony formation assays A: scramble siRNA group; B: SIRT1 siRNA group

图 4 Transwell实验检测转染SIRT1 siRNA DU145细胞的迁移情况Fig.4 Effect of SIRT1 siRNA on DU145 cell migration determined by transwell assays A: scramble siRNA group; B: SIRT1 siRNA group
Transwell实验显示,SIRT1 siRNA转染组细胞较Scramble siRNA转染组细胞的转移能力明显下降,这两组细胞48 h穿过微孔膜的细胞数分别为55.62±7.57、231.67±15.08,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。见图4。
5 干涉SIRT1的表达能够抑制DU145细胞中MMP2和MMP9基因的表达 Western blot检测转染SIRT1 siRNA对DU145细胞中细胞转移相关蛋白MMP2和MMP9表达的影响。结果显示,与Scramble siRNA组相比,SIRT1 siRNA组MMP2和MMP9蛋白的表达明显降低。见图5。

图 5 Western blot检测DU145细胞转染SIRT1 siRNA后MMP2和 MMP9蛋白表达Fig.5 MMP2 and MMP9 protein expression levels in DU145 cells transfected with SIRT1 siRNA detected by Western blot 1: scramble siRNA group; 2: SIRT1 siRNA group
讨论
研究已经表明,许多基因可以使肿瘤细胞的运动迁移能力发生改变,如MYC、RACK1等说明肿瘤细胞的运动迁移能力是影响肿瘤转移的重要因素[10-12]。为了研究SIRT1在前列腺癌中的作用,我们使用RNA干涉的方法下调SIRT1的表达,观察SIRT1对前列腺癌细胞DU145细胞迁移的影响。
划痕实验结果表明,SIRT1 siRNA组发生细胞运动愈合划痕的比例明显低于对照组,平板克隆形成实验也证实,特异性抑制SIRT1表达能够显著阻碍DU145迁移。Transwell迁移试验通过其小室内的微孔膜,检测细胞变形后运动迁移的能力,是肿瘤细胞转移能力的重要检测手段。我们通过Transwell迁移试验验证了SIRT1 siRNA组细胞穿过微孔膜发生迁移的细胞数量明显少于对照组,同划痕愈合实验结果相一致。通过肿瘤细胞细胞外基质迁移和入侵是肿瘤转移发生的关键一步,各种癌症已观察到其细胞外基质成分的改变[13-15]。一些分子如基质金属蛋白酶中的MMP2和MMP9可以降解细胞外基质的能力,促使上皮组织基底膜的破坏,使肿瘤细胞透过破损的基底膜发生转移,参与调节肿瘤的侵袭过程[16-18]。基质金属蛋白酶参与细胞表面受体的裂解和细胞凋亡配体的释放(如FAS配体),进而调节肿瘤细胞的浸润和转移[13]。我们对两组细胞中MMP2和MMP9蛋白表达的检测发现,SIRT1 siRNA组细胞中MMP2和MMP9蛋白表达较Scramble siRNA组显著下调。这提示SIRT1可能通过调节MMP2和MMP9蛋白的表达水平,影响前列腺癌DU145细胞的侵袭能力。
总之,本实验表明特异性干涉SIRT1的表达能够抑制前列腺癌细胞DU145的细胞迁移,可能与下调DU145细胞中MMP-2和MMP-9的蛋白表达有关,其具体机制还需进一步研究。我们后续的工作还会对SIRT1引起肿瘤侵袭、转移的分子机制进行深入的研究,为SIRT1可能作为人类前列腺癌一个潜在的治疗靶点提供实验依据。
1 Chen J, Li HM, Zhang XN, et al. Dioscin-induced apoptosis of human LNCaP prostate carcinoma cells through activation of caspase-3 and modulation of Bcl-2 protein family[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2014, 34(1):125-130.
2 Goyal J, Antonarakis ES. Clinical Evaluation of Abiraterone in the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer[J]. Clin Med Insights Urol, 2013, 2013, (7):1-14.
3 胡小龙,张春阳,于立春,等.抑癌PTEN基因联合p53基因转染对前列腺癌PC-3m细胞凋亡的影响[J].解放军医学院学报,2014,35(4):369-373.
4 Chen P, Huang Y, Zhang B, et al. EphA2 enhances the proliferation and invasion ability of LNCaP prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncol Lett,2014, 8(1): 41-46.
5 Ye L, Sanders AJ, Sun PH, et al. Capillary morphogenesis gene 2 regulates adhesion and invasiveness of prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2014, 7(6): 2149-2153.
6 Yuan H, Su L, Chen WY. The emerging and diverse roles of sirtuins in cancer: a clinical perspective[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2013, 6:1399-1416.
7 Li Y, Wong K, Giles A, et al. Hepatic SIRT1 attenuates hepatic steatosis and controls energy balance in mice by inducing fibroblast growth factor 21[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(2): 539-549.
8 Hwang BJ, Madabushi A, Jin J, et al. Histone/protein deacetylase SIRT1 is an anticancer therapeutic target[J]. Am J Cancer Res,2014, 4(3): 211-221.
9 Byles V, Zhu L, Lovaas JD, et al. SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell migration and metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(43):4619-4629.
10 Civenni G, Malek A, Albino D, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of Myc transcription inhibits stem-like cell maintenance and tumorigenicity in prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(22):6816-6827.
11 Li X, Liu X, Xu W, et al. c-MYC-regulated miR-23a/24-2/27a cluster promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by targeting sprouty2[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(25):18121-18133.
12 Li J, Guo Y, Feng X, et al. Receptor for activated C kinase 1(RACK1): a regulator for migration and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2012, 138(4):563-571.
13 Hadler-Olsen E, Winberg JO, Uhlin-Hansen L. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: their value as diagnostic and prognostic markers and therapeutic targets[J]. Tumour Biol, 2013, 34(4):2041-2051.
14 Li Y, Tan BB, Zhao Q, et al. ZNF139 promotes tumor metastasis by increasing migration and invasion in human gastric cancer cells[J]. Neoplasma, 2014, 61(3): 291-298.
15 Wang HL, Zhou PY, Zhang Y, et al. Relationships between abnormal MMP2 expression and prognosis in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2014, 29(4):166-172.
16 DI Carlo A. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and -2 in sera and urine of patients with renal carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2014, 7(3):621-626.
17 Stetler-Stevenson WG, Gavil NV. Normalization of the tumor microenvironment: evidence for tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 as a cancer therapeutic[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2014, 55(1): 13-19.
18 Wang F, Chang Z, Fan Q, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the proliferation and migration of human ovarian carcinoma cells by modulating p38 kinase and matrix metalloproteinase-2[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 9(3): 1085-1089.
Effects of small interfering RNA of SIRT1 on cell migration in prostate cancer DU145 cells
WANG Cui-yao1, WANG Zhong-li2
1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology;2Department of Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China
WANG Zhong-li. Email: wzlaily@126.com
ObjectiveTo observe the effects of double-stranded small interfering RNA (siRNA) of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) on the cell migration and the expression levels of MMP2 and MMP9 of matrix metalloproteinases in prostate cancer DU145 cells.MethodsDU145 cells were cultured in vitro and divided into scramble siRNA group and SIRT1 siRNA group randomly. The eff i ciency of SIRT1 siRNA was examined by Western blot, and the cell migration of DU145 cells was assayed by wound healing, colony formation and transwell migration experiment. The protein expression of MMP2 and MMP9 were determined by Western blot.ResultsCompared with scramble siRNA group, the protein expression of SIRT1 in SIRT1 siRNA group decreased, and the colony formation and cell migration of DU145 cells were restrained significantly and the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 also decreased.ConclusionThe cell migration of DU145 cells can be inhibited by down-regulating the expression of SIRT1, and its mechanism may relate to the changes of the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 in matrix metalloproteinases.
silent information regulator 1; siRNA; prostate cancer; DU145
R 581.3
A
2095-5227(2014)12-1253-04
10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2014.12.021
时间:2014-08-12 08:45
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3275.R.20140812.0845.002.html
前列腺在体内位置较表浅,基因治疗药物可通过安全的腔内方式直接注射到病灶,加强治疗效果,因此,人们开始尝试一些包括基因治疗在内的新方法治疗前列腺癌[1-3]。恶性细胞的特性是由许多调节重要的细胞功能包括细胞增殖、迁移运动和侵袭转移等信号通路来决定的,细胞的增殖和迁移运动是侵袭和转移的重要步骤[4-5]。沉默信息调节因子1(silent mating type information regulator 1,SIRT1)隶属于Sirtuin家族,是Ⅲ类去乙酰化酶中的重要一员,通过去乙酰化众多组蛋白和非组蛋白,参与调控体内众多病理生理过程[6-7]。其大多数的功能是通过对基因表达过程中起关键作用的调节蛋白的特定去乙酰化而实现的,SIRT1的作用靶点包括转录因子以及代谢调节中的辅酶因子[7-8]。SIRT1通过和上皮-间质转换(epithelialto-mesenchymal transition,EMT)相关的转录因子作用诱导EMT,进而增加前列腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移,但具体的机制还不是十分清楚[9]。本研究通过在前列腺癌DU145细胞株中特异性干涉SIRT1,探讨下调SIRT1的表达对人前列腺癌DU145细胞株转移的影响,为使SIRT1作为人类前列腺癌一个潜在的基因治疗靶点提供实验依据。
材料和方法
1 主要试剂与仪器 DMEM培养液(Corning公司);SIRT1 siRNA和Scrambled siRNA(上海吉玛公司合成);Lipofectamine 2000(Invitrogen);SIRT1 (鼠单克隆抗体,Merck Millipore公司)、MMP2和MMP9(兔多克隆抗体,Cell Signaling Technology公司);HRP标记的山羊抗兔,抗鼠IgG(北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司);BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(北京碧云天生物技术公司)。BB16UV CO2培养箱(Heraeus);凝胶自动成像仪GDS8000、水浴式电转印槽、电泳仪(Bio-Rad,美国)。
2014-06-03
王翠瑶,女,学士,高级实验师。研究方向:肿瘤分子生物学。Email: 1140379451@qq.com
王忠利,男,硕士,主治医生。Email: wzlaily@126.com

