激光与线性递增等离子体作用的非线性过程研究
陶志鹏,陶向阳
(江西师范大学物理与通信电子学院,江西 南昌330022)
0 引言
随着小型激光器(利用啁啾脉冲放大技术[1,2]可以产生超短强激光)的快速发展,激光在各种密度分布的等离子体中的应用受到广泛关注[3,4]。比如,激光等离子体加速场、单能电子的产生、X射线、谐波的产生和惯性约束聚变的快点火装置[5~7]。在等离子体中,如果激光频率超过电子振动的本征频率,那么电子就会被排出激光场[8]。因为聚焦激光束会对电子施加一个径向有质动力将电子向外排出,这就在中间产生了一个低密度区域,该区域会沿径向发生聚焦[9]。
在冷等离子体中,相对论振动增加电子有效质量和激光有质动力排出电子[10]都会使等离子体折射率增加,从而使等离子体介质变成一个正透镜[11~16]。其中,相对论效应引起自聚焦是因为介电常数是激光强度的增函数。而MAX[17]和Hafizi[18]已经研究了强激光有质动力效应。
本文以高斯型激光脉冲为例,讨论激光在线性分布的等离子体中传输时自聚焦的产生机制。由于高斯型激光脉冲受自身衍射效应的限制,激光仅能保持聚焦传输一个瑞利长度ZR的距离,ZR=ωr20/2c,r0是焦斑半径。为了克服衍射效应和引导激光束长距离传输,提出一个线性递增等离子体密度坡道,并研究了它对激光自聚焦的影响。
1 电子密度模型
在这里,用高强度激光与固体靶相互作用来产生低密度等离子体。该低密度无磁化等离子体存在沿Z方向的密度递增坡道,在柱坐标下研究高斯光束在该等离子体中的传播。电子矢势E的振幅可以表示为:

其中,A2|z=0=exp(-r2/)是z=0时的初始强度分布,k(z)=(ω/c)εr0(z)1/2。
激光波前的有质动力存在轴向和径向分量。径向有质动力推动电子沿径向向外排出,并产生一个径向空间电场= -∇φB,由泊松方程∇2φB=4πe(ne-n0),得到电子密度表达式


依照Tripathi[19]给出的方法,可以假设一个准稳态,即φp=-φB,由方程⑶代入式⑵,得到
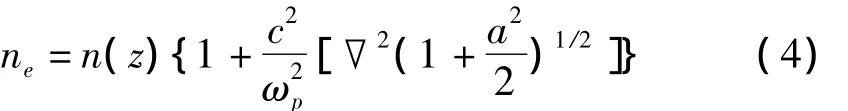
此时,假设振幅a为高斯分布

f是束腰宽度,r0是激光半宽,a0是轴向振幅,r是柱坐标系中的径向坐标,则
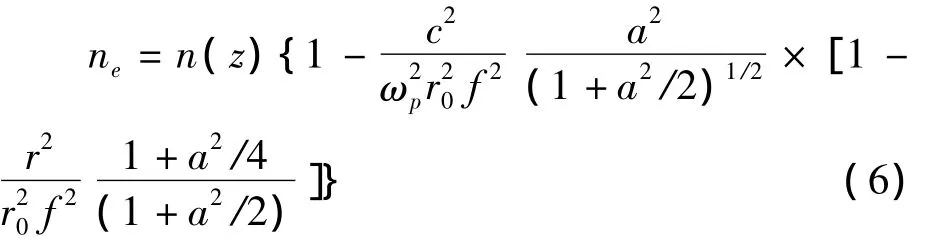
介电常数的表达式[20]为


2 光斑尺寸演化方程
从麦克斯韦方程出发,激光的波动方程
其中,A是激光矢势,在不均匀等离子体中,由WKB近似得到

其中,a(r,z)是慢变包络。把式(12)代入式(11)得到

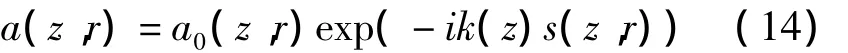
包络a(z,r)分解成实部振幅和虚部相位,并且a0和s都是z,r的函数。将式(14)代入式(13),并分离实部和虚部,得到
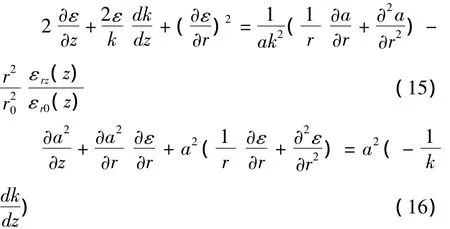
在近轴近似下,振幅a0(z,r)可以写成类似式(5)的形式,并引入光程函数
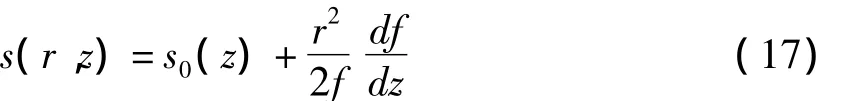
其中,s0(z)是相移,研究激光强度比相移更有意义,这里对s0(z)不做进一步讨论。把式(5)、式(14)和式(17)代入式(15),对比得到方程中r2的系数,有

其中,ξ=z/Rd0,Rd0=ω/c。边界条件:
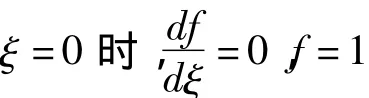
式(18)右边第1项是衍射项,第2项是由于等离子体在轴向不均匀引起的,最后一项是相对论自聚焦引起的非线性项。
3 数值分析与讨论
本文中,激光在非均匀线性递增分布的等离子体中发生自聚焦的重点在于等离子体电子密度分布的选取[26]。在此,假设线性等离子体介质的密度表示为:

这是一维的线性等离子体密度坡道分布,L是密度尺度。这里采用的强度为I=1.21×1018W/cm2,波长λ=1.06 μm的高斯激光。图1给出了3种不同密度分布的等离子体,初始密度n0=0.9×1021cm-3,L=3时,密度分布斜率最大,其次是L=6和L=9,并将这2种分布的束腰宽度研究结果与L=3时作为比较。

图1 不同密度尺度下的密度分布
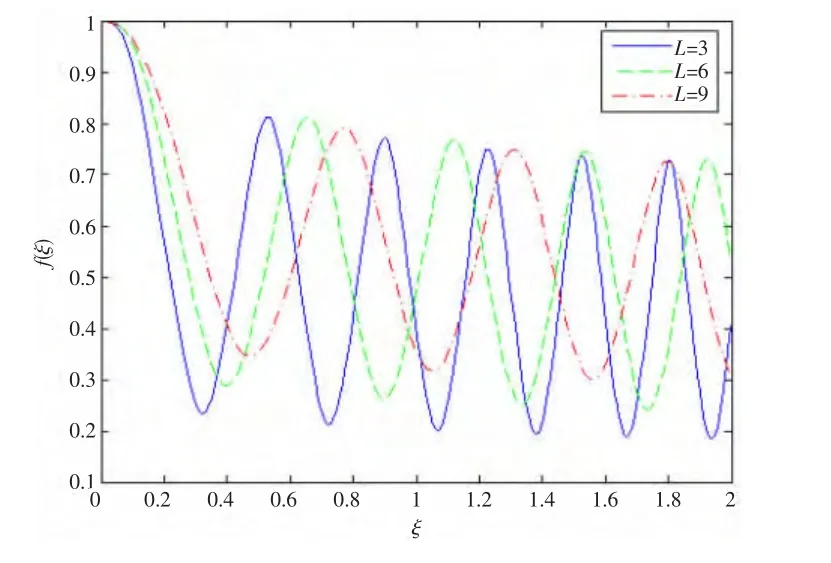
图2 不同密度尺度下束腰宽度f(ξ)的变化情况
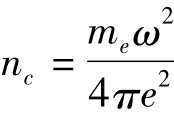

图3 均匀分布与线性递增分布的束腰宽度变化情况
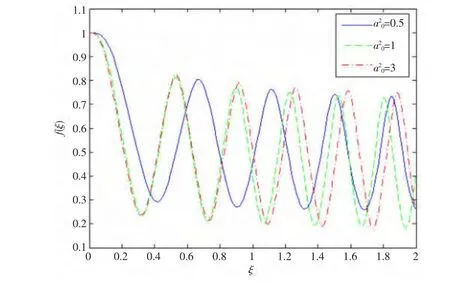
图4 不同激光强度下的束腰宽度变化
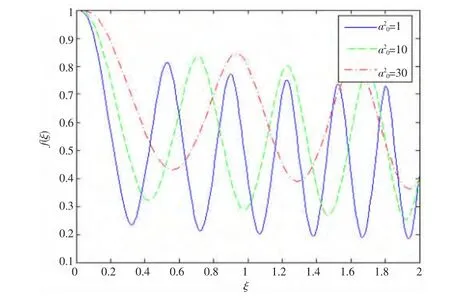
图5 激光强度对束腰宽度的影响
4 结论
利用四阶Runge-Kutta法进行数值求解,研究了密度梯度尺度、等离子体初始密度和激光强度对强激光与密度线性递增等离子体的自聚焦效应的影响。研究表明,密度梯度尺度越小,束腰宽度受相对论自聚焦的影响越大,又由于等离子体密度的线性递增分布,峰值会逐渐减小。密度线性递增,相对论自聚焦的效果越明显,之后束腰宽度峰值会由于不均匀密度项的影响而逐渐减小。高斯激光在线性递增等离子体中产生自聚焦还受到自身衍射作用的影响,随着激光强度的增大,衍射作用越明显,越不利于自聚焦的产生。
[1] Mourou G,Umstadter D.Development and applications of compact high-intensity lasers[J].Phys.Fluids,1992,4(7):2315.
[2] Perry M D,Mourou G.Terawatt to Petawatt Subpicosecond Lasers[J].Science,1994,264:917-924.
[3] Sadighi-Bonabi R,Habibi M,Yazdani E.Improving the relativistic self-focusing of intense laser beam in plasma using density transition[J].Phys.Plasmas,2009,16(8):83105.
[4] Gupta D N,Hur M S,Hwang I,et al.Additional focusing of a high-intensity laser beam in a plasma with a density ramp and a magnetic field[J].Appl.Phys.Lett,2007,91(8):81505.
[5] Faure J,Malka V,Marques J R,et al.Interaction of an ultra-intense laser pulse with a nonuniform preformed plasma[J].Phys.Plasmas,2000,7(7):3009.
[6] Yazdani E,Cang Y,Sadighi-Bonabi R,et al.Ion and Laser Beams as tools for High Energy Density Physics[J].Laser Part.Beams,2009,27(1):1-2.
[7] Sadighi-Bonabi R,Navid H A,Zobdeh P.Observation of quasi mono-energetic electron bunches in the new ellipsoid cavity model[J].Laser Part.Beams,2009,27 (2):223-231.
[8] Askaryan G A.Effect of the gradient of a strong electromagnetic beam on electrons and atoms[J].Sov Phys.Jetp,1962,15:1088-1090.
[9] Hora H.Self-focusing of laser beams in a plasma by ponderomotive forces[J].Z.Phys,1969,226(2):156-159.
[10]Chen X L,Sudan R N.Necessary and sufficient conditions for self-focusing of short ultraintense laser pulse in underdense plasma[J].Phys.Rev.Lett,1993,70 (14):2082-2085.
[11]Hora H.Theory of relativistic self-focusing of laser radiation in plasmas[J].J.Opt.Soc.Am,1975,65(8): 882-886.
[12]Hora H.Laser Plasmas and Nuclear Energy[M].Plenum,New York,1975:47.
[13]Kaur S,Sharma A K.Self focusing of a laser pulse in plasma with periodic density ripple[J].Laser Part.Beams,2009,27(2):193-199.
[14]Hora H.The transient electrodynamic forces at laserpl-asma interaction[J].Phys.Fluids,1985,28(12): 3705-3706.
[15] Faure J,Malka V,Marquès J R,et al.Effects of pulse duration on self-focusing of ultra-short lasers in underdense plasmas[J].Phys.Plasmas,2002,9(3): 756-759.
[16] Pukhov A.Strong field interaction of laser radiation[J].Rep.Prog.Phys,2003,66(1):47.
[17] Max C E.Strong self-focusing due to the ponderomotive force in plasmas[J].Phys.Fluids,1976,19(1): 74.
[18] Hafizi B,Ting A,Sprangle P,et al.Relativistic focusing and ponderomotive channeling of intense laser beams[J].Phys.Rev.E,2000,62:4120.
[19] Tripathi V K,Taguchi T,Liu C S.Plasma channel charging by an intense short pulse laser and ion Coulomb explosion[J].Phys.Plasmas,2005,12(4): 43106.
[20] Habibi M,Ghamari F.Non-stationary self-focusing of intense laser beam in plasma using ramp density profile[J].Phys.Plasmas,2011,18(10):3107.
[21] Sun G,Ott E,Lee Y C,et al.Self-focusing of short intense pulses in plasmas[J].Phys.Fluids,1987,30 (2):526-532.
[22] Sprangle P,Tang C M,Esarey E.Relativistic Self-Focusing of Short-Pulse Radiation Beams in Plasmas[J].IEEE Trans.Plasma Sci,1987,15(2):145-153.
[23] Prakash G,Sharma A,Verma M P,et al.Focusing of an intense Gaussian laser beam in a radially inhomogeneous medium[J].J.Opt.Soc.Am.B,2005,22 (6):1268-1275.
[24] Sadighi-Bonabi R,Habibi M,Yazdani E.Improving the relativistic self-focusing of intense laser beam in plasma using density transition[J].Phys.Plasmas,2009,16(8):3105.
[25] Akhmanov S A,Sukhorukov A P,Khokhlov R V.Selffocusing and diffarction of light in a nonlinear medium[J].Sov.Phys.Usp,1968,10(5):609.
[26] 王伟民,郑春阳.超强短脉冲激光在不同密度分布等离子体中的自聚焦[J].物理学报,2006,55(1): 310-320.
[27] Kelley P L.Self-focusing of optical beams[J].Phys.Rev.Lett,1965,15(26):1005-1008.

