人D-二聚体的制备及其冻干性质的分析
武建伟 才蕾 王继华 唐时幸
(广州万孚生物技术股份有限公司 自检型快速诊断国家地方联合工程实验室,广州 510663)
人D-二聚体的制备及其冻干性质的分析
武建伟 才蕾 王继华 唐时幸
(广州万孚生物技术股份有限公司 自检型快速诊断国家地方联合工程实验室,广州 510663)
以人源纤维蛋白原为原材料制备D-二聚体,将其制成冻干品并分析其冻干性质。使用凝血酶、Factor XIIIa酶解纤维蛋白原,获得交联纤维蛋白。经纤溶酶降解交联纤维蛋白,生成纤维蛋白降解产物。超滤除去纤维蛋白降解产物中的小分子物质,可获得较高纯度的D-二聚体。通过筛选和优化冻干方案,将D-二聚体制备成冻干品。经检测可知,D-二聚体冻干品可在37℃稳定保存12 d;复溶后在25℃稳定保存8 d;复溶后在4℃稳定保存30 d;复溶时,常用复溶溶剂对其复溶后的活性检测无明显影响。
纤维蛋白 纤维蛋白原 D-二聚体 血栓 冻干品
D-二聚体(D-dimer)是交联纤维蛋白发生纤溶的特异性标志物,由纤维蛋白原逐步水解而成[1]。纤维蛋白原是一种具有凝血功能的血浆球蛋白,主要作为凝血因子I参与体内凝血过程[2]。经凝血酶、Factor XIIIa作用,纤维蛋白原被水解成交联纤维蛋白;纤溶酶可使纤维蛋白(原)D-E区互补结构裂解,降解纤维蛋白原和纤维蛋白单体生成纤维蛋白原降解产物,以及降解交联纤维蛋白生成纤维蛋白降解产物,纤维蛋白降解产物中含有大量的D-dimer[3,4]。D-dimer分子量约为180 kD[5],在健康人体内含量极少,一般认定0.5 mg/L(FEU)为cut-off值[6]。另有研究表明,D-dimer的cut-off值与年龄呈正相关,年龄愈大,cut-off值愈高[7]。
机体内凝血和继发性纤溶系统的激活,均可使D-dimer水平升高[8]。临床诊断中,D-dimer检测常用于:静脉血栓栓塞(Venous thrombus embolism,VTE)、深静脉血栓(Deep vein thrombosis,DVT)和肺血栓(Pulmonary embolism,PE)的排除,以及弥漫性血管内凝血(Disseminated intravascular coagulation,DIC)的诊断、溶栓治疗的监测[9-12];
急性心肌梗塞(Acute myocardial infarction,AMI)、冠状动脉缺血(Coronary ischemia)、脑梗塞(Cerebral infarction)[12-14]的诊断和预后判断;恶性肿瘤,如肺癌(Lung cancer)、卵巢癌、结肠直肠癌(Colorectal cancer)、乳腺癌(Breast cancer)[15-18],以及肝脏疾病[19]、糖尿病[20]、妊娠高血压综合征高凝状态[21]等的诊断和预后判断。
真空冷冻干燥(Vacuum Freeze-drying),简称“冻干”,是在适宜的真空度下将物质中的水分析出的技术,已广泛应用于生物制品、医药、食品、花卉产业、标本制作和古书籍保护等领域[22]。生物制品通过真空冷冻干燥制成冻干品后,具有稳定、易复溶等优势,便于保存和运输。商品化的人源D-dimer蛋白多以液体形式保存于血清中,对保存和运输条件要求苛刻。以健康新生牛血清作为冻干基质对D-dimer蛋白进行冻干,制备的D-dimer冻干品具有良好的稳定性和实用性。
近年来,D-dimer研究多集中于生理意义的剖析和医学价值的探讨,本研究着重介绍人源D-dimer的制备及其冻干性质的分析。通过逐步酶解和真空冷冻干燥获得稳定高效的D-dimer冻干品,旨在为人源蛋白的制备和保存提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
人源纤维蛋白原、人源凝血酶、人源纤溶酶、抑肽酶、Tris-base购自Sigma公司;人源Factor XIIIa购自AssayPro公司;0.22 μm滤器、Amicon Ultra-15(MWCO:100KDa)购自Millipore公司;健康新生牛血清、PageRuler Unstained High Range Protein Ladder购自Thermo Scientific公司;D-二聚体(D-dimer)定量检测试剂盒(免疫层析法)为广州万孚生物技术股份有限公司(Wondfo)自主研发;其它试剂均为国产分析纯。
蛋白电泳仪、Bio-Rad Gel Doc XR+ 凝胶成像系统购自Bio-Rad公司;医用冷藏箱购自中科美菱公司;AutoRep E 连续分配器购自RAININ公司;CHRIST ALPHA 1-2/ LD PLUS冻干机购自Martin Christ公司;-86℃立式医用低温保存箱购自SANYO公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 D-dimer的制备
1.2.1.1 纤维蛋白原的酶解 称取适量纤维蛋白原至离心管中,溶入TBS(20 mmol/L Tris-HCl,0.15 mol/L NaCl,2 mmol/L KCl,pH7.4)至终浓度为5 mg/mL,加入凝血酶(终浓度1 U/mL)、Factor XIIIa(终浓度5 μg/mL),37℃水浴4-6 h,即得到白色胶状交联纤维蛋白。
1.2.1.2 交联纤维蛋白的洗涤 取出交联纤维蛋白至50 mL离心管中,使用TBS颠倒洗涤数次,放于37℃恒温摇床中振荡洗涤约2-3 h。
1.2.1.3 交联纤维蛋白的酶解 取出洗涤完毕的交联纤维蛋白至干净的离心管,加入TBS(交联纤维蛋白湿重终浓度200 mg/mL)、纤溶酶(终浓度5 mU/mL),37℃水浴至溶液中不再有絮状交联纤维蛋白。向反应体系中加入抑肽酶(终浓度1 μg/mL),充分混匀。
1.2.1.4 D-dimer的超滤 使用0.22 μm无菌滤器将新制的D-dimer溶液过滤至超滤管(MWCO:100KDa)中,超滤浓缩(2 000×g,20 min,4℃)。向浓缩液中加入适量TBS,再次进行超滤浓缩(2 000×g,20 min,4℃),分装制得的D-dimer浓缩液,保存于-80℃冰箱中。
1.2.2 D-dimer冻干性质的分析
1.2.2.1 D-dimer的活性检测与冻干方案的筛选 使用D-二聚体(D-dimer)定量检测试剂盒(免疫层析法,线性范围:0.1-10 mg/L)检测制备的D-dimer活性。为提高D-dimer稳定性,将其制成D-dimer冻干品。以3 mL棕色玻璃瓶为容器,每瓶加入500 μL D-dimer冻干工作液。通过调节真空冷冻干燥时的真空度及冻干时间、冻干稀释液组份及pH,对冻干方案进行筛选及优化。根据D-dimer冻干品的精密度和系列稳定性,选定最佳冻干方案。
1.2.2.2 D-dimer冻干品的稳定性分析 为验证D-dimer冻干品的稳定性,使用Wondfo D-二聚体(D-dimer)定量检测试剂盒监测D-dimer冻干品在37℃稳定性、复溶后4℃/25℃稳定性、不同溶剂复溶冻干品对其活性检测的影响等。
2 结果
2.1 D-dimer的制备和超滤
将纤维蛋白原酶解体系置于37℃水浴中,白色交联纤维蛋白迅速生成,反应体系完全呈胶状。酶解体系中的交联纤维蛋白在37℃水浴中逐渐萎缩,直至完全消失。新制的D-dimer溶液活性远超出D-二聚体(D-dimer)定量检测试剂盒的检测范围,需适度稀释后用于定量检测。经SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳和Bio-Rad Gel Doc XR+凝胶成像系统分析,交联纤维蛋白的降解产物中,D-dimer纯度约为60%;超滤后,小分子蛋白被大量除去,D-dimer纯度升高至90%(图1)。使用A280nm紫外吸收法检测D-dimer溶液浓度,发现D-dimer蛋白总量约为纤维蛋白原的一半,即制备得率约为50%。
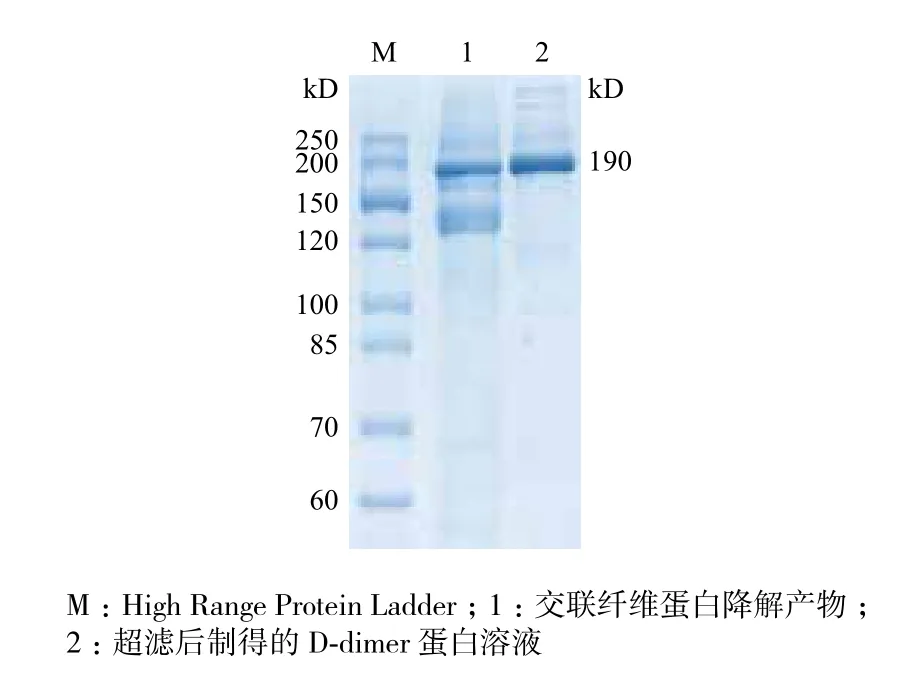
图1 D-dimer的SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳纯度分析
2.2 D-dimer的活性检测与冻干方案的筛选
经过多次摸索和验证,按照一定的比例将D-dimer蛋白溶液稀释成位于D-二聚体(D-dimer)定量检测试剂盒检测范围内的3个不同的浓度(高浓度H、中浓度M、低浓度L)。鉴于临床检测的D-dimer样品多以全血或血浆为基质,本研究拟以健康新生牛血清作为D-dimer蛋白的冻干保护剂。冻干前,使用冻干稀释液(50 mmol/L Tris-HCl,0.1 mol/L NaCl,0.5 mmol/L EDTA,pH8.0)调节新生牛血清比例(冻干稀释液组份及pH经多次正交试验筛选和优化而得,详细步骤略)。根据冻干品的系列稳定性检测结果,将冻干保护剂定为12%新生牛血清,真空冷冻干燥真空度:0.025 mbar(Main Drying)/0.012 mbar(Final Drying),冻干时间由冻干样品的总装液量而定。冻干后,从每个浓度的冻干品中随机取出10支进行检测。稀释后的D-dimer冻干品活性值均位于检测试剂的检测范围内,3个浓度冻干品的批内精密度(C.V)均小于15%(表1)。
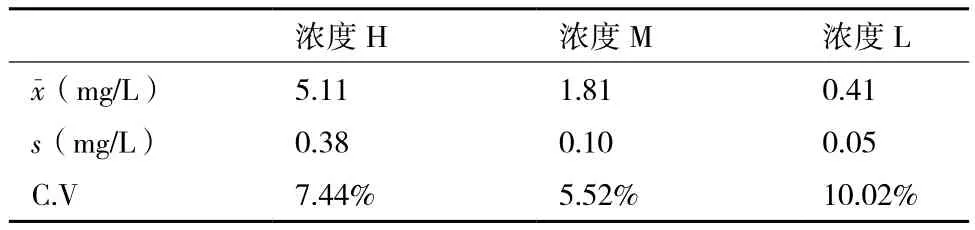
表1 Wondfo试剂检测D-dimer冻干品均值与精密度
2.3 D-dimer冻干性质的分析
随机选取D-dimer冻干品用于各项检测,参考区间由检测精密度时的均值而定,即:x-±25%。检测发现,D-dimer冻干品可在37℃稳定保存12 d(表2),复溶后在4℃稳定保存30 d(表3),复溶后在25℃稳定保存8 d(表4)。
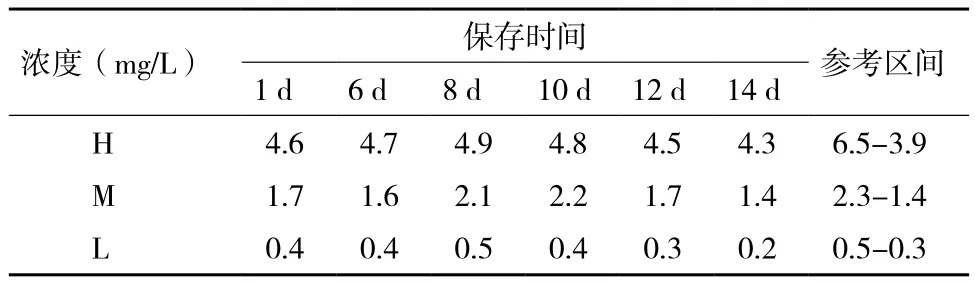
表2 D-dimer冻干品37℃稳定性
检测不同溶剂复溶冻干品对其活性检测的影响时,选用去离子水、三蒸水、生理盐水、瓶装矿泉水(农夫山泉)和自来水复溶冻干品。经检测,选用的5种溶剂复溶冻干品时对其活性检测均无明显影响(表5)。
3 讨论
继Ruckley等[23]于1970年发现血清FDP对肺栓塞具有重要的诊断价值之后,Gaffney在FDP中分离得到将近200 kD大小的“γ-γ dimers”,将其命名为 D-dimer,并预言“D-dimer检测可能会成为有用的诊断依据”[24-26]。经过多年的研究和临床验证,研究人员发现D-dimer分子量约为180 kD,等电点(pI)为4.9-5.3,在健康人体内的半衰期约为8 h[27],是交联纤维蛋白降解的特异性产物,对多项疾病的诊断具有重要的检测意义。由于D-dimer不存在疾病特异性,在临床诊断中,D-dimer以
其高度的敏感性和阴性预示能力时常用于筛查项目和辅助诊断。据世界卫生组织(World Health Organization,WHO)发布的《Global status report on noncommunicable diseases(2010)》报告称,心脑血管疾病已成为全球头号死因,每年死于心脑血管疾病的人数约占全球死亡人数的30%[28]。鉴于D-dimer可作为血栓形成性疾病诊断和溶栓药物疗效监测的特异性标志物,D-dimer检测对血栓导致的心脑血管疾病的及早诊断和治疗,便显得尤为重要。
目前,国内多采用进口D-dimer抗原进行相关研究或制备单克隆抗体。进口抗原纯度虽高,但价格昂贵,且多以液体形式保存,严重制约了D-dimer的研究及其运输和保存。本研究采用逐步酶解法和超滤即获得高纯度高活性的D-dimer蛋白,并通过真空冷冻干燥将其制成稳定的D-dimer冻干品。选用健康新生牛血清为冻干基质,冻干品复溶后几乎可作为天然D-dimer抗原使用。制备的D-dimer蛋白浓度约为5.6 mg/mL,使用Wondfo D-二聚体(D-dimer)定量检测试剂盒检测1 000倍稀释后的蛋白溶液冻干前的活性约为5.0 mg/L,冻干后的活性约为4.5-5.0 mg/L,检测时的活性收率和冻干时的活性收率均超过90%。
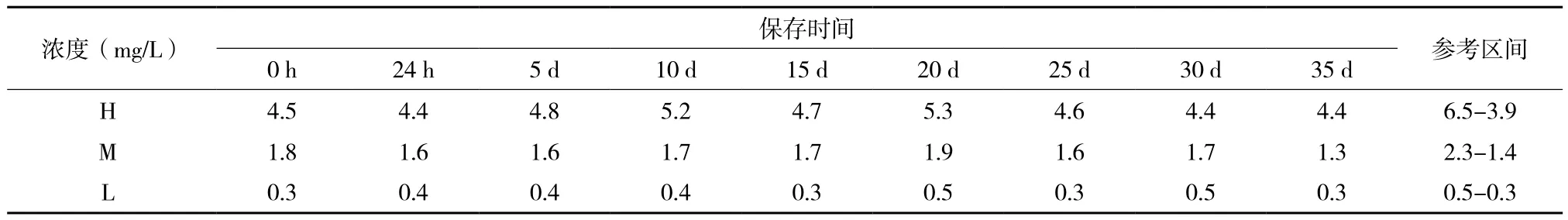
表3 D-dimer冻干品复溶后4℃稳定性
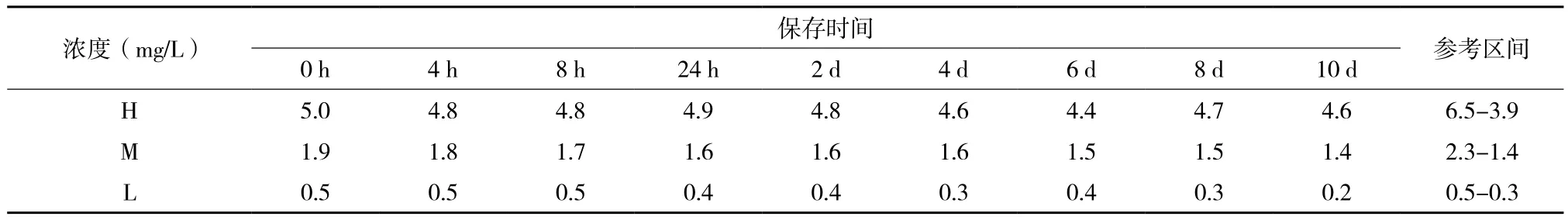
表4 D-dimer冻干品复溶后25℃稳定性
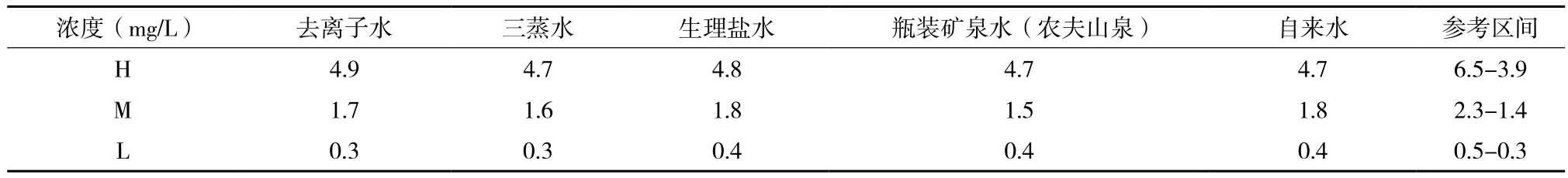
表5 不同溶剂复溶D-dimer冻干品对其活性检测的影响
笔者曾在D-dimer超滤浓缩前,使用HiPrep 16/60 Sephacryl S-300 HR(GE)对其进行多次纯化,纯化效率均不理想。D-dimer经HiPrep 16/60 Sephacryl S-300 HR纯化后,蛋白纯度未能明显提高,蛋白浓度却因被稀释而明显降低。鉴于超滤后的D-dimer纯度约为90%,可满足D-dimer常规研究使用,如用作室内质控品/物、阳性对照、免疫或初筛单克隆抗体。
Shackell[29]于1909年使用真空干燥技术将补体、抗毒素、狂犬病毒及其它生物制品进行冻干,制成可以稳定保存的冻干品。随着冻干原理的深入研究和冻干设备的改良,真空冷冻干燥技术现已发展成为集多门学科于一体的综合技术工艺。在冻干过程中,预冻过的物料置于真空条件下进行升华干燥,除去冰晶(约占全部水分的90%),升华干燥完成后进入解析干燥,除去未冻结水,至物料中水分含量<3%[30]。制成的D-dimer冻干品呈多孔饼状,对温度、浓度或蛋白酶都具备较高的耐受程度,且易复溶和恢复活性。为使制备的D-dimer冻干品更接近于D-dimer天然抗原,以符合临床检测标准,本研究使用新生牛血清作为冻干基质对D-dimer进行冻干。D-dimer冻干品在37℃稳定保存12 d;复溶后
在4℃稳定保存30 d;复溶后在25℃稳定保存8 d;使用常规溶剂复溶对活性检测无明显影响。
4 结论
本研究阐述了一项简捷高效的人源D-dimer制备方案,以人源纤维蛋白原为原材料,先后经过凝血酶、Factor XIIIa、纤溶酶等酶解和超滤即制得高纯度的人源D-dimer蛋白,适于临床研究的D-dimer冻干品具备较好的稳定性。
[1]Soheir SA, Nigel SK, Charles SG. D-dimer antigen:current concepts and future prospects[J]. Blood, 2009, 113(13):2878-2887.
[2]Michael WM, Kevin RS, David AM. The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2001, 936(1):11-30.
[3]Dempfle CE, Mosesson MW. Theme issue:fibrinogen and fibrin--structure, function, interactions and clinical applications[J]. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2003, 89(4):599-600.
[4]Reganon E, Aznar J, Vila V. Degradation of human fibrinogen by plasmin:A kinetic study[J]. Thrombosis Research, 1977, 10(3):411-419.
[5]Francis CW, Marder VJ, Martin SE. Plasmic degradation of crosslinked fibrin. I. Structural analysis of the particulate clot and identification of new macromolecular-soluble complexes[J]. Blood, 1980, 56(3):456-464.
[6]Tsuneaki S, Motoaki S, Satoshi O. Evidence that D-dimer levels predict subsequent thromboembolic and cardiovascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation during ora anticoagulant therapy[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2010, 55(20):2225-2231.
[7]Renee AD, Melanie T, Roger EG, et al. Using an age-dependent D-dimer cut-off value increases the number of older patients in whom deep vein thrombosis can be safely excluded[J]. Haematol, 2012, 97(10):1507-1513.
[8]Bastos RD, Bogutchi T, Rezende SM, et al. Duration of symptoms and D-dimer testing in the ruling-out of venous thromboembolism[J]. J Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2006, 4(9):2079-2080.
[9]Wells PS. Integrated strategies for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism[J]. J Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 2007, 5(1):41-50.
[10]Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Evaluation of D-dimer in the diagnosis of suspected deep-vein thrombosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 349(13):1227-1235.
[11]Carr JM, McKinney M, McDonagh J. Diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Role of D-dimer[J]. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1989, 91(3):280-287.
[12]Lawler CM, Bovill EG, Collen DJ, et al. Fibrin fragment D-dimer and fibrinogen B beta peptides in plasma as markers of clot lysis during thrombolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction[J]. Blood, 1990, 76(7):1341-1348.
[13]Bayes-Genis A, Mateo J, Santalo M, et al. D-Dimer is an early diagnostic marker of coronary ischemia in patients with chest pain[J]. American Heart Journal, 2000, 140(3):379-384.
[14]Dougu N, Takashima S, Sasahara E, et al. Differential diagnosis of cerebral infarction using an algorithm combining atrial fibrillation and D-dimer level[J]. European Journal of Neurology, 2008, 15(3):295-300.
[15]Antoniou D, Pavlakou G, Stathopoulos GP, et al. Predictive value of D-dimer plasma levels in response and progressive disease in patients with lung cancer[J]. Lung Cancer, 2006, 53(2):205-210.
[16]Mirshahi SS, Pujade-Lauraine E, Soria C, et al. D-dimer and CA 125 levels in patients with ovarian cancer during antineoplastic therapy prognostic significance for the success of anti-cancer treatment[J]. Cancer, 1992, 69(9):2289-2292.
[17]Oya M, Akiyama Y, Yanagida T, et al. Plasma D-dimer level in patients with colorectal cancer:Its role as a tumor marker[J]. Surg Today, 1998, 28(4):373-378.
[18]Sutherland DE, Weitz IC, Liebman HA. Thromboembolic complications of cancer:epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatmen[tJ]. American Journal of Hematology, 2003, 72(1):43-52.
[19]Roberts LN, Patal RK, Arya R. Haemostasis and thrombosis in liver disease[J]. British Journal of Haematology, 2009, 148(4):507-521.
[20]Ceriello A, Taboga C, Giacomello R, et al. Fibrinogen plasma levels as a marker of thrombin activation in diabetes[J]. Diabetes, 1994, 43(3):430-432.
[21]Zhou HY, Chen R, Liu XP, et al. Determination of plasma D dimer in patients with pregnancy induced hypertension[J]. Chinese
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1997, 32(6):347-349.
[22]Przic DS, Ruzic NL, Petrovic SD. Lyophilization-the process and industrial use[J]. Hemijska Industrija, 2004, 58(12):552-562.
[23]Ruckley CV, Das PC, Leitch AG, et al. Serum fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products associated with postoperative pulmonary embolus and venous thrombosis[J]. Br Med J, 1970, 4(5732):395-398.
[24]Gaffney PJ, Brasher M. Subunit structure of the plasmin-induced degradation products of crosslinked fibrin[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1973, 295(1):308-313.
[25]Gaffney PJ. Distinction between fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products in plasma[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta, 1975, 65(1):109-115.
[26]Gaffney PJ. D-dimer. History of the discovery, characterization and utility of this and other fibrin fragments[J]. Fibrinolysis, 1993, 7(2):2-8.
[27]Franks JJ, Kirsch RE, Kao B, et al. Fibrinogen and fibrinogenrelated peptides in cancer[J]. Pathophysiology of Plasma Protein Metabolism, 1984:265-278.
[28]Alwan A. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010[R]. World Health Organization, 2011.
[29]Shackell LF. An improved method of desiccation, with some applications to biological problems[J]. American Journal of Physiology, 1909, 24(3):325-340.
[30]Wang W. Lyophilization and development of solid protein pharmaceuticals[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2000, 203(1):1-60.
(责任编辑 马鑫)
Preparation and Analysis of Lyophilization Characterization of Human D-dimer
Wu Jianwei Cai Lei Wang Jihua Tang Shixing
(National Engineering Laboratory of Rapid Diagnostic Test, Guangzhou Wondfo Biotech Co.,Ltd.,Guangzhou 510663)
D-dimer is formed by sequential action of 3 enzymes from fibrinogen. After producing D-dimer, we did the research on its lyophilization process. To produce cross-linked fibrin, fibrinogen was digested by thrombin and Factor XIIa. Then, fibrin degradation products(FDP)was prepared from cross-linked fibrin being degraded by plasmin. D-dimer was purified from FDP through ultrafiltration and prepared into lyophilized powder. By optimizing the lyophilization program, lyophilized D-dimer was stable for at least 12 days at 37℃, stable for at least 8 days at 25℃ and 30 days at 4℃ after reconstitution, and not different when being dissolved by different solvent.The preparation system established in this research is feasible and efficient. Depend on its stability, lyophilized D-dimer could be provided as biological raw materials for further research.
Fibrin Fibrinogen D-dimer Thrombus Lyophilized power
2014-05-12
国家高技术研究发展计划(“863”计划)(2011AA02A103),广东省战略新兴产业核心技术攻关项目(2012A080800007)
武建伟,男,硕士,研究方向:免疫诊断;E-mail:Jarviswu@hotmail.com
唐时幸,男,博士,研究方向:免疫诊断;E-mail:tang.shixing@wondfo.com.cn

