湿玉米纤维饲料的营养价值评定和贮运技术研究
潘春方,张永根,李 洋,李春雷,刘凯玉
(东北农业大学动物科学技术学院,哈尔滨 150030)
湿玉米纤维饲料的营养价值评定和贮运技术研究
潘春方,张永根*,李 洋,李春雷,刘凯玉
(东北农业大学动物科学技术学院,哈尔滨 150030)
湿玉米纤维饲料是玉米湿磨法生产淀粉的副产物。随着玉米深加工的迅速发展,湿玉米纤维饲料产量非常大,其含有较高的蛋白和可消化纤维,且淀粉含量较低,对奶牛而言是优质的饲料来源。文章就湿玉米纤维饲料的营养价值及其贮存技术进行概述,为湿玉米纤维饲料大规模开发利用提供参改。
湿玉米纤维饲料;奶牛;营养价值;贮存
饲料资源短缺已成为畜牧业发展的重要制约因素。我国草原退化、沙化、碱化日益严重,各种自然灾害的侵袭,饲草严重缺乏(北方草原产草量比50年代下降30%~50%)。畜牧业发展需要积极寻找、开发新的、有利用潜力的饲料资源。当前我国淀粉深加工工业发展迅速,产生大量副产物,以往是将湿玉米纤维饲料烘干后作为蛋白饲料使用。此工艺不但成本高(每吨饲料烘干费用为250~300元),且营养价值有损失。如果能将湿玉米纤维饲料直接喂将节省大量能源,同时也可避免烘干造成的营养损失和空气污染(CO2、SO2及大量的烟尘)。湿玉米纤维饲料能够大规模开发利用的前提,是全面掌握湿玉米纤维饲料的营养成分与贮运技术。
1 湿玉米纤维饲料来源
湿玉米纤维饲料是玉米湿磨法生产淀粉的副产物,在湿磨生产中将玉米进行去杂处理后,将玉米浸泡在亚硫酸溶液中,浸泡能够分散玉米胚体细胞中的蛋白质网,削弱保持淀粉的联结键,使得玉米籽粒能够更容易将种皮、胚芽和胚乳进行分离,在浸泡过程中有一部分营养物质流入玉米浸泡水中,浸泡后将玉米浸泡水排出并进行浓缩。胚芽进一步分离后用于生产玉米油。剩下部分如种皮、淀粉等各部分进行筛选和分离[1]。最后将玉米种皮混合到浓缩后玉米浸泡水中形成湿玉米纤维饲料,主要为玉米浆和玉米皮混合物,也包含在湿磨过程中胚芽粕等其他蒸馏可溶物[2]。
2 湿玉米纤维饲料营养成分
本文对湿玉米纤维饲料氨基酸含量、蛋白组分和碳水化合物组分进行测定。结果见表1~3。从表1可见,本试验所采用的来自松原嘉吉生化有限公司生产的湿玉米纤维饲料与国外湿玉米纤维饲料常规营养成分存在差异,但总主要特征如含有较高粗蛋白、纤维含量以及高磷相似。生产厂家采购玉米的质量不同,或是生产工艺存在差异等,使得湿玉米纤维饲料营养成分不可能完全一致。湿玉米纤维饲料与玉米相比,湿玉米纤维饲料含有较高的粗蛋白,从约9%增加到18%,由于湿玉米纤维饲料的粗蛋白含量较高,可被用作蛋白质原料。湿玉米纤维饲料中性洗涤纤维(NDF)含量较高,从16%到49.93%。且木质素含量(1.10%(本实验室实测值))很低,这种容易消化的纤维可部分替代奶牛日粮中的牧草和精料。对于高产奶牛而言,可替代部分精料,但不适合大剂量替代牧草,因为湿玉米纤维饲料的颗粒小,物理有效纤维含量较低,易造成奶牛乳中乳脂率下降。湿玉米纤维饲料中非粗饲料来源的粗纤维,可为奶牛提供必要的能量,不会因为淀粉(25.44%,本实验室实测值)快速发酵而造成奶牛瘤胃酸中毒[12-14]。
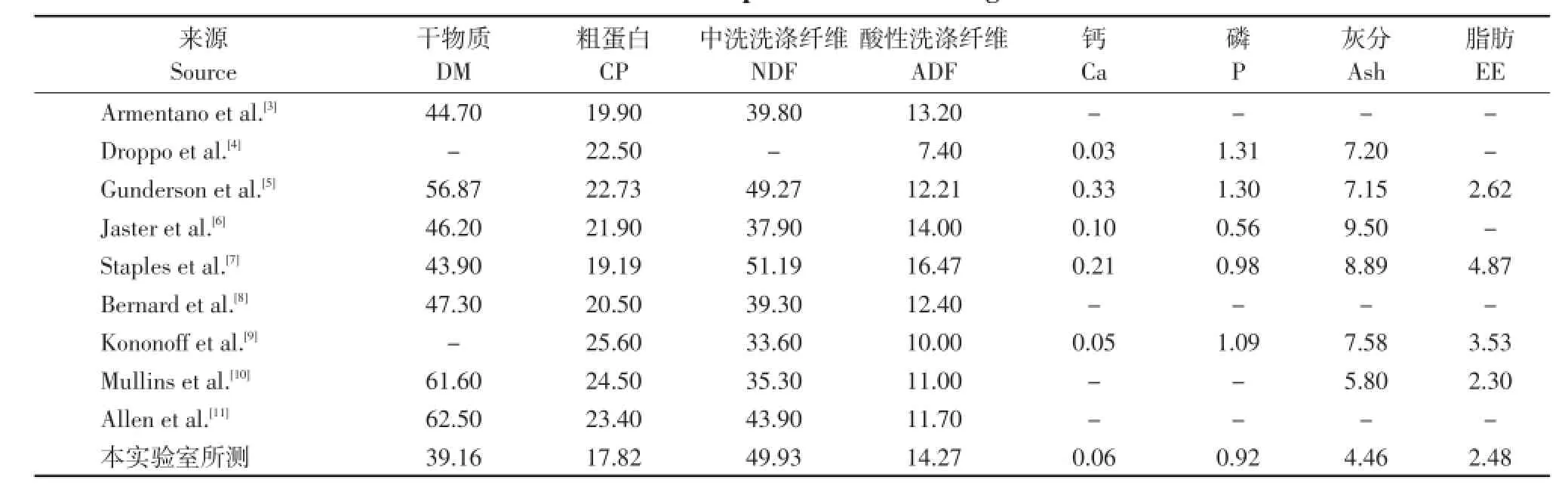
表1 湿玉米纤维饲料常规营养成分测定Table 1 Nutrient composition of wet corn gluten feed (DM%)
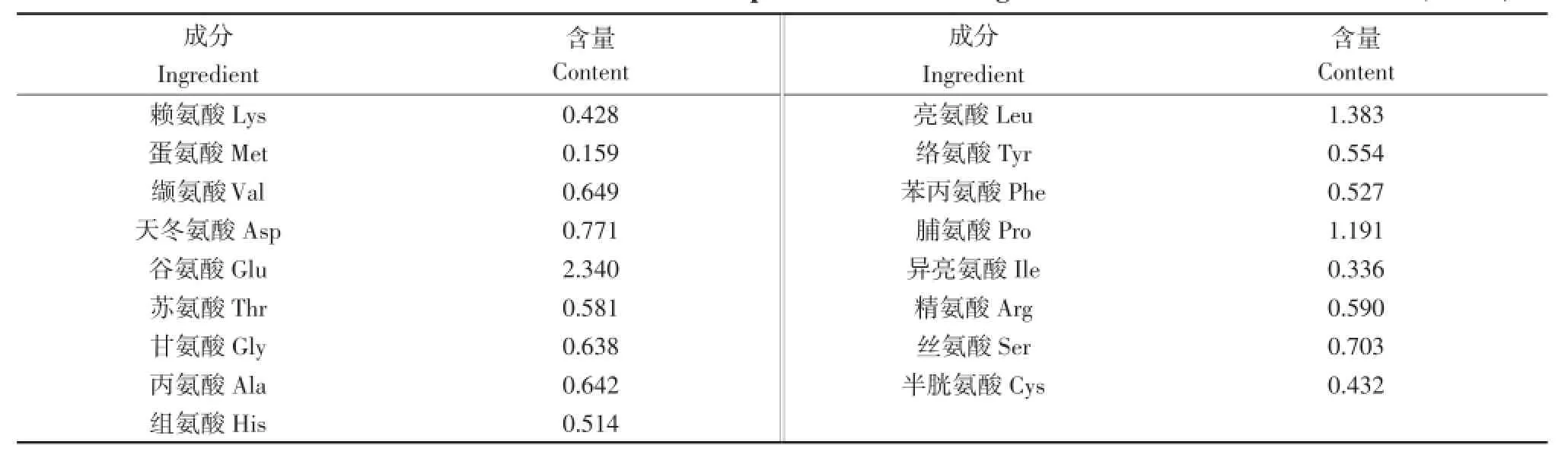
表2 湿玉米纤维饲料的氨基酸含量Table 2 Amino acid composition of wet corn gluten feed (DM%)
从表2可见,湿玉米纤维饲料的氨基酸种类较丰富,但与玉米相似,赖氨酸仍然是第一限制氨基酸,在饲喂湿玉米纤维饲料时要防止氨基酸缺乏。
湿玉米纤维饲料粗蛋白组分和碳水化合物组分含量见表3。
对于奶牛而言,湿玉米纤维饲料作为非粗饲料中性洗涤纤维来源,含有较低的能迅速发酵的碳水化合物且淀粉含量较低,能降低瘤胃酸中毒发生几率。可作为蛋白饲料来源,也是奶牛日粮能量来源,脂肪含量适中且纤维易消化,使得湿玉米纤维饲料的能值较高,具有很好的饲用价值。
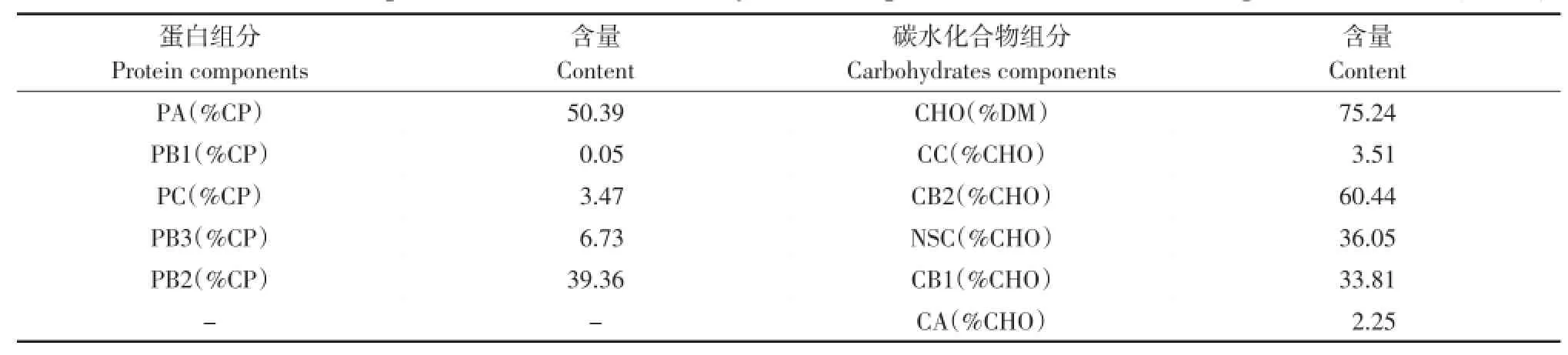
表3 湿玉米纤维饲料粗蛋白组分含量和碳水化合物组分含量Table 3 Protein components contents and carbohydrates components contents of wet corn gluten feed (DM%)
3 湿玉米纤维饲料的运输和贮存
3.1 湿玉米纤维饲料的运输
湿玉米纤维饲料的运输与其主要特征如含水量、贮存期及密度等密切相关。湿玉米纤维饲料含水量为60%,不仅增加运输成本,也限制市场范围。由于存在较大的含水量,湿玉米纤维饲料流动性也给运输过程带来难题。建议以密闭箱式货车运输,并采取必要措施防止对车体的腐蚀。
3.2 湿玉米纤维饲料的贮存
有研究表明,在特定的温度、水分和氧含量到达酶和微生物活动的最佳水平时,将加速腐败的产生[15]。当微生物降解其营养素而产生挥发性化合物时即可产生强烈腐烂变质臭味[16]。产生腐败微生物主要包括细菌、酵母和霉菌[17],酵母和霉菌更能承受恶劣环境。
常用的高水分饲料贮存方法包括贮存袋、桶或窖贮和增加添加物贮存[18]。青贮袋是最普遍、实用方法,但靠近存贮袋边缘容易产生腐败,贮存袋承受压力有限,易破裂[19-22];开封后暴露于空气中迅速变质。进一步改为用桶贮或是窖贮,但由于高水分的饲料流动性太大[23-24],在存贮时需将高水分饲料与饲草混合贮存。增加添加物贮存方式物理处理和化学处理贮存。物理方法主要包括添加干草、玉米秸秆、麦秸和大豆皮等[19,22],对高水分饲料起到中和作用。化学处理方法主要是添加化学试剂。添加化学试剂容易对贮存饲料的化学组成成分造成影响[24-27]。
采用物理方法对高水分饲料进行桶或窖贮试验已有研究。Strohbehn等将WDGS与干草按照80%/20%混合贮存90 d,结果显示在贮存袋的边缘发生腐败现象[19]。而Christensen等将湿酒精糟(WDGS)和玉米秸(DM基础)按照70∶30的比例混合存储在55加仑的铁桶里进行贮存效果试验[25],其处理分别有五种不同的覆盖方式,分别为无盖、塑料、盐、可溶物和可溶物加盐。处理效果为塑料组最好,随后是可溶物、盐、可溶物与盐混合和无盖。Yelden等将湿酒精糟(WDGS)和稻秸(DM基础)进行混合贮存效果试验[26],结果表明,混合贮存后脂肪含量损失,但是增加灰分和中性洗涤纤维含量。Schingoethe等将WDGS与大豆皮按照0、15%和30%混合贮存,得出结果是WDGS与大豆皮混合后能很好进行发酵[27]。Orosz等研究将湿玉米纤维饲料与玉米(10%)和玉米青贮(20%)分别存储,研究30 d厌氧存储和10 d有氧存储的发酵模式及有氧稳定性[28],研究结果表明,在有氧存储阶段,玉米青贮混合组霉菌数增加,而湿玉米纤维饲料与干玉米混合组霉菌的生成减少;在厌氧存储阶段,玉米青贮混合组对有氧稳定性有不良影响,而湿玉米纤维饲料与干玉米混合组的稳定性增加。本研究将湿玉米纤维饲料单独以及与常用的粗饲料羊草和苜蓿在模拟青贮桶中分别进行混合贮存。羊草和苜蓿与湿玉米纤维饲料的混合比例分别为10%、20%和30%。贮存时间为60 d。试验结果是湿玉米纤维饲料与羊草按70∶30的比例混合青贮效果最好,而与苜蓿混合的比例以90∶10最好。
4 结论
随着玉米深加工产业的发展,玉米湿磨法生产淀粉的副产物湿玉米纤维饲料产量庞大。将其作为动物饲料在动物生产中进行开发饲喂,为养殖业提供一种新型非饲草饲料资源,可替代日粮中的部分精料或部分粗料,降低养殖户养殖成本。湿玉米纤维饲料过瘤胃蛋白含量较高,是动物尤其是反刍动物日粮中能量纤维来源,纤维易消化,饲料能值较高,可在养殖中广泛应用。为防止湿玉米纤维饲料发生腐败,建议使用桶/窖混合贮存方式。
[1]Hoffman P C.Corn gluten feed[M].USA:University of Wisconsin-Extension Publication,1991.
[2]Macken C N,Erickson G E,Klopfenstein T J,et al.Effects of concentration and composition of wet corn gluten feed in steam-flaked corn-based finishing diets[J].Journal of Animal Science,2004,82:2718-2723.
[3]Armentano L E,Dentiue M R.Wet corn gluten feed as a supplement for lactating dairy cattle and growing heifers[J].Journal of Dairy Science,1988,71:990-995.
[4]Droppo T E,Macleod G K,Grieve D G.Composition and storage characteristics of wet corn gluten feed[J].Canadian Journal of Animal Science,1985,65:265-268.
[5]Gunderson S L,Aguilar A A,Johnson D E,et al.Nutritional value of wet corn gluten feed for sheep and lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,1988,71:1204-1210.
[6]Jaster E H,Staples C R,McCoy G C,et al.Evaluation of wet corn gluten feed,oatlage,sorghum soybean silage,and alfalfa haylage for dairy heifers[J].Journal of Dairy Science,1984,67:1976-1982.
[7]Staples C R,Davis C L,McCoy G C,et al.Feeding value of wet corn gluten feed for lactating dairy cows[J].Journal of Dairy Science,1984,67(6):1214-1220.
[8]Bernard J K,Delost R C,Mueller F J,et al.Effect of wet corn gluten feed on nutrient digestibility and milk yield and composition[J].Journal of Dairy Science,1991,74:3913-3919.
[9]Kononoff Ivan P J S K,Matzke W,Grant R J,et al.Milk production of dairy cows fed wet corn gluten feed[J].Journal of Dairy Science,2006,89:2608-2617.
[10]Mullins C R,Grigsby K N,Anderson D E,et al.Effects of feeding increasing levels of wet corn gluten feed on production and ruminal fermentation in lactating dairy cows[J].Journal of Dairy Science,2010,93(11):5329-5337.
[11]Allen D M,Grant R J.Interactions between forage and wet Ccorn gluten feed as sources of fiber in diets for lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2000,83:322-331.
[12]Herold D,Klemesrud M,Klopfenstein T J,et al.Solvent-extracted germ meal,corn bran and steep liquor blends for finishing steers [J].Nebraska Beef Cattle Reports,1998,337:50-53.
[13]Sindt J J,Drouillard J S,Thippareddi H,et al.Evaluation of finishing performance,carcass characteristics,acid-resistant E.coli and total coliforms from steers fed combinations of wet corn gluten feed and steam-flaked corn[J].Journal of Animal Science,2002, 80:3328-3335.
[14]Montgomery S P,Drouillard J S,Titgemeyer E C,et al.Effects of wet corn gluten feed and intake level on diet digestibility and ruminal passage rate in steers[J].Journal of Animal Science, 2004,82(12):3526-3536.
[15]Doyle E M.Microbial food spoilage-losses and control strategies [C].European Union:Food Research Institute.University of Wisconsin-Madison.Assessmentoffish and fish products. Weekly Report.2007:13-14.
[16]Blackburn C W.Food spoilage microorganisms[M].Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing Ltd Publication,2006.
[17]Gram L,Ravn L,Rasch M,et al.Food spoilage-interactions between food spoilage bacteria[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2002,78:79-97.
[18]Nelson A,Baskett J,Vincent K,et al.Handling and storage of high moisture coproducts from ethanol production in beef opera-tions[C].USA:Agricultural and Biosystems Department.Iowa State University,2009.
[19]Strohbehn D,Loy D D,Morrical D,et al.Modified distillers'grain with solubles stored for an extended period in a silo bag used to develop breeding heifers[C].USA:Iowa State University Report.A. S.Leaflet R2288,2008.
[20]Strohbehn D R,Loy D D,Morrical D G,et al.Evaluation of bagging to extend storage life of wet and modified distillers' grains-A demonstration project[J].Animal Industry Report,2008, 654(1):38.
[21]Erickson G E,Klopfenstein T J,Rasby R J,et al.Storage of wet corn co-products[J].Faculty Papers and Publications in Animal Science,2008,506:1-17.
[22]Walker P M,Forster L A.Case Study:The evaluation of a vacuum storage method for high moisture distillers grain and its effect as a protein and energy supplement for beef cows[J].The Professional Animal Scientist,2008,24(6):648-655.
[23]Kung Jr L.Managing high moisture co-product feeds for improved aerobic stability[C].Newark:Processing of the Four State Dairy Conference,2005:229-232.
[24]Drackley J K,Hutjens M F,Ipharraguerre I,et al.Efficacy of a preservative product(Zenipro)for wet distiller's grains[C].Illinois: Final Report to Kemin Americas,Inc.University of Illinois,2004.
[25]Christensen D L,Rolfe K M,Klopfenstein T J,et al.Evaluation of storage of covers when wet distillers byproducts are mixed and stored with forages[C].USA:Nebraska Beef Reports MP,2010.
[26]Yelden J R,Buckner C D,Rolfe K M,et al.Nutrient composition of spoiled and non-spoiled wet byproducts mixed and stored with straw[J].Nebraska Beef Cattle Reports,2011,644:18-19.
[27]Schingoethe D J.Utilization of DDGS by cattle[C].Canada:27thWestern Nutrition Conference.2006:61-74.
[28]Orosz S,Kapas S.Long-term storage of wet CGF:Effluent,optimal density,fermentation and aerobic stability[J].Forage Conservation,2010(3):173-175.
Research on nutritional value evaluation and storage technology of wet corn gluten feed
PAN Chunfang,ZHANG Yonggen,LI Yang,LI Chunlei,LIU Kaiyu(School of Animal Sciences and Technology,Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin 150030,China)
Wet corn gluten feed is co-produced in corn wet milling.With the rapid development of corn deep processing,producing a large number of wet corn gluten feed,which contains high protein and digestible fiber,but starch content is low,which is a high quality source of feed for the cows.The paper overviewed nutritional value evaluation and storage technology of wet corn gluten feed,and aimed to provide some guidances for wet corn gluten feed for large-scale development and utilization.
wet corn gluten feed;dairy cow;nutritional value;storage
S767;S823.5
A
1005-9369(2014)03-0117-05
时间2014-3-21 9:10:00 [URL]http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1391.S.20140321.0910.005.html
潘春方,张永根,李洋,等.湿玉米纤维饲料的营养价值评定和贮存技术研究[J].东北农业大学学报,2014,45(3):117-121.
Pan Chunfang,Zhang Yonggen,Li Yang,et al.Research on nutritional value evaluation and storage technology of wet corn gluten feed[J].Journal of Northeast Agricultural University,2014,45(3):117-121.(in Chinese with English abstract)
2013-07-16
国家奶牛产业技术体系项目(CARS-37)
潘春方(1984-),女,博士研究生,研究方向为动物营养与饲料科学。E-mail:pancf001@163.com
*通讯作者:张永根,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为动物营养与饲料科学。E-mail:zhangyonggen@sina.com

