两种钢管混凝土轴压短柱有限元模型的比较
王志滨,李毅
(福州大学土木工程学院,福建福州 350116)
钢管混凝土由于强度高、抗震性能良好、经济性和施工速度快等优点,已被广泛的应用于大跨、高耸的建筑和结构中.其截面形式主要包括圆形、方形和矩形三种.国内外研究者针对以上三种钢管混凝土轴压短柱进行了大量的试验研究.但仅有试验研究是不够的,有限元法作为一种有效的补充可进一步扩大研究的参数范围,同时还可较为深入的分析钢管混凝土中应力、应变和约束力的大小和变化规律.而有限元软件ABAQUS由于其强大的非线性功能,正受到越来越多研究者的青睐.研究者们建议了多种适合该软件使用的钢管混凝土轴压短柱的有限元模型.其中文献[1]和文献[2]中建议的模型被许多研究者所采用.
本文分析了340个圆形、方形和矩形钢管混凝土轴压短柱的试验数据[3-23],并利用以上试验数据验证文献[1]和文献[2]中建议的有限元模型的精度,给出以上两个模型适用范围的建议.
1 有限元模型
混凝土采用C3D8R单元,钢管采用SR4单元.混凝土和钢管的切线接触采用库伦摩擦,摩擦系数统一取为0.6;法线接触采用硬接触.
1.1 模型1
对钢材,文献[1]采用理想弹塑性模型.对于混凝土,文献[1]采用ABAQUS软件中的“Drucker Prager”模型,其摩擦角取为20°;双轴等压抗压强度和等三轴抗压强度的比值取为0.8;并建议了如下混凝土单轴受压应力(σ)-应变(ε)关系模型:

圆形截面:

方形截面:

圆形截面:

方形截面:

其中:r为文献[24]建议的考虑混凝土强度影响的折减系数,当fcu等于30和100 MPa时该值分别取为1和0.5,其余情况可采用插值求得.
1.2 模型2
文献[2]中钢材单轴应力-应变关系采用考虑二次塑流的五段式模型.对于混凝土,文献[2]采用ABAQUS中混凝土塑性损伤模型,其膨胀角取为30°;双轴等压抗压强度和单轴抗压强度的比值取为2/3;并建议了如下混凝土单轴受压应力(σ)-应变(ε)关系模型:

式中:x=ε/εcc;y=σ/fc';εcc=εc0+800ξ0.2×10-6;εc0=(1 300+12.5fc')×10-6;ξ为钢管约束效应系数(ξ=fyAs/(fckAc),其中:fy和fck分别为钢材屈服强度和混凝土轴心抗压强度标准值;As和Ac分别为钢管和核心混凝土的横截面积);η和β0的计算详见文献[2].
2 模型验证与讨论
采用模型1和模型2对现有的340个试验数据进行模拟,有限元计算的极限承载力和试验实测结果的对比列于图1和图2中.图中:Nue和Nuc分别代表钢管混凝土轴压构件的试验实测承载力和有限元模拟的承载力.两个模型计算求得的Nue/Nuc的均值和方差均列于表1中.由图1、图2和表1可发现:两个模型均可很好预测钢管混凝土轴压短柱的极限承载力.对于圆钢管混凝土构件,当约束效应系数(ξ)介于0.5~2.5之间时,两个模型预测极限承载力的精度均较高;当ξ小于0.5时,两个有限元模型预测的极限承载力均偏低;当ξ大于2.5时,两个有限元模型预测的极限承载力均偏高.
同时,图3中给出了部分实测钢管混凝土轴压短柱荷载-变形关系曲线和有限元模拟结果的比较.可见,采用模型2模拟的荷载-变形关系曲线和试验实测曲线吻合的更好;采用模型1求得的荷载-变形关系曲线的后期承载力要高于试验实测值.
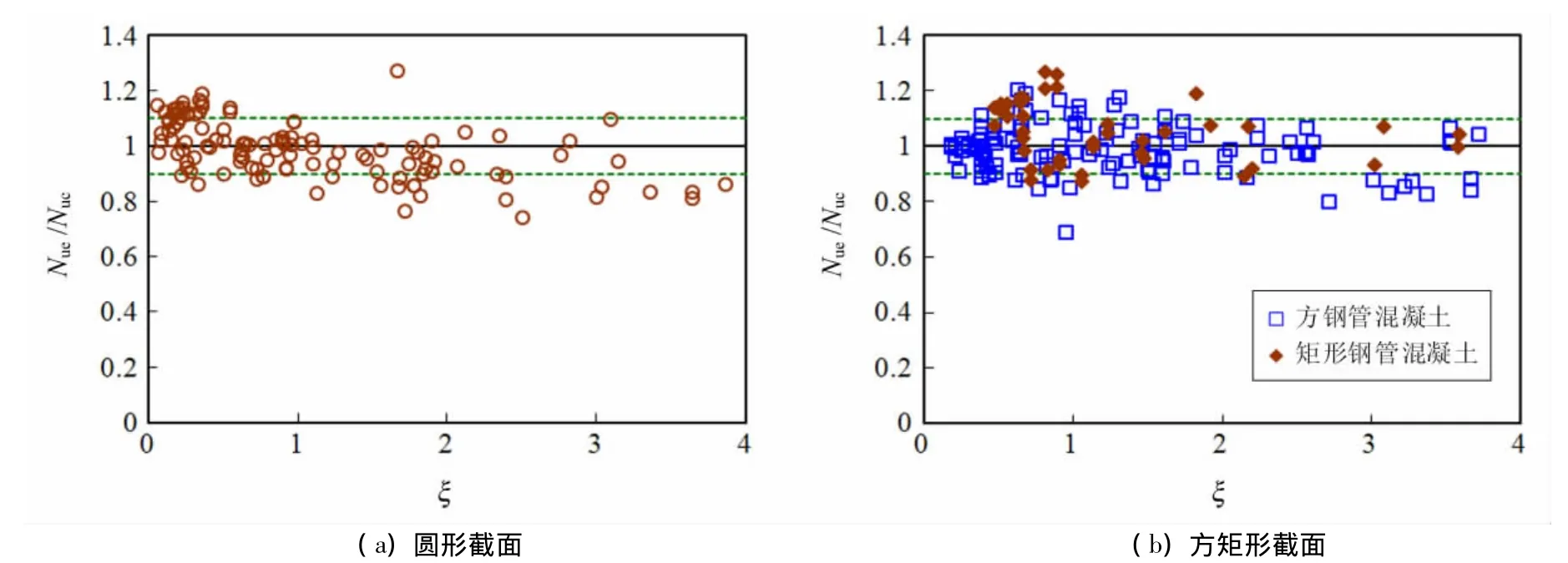
图1 采用模型1预测的极限承载力和试验实测极限承载力的比较Fig.1 Comparison between measured strength and predicted strength using model 1

图2 采用模型2预测的极限承载力和试验实测极限承载力的比较Fig.2 Comparison between measured strength and predicted strength using model 2

表1 有限元预测极限承载力和试验实测值的比较Tab.1 Comparison results of FE predictions with measured ultimate strength

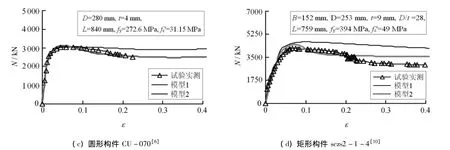
图3 钢管混凝土构件N-ε计算曲线和试验实测曲线的比较Fig.3 Comparison between predicted and measured N - ε curves for CFST specimens
3 结语
1)两个模型均可很好的预测钢管混凝土轴压短柱的极限承载力.
2)对于圆钢管混凝土构件,当约束效应系数(ξ)介于0.5~2.5之间时,两个模型预测极限承载力的精度均较高;当ξ小于0.5时,两个有限元模型预测的极限承载力均偏低;当ξ大于2.5时,两个有限元模型预测的极限承载力均偏高.
3)采用文献[2]建议的有限元模型模拟的钢管混凝土构件的荷载-变形曲线和试验实测曲线吻合的更好.
[1]Hu Hsuan-The,Huang Chiung-Shiann,Wu Ming-Hsien,et al.Nonlinear analysis of axially loaded concrete-filled tube columns with confinement effect[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2003,129(10):1 322 -1 329.
[2]Han Lin-hai,Yao Guo-huang,Tao Zhong.Performance of concrete-filled thin-walled steel tubes under pure torsion[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2007,45(1):24-36.
[3]Tomii M,Yoshimura K,Morishita Y.Experimental studies on concrete filled steel tubular stub columns under concentric loading[C]//Proceedings of the International Colloquium on Stability of Structures under Static and Dynamic Loads.Washington:[s.n.],1977:718 -741.
[4]Schneider S P.Axially loaded concrete- filled steel tube[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1998,124(10):1 125 -1 138.
[5]Yamamoto T,Kawaguchi J,Morino S.Experimental study of scale effects on the compressive behavior of short concrete-filled steel tube columns[C]//Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Composite Construction in Steel and Concrete.Alberta:[s.n.],2000:879 -890.
[6]Huang C S,Yeh Y K,Liu G Y,et al.Axial load behavior of stiffened concrete -filled steel columns[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2002,128(9):1 222-1 230.
[7]Sakino K,Nakahara H,Morino S,et al.Behavior of centrally loaded concrete-filled steel-tube short columns[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2004,130(2):180-188.
[8]Han Lin-hai,Yao Guo-huang.Experimental behaviour of thin-walled hollow structural steel(HSS)columns filled with self-consolidating concrete(SCC)[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2004,42(9):1 357-1 377.
[9]Han Lin-hai,Yao Guo-huang,Zhao Xiao-ling.Tests and calculations for hollow structural steel(HSS)stub columns filled with self-consolidating concrete(SCC)[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2005,61(9):1 241-69.
[10]Lu Y Q,Kennedy D J L.The flexural behaviour of concrete- filled hollow structural sections[J].Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering,1994,21(1):111-130.
[11]Varma A H.Seismic behavior,analysis,and design of high strength square concrete filled steel tube(CFT)columns[D].Bethlehem:Lehigh University,2000.
[12]Uy B.Strength of concrete filled steel box columns incorporating local buckling[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2000,126(3):341-352.
[13]Han Lin-hai,Zhao Xiao-ling,Tao Zhong.Test and mechanics model for concrete-filled SHS stub columns,columns,and beam-columns[J].Steel and Composite Structures 2001,1(1):51-74.
[14]Han L H.Tests on stub columns of concrete- filled RHS sections[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2002,58(3):353-372.
[15]Liu D,Gho W M,Yuan J.Ultimate capacity of high-strength rectangular concrete-filled steel hollow section stub columns[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2003,59(12):1 499-1 515.
[16]Lam D,Williams C A.Experimental study on concrete filled square hollow sections[J].Steel and Composite Structures,2004,4(2):95-112.
[17]Liu D,Gho W M.Axial load behaviour of high-strength rectangular concrete-filled steel tubular stub columns[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2005,43(8):1 131 -1 142.
[18]Liu D.Tests on high-strength rectangular concrete-filled steel hollow section stub columns[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2005,61(7):902-911.
[19]Tao Z,Han L H,Wang Z B.Experimental behaviour of stiffened concrete-filled thin-walled hollow steel structural(HSS)stub columns[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2005,61(7):962 -983.
[20]Tao Z,Han L H,Wang D Y.Strength and ductility of stiffened thin-walled hollow steel structural stub columns filled with concrete[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2008,46(10):1 113-1 128.
[21]Tao Z,Uy B,Han L H,et al.Analysis and design of concrete-filled stiffened thin-walled steel tubular columns under axial compression[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2009,47(12):1 544-1 556.
[22]Liew J Y R,Xiong D X,Zhang M H.Experimental studies on concrete filled tubes with ultra-high strength materials[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Steel Structures.Seoul:[s.n.],2011:377 -384.
[23]Chen C C,Ko J W,Huang G L,et al.Local buckling and concrete confinement of concrete-filled box columns under axial load[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2012,78:8 -21.
[24]Ellobody E,Young B.Nonlinear analysis of concrete - filled steel SHS and RHS columns[J].Thin - Walled Structures,2006,44(8):919-930.

