Radical-scavenging activity,ACE-inhibiting capability and identificatio of rapeseed albumin hydrolysate
Zhohui Xue Xiohong Kou Yifn Wng Lijun Zhi
a Tianjin Research Center of Agricultural Biotechnology,Tianjin 300384,China
b School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
Abstract Albumin derived from rapeseed was hydrolyzed sequentially using alcalase and fl vorzyme to produce antioxidant peptides.To identify antioxidant peptides,rapeseed albumin hydrolysate(RAH)was fractionated using size exclusion chromatography(G-25).The antioxidant activity and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibiting activity of rapeseed peptides (RSP) purifie from RAH were evaluated.The results revealed that RSP-4 had the highest ABTS radical-scavenging activity (TEAC value=0.24) and ACE-inhibiting capacity (IC50=0.19 mg/mL) compared to other fractions.Moreover,RSP-4 was identifie as PFDSYFVC(977 D)by electrospray ionization(ESI)mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS).
Keywords: Radical-scavenging activity;ACE-inhibiting capability;Rapeseed albumin hydrolysate(RAH);Rapeseed peptide(RSP);Mass spectrometry
1.Introduction
The quality of food products can be affected by lipid peroxidation,which can result in alterations in fl vor,texture,color,or nutritive value,or cause potentially toxic reactions in the food during processing and storage.Antioxidant peptides,a class of safe and widely distributed natural antioxidants,have been derived from different protein resources such as porcine plasma[1],jellyfis [2],rice endosperm [3]and algae [4],and can be used to prevent or delay food deterioration and extend the halflife time of foods.In addition to inhibiting lipid peroxidation and the formation of free radicals,antioxidant peptides also exhibit typical characteristics of natural antioxidants compared with synthetic antioxidants such as butylated hydroxyanisole(BHA)and butylated hydroxytoluene(BHT),which have potential side effects.The antioxidant properties of these hydrolysates,such as free radical-scavenging activity and metal ion chelation,have been ascribed to the cooperative effects of multiple properties[5].
Another important application of these natural polypeptides is antihypertensive treatment.Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease,affecting up to 30%of the adult population around the world[6].It is known that the balance between the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and the Kallikrein-Kinin system (KKS) plays a significan role in the regulation of water,electrolytes and blood in organisms [7],as angiotensin I-converting enzyme(ACE)can participate in the regulation of blood pressure by converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II.Currently,different ACE inhibitors such as enalapril and captopril for antihypertensive therapy have been synthesized.However,these synthesized inhibitors could result in a number of undesirable side effects,such as cough,loss of taste,renal impairment,and angioneurotic edema[8].Therefore,natural ACE inhibitors have gained more and more attention,and antihypertensive activities of natural ACE inhibitors from several protein hydrolysates such as casein[9],whey[10],fis [11,12]and algae[13]have already been identified
As one of the most important oilseed crops in the world,rapeseed is increasingly becoming a major crop worldwide.According to FAO requirements,rapeseed not only has wellbalanced compositions of amino acids,but also is rich in lysine,which is correspondingly limited in legumes and cereals.Therefore,it can be considered an excellent source of protein for humans[14].Meanwhile,rapeseed protein hydrolysates(RPH)as a source of bioactive peptides as well as.The solubility,oil-holding capacity,foaming capacity,foaming stability,emulsifying capacity,and emulsion stability of rapeseed peptides(RSP) have been systematically explored [15,16].Moreover,RSP has also been reported to have the bioactive functions such as HIV inhibition [17],insulin resistance inhibition [18]and antioxidant activity[19].Since the functional properties of peptides are highly associated with amino acid sequences and spatial structures,the identificatio of molecular structure and mass weight using mass spectrometry is extremely desired[20].
In order to uncover the potential bioactivities of RSP,ABTS radical-scavenging activity and ACE inhibitory capacity of RSP have been evaluated in the present study.Moreover,the molecular mass and amino acid sequence of RSP-4(the forth rapeseed peptide fraction) were measured using electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS).They might provide a reasonable explanation for the structure-activity relationship of RSP-4,and a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of bioactive peptides.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Materials
Rapeseed was kindly provided as the gift from Huazhong Agricultural University.Sephadex G-25,2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline 6-sulfonate) (ABTS),ACE and Hip-His-Leu (HHL) were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co.,USA.Alcalase and fl vorzyme were purchased from Novo Co.,Denmark.Lotensin was purchased from Novartis Co.,China.All other reagents used for the experiments were of analytical grade.
2.2.Preparation of RAH
RAH was produced according to the method described previously [21].Rapeseed flou 100 g was stirred for 1 h at room temperature in 1000 mL distilled water.The resultant slurry was centrifuged at 2200×gfor 10 min and the supernatant was collected.The residue was extracted with 500 mL of distilled water for 1 h and separated as mentioned previously.Supernatants were pooled,and the pH was adjusted by 1.0 mol/L HCl to pH 4,where most of the proteins were precipitated.The precipitate was rapeseed albumin,and removed by centrifugation at 4000×gfor 15 min and then lyophilized and stored at-30°C.Rapeseed albumin was then resuspended in distilled water as 4.87 g/100 mL and the alcalase-substrate ratio was adjusted to 0.38 AU enzyme/g under optimal conditions of 50°C,1 h,and pH 8.0.Proteins were withdrawn at 1 h of hydrolysis,and the pH was adjusted to 7.0 followed by the addition of fl vorzyme at 50 LAPU/g([E]/[S]).The sample was hydrolyzed for 2 h at pH 7.0,which was adjusted with 1 mol/L NaOH.The hydrolysate was subsequently transferred to a water bath at 80°C for 10 min to inactivate the enzyme.After cooling,the supernatant was harvested by centrifugation at 2200×gfor 10 min.The supernatant was then lyophilized and used as the RAH.
2.3.Preparation of RSP
RAH was purifie on a Sephadex G-25 gel filtratio column(1.6 cm×50 cm) and eluted with distilled water at a f ow rate of 0.6 mL/min.The eluted fractions were pooled after spectrophotometric measurement at 280 nm.The respective fractions were named as RSP-separation,pooled and lyophilized.
2.4.ABTS radical-scavenging activity
The free radical-scavenging activity was measured according to the method described previously[22].The reaction mixtures were reacted for 6 min by mixing 1 mL of sample and 2 mL of ABTS free radical solution diluted with PBS,and the initial absorbance at 734 nm was almost 0.7.The absorbance of the resultant solution was recorded at 734 nm.A lower absorbance indicated a higher ABTS radical-scavenging activity.
The scavenging activity was expressed as the following Eq.(1):
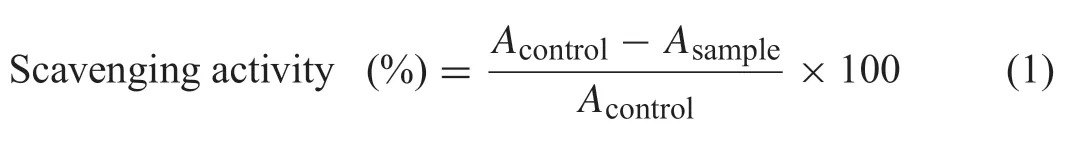
WhereAcontrolis the absorbance of the ABTS radical without any protein hydrolysates.
The antioxidant ability of the sample to scavenge ABTS free radicals was then expressed as a Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity(TEAC)value using the formula(2):

2.5.ACE inhibitory activity
The ACE inhibitory activity was measured according to the method from Cushman and Cheung[23]with minor modifica tions.Totally 100 μL of each sample was mixed with 100 μL of 5 mmol/L HHL dissolved in 0.5 mol/L sodium borate buffer(pH 8.3,containing 0.3 mol/L NaCl).After pre-incubating at 37°C for 4 min,the mixture was incubated with 10 μL of 10 mg/mL ACE solution for 30 min at the same temperature.The reaction was terminated by adding 200 μL of 1 mol/L HCl.The hippuric acid liberated by ACE was extracted by ethyl acetate and determined directly at 228 nm.The IC50value represents the concentration of ACE inhibitor at the reduction of 50%.Lotensin,a commonly used antihypertensive drug,was also tested as the positive control.
The inhibitory rate of ACE activity was calculated as the following Eq.(3):

whereA0represents the absorbance of the sample andAcrepresents the absorbance of the control.

Fig.1.Elution profil of RSP fractions separated by gel filtratio on Sephadex G-25 column.The column (1.6 cm×50 cm) was equilibrated and eluted with distilled water at a f ow rate of 0.6 mL/min at the wavelength of 280 nm.4 peptide fractions(RSP-1,RSP-2,RSP-3 and RSP-4)were harvested according to molecular sizes.
2.6.Identification of peptide
The molecular weight of RSP-4 was determined by electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) with a positive ion detection mode(Finnigan LCQ Advantage Max,USA).The molecular sequencing was analyzed with tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS).
2.7.Database analysis
All MS/MS spectra were initially subjected to analysis with the SALSAalgorithm(Bioworks 3.3 version,Thermo Finnigan),a tool for identifying MS/MS spectra with user-define parameters.Afterwards,a rapeseed database was used to search and identify the sequences of the peptides (Bioworks 3.3 version,Thermo Finnigan).
2.8.Statistical analysis
All tests were performed in triplicate and the data were expressed asM±SD.Data were subjected to the analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s multiple-range post hoc test,and a significan difference was considered atP<0.05.
3.Results
3.1.RSP fractionation
The fina RAH obtained by sequential enzymatic hydrolysis with alcalase and fl vorzyme was injected into a G-25 gel filtratio column (Fig.1).RSP was characterized by a profil with separated peaks,suggesting the present peptides were quite heterogeneous in size.Four major fractions named as RSP-1,RSP-2,RSP-3,and RSP-4 were obtained and lyophilized for further studies.

Fig.2.ABTS radical-scavenging activity of RSP and its fractions.RSP-1,RSP-2,RSP-3 and RSP-4 were four major fractions that was obtained and lyophilized from RSP by gel filtratio on Sephadex G-25 column.
3.2.ABTS radical-scavenging activity
ABTS is a stable organic free radical,which can directly reflec the scavenging ability of a sample by measuring the changes in absorbance [24].Fig.2 shows the ABTS radicalscavenging activity of RSP and each fraction.The scavenging rate of ABTS was enhanced at the improved concentration of RSP.The TEAC values of RSP and each fraction(RSP-1,RSP-2,RSP-3,or RSP-4)were 0.168,0.186,0.140,0.120 and 0.240,respectively.Among these fractions,RSP-4 exhibited the highest radical-scavenging activity,suggesting that RSP-4 has a high antioxidant capacity and could be used as an important resource during the development of functional foods.
3.3.ACE inhibitory activity

Fig.3.Inhibition of ACE activity by the RSP and its fractions.RSP-1,RSP-2,RSP-3 and RSP-4 at the concentration of 1 mg/mL were four major fractions that were obtained and lyophilized from RSP by gel filtratio on Sephadex G-25.
ACE catalyze the cleavage of the C-terminal dipeptide from the vasodilator bradykinin,to promote angio-activity and consequently increase blood pressure[25].ACE inhibitory peptides are considered to be useful for preventing hypertension.Fig.3 revealed that the ACE inhibitory activity of RSP(66.59%)was lower than that of RSP-4 (97.05%) at 1 mg/mL,suggesting that bioactive components were extracted during the separation process of RSP.The inhibitory efficien y of 60 ng/mL lotensin was 91.15%.The ACE inhibitory capability of RSP-4 at various concentrations was also investigated in the present study.When the concentration of RSP-4 was increased to 1.00 mg/mL,the ACE inhibitory activity was 97.05%(Fig.4),indicating that RSP-4 was a strong ACE inhibitor(IC50=0.19 mg/mL).

Fig.4.Inhibition of ACE activity by RSP-4.

Fig.5.Identificatio of amino acid sequence of RSP-4.(a)RPLC-PDA chromatogram of RSP-4.The resultant chromatograms had a major peak with retention time of 21.99 min as consistent with the target peptide and several small peaks from unidentifie substances.(b)The ESI/MS and MS/MS spectrum of RSP-4 separated from ultra performance liquid chromatography.
3.4.Identification of RSP-4
To elucidate the relationship between the bioactivity and structure of RSP-4,the molecular mass and sequence of RSP-4 were determined.Most food protein-derived peptides with bioactivities have relatively low molecular mass,generally less than 1500 D.The ESI/MS spectrum of a single positively charged ion with anm/zof 978 was shown in Fig.5(b),indicating the molecular mass of 977 D.Based on this molecular mass and MS/MS database search,the amino acid sequence of RSP-4 was deduced to be PFDSYFVC.According to our previous studies(data not shown),RSP-4 was rich in Asp,Leu,Phe,Tyr,and Pro,which are consistent with the results from mass spectrometric analysis.
4.Discussion
The radical-scavenging capability of RSP is associated with the substrate as the electron donor that can react with free radicals to generate more stable products and terminate the radical chain reaction [26].Aromatic amino acids including Tyr and Phe can be regarded as the direct radical scavenger.Tyr at the Cterminus of tripeptides reveals the highest antioxidant activity,but very weak peroxynitrite-scavenging activity[27].Phe plays an important role in the radical-scavenging activity due to its proton donation and stability in a resonance structure[28-30].Phe has been reported to have strong peroxidation inhibition by increasing the solubility of peptides in lipids [31,32].Leu is especially effective for inhibiting the oxidation of fatty acids tested in a linoleic acid model system [33].Asp has reported to interact with metal ions due to the negatively charged properties,thus inactivating the pro-oxidant activity of metal ions[34].
The polypeptide structure also reveals the limitation to the activity of these amino acid residues [35].Pro-His-His has been identifie as the active center [36]and antioxidant peptides derived from marine fish bovine skin and Hoki fis skin contain Gly-Pro[37],which may contribute to the activity.Our hypothesis is that higher hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity may be due to these structures.
ACE is a metal-peptide enzyme containing two binding sites of Zn2+.A common method used for a variety of antihypertensive peptides (including ACE inhibitors) is the incubation between Zn2+and ACE for the inactivation of ACE.The functions of an ACE inhibitory peptide are also correlated with its own spatial structure and amino acid compositions.The structure-activity relationship of naturally occurring ACE inhibitory peptides have indicated that the bioactivity of these ACE inhibitory peptides are resulted from Pro or aromatic amino acid residues[38].The presence of phenylalanine,tyrosine,or proline at the C-terminus offers tripeptides or dipeptides a higher potency of inhibitory activity [39].N-terminal amino acids with long-chain or hydrophobic can provide peptides strong inhibitory activity[40,41],while Phe,Asn,Ser,or Gly at the Nterminus can mitigate the activity.The hydrophilic-hydrophobic property of the peptide is also a critical factor affecting its inhibitory activity [42].Hydrophobic amino acids in ACE inhibitory peptides are proficien at the entrance of the active center sites so that hydrophilic amino acids can reduce the activity.The molecular electrostatic potentials of ACE inhibitory peptides are significantl different from those of inactive peptides,although a similar positive potential is existed in the same region at the C-terminal end[43].
5.Conclusion
RSP can be obtained from the enzymatic hydrolysis of rapeseed protein,and can be fractionated into four fractions with various molecular masses by gel filtratio on a Sephadex G-25 column.Fraction RSP-4 revealed the highest ABTS radical-scavenging activity and ACE-inhibiting capacity.Meanwhile,the amino acid sequence of RSP-4 was identifie as PFDSYFVC,with a molecular mass of 977 D.Based on these studies,RSP has high potential to develop as a valuable antioxidant peptide for food additives.However,further structural analysis of RAH still needs to be conducted.
Acknowledgements
This work was finicall supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.30800767 and 31271979),and the Opening Foundation of Large-scale Equipment in Tianjin University.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- About the Beijing Academy of Food Sciences
- Anti-inflammator and anti-arthritic activity of type-A procyanidine polyphenols from bark of Cinnamomum zeylanicum in rats
- Composition and antioxidant activity of anthocyanins isolated from Yunnan edible rose(An ning)
- Health risk from fluorid exposure of a population in selected areas of Tamil Nadu South India
- Effect of pH,temperature and heating time on the formation of furan in sugar-glycine model systems
- Red onion extract(Allium cepa L.)supplementation improves redox balance in oxidatively stressed rats

