多层螺旋CT血管成像在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的价值
张文洪 陈文华 邢 伟 王 祁
1.江苏省江阴市中医院 南京中医药大学江阴附属医院放射科,江苏江阴 214400;2.苏州大学附属第三医院放射科,江苏常州 213003
多层螺旋CT血管成像在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的价值
张文洪1陈文华2邢 伟2王 祁2
1.江苏省江阴市中医院 南京中医药大学江阴附属医院放射科,江苏江阴 214400;2.苏州大学附属第三医院放射科,江苏常州 213003
目的 通过与三维数字血管减影(DSA)对比,评价64层螺旋CT血管成像(CTA)对颅内动脉瘤尤其是<3mm动脉瘤的诊断价值。 方法选择怀疑有颅内动脉瘤的310例患者纳入研究,所有患者均行64层螺旋CTA和DSA检查。64层螺旋CTA技术参数:120 kV、250mAs、准直0.75 mm、重建层厚0.75mm和间隔0.4 mm。 结果 三维DSA作为诊断标准,在310例患者中,220例发现264个动脉瘤。CTA漏诊4个动脉瘤,7个动脉瘤在常规DSA检查中漏诊,但被64层螺旋CTA诊断,均得到三维DSA的证实。64层螺旋CTA诊断<3mm颅内动脉瘤的敏感性、特异性和准确性分别是94.0%、100.0%和97.9%。 结论 64层螺旋CTA对于颅内动脉瘤包括<3mm动脉瘤是一种准确的影像学检查方法,可以作为颅内动脉瘤诊断的首选影像检查。
颅内动脉瘤;CT血管造影术;数字减影血管造影;诊断
蛛网膜下腔出血临床常见,由颅内动脉瘤破裂引起者约占80%,早期诊断和治疗颅内动脉瘤可明显减少致残和致死率。 数字血管减影(digital subtraction angiography,DSA)是颅内动脉瘤诊断的“金标准”[1],然而,文献报道脑血管DSA检查中伴有0.5%的永久神经并发症和0.6%的严重非神经系统并发症,并且由于DSA操作时间长,检查过程中伴有更高脑动脉瘤再出血的发生率,这些缺点可能限制其应用[2]。因此,找到一种准确微创的影像学方法评价颅内动脉瘤相当重要。CT血管成像(CT angiography,CTA)是一种常用的脑血管非创伤性检查方法。关于16层螺旋CTA评价脑动脉瘤的研究较多[3-6],然而,16层螺旋CTA对于<3 mm颅内小脉瘤容易漏诊。随着64层螺旋CT广泛应用,64层螺旋CTA受到明显关注[7-9],本研究通过与DSA对比,评价64层螺旋CTA诊断颅内动脉瘤的价值,尤其是<3mm的小动脉瘤。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2008年7月~2011年7月南京中医药大学江阴附属医院和苏州大学附属第三医院310例怀疑动脉瘤患者纳入研究,男145例,女165例,年龄最小4岁,最大87岁,平均52岁。入院原因:蛛网膜下腔出血(subarachnoid hemorrhage,SAH)216例,SAH伴有脑室出血和(或)颅内血肿47例,颅内自发血肿20例,脑室出血、占位、头痛和眼睑下垂27例。
1.2 64 层螺旋CTA检查
310 例患者使用西门子Somaton Sensation 64层CT扫描机,扫描参数:层厚0.75 mm,重建间隔 0.40 mm,100 kv和200mAs,扫描范围从第一颈锥至颅顶。使用高压注射器团注85~100mL非离子型对比剂三代(350mg I/mL),流率3.5mL/s,动脉期扫描延迟采用Bolus tracking技术。17例患者因不配合检查静脉注射少量镇静剂。
1.3 DSA检查
使用西门子AXIOM Artis dTA数字血管造影机,经股动脉穿刺插管,310例患者均应用Seldinger技术行动脉内血管造影,常规血管造影过程通过标准诊断导管完成,如果怀疑有动脉瘤存在,在导管移出血管前行三维数字血管造影(3D rotationalangiography,3DRA)。数字血管造影机的视野是38 cm(前后位)和30 cm(侧位和斜位),空间分辨率为0.32 mm×0.32mm。20例患者因不配合检查行全身麻醉。
1.4 图像分析
所有CTA图像及DSA脑血管造影图像均由4名神经放射学专家独立进行分析评价。CT图像观察者通过工作站(Leonardo; Siemens Medical Systems)进行血管成像,成像重建方法为容积再现技术(volume rendering,VR)和最大密度投影(maximum intensity projection, MIP)重建,每例患者的图像分析10~15min(平均12 min)。CTA观察者在CT工作站上进行评价,测量每个动脉瘤的最大直径,分成3个等级:大(>8 mm)、中(3~8mm)和小(<3 mm)。 两名神经放射学专家有重点地评价两种检查方法对动脉瘤的显示能力,如对瘤体定位显示是否确切,瘤体、瘤颈和载瘤动脉及颅骨结构之间的三维空间关系等。当CTA漏诊颅内动脉瘤时,3DRA图像被用来测量动脉瘤的大小。另外两名神经放射科专家在DSA荧光屏和3D工作站 (Syngo Inspace;Siemens Medical Systems)进行评价,其重点评价有无颅内动脉瘤,如果有颅内动脉瘤则重点评价动脉瘤的位置、大小和形态等。文献报道3DRA可以避免常规DSA的限制[8-10]。因此,在本研究中将3DRA作为诊断标准。
1.5 统计学方法
采用Stata 9.2统计学软件进行数据分析,计数资料用率表示,采用四格表评价64层CTA和常规DSA的假阴性、假阳性、真阳性和真阴性,通过与3DRA结果进行比较,计算64层CTA和常规DSA发现颅内动脉瘤的准确性、敏感性、特异性、阳性和阴性预测率[11],计算单侧97.5%和双侧95%可信区间(CI),以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
据3DRA参考标准,310例疑似病例中,69例阴性结果,动静脉畸形16例,烟雾病5例,颅内动脉瘤220例,其中,1个动脉瘤者185例(图1),2个动脉瘤者29例,3个动脉瘤者3例,4个动脉瘤者3例。动脉瘤最常见的部位是后交通动脉(33%,88/264),其次是前交通动脉(28%,74/264)。 79%(210/264)的动脉瘤呈囊状,5%(12/264)的动脉瘤呈梭形,16%(42/264)的动脉瘤呈不规则形。动脉瘤的平均直径为5.9mm(1.2~38.0mm),平均瘤体为 4.6mm(1.0~29.6mm),平均瘤颈为 3.5mm(1.1~13.1mm)。
两名CTA评价者在216例患者发现260个动脉瘤,漏诊4个 (图1),没有一例颅内动脉瘤被认为是假阳性。两名CTA评价者结果一致,见表1。常规DSA在215例患者中发现257个动脉瘤,漏诊7个(图2),没有一例颅内动脉瘤被认为是假阳性。常规DSA检查诊断动脉瘤的详细统计资料见表1。虽然64层螺旋CTA检查结果不同于3DRA,但是两者之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.13>0.05)。
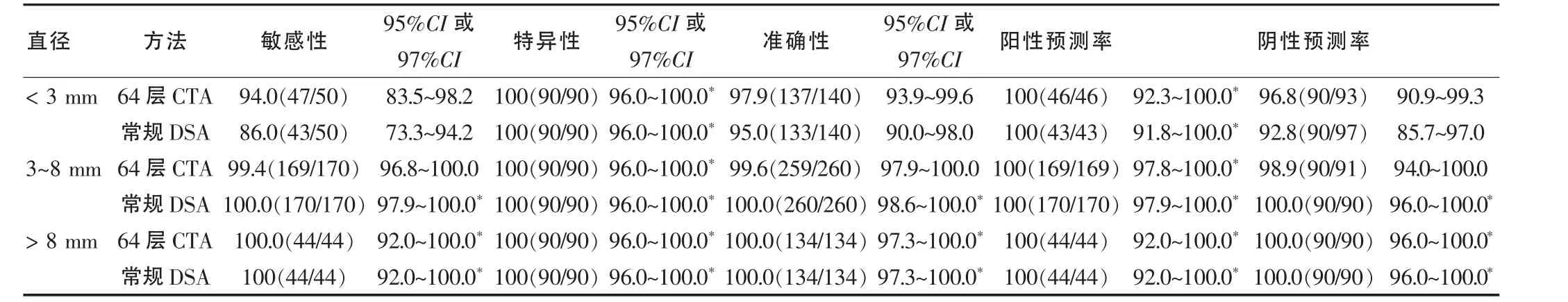
表1 64层螺旋CT血管成像和常规数字血管减影诊断动脉瘤的敏感性、特异性、准确性、阳性预测率和阴性预测率[%(n1/n2)]
3 讨论
目前关于CTA诊断颅内动脉瘤的研究较多,但是许多文献表明对于颅内小动脉瘤CTA诊断的敏感性相对较低。Teksam等[12]利用4层CT检查了103例患者,共检出49个小动脉瘤(直径<5 mm),对于全部小动脉瘤的敏感性、特异性和准确性分别是85%、65%和79%。Yoon等[13]利用16层螺旋CTA检查了85例患者,共检出85个动脉瘤,16层螺旋CTA诊断颅内动脉瘤总的敏感性、特异性和准确性分别为92.5%、93.3%和92.6%,但是对于直径<3 mm的动脉瘤,16层螺旋CTA的敏感性为74.1%和77.8%。另一项研究表明,16层螺旋CTA诊断颅内动脉瘤的敏感性和特异性分别都为96.2%和100.0%,对于直径<3 mm的动脉瘤,16层螺旋CTA的敏感性为91.7%。目前关于64层螺旋CTA诊断颅内小动脉瘤的敏感性有所提高。Pozzi-Mucelli等[14]利用64层螺旋CTA检查了29例患者,共检出26个动脉瘤,其诊断颅内动脉瘤的敏感性、特异性、阳性、阴性预测值和诊断准确率分别为92.8%、100.0%、100.0%、99.4%和 99.5%。McKinney等[8]利用64层螺旋CTA检查了63例患者,共检出41个动脉瘤,通过与三维DSA比较研究表明,直径<4 mm的颅内动脉瘤64层螺旋CTA的敏感性为92.3%,而其对直径>4mm的颅内动脉瘤敏感性为100.0%。
本研究中64层螺旋CTA诊断<3 mm的颅内微小动脉瘤敏感性为94.0%,较文献报道有所提高,可能是由于64层螺旋CT技术提供了更好的后处理软件,层厚更薄,并缩短了采集时间,此外,还可能与评价专家具有丰富的CTA评估经验密切相关。本研究中仅有4个动脉瘤被CTA漏诊,但当图像进行回顾分析时,其中3个后交通小动脉瘤可以清楚显示。随着医师经验的增加,漏诊这种动脉瘤的机会将会越来越少[15]。另外1个小脑上动脉瘤仍不能明确诊断。分析后交通动脉瘤漏诊的可能原因是CTA评价专家将后交通动脉瘤误认为是动脉圆椎(图1)。在以往的文献报道中也发现有将后交通动脉瘤误认为是动脉圆椎,或将动脉圆椎误诊断为后交通动脉瘤的案例。小脑上动脉瘤漏诊的原因是该小脑上动脉瘤位于动脉远端且载瘤动脉较细,动脉早期不易清楚显示,回顾分析DSA动态图像也发现动脉早期不能明确诊断该动脉瘤,这也是本研究中诊断中等大小动脉瘤的准确性稍低的原因。
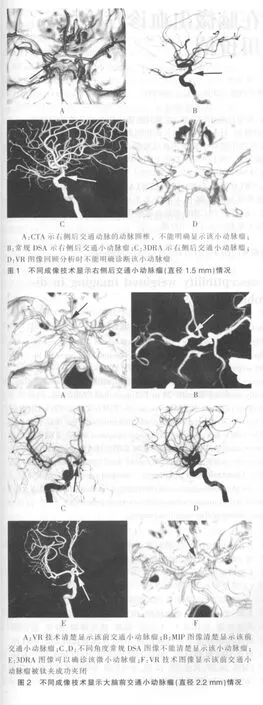
在以往的文献报道中,一般认为传统DSA可以作为诊断颅内动脉瘤的“金标准”[6,16]。然而,近几年3DRA已经广泛应用,3DRA和传统DSA结合可以比单独运用传统DSA发现更多的脑动脉瘤[17]。另外有文献中报道,当CTA发现动脉瘤而DSA没有检出时,这些动脉瘤将被诊断为假阳性[1,6]。事实上,这种动脉瘤不一定是假阳性,常规DSA常常会漏诊一些非常小的颅内动脉瘤。在笔者以前的研究中,有3个小动脉瘤在CTA图像可以清楚显示,常规DSA不能明确诊断,但这3个小动脉瘤患者SAH明显,临床高度怀疑有破裂动脉瘤的存在,最后通过外科手术证实了这3个小动脉瘤存在[4]。在本研究中,有7例小动脉瘤常规DSA漏诊,但CTA和3DRA图像可以清楚显示(图2)。当对常规DSA图像进行回顾性分析时,其中5个小动脉瘤能够诊断,但另外2个小动脉瘤仍然不能显示(图2)。漏诊的主要原因是常规DSA二维图像的限制和与动脉瘤直径较小有关。如果常规DSA漏诊的小动脉瘤没有被3RDA证实,这些动脉瘤将会被认为是假阳性。因此,笔者研究认为,3DRA应该作为诊断颅内动脉瘤的金标准。
总之,64层CTA对于颅内动脉瘤诊断具有很高的价值,能够作为颅内动脉瘤诊断的首选影像学检查方法。另外,笔者认为3DRA应该作为诊断颅内动脉瘤的金标准。
[1]Teksam M,McKinney A,Casey S,et al.Multi-section CT angiography for detection of cerebral aneurysms[J].AJNR 2004,25(9):1485-1492.
[2]Willinsky RA,Taylor SM,TerBrugge K,etal.Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography:prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature[J].Radiology,2003,227(2):522-528.
[3]ChenW,Wang J,XingW,etal.Accuracy of 16-rowmultislice computerized tomography angiography for assessmentof intracranial aneurysms[J].Surg Neurol,2009,71(1):32-42.
[4]Chen W,Wang J,XingW,etal.Accuracy of 16-row multislice computed tomographic angiography for assessment of small cerebral aneurysms[J].Neurosurgery,2008,62(1):113-121.
[5]毛俊,王艳萍,彭秀斌,等.16层螺旋CT血管成像在颅内血管性病变的临床应用[J].中国 CT 和 MRI杂志 2007,5(2):10-12.
[6]Tipper G,Jmuk I,Price SJ,et al.Detection and evaluation of intracranial aneurysms with 16-row multislice CT angiography [J].Clin Radiol,2005,60(5):565-572.
[7]Li Q,Lv F,Li Y,et al.Evaluation of 64-section CT angiography for detection and treatment planning of intracranial aneurysms by using DSA and surgical findings[J].Radiology,2009,252(3):808-815.
[8]McKinney AM,Palmer CS,Truwit CL,et al.Detection of aneurysms by 64-section multidetector CT angiography in patients acutely suspected of having an intracranial aneurysm and comparison with digital subtraction and 3D rotational angiography[J].AJNR,2008,29(3):594-602.
[9]Lubicz B,Levivier M,Francois O,et al.Sixty-four-row multisection CT angiography for detection and evaluation of ruptured intracranial aneurysms:interobserver and intertechnique reproducibility[J].AJNR,2007,28(10):1949-1955.
[10]Dammert S,Krings T,Moller-Hartmann W,et al.Detection of intracranial aneurysms with multislice CT:comparison with conventional angiography[J].Neuroradiology,2004,46(6):427-434.
[11]Walter SD.Methods of reporting statisticalResultsfrom medical research studies[J].Am JEpidemiol 1995,141(10):896-906.
[12]Teksam M,McKinney A,Cakir B,et al.Multi-slice CT angiography of small cerebral aneurysms:is the direction of aneurysm important in diagnosis[J].European Journal of Radiology,2005,53(3):454-462.
[13]Yoon DY,Lim KJ,Choi CS,et al.Detection and characterization of intracranial aneurysms with 16-channelmultidetector row CT angiography:a prospective comparison of volume-rendered images and digital subtraction angiography[J].AJNR,2007,28(1):60-67.
[14]Pozzi-Mucelli F,Bruni S,Doddi M,et al.Detection of intracranial aneurysms with 64 channel multidetector row computed tomography:comparisonwith digital subtraction angiography[J].European Journal of Radiology,2007,64(1):15-26.
[15]Pedersen HK,Bakke SJ,Hald JK,et al.CTA in patients with acute subarachnoid haemorrhage.A comparative study with selective,digital angiography and blinded,independent review[J].Acta Radiol,2001,42(1):43-49.
[16]Teksam M,McKinney A,Cakir B,et al.Multi-slice computed tomography angiography in the detection of residual or recurrent cerebral aneurysmsafter surgical clipping[J].Acta Radiol,2004,45(5):571-576.
[17]郭晓明,李安民,王星星,等.3D-DSA在颅内动脉瘤诊断中的临床应用[J].中华神经外科杂志,2003,19(5):364-367.
Value ofmultislice CT angiography in diagnosis of intracranial aneurysms
ZHANGWenhong1 CHENWenhua2 XINGWei2 WANGQi2
1.Department of Radiology,Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangyin City Jiangyin Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine,Jiangsu Province,Jiangyin 214400,China;2.Department of Radiology,the Third Affiliated Hospital of Suzhou University,Jiangsu Province,Changzhou 213003,China
Objective To assess the diagnostic value of 64-row multislice CT angiography (CTA)for intracranial aneurysms,especially small aneurysms (<3 mm)by comparing with three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography(DSA).MethodsA total of 310 patients suspected intracranial aneurysm were included in this study and successively underwent 64-slice CTA and DSA examination.The 64-slice CTA data acquisition and reconstruction parameters were performed according to the following protocol:120 kV,250 mAs,collimation 0.75mm,postprocessing reconstruction 0.75 mm and interval 0.4 mm.ResultsThree-dimensional DSA was considered as the gold standard,and among 310 cases of patients,264 aneurysms were detected from 220 patients.4 aneurysms were missed when by CTA detection.7 aneurysms were not clearly displayed at conventional DSA,but diagnosed by 64-slice CTA,and allmissed aneurysmswere proved by three-dimensional DSA.The sensitivity,specificity,and accuracy of 64-slice CTA in detecting less than 3 mm aneurysms were 94.0%,100.0%and 97.9%respectively.Conclusion64-slice CTA is an accurate imaging examination for intracranial aneurysms detection including less than 3 mm aneurysms.It can be used as a preferred imaging examination for intracranial aneurysm diagnosis.
Intracranial aneurysm;Computerized tomography angiography;Digital subtraction angiography;Diagnosis
R739.41
A
1673-7210(2012)12(a)-0091-04
江苏省高校自然科学研究面上资助项目 (项目编号:11KJB320012)。
2012-08-17 本文编辑:程 铭)

