利用量子逻辑网络实现1→2最佳量子克隆
张大伟
(营口大学园管理委员会,辽宁 营口115014)
利用量子逻辑网络实现1→2最佳量子克隆
张大伟
(营口大学园管理委员会,辽宁 营口115014)
提出了1个利用量子逻辑网络来实现1→2最佳量子克隆的量子克隆机.该方案利用受控旋转和受控非操作来实现1→2的最佳量子克隆,并通过选择不同的旋转角度实现通用克隆、相位协变克隆和x-z面上的实态克隆.
克隆;旋转;受控非
0 引言
量子信息的出现源自于量子力学与信息技术的有效结合,量子力学为处理量子信息问题提供了强有力的工具,但也带来了一些限制.量子信息学中的非克隆理论[1],使得量子信息学迥异于经典信息学,它意味着不可能对1个任意的输入态进行完美的克隆[2-3].量子克隆在量子密码术和量子通信方面具有非常重要的作用[4-7].1996年,Buzek和Hillery[2]首先提出了实现二维空间下的量子态克隆方案,细致地描述了对于1个完全未知态进行克隆的过程,其输出端可以得到保真度为5/6(≈0.833)的独立于输入态的通用克隆(UQCM).Brub等[8]在2000年提出了对于输入信息部分未知时的相位协变克隆(PCCM),其保真度为年,樊恒等[9]提出了对于另1种输入信息部分已知时的实态克隆(RSCM),其保真度也是最近,文献[10-16]报道了多种实现量子克隆的方案,而且部分学者还利用现有的多种物理系统,提出了1→M 的量子克隆和远程克隆方案[17-18].受Buzek等[11]网络方案的启发,本文提出了1个实现量子克隆的网络方案:利用受控旋转和受控非门操作来实现二维空间下的1→2最佳量子克隆,通过选择不同的旋转角度,3种类型的量子克隆都可以实现.
1 3种形式的最佳克隆
在量子力学中,每1个量子态都可以看成是对应布洛赫球面上的1个点,可表示为

其中α,β,φ∈[0,2π).克隆可以理解为是向空白的量子态上复制信息的过程,对1个初始输入态的信息了解的越多,克隆的保真度就越高.目前,常见的量子克隆机有以下3种形式:
1)初始信息完全未知(α,β,φ完全未知).此时的克隆过程称为通用量子克隆,可表示为
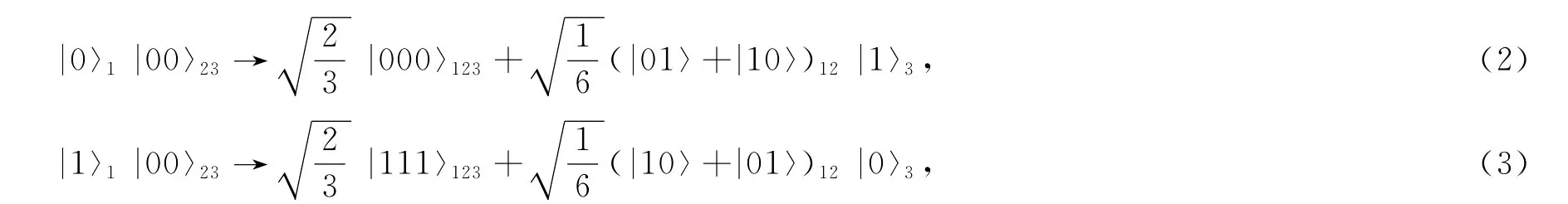
其中的角标1、2、3分别表示要克隆的粒子态、空白粒子态和辅助粒子态.输出2个粒子态1和2的约化密度算符是相同的,即


3)对于另1种克隆变换,初始条件限定于φ=0,α,β∈[-1,1],α和β都是实数,此时初始信息被限定在x-z赤道面上,可理解为输入态为纯态[9-10].此时的克隆变换形式为
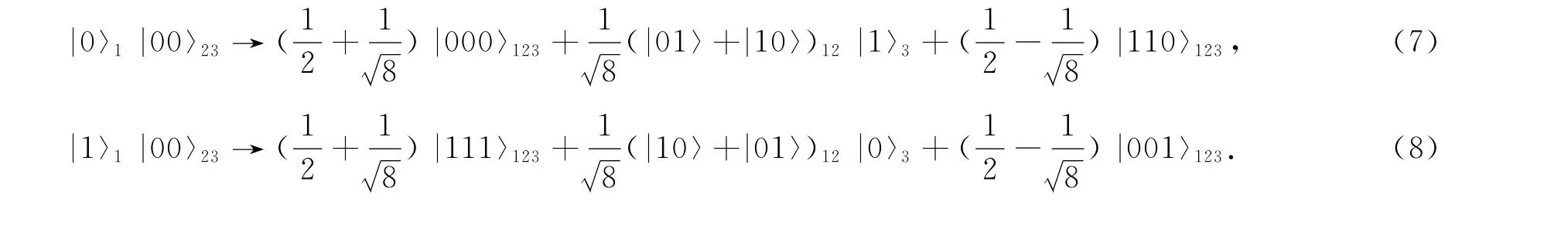
上述3种不同的克隆都是对应于不同的初始条件得到的,其保真度都是独立于输入态.
2 3种量子克隆实现方案
受文献[11]中网络方案的启发,本文提出的网络方案如图1所示,整个逻辑网络分为制备(prep)和克隆(cloning)2个部分.图中的1、2、3分别表示输入、空白和辅助粒子.

图1 最佳1→2量子克隆网络
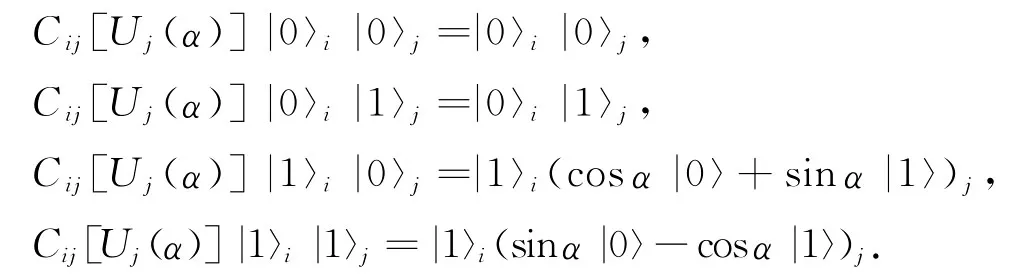
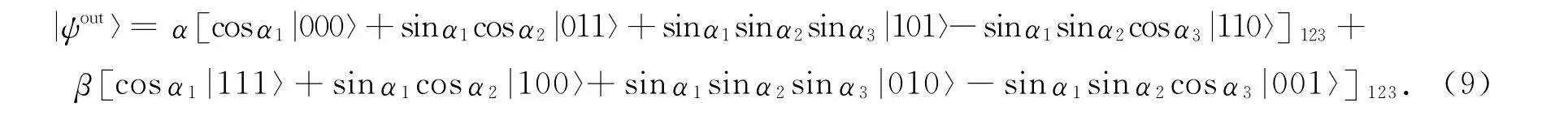
对于3种不同类型的克隆,需要对其所得态系数的角度进行确定[9].从(9)式可以看出,量子态前的系数之间都存在着相互联系.将输出态中的系数定义为:cosα1=a,sinα1cosα2=b,sinα1sinα2sinα3=c,-sinα1sinα2cosα3=d.当选择旋转角度则输出态变为

即得到了通用量子克隆的形式.而对于均衡相位协变克隆来说,只需将旋转角度定为则系统的输出态为


此时对应的克隆形式即为最佳实态克隆.
3 结论
本文利用量子网络实现了通用量子克隆、相位协变量子克隆以及实态克隆3种不同类型的1→2最佳量子克隆.与Buzek等的方案相比,本文方案用了更少的操作.2001年,黄运峰等[19]利用极化分束器和半波片等线性光学设备实现了通用量子克隆;2002年,文献[20-21]报道了利用核磁共振技术和量子光学方法的通用克隆实验.本方案中所需要的单比特和两比特受控操作,可以通过目前所广泛应用的核磁共振技术、线性光学、腔QED技术等物理模型来实现[22-23],因此本文方案在实验上具有可操作性.
[1] Wootters W,Zurek W H.A single quantum cannot be cloned[J].Nature,1982,239:802.
[2] Buzek V,Hillery M.Quantum copying:beyond the no-cloning theorem[J].Phys Rev A,1996,54:1844.
[3] 段路明,郭光灿.量子态的概率克隆和认证[J].研究快讯,1999,28(10):35-36.
[4] Ekert A.Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem[J].Phys Rev Lett,1991,67(6):661-663.
[5] Bennett C H.Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states[J].Phys Rev Lett,1992,68(21):3121-3124.
[6] Pan J W,Gasparonis,Aspelmeyer M,et al.Experimental realization of freely propagating teleported qubits[J].Nature(London),2003,421:721.
[7] Zhao Z,Chen Y A,Zhang A N,et al.Experimental demonstration of five photon entanglement and open-destination teleportation[J].Nature(London),2004,430:54-58.
[8] Brub D,Cinchetti M,D’Ariano G M,et al.Phase-covariant quantum cloning[J].Phys Rev A,2000,62(1):012302-012307.
[9] Fan H,Mastumoto K,Wang X B,et al.Quantum cloning machine for equatorial qubits[J].Phys Rev A,2001,65:012304.
[10] Gisin N,Massar S.Optimal quantum cloning machines[J].Phys Rev Lett,1997,79(11):2153-2156.
[11] Buzek V,Braunstein S L,Hillery M,et al.Quantum copying:a network[J].Phys Rev A,1997,56(5):3446-3452.
[12] Zhang W H,Wu T,Ye L,et al.Optimal real state cloning in d-dimensions[J].Phys Rev A,2007,75(4):044303-044306.
[13] Zhu A D,Yeon K-H,Yu S-C.Optimal universal and phase-covariant cloning machines with quantum-dot spins in cavity QED[J].J Phys B,2009,42:235501-235505.
[14] Zhang D W,Shao X Q,Zhu A D.Quantum logic network for cloning a state near a given one based on cavity QED[J].Chin Phys Lett,2008,25:1954.
[15] Zhang W H,Yu L B,Ye L.Optimal asymmetric phase-covariant quantum cloning[J].Phys Lett A,2006,356:195-198.
[16] Zou X B,Li K,Guo G C.Linear optical scheme for implementing the universal and phase-covariant quantum cloning machines[J].Phys Lett A,2007,366:36-41.
[17] Meng F Y,Zhu A D,Yeon K-H,et al.Implementing 1→M economical phase-covariant cloning and telecloning in cavity QED[J].J Phys B,2009,42:165504.
[18] Zhou Y H,Wang L.Scheme for implementing 1→M symmetric economical phase-covariant telecloning based on quantum logic network[J].J Mod Opt,2012,59:658-662.
[19] Huang Y F,Wan L L,Li C F,et al.Optical realization of universal quantum cloning[J].Phys Rev A,2001,64(1):012315-012319.
[20] Cummins H K,Jones C,Furze A,et al.Approximate quantum cloning with unclear magnetic resonance[J].Phys Rev Lett,2002,88(18):187901-187904.
[21] Lamas-Linares A,Simon C,Howell J C,et al.Experimental quantum cloning of single photons[J].Science,2002,296(5568):712-714.
[22] Song K H,Zhou Z W,Guo G C.Quantum logic gate operation and entanglement with superconducting quantum interference devices in a cavity via Raman transition[J].Phys Rev A,2005,71(5):052310-052313.
[23] Shao X Q,Zhu A D,Zhang S,et al.Efficient scheme for implementing an N-qubit Toffoli gate by a single resonant interaction with cavity quantum electrodynamics[J].Phys Rev A,2007,75(3):034307-034310.
Implementing 1→2 optimal quantum cloning based on quantum logic network
ZHANG Da-wei
(Management Committee of Yingkou University Zone,Yingkou 115014,China)
A quantum logic network is proposed to implement 1→2 optimal quantum cloning,which compose of controlled-rotation operations and controlled-NOT operations.We can implement universal quantum cloning(UQCM),phase-covariant cloning(PCCM)and real state cloning of x-z equatorial plane(RSCM)by choosing different rotation angles.
cloning;rotation;controlled-NOT
O431
A
1004-4353(2012)03-0204-04
20120627
张大伟(1983—),男,助教,研究方向为量子信息.

