16SrRNA gene based genospecies identification of Leptospirastrains isolated from Apodemus agrarius in Guizhou Province,2011
LI Shi-jun,WANG Ding-ming,ZHANG Chui-cai ,LI Xiu-wen,TIAN Ke-cheng,LIU Ying,TANG Guang-peng,JIANG Xiu-gao
(1.Institute of Communicable Disease Control and Prevention,Guizhou Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention,Guiyang550004,China;2.Institute of Communicable Disease Prevention and Control,Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention,Beijing102206,China)
Leptospirosis is one of the most widespread zoonoses and is caused by infection with pathogenic spirochetes of theLeptospiragenus[1].The disease in human is most frequent in developing countries,and the spectrum ranges from subclinical infection to severe symptoms of multiorgan dysfunction with high case-fatality rates,reaching a mortality rate as high as 70%in the case of severe pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome[2-5].In contrast,most of the infected mammalian reservoirs,such as rodents,only presents mild chronic disease or are asymptomatic,and shed infectious organisms in the urine for their lifetime[6,7].Leptospires dwell in the renal tubules of their maintenance hosts and are excreted into the environment with the urine.Humans may be infected indirectly from animals by contacting with contaminated water,soil or mud in a moist environment,or by direct contact from urine,fresh carcasses or organs[8].Rodents are recognized as important mammal reservoirs ofLeptospiraspp[9-10].Infection may occur early in the lifespan of the animal and the chances of infection increases with age[1,11].After infection,the spirochetes are localized in the kidneys and excreted by urine discontinuously[1,11].Once excreted,the bacteria can survive in a favorable environment for months or years before infecting new hosts,including humans.So,surveillance on carrier status of reservoir hosts and analysis on the characteristic of causative agents contribute to the clinic laboratory diagnosis,active surveillance,outbreak investigation and source tracking for leptospirosis.
There were several cases of leptospirosis patients as well as death cases reported in Rongjiang,Jingping and Liping counties,Southeast of Guizhou,every year in recent decade,which were only clinically and serologically diagnosed.For example,127human leptospirosis cases including 28 death cases reported in Liping County from 2001to 2008[12].However,L.interroganswere never isolated from patients in recent years,and the epidemic bacteria genospecies remains unclear.
Traditionally,several hundred serovars ofLeptospirawere classified into two species,(Leptospira interrogans(L.interrogans)andLeptospira biflexa(L.biflexa)[13],which contained pathogenic and saprophytic strains,respectively.PathogenicLeptospiraare classified into more than 200serovars based on serological methods[15].And based upon the most recent DNA-based classification,to date 17Leptospiraspecies have been described,which can be divided into pathogenic(i.e.,having the potential to cause disease in humans and animals)and saprophytic(i.e.,free living and considered not to cause disease)species.Some strains show unclear pathogenicity and are termed intermediates[15].Therefore,identification ofLeptospiragenospecies is important for the control and prevention of leptospirosis in the local area.
The objective of this study was to reveal the etiologic characteristics of leptospirosis in Guizhou Province by 16SRNA gene analysis and genospecies identification ofLeptospirastrains isolated from the rodents in the local epidemic area,which will contribute to clinical laboratory diagnosis,active surveillance,outbreak investigation and source tracking for leptospirosis.
Materials and Methods
Leptospiral strains and cultivation
FourLeptospirastrains(Table 1)used in this study were strain JP13,JP15,JP19and LP62isolated fromApodemus agrariusin the rice-field environment of epidemic region of leptospirosis in Guizhou Province,which was identified as pathogenicLeptospiraby PCR and cultivated with liquid Ellinghausen-McCullough-Johnson-Harris (EMJH)medium (Difco,USA)at 28℃[14].

Tab.1 Background information of Leptospirastrains used in this study
16SrRNA gene sequencing
DNA was extracted from cultures of strains ofLeptospiraceaeusing DNA Extraction Kit(SBS GenenTech,Beijing,China)according to the manufacturer's directions,and the DNA concentration were diluted to 1ng/μL with ND-1000Spectrophotometer(Nanodrop,USA).The 16SrRNA genes were amplified from the purified DNA using the PCR Kit(TaKaRa,Otsu,Japan).Briefly,each 50μL reaction system contained 19μL of deionized water,25μL of PreMix Taq,2μL of DNA,and 2μL of fD1 (forward:5′-CCG AAT TCG TCG ACA ACA GAG TTT GAT CCT GGC TCAG-3′)and rP2 (reverse:5′-CCC GGG ATC CAA GCT TAC GGC TAC CTT GTT ACG ACTT-3′)prim-ers with concentrations of 5pmol/μL corresponding to positions 8and 1 492,respectively[13].Amplification was performed on an TProfessional PCR thermocycler at 94℃for 5min,followed by 35cycles of 94℃for 15s,50℃for 5s,and 72℃for 90s,with a final single extension of 72℃for 5 min,and then held at 4℃.Amplified products were characterized by electrophoresis of 1μL of each reaction on a 1.2%agarose gel for 30min at 85V.The PCR products were sent to TaKaRa Company(Dalian,China)for purification,sequencing and sequence assembly.
Phylogenetic analysis
The homologies among the 16SrRNA gene sequences obtained from leptospires were analyzed using the MegAlign program in the DNAStar software package(Inc.,United States).Phylogenetic trees were constructed for the 16SrRNA gene sequences of leptospires isolated fromApodemus agrariusin Guizhou and representative strains of 17Leptospiragenospecies,Leptonema illiniandTurneriella parvausing the Neighbor-Joining(NJ)method[13].The 16SrRNA gene sequences of the representative strains of 17genospecies used for comparison with those obtained in this study were downloaded from the NCBI database(Table 2).
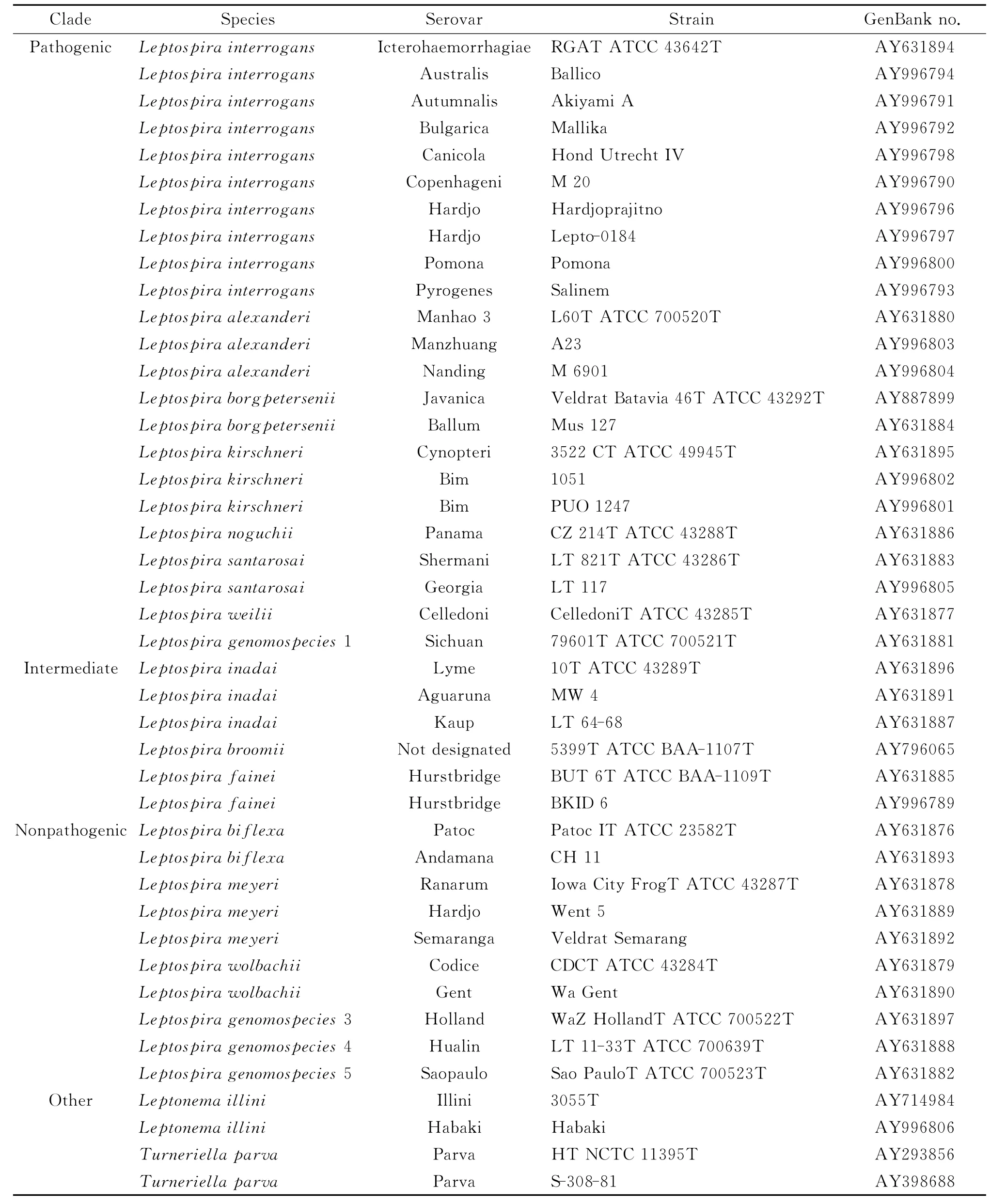
Tab.2 GenBank accession numbers of leptospiral 16Sribosomal RNA gene sequences used in this study[13]
Results
16SrRNA gene sequence analysis
Nearly full length (1 492bp)of 16SrRNA gene for strain JP13,JP1,JP19and LP62were amplified by using the primer pair of rP2and fD1(Figure 1)and subsequently successfully sequenced.These sequences were compared to each other and to the sequence of strains from the seventeen genospecies ofLeptospiraceae[13].The alignment showed that the homogeny of sequences within the four strains in this study and the three strains isolated fromRattus tanezumiin Rongjiang in 2007was 100%,the homogenies among the four isolates and strains from pathogenic genospecies,includingLeptospira alexanderi,Leptospira borgpetersenii,Leptospira interrogans,Leptospira kirschneri,Leptospira noguchii,Leptospira santarosai,Leptospira weilii,andLeptospiragenomospecies 1,were from 98.8%to 99.9% ,with the highest percentage (99.9%)compared withLeptospira interrogansserovar icterohaemorrhagiae strain RGAT ATCC 43642T,while the homogenies among the four isolates and strains of intermediate genospecies,includingLeptospira inadai,Leptospira broomii,andLeptospira fainei,were from 95.0%to 95.2%,reaffirming the high degree of species conservation among spirochetes.But the homogenies of the four isolates andLeptospirareference strains belonging to the nonpathogenic genospecies,such asLeptospira alexanderi,Leptospira borgpetersenii,Leptospira noguchii,were only 88.4%-88.6%.
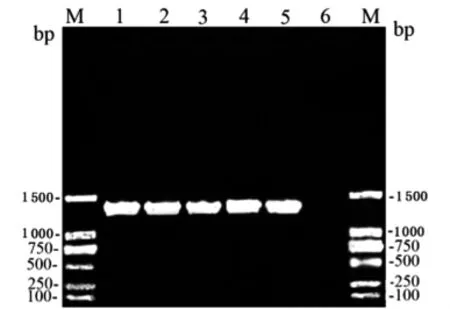
Fig.1 PCR detection results of leptospiral 16SrRNA gene with the amplification fragment at the sides of 1 492bp
Phylogenetic tree of 16SrRNA gene
Phylogenetic analysis of 16SrRNA gene sequences showed that leptospiral strains isolated fromApodemus agrariusin Jinping(strain JP13,JP15and JP19),Liping(strain LP62)in 2011and the representative strains of 17Leptospiragenospecies,Leptonema illiniandTurneriella parvaformed four main clusters(pathogenic,intermediate,nonpathogenic,and other)of species(Figure 2).The isolates of Guizhou as well as the strains from the eight pathogenic species(Leptospira alexanderi,Leptospira borgpetersenii,Leptospira interrogans,Leptospira kirschneri,Leptospira noguchii,Leptospira santarosai,Leptospira weilii,andLeptospiragenomospecies 1)group could be divided into the pathogenic clade,in which the seven strains from Guizhou were most related to genospeciesLeptospira interrogans,such asLeptospira interrogansserovar icterohaemorrhagiae strain RGAT ATCC 43642T,L.interrogansserovar Autumnalis,strain Akiyami A and so on.The intermediate clade comprised speciesLeptospira inadai,Leptospira broomii, andLeptospira fainei,while speciesLeptospira biflexa,Leptospira Meyer,Leptospira wolbachii,Leptospiragenomospecies 3,Leptospiragenomospecies 4,andLeptospiragenomospecies 5formed the nonpathogenic clade.In addition,Leptonema illiniandTurneriella parvawere included in another clade separated clearly from the pathogenic,intermediate and nonpathogenic clade.
Discussion
The present study demonstrates that nearly full length of 16SrRNA gene of the four leptospires isolated from the kidney ofApodemus agrariuswere sequenced in Jinping and Liping counties,Guizhou Province,Southwest China.Homogeny analysis and phylogenetic tree indicated the four isolates belonged to genospeciesL.interrogans,which is consistent with the identification results of Microscopic Agglutination Test(MAT).
There were several cases of leptospirosis patients as well as death cases reported in Guizhou Province in every year of recent years.For example,according to the China National System for Disease Control and Prevention,twelve human leptospirosis cases with one death case were reported in Guizhou in 2011.However,these reported cases were only clinically and serologically diagnosed,and the source of infection and the characteristic of epidemic bacteria remain unclear.
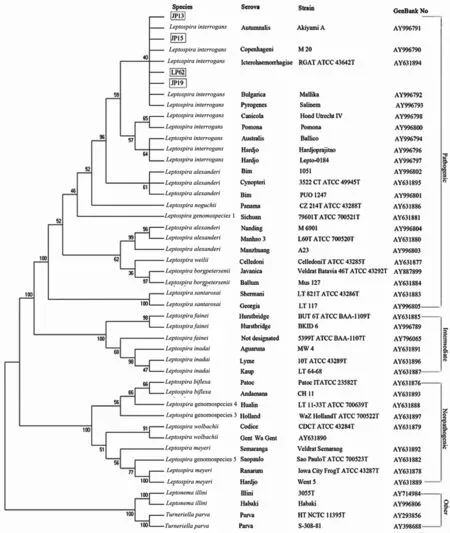

Fig.2 Phylogenetic tree of leptospiral isolates and Leptospiraceae 16SrRNA gene sequences
Guizhou has been proved to be the old foci of leptospirosis in China[15-17].Liping,Rongjiang and Jinping counties,belonging to Qiandongnan Prefecture,were the high-incidence region of leptospirosis in Guizhou Province.For example,14 126 human leptospirosis cases with 534deaths were reported in Qiandongnan Prefecture from 1958to 2005.Investigation on the epidemiology of leptospirosis in Liping county,a county in southeast Guizhou,revealed that a total of 127leptospirosis cases with 28deaths were reported from 2001to 2008[12].And China National System for Disease Control and Prevention revealed that the incidence peak time was from September to October,but these reported patients were only clinically diagnosed.
Rodents are recognized as important mammal reservoirs ofLeptospiraspp[9,10].A study performed in 1992in Guizhou Province revealed that the animal carrier,Apodemus agrarius,was a very important reservoir host of leptospirosis,with a carrier rate of 7.36%,accounting for 95.84%of all the checked rats.The geographic distribution of host animal in local area had a close relation with cases of leptospirosis aggregate distribution[16].However,few studies on the carrier status in recent year were reported.To trace the source of infection,three strains(JP13,JP15and JP19)ofLeptospirawere isolated fromApodemus agrariusin Jinping County and one strain(LP62)from Liping County.Detection results suggest thatApodemus agrariusmay be the main carrier ofLeptospirain the localities.
MAT and cross-agglutinin absorption test(CAAT)are,traditionally,used to identify leptospires.However,these techniques are laborious and time-consuming,requiring the maintenance of a collection of more than 200reference strains and correspondent rabbit antisera.Based upon DNADNA hybridization data,the genus is now classified into 17species[13].Morey RE et al[13]determined nearly full-length 16SrRNA gene sequences of approximately 1 430bp from well-characterized type strains and representative serovars ofLeptospiraspecies for species identification of leptospires,and concluded that 16SrRNA gene sequencing was a powerful method for identification in the clinical laboratory and offers a simplified approach to the identification ofLeptospiraspecies.In this study,the four strains ofLeptospirawere identified as genospeciesL.interrogansby using 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis.It is consistent with the species identification result for the threeLeptospiraisolated fromRattus tanezumiin Rongjiang County in 2007[18]and is also consistent with the antibody detection results of local leptospirosis patients in recent years.
In the present study,four leptospires isolated fromApodemus agrariusin Jinping and Liping counties in 2011were identified asL.interroganswhich belongs to the genospecies of pathogenic clade,which is consistent with MAT detection results for theLeptospiraantibody of the patients in the local area.Our results suggest thatApodemus agrariusmay be the main carrier ofLeptospirain Jinping and Liping counties,andL.interrogansmay be the epidemic genospecies ofLeptospirain the local area,which will contribute to the clinical laboratory diagnosis,active surveillance,outbreak investigation and source tracking for leptospirosis in Guizhou Province.
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge the contribution of Jingping County CDC,Liping County CDC and Rongjiang County CDC for rodent trapping.
[1]Levett PN.Leptospirosis[J].Clin Microbiol Rev,2001,14(2):296-326.DOI:10.1128/CMR.14.2.296-326.2001
[2]Vijayachari P,Sugunan AP,Shriram AN.Leptospirosis:an emerging global public health problem [J].J Biosci,2008,33(4):557-569.DOI:10.1007/s12038-008-0074-z
[3]Bezerra da Silva J,Carvalho E,Hartskeerl RA,et al.Evaluation of the use of selective PCR amplification of LPS biosynthesis genes for molecular typing of leptospira at the serovar level[J].Curr Microbiol,2011,62(2):518-524.DOI:10.1007/s00284-010-9738-7
[4]Gouveia EL,Metcalfe J,de Carvalho AL,et al.Leptospirosisassociated severe pulmonary hemorrhagic syndrome,Salvador,Brazil[J].Emerg Infect Dis,2008,14(3):505-508.DOI:10.3201/eid1403.071064
[5]McBride AJ,Athanazio DA,Reis MG,et al.Leptospirosis[J].Curr Opin Infect Dis,2005,18(5):376-386.DOI:10.1097/01.qco.0000178824.05715.2c
[6]Vinetz JM.Leptospirosis[J].Curr Opin Infect Dis,2001,14(5):527-538.DOI:10.1097/00001432-200110000-00005
[7]Plank R,Dean D.Overview of the epidemiology,microbiology,and pathogenesis ofLeptospiraspp.in humans[J].Microbes Infect,2000,2(10):1265-1276.DOI:10.1016/S1286-4579(00)01280-6
[8]Mayer-Scholl A,Draeger A,Luge E,et al.Comparison of two PCR systems for the rapid detection ofLeptospiraspp.from kidney tissue[J].Curr Microbiol,2011,62(4):1104-1106.DOI:10.1007/s00284-010-9829-5
[9]Guerra MA.Leptospirosis[J].J Am Vet Med Assoc,2009,234(4):472-478.DOI:10.2460/javma.234.4.472
[10]Meerburg BG,Singleton GR,Kijlstra A.Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health[J].Crit Rev Microbiol,2009,35(3):221-270.DOI:10.1080/10408410902989837
[11]Koizumi N,Muto M,Yamamoto S,et al.Investigation of reservoir animals ofLeptospirain the northern part of Miyazaki Prefecture[J].Jpn J Infect Dis,2008,61(6):465-468.
[12]Yang K,Jiang YQ,Luo,YP,et al.Epidemiology of leptospirosis in Liping County,Guizhou,2001-2008[J].Dis Surveill,2009,24(10):768-769.(in Chinese)杨科,姜永全,罗永平,等.2001-2008年贵州省黎平县钩端螺旋体病流行病学特征分析[J].疾病监测,2009,24(10):768-769.
[13]Morey RE,Galloway RL,Bragg SL,et al.Species-specific identification ofLeptospiraceaeby 16SrRNA gene sequencing[J].J Clin Microbiol,2006,44(10):3510-3516.DOI:10.1128/JCM.00670-06
[14]Ivanova S,Herbreteau V,Blasdell K,et al.Leptospiraand rodents in Cambodia:rnvironmental reterminants of infection[J].Am J Trop Med Hyg,2012,86(6):1032-1038.DOI:10.4269/ajtmh.2012.11-0349
[15]Guo SH,Deng ZH,Li JH.Analysis of leptospirosis epidemic in 31provinces(1991-2005)[J].J Publ Health Prev Med ,2006,6:8-10.(in Chinese)郭绶衡,邓志红,李俊华.1991~2005年31个省市自治区钩体病流行情况分析[J].公共卫生与预防医学,2006,6:8-10.
[16]Yang MW,Mo RJ.Exploration of space distribution on Lepto-spirosis epidemic focus with host animal[J].Practical Prev Med,2007,14:46-54.(in Chinese)杨茂文,莫荣杰.黔南州钩端螺旋体疫区空间划分与宿主动物关系的探讨[J].适用预防医学,2007,14:46-45.
[17]Li SJ,Zhang CC,Li XW,et al.Molecular typing ofLeptospira interrogansstrains isolated fromRattus tanezumiin Guizhou Province,Southwest of China[J].Biomed Environ Sci,2012,25(5):542-548.DOI:10.3967/0895-3988.2012.05.007

