Obestatin与Ghrelin在炎症性肠病中的表达及临床价值
沈 骏,乔宇琪,冉志华,童锦禄,朱明明,王天蓉,黄美兰
1.上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院消化内科,上海 200001;2.上海市消化疾病研究所
Obestatin与Ghrelin在炎症性肠病中的表达及临床价值
沈 骏1,2,乔宇琪1,2,冉志华1,2,童锦禄1,2,朱明明1,2,王天蓉1,2,黄美兰1,2
1.上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院消化内科,上海 200001;2.上海市消化疾病研究所
目的研究炎症性肠病患者血浆Obestatin和Ghrelin的表达水平,分析血浆Obestatin和Ghrelin表达水平对炎症性肠病的诊断和鉴别意义。方法应用酶联免疫吸附试验(Enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay,ELISA)对克罗恩病患者、溃疡性结肠炎患者和正常对照者血浆中Obestatin及Ghrelin的表达进行分析。通过受试者工作特征曲线(receiver-operating characteristic,ROC)观察血浆Obestatin、Ghrelin水平及Obestatin/Ghrelin比值在克罗恩病和溃疡性结肠炎的诊断和鉴别价值,数据处理使用GraphPad Prism 5。结果溃疡性结肠炎患者(P<0.0001)和克罗恩病患者(P=0.0001)血浆Obestatin水平均显著高于正常对照者,并且溃疡性结肠炎患者血浆Obestatin水平显著高于克罗恩病患者(P=0.0003)。溃疡性结肠炎患者(P=0.0279)和克罗恩病患者(P=0.0192)血浆Ghrelin水平均显著高于正常对照者,但是溃疡性结肠炎患者和克罗恩病患者间血浆Ghrelin水平无显著性差异(P=0.9331)。溃疡性结肠炎患者血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值显著低于正常对照者(P=0.0487),但是克罗恩病患者血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值与溃疡性结肠炎患者(P=0.1076)和正常对照者(P=0.8136)无显著性差异。血浆Obestatin水平对于区分溃疡性结肠炎患者和正常对照者(AUC=0.8791,P<0.0001)、克罗恩病患者和正常对照者(AUC=0.7317,P=0.0001)以及溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病患者(AUC=0.7340,P=0.0001)具有显著的鉴别诊断价值。血浆Ghrelin水平对于区分克罗恩病患者和正常对照者具有显著的诊断价值(AUC=0.6660,P=0.0059)。但是,血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值对于区分溃疡性结肠炎和正常对照者无显著的鉴别诊断价值(AUC=0.5608,P=0.2923)。结论溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病患者血浆Obestatin及Ghrelin水平增高,综合评估溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病患者血浆Obestatin、Ghrelin以及Ghrelin/Obestatin比值对疾病的诊断和鉴别有一定意义。
Obestatin;Ghrelin;克罗恩病;溃疡性结肠炎
炎症性肠病(Inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)是一种发病机制尚不清除的疾病,综合致病因素较多。通常认为炎症性肠病的致病过程与遗传因素、环境因素、免疫因素及感染因素有关,但关于各因素在疾病的发生发展过程中的具体作用机制并不明确,探寻炎症性肠病的发病机制正在逐渐成为近年来研究的热点。Ghrelin是一种由胃和十二指肠共同合成的多肽,又被称为饥饿激素或胃促生长激素,可以调节生长激素、催乳素、肾上腺素等多种激素的释放,促进摄食、促进胃动力及保护胃黏膜的作用,其在炎症性肠病中的作用和价值,近年来正越来越多地受到关注[1-2]。Obestatin是与Ghrelin同一基因编码的另一种多肽,同样与食物的摄取有关,也被称为肥胖抑制素。一些研究显示其对Ghrelin的功能存在一定的相关性,这两种激素的共同作用在炎症性肠病发病过程可能起到了重要的作用[3]。本研究旨在了解Obestatin、Ghrelin在炎症性肠病患者与正常对照者中的表达水平差异,了解两者与炎症性肠病发病的关系,为进一步深入研究炎症性肠病的胃肠激素打下基础。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象 回顾性研究2005年12月-2008年6月间在上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院就诊的42例克罗恩病(Crohn’s disease)患者和49例溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis)患者的外周血标本。同时,在2008年1月-2008年6月间,纳入了52例正常对照(healthy controls)者外周血标本。所有患者和正常对照者在标本留取前均签署知情同意书。
1.2 酶联免疫吸附试验 ELISA试剂盒购自Adlitteram Diagnostic Labortories(San Diego,CA,USA)。所有对象经12 h空腹,于第2天早晨肘正中静脉采血,采血使用EDTA真空抗凝管,2500×g离心10 min分离血浆-80℃保存。按照ELISA试剂盒进行操作,在450 nm 处测出吸光值,以标准品 0、0.5、1、2.5、5、10 ng/mL之OD值,使用计算机软件,绘制出标准曲线,计算样品含量。
1.3 统计分析 应用统计软件GraphPad Prism 5进行统计分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。一般数据描述采用均数和95%置信区间(confidence interval,CI)表示,计数资料用频数和构成表示;缺失值不纳入统计。采用单因素方差分析(one way ANOVA)比较克罗恩病患者、溃疡性结肠炎患者和正常对照者血浆Obestatin、Ghrelin水平及Ghrelin/Obestatin比值差异。受试者工作曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)分析血浆 Obestatin、Ghrelin水平及Obestatin/Ghrelin比值在克罗恩病和溃疡性结肠炎的诊断和鉴别价值。
2 结果
2.1 一般资料 共有42例克罗恩病患者(男29例,女13例)、49例溃疡性结肠炎患者(男32例,女17例)以及52例正常对照者(男26例,女26例)纳入本研究。克罗恩病、溃疡性结肠炎患者以及正常对照者的中位年龄分别为32.21 岁(95%CI:28.53 ~35.90)、41.96 岁(95%CI:38.28 ~45.64)和 34.44 岁(95%CI:31.14 ~37.75)。
2.2 炎症性肠病患者和正常对照者血浆中Obestatin、Ghrelin表达及Obestatin/Ghrelin比值的差异 ELISA分析表明,溃疡性结肠炎患者、克罗恩病患者以及正常对照者的血浆Obestatin的分别为2.466 ng/mL(95%CI:2.304 ~ 2.628)、1.928 ng/mL(95%CI:1.697 ~2.160)和 1.307 ng/mL(95%CI:1.093 ~1.520);血浆Ghrelin浓度分别为 12.98 ng/mL(95%CI:8.135 ~17.83)、12.71 ng/mL(95%CI:8.454 ~16.97)和 7.194 ng/mL(95%CI:5.416 ~8.971);血浆 Ghrelin/Obestatin比值分别为5.330(95%CI:3.544 ~7.116)、10.14(95%CI:4.492 ~ 15.79)和 9.352(95%CI:5.739 ~ 12.96)。方差分析结果提示溃疡性结肠炎患者(P<0.0001)和克罗恩病患者(P=0.0001)血浆Obestatin水平均显著高于正常对照者,并且溃疡性结肠炎患者血浆Obestatin水平显著高于克罗恩病患者(P=0.0003)。溃疡性结肠炎患者(P=0.0279)和克罗恩病患者(P=0.0192)血浆Ghrelin水平均显著高于正常对照者,但是溃疡性结肠炎患者和克罗恩病患者间血浆Ghrelin水平无显著差异(P=0.9331)。溃疡性结肠炎患者血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值显著低于正常对照者(P=0.0487),但是克罗恩病患者血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值与溃疡性结肠炎患者(P=0.1076)和正常对照者(P=0.8136)无显著性差异(见图1)。

图1 溃疡性结肠炎患者、克罗恩病患者以及正常对照者的血浆Obestatin、Ghrelin的水平及Ghrelin/Obestatin比值差异Fig 1 Different levels of plasma Obestatin,Ghrelin and Ghrelin/Obestatin ratio in patients with ulcerative colitis,patients with Crohn’s disease and healthy controls
2.3 溃疡性结肠炎患者、克罗恩病患者血浆中Obestatin、Ghrelin表达及 Ghrelin/Obestatin比值对疾病的诊断和鉴别价值分析 在分析表明溃疡性结肠炎患者与克罗恩病患者血浆中Obestatin、Ghrelin的水平存在差异的基础上,本研究进一步通过ROC曲线分析血浆 Obestatin、Ghrelin水平及 Obestatin/Ghrelin比值在克罗恩病和溃疡性结肠炎的诊断和鉴别价值。ROC曲线的分析表明,血浆Obestatin水平对于区分溃疡性结肠炎患者和正常对照者(AUC=0.8791,P<0.0001,见图2A)、克罗恩病患者和正常对照者(AUC=0.7317,P=0.0001,见图 2B)以及溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病患者(AUC=0.7340,P=0.0001,见图2C)具有显著的鉴别诊断价值。血浆Ghrelin水平对于区分克罗恩病患者和正常对照者具有显著的诊断价值(AUC=0.6660,P=0.0059,见图 2D)。但是,血浆Ghrelin水平对于区分溃疡性结肠炎患者和正常对照者(AUC=0.6026,P=0.0757)以及克罗恩病患者(AUC=0.5746,P=0.2218)无显著的鉴别价值。此外,虽然溃疡性结肠炎患者血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值显著低于正常对照者,但是血浆Ghrelin/Obestatin比值对于区分溃疡性结肠炎和正常对照者(AUC=0.5608,P=0.2923)无显著鉴别价值。
3 讨论
Ghrelin是一种脑肠肽,主要由胃合成,在白色脂肪组织中有痕量表达。它是生长激素促分泌受体(growth hormone secretagogue receptor,GHS-R)的配体,具有多种生理功能[4]。Ghrelin可以被单核细胞及T细胞表达,抑制部分细胞因子的活化,包括白介素(interleukin)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factorα,TNF-α)以及瘦素(leptin)[5]。在胃肠道疾病方面,有学者发现在乳糜泻(celiac disease)患者中,Ghrelin的血浆水平升高,但机制尚不清楚[6]。在活动性炎症性肠病患者中,Ghrelin的血浆水平增高[7]。本研究同样发现了炎症性肠病患者中Ghrelin血浆水平高于正常对照者的现象,这和目前已有的研究一致。由于Ghrelin存在一定程度的对抗炎症的作用,使之成为一种可能的潜在治疗药物。尽管Ghrelin所扮演的角色尚不清除,但其减轻炎症的作用在部分动物模型中已经得到了验证[2]。同时Ghrelin可以增加肠道运动,增加食物摄取量,对炎症性肠病的恢复可能存在帮助。有学者发现,Ghrelin的使用可以使结肠炎大鼠模型的结肠血流量增加,但其与疾病是否存在直接或间接联系尚无法确定[8]。尽管Ghrelin可以促进生长激素分泌,但由于既往研究认为生长激素并无确切的改善炎症性肠病的作用,所以并不作为改善炎症性肠病机制进行考虑[9]。从本文的研究结果来看,作为临床指标,Ghrelin在炎症性肠病与正常对照组之间存在明显的差异,但是其诊断效果似乎并不理想。在既往研究中发现,Ghrelin在炎症性肠病活动期患者中升高更为明显,本研究的数据尚无法对这一观点进行确认,需有待进一步研究。
Obestatin是由Ghrelin同一基因编码的另一种胃肠激素,Obestatin与Ghrelin在功能上存在一定的相关性,与Ghrelin结合 GHS-R不同,Obestatin与脑中的“Orphan”G蛋白结合,这两种激素受体均属于促生长激素释放激素受体家族,目前Obestatin与炎症性肠病活动的相关性尚不明确[10]。本研究发现,Obestatin在克罗恩病与溃疡性结肠炎患者中存在差异,作为临床指标而言,有一定的鉴别价值,但无法确定Obestatin是否与疾病的活动存在相关性。Alexandridis等[10]研究发现,Ghrelin/Obestatin的比值与炎症性肠病的活动存在相关性,但研究结果并未对克罗恩病及溃疡性结肠炎进行区分。本研究中对克罗恩病、溃疡性结肠炎的Ghrelin/Obestatin比值进行了区分,溃疡性结肠炎的Ghrelin/Obestatin的比值低于正常对照者。
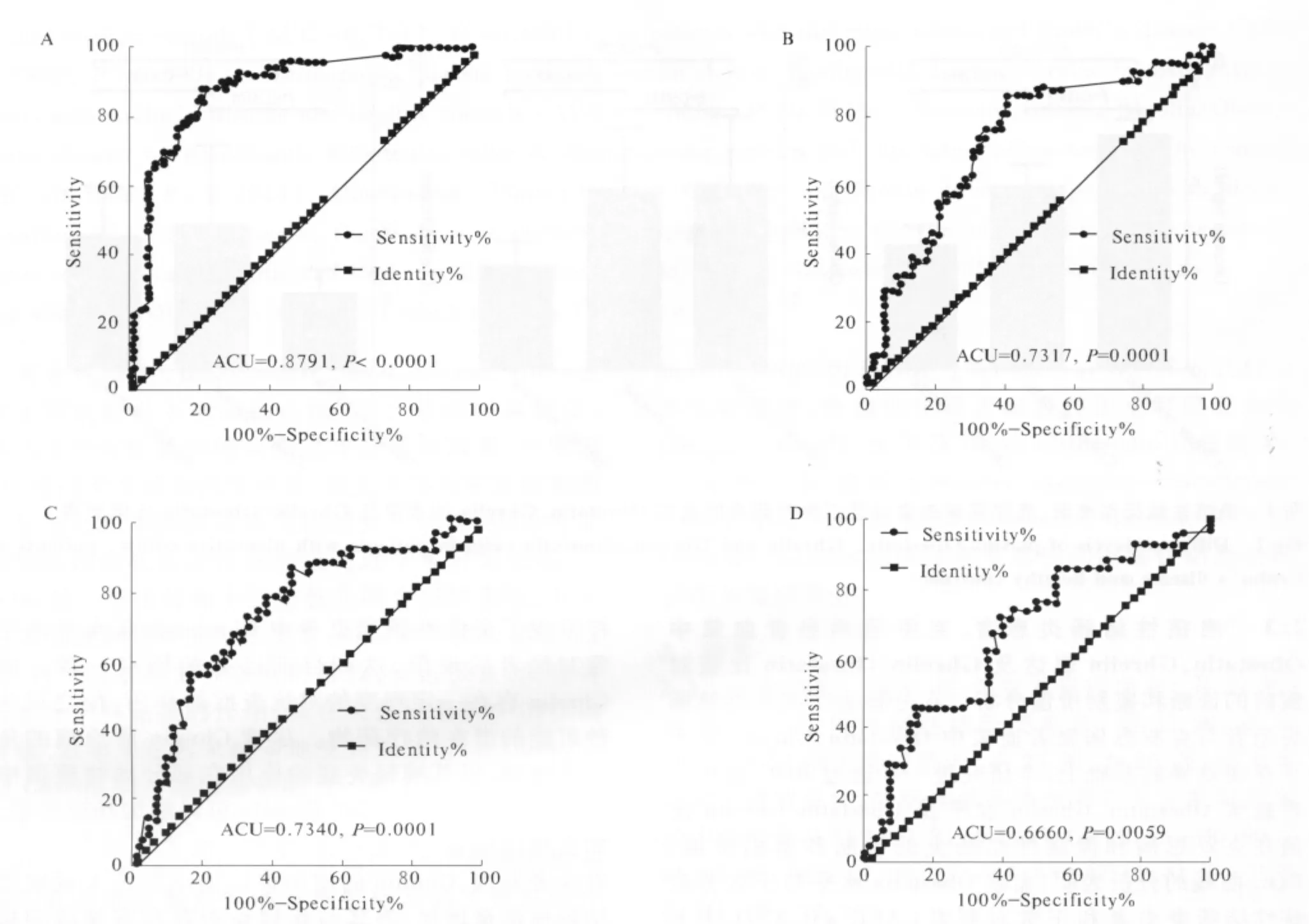
图2 溃疡性结肠炎患者、克罗恩病患者和正常对照者血浆中Obestatin、Ghrelin水平及Ghrelin/Obestatin比值对疾病的诊断和鉴别价值ROC曲线 A:血浆Obestatin水平区分溃疡性结肠炎患者和正常对照者的ROC曲线;B:血浆Obestatin水平区分克罗恩病患者和正常对照者的ROC曲线;C:血浆Obestatin水平区分溃疡性结肠炎患者和克罗恩病患者的ROC曲线;D:血浆Ghrelin水平区分克罗恩病患者和正常对照者的ROC曲线Fig 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves of disease diagnostic and differential value for plasma levels of Obestatin,Ghrelin and Obestatin/Ghrelin ratio in patients with ulcerative colitis,Crohn’s disease and healthy controls. A:ROC curves of obestatin and healthy controls in different plasmal levels of obestatin;B:ROC curves of Ghrelin and healthly controls in different plasmal levels of obestatin;C:ROC curves of Obestatin and Ghrelin in different plasmal levels of obestatil;D:ROC curvels of Ghrelin and healthly contrals in different plasmal levels of obestatil
Obestatin及Ghrelin作为两种近年来新发现的胃肠激素,其在胃肠道疾病诊断中的价值已经越来越多地得到了重视,然而目前关于这两种胃肠激素在炎症性肠病发病中的研究主要停留在血浆学定量分析,较少涉及其信号通路的研究。目前患者血浆学及动物模型研究已经证实Obestatin及Ghrelin与炎症性肠病的活动性可能存在一定的关系,Ghrelin在免疫细胞中的表达也得到了证实,为其作用机制的研究打下了良好的基础。同时Obestatin及Ghrelin作为潜在诊断及鉴别诊断指标,需要进一步扩大样本以证实。
[1] Ates Y,Degertekin B,Erdil A,et al.Serum ghrelin levels in inflammatory bowel disease with relation to disease activity and nutritional status[J].Dig Dis Sci,2008,53(8):2215-2221.
[2] Deboer MD.Use of ghrelin as a treatment for inflammatory bowel disease:mechanistic considerations[J].Int J Pept,2011,2011:189242.
[3] Alexandridis E,Zisimopoulos A,Liratzopoulos N,et al.Obestatin/ghrelin ratio:a new activity index in inflammatory bowel diseases[J].Inflamm Bowel Dis,2009,15(10):1557-1561.
[4] Korbonits M,Goldstone AP,Gueorguiev M,et al.Ghrelin-a hormone with multiple functions[J].Front Neuroendocrinol,2004,25(1):27-68.
[5] Dixit VD,Schaffer EM,Pyle RS,et al.Ghrelin inhibits leptin-and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells[J].J Clin Invest,2004,114(1):57-66.
[6] Peracchi M,Conte D,Terrani C,et al.Circulating ghrelin levels in celiac patients[J].Am J Gastroenterol,2003,98(11):2474-2478.
[7] Peracchi M,Bardella MT,Caprioli F,et al.Circulating ghrelin levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J].Gut,2006,55(3):432-433.
[8] Konturek PC,Brzozowski T,Engel M,et al.Ghrelin ameliorates colonic inflammation.Role of nitric oxide and sensory nerves[J].J Physiol Pharmacol,2009,60(2):41-47.
[9] Denson LA,Kim MO,Bezold R,et al.A randomized controlled trial of growth hormone in active pediatric Crohn disease[J].J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr,2010,51(2):130-139.
[10] Alexandridis E,Zisimopoulos A,Liratzopoulos N,et al.Obestatin/ghrelin ratio:a new activity index in inflammatory bowel diseases[J].Inflamm Bowel Dis,2009,15(10):1557-1561.
Expression and clinical significance of Obestatin and Ghrelin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
SHEN Jun,QIAO Yuqi,RAN Zhihua,TONG Jinlu,ZHU Mingming,WANG Tianrong,HUANG Meilan
1.Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine Renji Hospital;2.Shanghai Institute of Digestive Disease,Shanghai 200001,China
ObjectiveTo investigate plasma levels of Obestatin and Ghrelin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and to analyze diagnostic and differential significance of Obestatin and Ghrelin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.MethodsEnzyme-linked immuno-sorbent assay(ELISA)was applied to analyze plasma expression of Obestatin and Ghrelin in patients with Crohn’s disease,Ulcerative colitis and healthy controls.Receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC)was used to observe diagnostic and differential value of plasma Obestatin,Ghrelin levels and Obestatin/Ghrelin Ratio in patients with Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis.Data was analyzed with GraphPad Prism 5.ResultsPlasma levels of Obestatin were significant higher in patients with ulcerative colitis(P <0.0001)and Crohn’s disease(P=0.0001)than that in healthy controls.And plasma levels of Obestatin were significantly higher in patients with ulcerative colitis than that in patients with Crohn’s disease(P=0.0003).Plasma levels of Ghrelin were significantly higher in patients with Ulcerative colitis(P=0.0279)and Crohn’s disease(P=0.0192)than that in healthy controls.However,there was no significant difference of plasma levels of Ghrelin in patients with ulcerative colitis and in patients with Crohn’s disease(P=0.9331).Moreover,plasma Ghrelin/Obestatin ratio was significant lower in patients with ulcerative colitis than that in healthy controls(P=0.0487).However,plasma Ghrelin/Obestatin ratio showed no significant difference in patients with Crohn’s disease than that in patients with ulcerative colitis(P=0.1076)or healthy controls(P=0.8136).Plasma level of Obestatin showed significantly differential value in distinguishing patients with ulcerative colitis and healthy controls(AUC=0.8791,P <0.0001),patients with Crohn’s dis-ease and healthy controls(AUC=0.7317,P=0.0001),or patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease(AUC=0.7340,P=0.0001).Furthermore,plasma levels of Ghrelin showed significantly diagnostic value in distinguishing patients with Crohn’s disease and healthy controls(AUC=0.6660,P=0.0059).However,plasma Ghrelin/Obestatin ratio showed no significantly differential value in distinguishing patients with ulcerative colitis and healthy controls(AUC=0.5608,P=0.2923).ConclusionPlasma levels of Obestatin and Ghrelin increase in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.Comprehensive assessment of plasma Obestatin,Ghrelin and Ghrelin/Obestatin ratio in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease show certain value in diagnosis and differentiation.
Obestatin;Ghrelin;Crohn's disease;Ulcerative colitis
R575.2
A
1006-5709(2012)11-1073-04
2012-04-10
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2012.11.024
国家自然科学基金(81000161);上海交通大学医学院科技基金(YZ1036);上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院学科建设(RJ4101305)
沈骏,主治医师,博士,研究方向:炎症性肠病。E-mail:shengjun@vip.163.com
冉志华,教授,博士,研究方向:炎症性肠病。E-mail:zhihuaran62@yahoo.cn

