弹性髓内钉治疗儿童前臂骨折的疗效评价
夏羿凡,吴青,蒲劲松
(川北医学院附属医院骨科,四川 南充 637000)
弹性髓内钉治疗儿童前臂骨折的疗效评价
夏羿凡,吴青,蒲劲松△
(川北医学院附属医院骨科,四川 南充 637000)
目的:通过使用弹性髓内钉治疗患儿前臂骨折,评价其对骨折术后功能恢复的影响。方法:2005年至2011年90例移位的患儿前臂骨折,其中8例开放性骨折,77例双前臂骨折。均采用手法或开放复位,弹性髓内钉内固定,并随访平均6.6个月。结果:骨折全部愈合,愈合时间平均2.9个月。功能评价优秀或良好76例(84%),并发症包括8例创口相关并发症,1例桡神经浅支麻痹,1例畸形愈合和1例术后骨筋膜室综合征。骨折愈合率与患儿骨折部位之间无统计学意义。结论:弹性髓内钉技术在儿童前臂骨折中是一种容易使用的,预后良好的治疗技术。
儿童;前臂骨折;弹性髓内钉
大多数儿童前臂骨折可以通过闭合复位石膏外固定治愈[1],部分复位不良、复位后不稳定及开放性前臂骨折需手术治疗。近年来儿童骨折尤其是前臂骨折手术率上升[2],弹性髓内钉技术(elastic stable intramedullary nailing,ESIN)成为流行的治疗方式[3]。虽有部分报道,但鲜于前瞻性功能评估[4-6]。
1 资料和方法
1.1 临床资料
从2005年至2011年有90例患儿施行弹性髓内钉内固定,年龄2~15岁,平均8.4岁骨折按照OA/OTA分型(表1)。
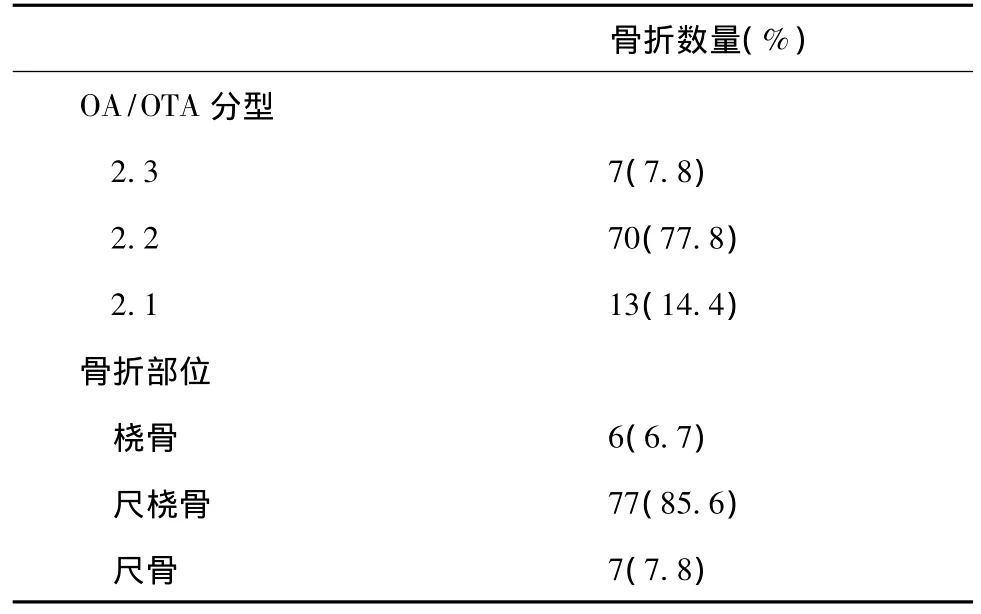
表1 骨折AO/OTA分型及骨折部位
1.2 方法
所有患儿均进行全身麻醉,采用直径2 mm或2.5 mm弹性髓内钉,进行闭合手法复位后,每例长骨进行单根髓内钉固定。如果手法复位失败,桡骨采用背侧Thompson入路[7],尺骨采用尺背侧入路进行切开复位。桡骨髓内钉从桡腕部穿入至桡骨头固定,尺骨髓内钉从鹰嘴处穿入至尺骨远端固定,所有髓内钉均埋于皮下。术后74例骨折(82.2%)患儿进行石膏外固定,13例(14.4%)未使用石膏外固定。石膏固定时间平均33 d(0~53 d),在X线片证实骨折愈合后,手术拔除髓内钉。
1.3 评价系统
根据Daruwalla[8]所设计的术后功能分级(表2)进行功能评估。

表2 术后功能评估
1.4 统计学分析
采用SPSS 11.0统计学软件包进行统计学处理。采用Fisher精确卡方检验,以评估骨折愈合率与患儿骨折部位之间的差异,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 骨折愈合及功能恢复
90例患儿中,10例非手术治疗失败后进行ESIN,8例为开放性骨折。72例被认为具有手术指征直接进行ESIN。其手术指征为成角移位>10°,旋转移位>45°,手法复位后桡骨弓未能重建。
后前位及侧位X片显示骨痂厚度大于3/4骨皮质厚度时可拔除内固定,拔除内固定时间平均为术后4个月(0.8~17.4个月),随访时间为平均6.6个月(2~17.6个月)。术后均在康复治疗师监督下进行正规康复治疗。
表2所显示有76例结果优秀或良好,最终随访中无疼痛及功能受限。比较骨折部位对功能恢复的差异时,发现无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2 并发症
13例患儿出现并发症(表3),其中8例有创口相关并发症,包括创口感染及钉尾处皮肤破损。创口感染通过3周抗生素治疗[9]后治愈,钉尾处皮肤破损在拔除内固定后愈合。2例出现了短暂的桡神经浅支支配区麻痹,未行任何治疗自行恢复。1例骨筋膜室综合征进行前臂切开减压,未出现创口相关并发症。1例延迟愈合患者在进行6周超声刺激治疗后于术后9个月愈合。1例畸形愈合患儿术后15个月骨折重塑后愈合,功能无障碍。
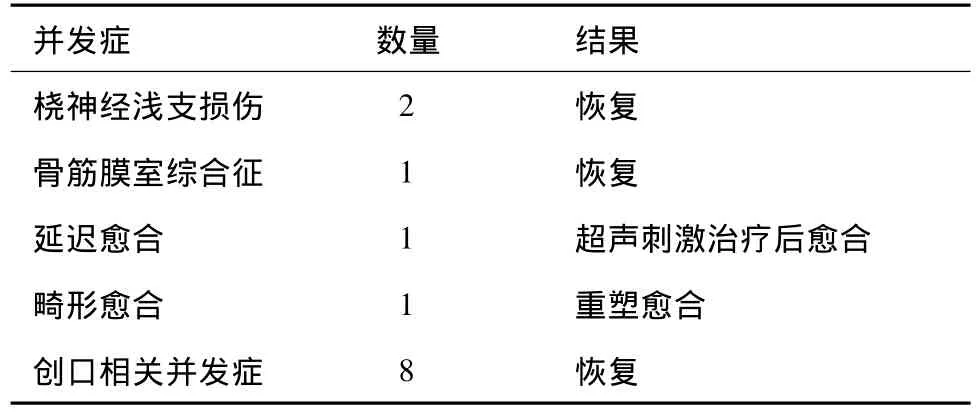
表3 13例患儿出现的相关并发症
3 讨论
成角畸形是公认为和前臂旋转功能受限成正相关。在尸体研究中,Rupasinghe等[10]发现成角角度和旋转畸形≥10°就可导致旋前和旋后受限。然而儿童与与成年人不同,随着年龄的增长,骨的重塑将使儿童前臂成角移位和旋转移位得以纠正[11]。
接骨板支持者[12]非常强调重建桡骨解剖弓,因其对前臂的旋转意义重大[13],所以认为只有接骨板才能解剖复位并重建桡骨弓。本前瞻性研究其中一项为评价前臂旋转功能的恢复,从表2中可知,本术式对前臂的旋转功能恢复效果良好。结果显示,ESIN在对于儿童,不需要解剖重建桡骨弓,亦能获得良好的功能恢复[14]。
本研究中76例(84.4%)患儿前臂旋转功能良好,本手术方式相对于接骨板来说技术要求简单,经验不足的医师也可采用本技术治疗患儿前臂骨折[15]。不暴露或者有限暴露骨折端也有效地减少了骨膜剥离,对于骨折的愈合来说符合了骨折治疗的生物学原理[16]。
Weinberg等[17]在传统教学中演示在插入弹性髓内钉前需要预弯髓内钉,以恢复桡骨弓。然而近年来一系列研究发现这是没有必要的[18],仅仅在患儿股骨和胫骨骨折中需要对弹性髓内钉进行预弯。
相对于接骨板治疗前臂双骨折而言,其优点在于手术时间较短且较小的创口使外观更加美观[19]。技术要求简单,大多数对患儿骨折治疗经验不足的医师也能安全使用这一方法对患儿前臂骨折进行治疗,适合在基层进行推广。
由于在绝大多数患儿的治疗中ESIN取得了优秀或良好的临床效果,建议使用ESIN治疗无法复位或复位后不稳定的前臂骨折患儿。
[1]Dhoju D,Shrestha D,Parajuli N,et al.Ipsilateral Supracondylar Fracture and Forearm Bone Injury in Children:A Retrospective Review of Thirty one cases[J].Kathmandu Univ Med J(KUMJ),2011,9(34):11-16
[2]Helenius I,Lamberg TS,Kriinen S,et al.Operative treatment of fractures in children is increasing:a population-based study from Finland[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2009,91(11):2612-2616
[3]Furlan D,PogoreliZ,BioM,et al.Elastic stable intramedullary nailing for pediatric long bone fractures:experience with 175 fractures[J].Scand J Surg,2011,100(3):208-215
[4]Kapoor V,Theruvil B,Edwards SE,et al.Flexible intramedullary nailing in displaced diaphyseal forearm fractures in children[J].Injury,2005,36(10):1221-1225
[5]Jubel A,Andermahr J,Isenberg J,et al.Outcomes and complications of elastic stable intramedullary nailing for forearm fractures in children[J].J Pediatr Orthop B,2005,14(5):375-380
[6]Zionts LE,Zalavras CG,Gerhardt MB.Closed treatment of displaced Diaphyseal both-bone forearm fractures in older children and adolescents[J].J Pediatr Orthop,2005,25(4):507-512
[7]Thompson,Wheeless CR 3rd.Dorsal approach(J/OL).[2010-10-22].http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/dorsal_approach_thompson
[8]Daruwalla JS.A study of radioulnar movements following fractures of the forearm in children[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1979,(139):114-120
[9]夏羿凡,蔚芃,吴青,等.人工髋关节置换术后感染的治疗[J].川北医学院学报,2009,24(6):183-185
[10]Rupasinghe SL,Poon PC.Radius morphology and its effects on rotation with contoured and noncontoured plating of the proximal radius[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2012,21(5):568-573
[11]Fuller DJ,McCullough CJ.Malunited fractures of the forearm in children[J].J Bone Joint Surg Br,1990,10(6):705-712
[12]Schemitsch EH,Richards RR.The effect of malunion on functional outcome after plate fixation of fractures of both bones of the forearm in adults[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1992,74(7):1068-1078
[13]Firl M,Wünsch L.Measurement of bowing of the radius[J].J Bone Joint Surg Br,2004,86(7):1047-1409
[14]Vinz H,Neu J,Festge OA.Malpractice in the treatment of supracondylar humeral fractures in children-experience of the arbitration office of the Northern German Medical Boards[J].Z Orthop Unfall,2010,148(6):697-703
[15]Slongo TF.The choice of treatment according to the type and location of the fracture and the age of the child[J].Injury,2005,36(Suppl 1):12-9
[16]Lascombes P,Haumont T,Journeau P.Use and abuse of flexible intramedullary nailing in children and adolescents[J].J Pediatr Orthop,2006,26(6):827-834
[17]Weinberg AM,Amerstorfer F,Fischerauer EE,et al.Paediatric diaphyseal forearm refractures after greenstick fractures:operative management with ESIN[J].Injury,2009,40(4):414-417
[18]Calder PR,Achan P,Barry M.Diaphyseal forearm fractures in children treated with intramedullary fixation:outcome of K-wire versus elastic stable intramedullary nail[J].Injury,2003,34(4):278-282
[19]Fernandez FF,Egenolf M,Carsten C,et al.Unstable diaphyseal fractures of both bones of the forearm in children:plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing[J].Injury,2005,36(10):1210-1216
Treatment for pediatric fractures of the forearm by elastic intramedullary nailing
XIA Yi-fan,WU Qing,PU Jin-song△
(Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College,Nanchong 637000,Sichuan,China)
Objective:To evaluate the functional recovery through the use of an elastic intramedullary nail in treatment of pediatric forearm fractures.MethodsResults of 90 consecutive children with displaced fractures of the forearm treated by elastic stable intramedullary nailing with a mean follow-up of 6.6 months were presented.Eight had open fractures and 77 had sustained a fracture of both bones.ResultsAll fractures healed at a mean of 2.9 months.An excellent or good functional outcome was achieved in 76 patients.Complications included eight cases of problematic wounds,two transient palsies of the superficial radial nerve,and one case each of malunion and a post-operative compartment syndrome.Healing rate of the forearm fracture had no significant differences with the bone site.ConclusionFindings indicate that the functional outcome following pediatric fractures of the forearm treated by elastic stable intramedullary nailing is good.
Pediatric;Forearm fracture;Elastic intramedullary nail
1005-3697(2012)04-0345-03
R726.8
A
10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2012.04.011
四川省教育厅科研项目(12ZB047)
2012-05-08
夏羿凡(1978-),男,四川南充人,硕士研究生,讲师,主要从事骨科临床工作及相关研究。
△通讯作者:蒲劲松,E-mail:peterpu@163.com网络出版时间:2012-7-80∶29
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1254.R.20120708.0029.201204.342_010.html
(学术编辑:蔚芃)

