胰十二指肠同源框因子-1联合细胞因子诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛β样细胞的研究
王博 吴汉青 吴河水 王春友
·论著·
胰十二指肠同源框因子-1联合细胞因子诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛β样细胞的研究
王博 吴汉青 吴河水 王春友
目的探讨人脐带间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells, MSCs)体外诱导分化为胰岛β样细胞的方法。方法用含胰十二指肠同源框因子-1基因(pancreatic and duodenal homeobox factor 1,PDX1)重组腺病毒(Adxsi-CMV-PDX1)感染人脐带MSCs,再联合多种细胞因子进行诱导分化。应用RT-PCR、免疫荧光染色法检测诱导后细胞的PDX1、胰岛素(insulin)、神经元素3(ngn3)、葡萄糖转运体2(glut2)、NK转录因子6.1(NKX6.1)mRNA的表达;化学发光法检测诱导后细胞培养上清中胰岛素和C肽的分泌量;流式细胞仪检测胰岛素阳性细胞率。结果Adxsi-CMV-PDX1感染脐带MSCs并联合细胞因子诱导后,细胞从短梭形变成长梭形,并聚集形成胰岛样细胞团,经双硫腙染成亮红色。诱导17 d后的细胞表达PDX1、ngn3、NKX6.1、insulin、glut-2的mRNA;细胞胞质内有胰岛素和C肽;细胞培养上清中胰岛素和C肽含量分别为(473.1±51.5)mU/L和(1.61±0.41)ng/ml,用25 mmol/L高糖刺激1 h后,胰岛素和C肽分泌量高达(964.4±68.1)mU/L和(3.72±1.52) ng/ml;胰岛素阳性细胞率达(11.6±4.8)%。结论PDX1转入脐带MSCs后,联合细胞因子在体外能够诱导其分化为胰岛β样细胞,胰岛素和C肽分泌水平较高,且对高糖刺激有反应,但还不是完全成熟的β细胞。
脐带; 间质干细胞; 胰腺十二指肠同源框因子-1; 胰岛β样细胞; 细胞分化
胰岛移植为糖尿病治疗带来了曙光,但是由于供体有限、移植后易引起免疫排斥反应、移植细胞的数量难以控制等问题限制了其临床应用。最近的研究报道,胚胎干细胞和成体干细胞都可以分化为胰岛素分泌细胞[1-2],但诱导效率和胰岛素分泌水平低下,不能满足临床治疗需要。胰十二指肠同源框因子-1(pancreatic and duodenal homeobox factor 1,PDX1)是胰腺发生和胰岛发育的一个重要调节基因,在胚胎发育过程中促进胰腺的早期发育和晚期β细胞分化,成体中维持β细胞的形态和功能[3]。Kajiyama等[4]和Hisanaga等[5]分别以PDX1、细胞因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells, MSCs)分化为胰岛素分泌细胞,但胰岛素分泌水平均低下。因此,本研究联合应用PDX1及细胞因子诱导MSCs,观察其诱导效率及胰岛素分泌量。
材料与方法
一、人脐带间充质干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定
无菌取健康胎儿4~5 cm脐带, PBS洗涤后剪成约1 mm3组织块,胶原酶Ⅳ消化、过网后收集细胞滤液,离心、洗涤后置含10%FBS的DMEM/F12常规培养6~7 d,弃未贴壁细胞,3~4 d 换液1次。待细胞达80%融合后,按1∶3的比例传代。取第4代细胞,以(1~2)×106/ml的细胞悬液分装6管,每管0.1 ml,分别加入鼠抗人抗体CD45-PE、CD34-PE、CD29-FITC、CD44-FITC、HLA-DR-FITC、鼠IgG-FITC+IgG-PE,室温孵育30 min后流式细胞仪检测。
二、脐带MSCs的诱导
第4代MSCs培养达70%~80%融合时分为4组:含荧光蛋白GFP的重组腺病毒Adxsi-CMV-PDX1(本所保存)+细胞因子组(联合组)、Adxsi-CMV-PDX1组、空病毒+细胞因子组和对照组。病毒感染MSCs 7 d后,先联合应用100 ng/ml人表皮生长因子(EGF)+2% B27诱导3 d,再联合应用10 ng/ml胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)、10 ng/ml人β细胞调节素(β-cellulin)、10 ng/ml肝细胞生长因子(HGF)、10 mmol/L烟酰胺(NIC)、0.1 mmol/L β-巯基乙醇、2% B27,在含5% FBS的DMEM/F12中诱导7 d。对照组仅常规培养。用双硫腙行细胞染色。
三、MSCs感染后PDX1表达的检测
取Adxsi-CMV-PDX1感染7 d的MSCs,行细胞爬片,取片行常规免疫荧光法检测PDX1的表达。
四、诱导后细胞胰岛素和C肽表达的检测
取各组诱导后细胞行爬片培养,常规免疫荧光法检测细胞胰岛素及C肽的表达。兔抗人胰岛素多抗购自美国Abcam公司。
五、胰岛素相关基因NKX6.1、insulin、glut2、ngn3 mRNA及PDX1 mRNA检测
抽提各组细胞总RNA,采用RT-PCR检测各基因mRNA的表达。引物应用Primer5.0软件设计,由上海英骏生物技术公司合成。NKX6.1上游5′-CCATCTTCTGGCCCGGAGT-3′,下游5′-CGGACG-CGTGCAGTAGGAG-3′,扩增片段480 bp,退火温度55℃;insulin上游5′-AACCAACACCTGTGCGGC-TCA-3′,下游5′ -TGCCTGCGGGCTGCGTCTA-3′,扩增片段271 bp,退火温度60℃;glut-2上游5′-GCGAATAAACAGGCAGGAGC-3′,下游5′-GCTGGATACAGACAGGGACC-3′ ,扩增片段392 bp,退火温度53℃;ngn3上游5′-AAAGCGAGTTGGCACTAAGCA-3′,下游5′-CGTCTGGGAAGGTGGGAAGTA-3′,扩增片段132 bp,退火温度57℃;PDX-1上游,5′-GGATGAAGTCTACCAAAGCTCACGC-3′,下游5′-CCAGATCTTGATGTGTCTCTCGGTC-3′,扩增片段230 bp,退火温度60℃;内参GAPDH上游5′-AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG-3′,下游5′-AGGGGCCATCCACAGTCTTC-3′,扩增片段285 bp,退火温度58℃。
六、胰岛素与C肽分泌量测定
取各组细胞培养液上清置-20℃保存待测。取诱导后胰岛样细胞团,洗涤2次后置无血清H-DMEM(含25 mmol/L葡萄糖)孵育1 h,取上清,置-20℃保存。采用化学发光法测定胰岛素和C肽含量,试剂盒均购自美国Abbott Axsym System公司。实验重复5次。
七、胰岛素阳性细胞率检测
取诱导第17天的细胞,胰蛋白酶消化、PBS洗涤后加insulin-Cy5,流式细胞仪计数105个细胞,测定胰岛素阳性细胞率。
八、统计学处理

结 果
一、人脐带MSCs的形态和表面标志表达
单个核细胞培养48~72 h内开始贴壁,细胞呈短梭形、多角形;7 d内大部分细胞贴壁,呈短梭形;培养15 d接近80%融合,呈长梭形。传到第4代时细胞形态均一,CD29+、CD44+细胞分别占98.7%和99.6%,而CD45+、CD34+、 HLADR+细胞仅分别占2.3%、1.6%和0.68%(图1)。
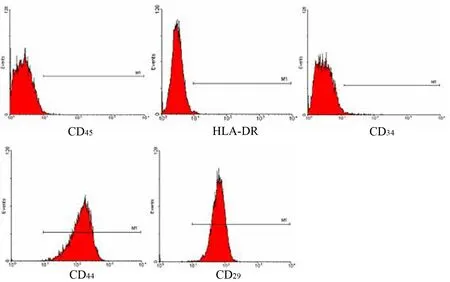
图1 第4代脐带MSCs的形态及表面标志表达
二、重组病毒感染后MSCs的PDX1表达
感染72 h后脐带MSCs表达GFP(图2a),感染率约90%。外源基因PDX1定位于细胞核(图2b、c)。
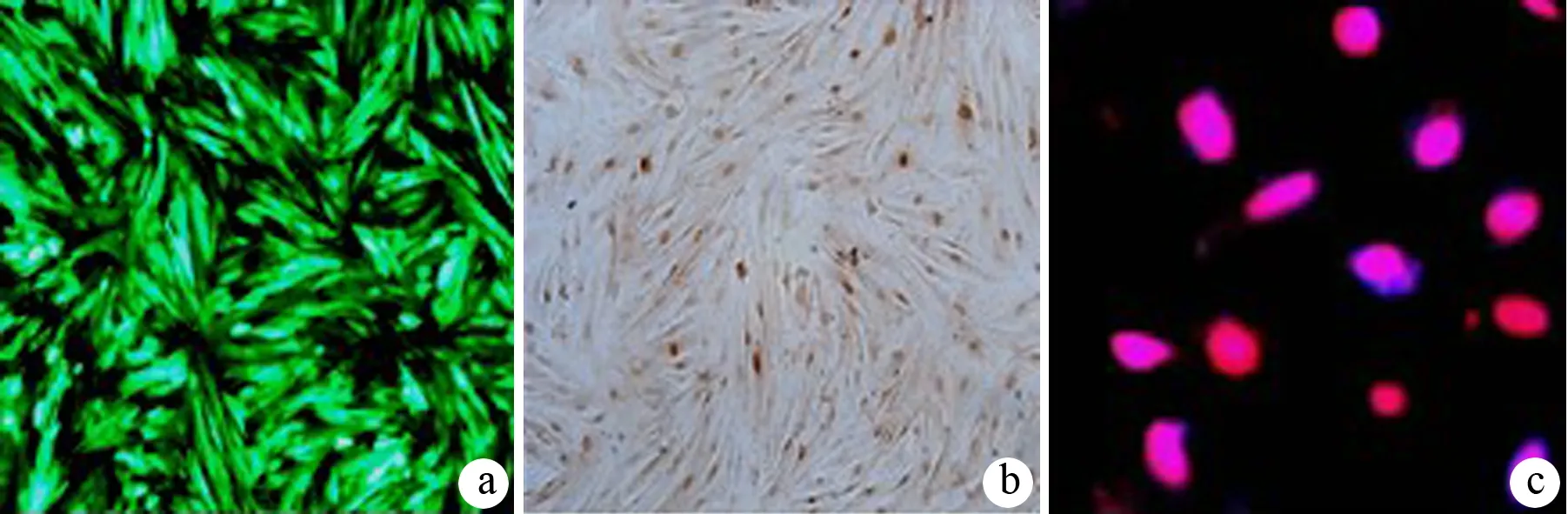
图2 重组病毒感染MSCs 7 d后GFP(a)及PDX1(b、c)表达
三、脐带MSCs的诱导分化
重组病毒感染后联合EGF、B27培养,细胞由长梭形逐渐变圆,相邻细胞开始聚集,形成一个个由圆形或卵圆形细胞组成的细胞团,形如胰岛小体样结构,再联合其他因子培养后,细胞聚集更紧密(图3a),经双硫腙染成亮红色(图3b);胞质内C肽被染成绿色(图3c); insulin被染成红色(图3d)。
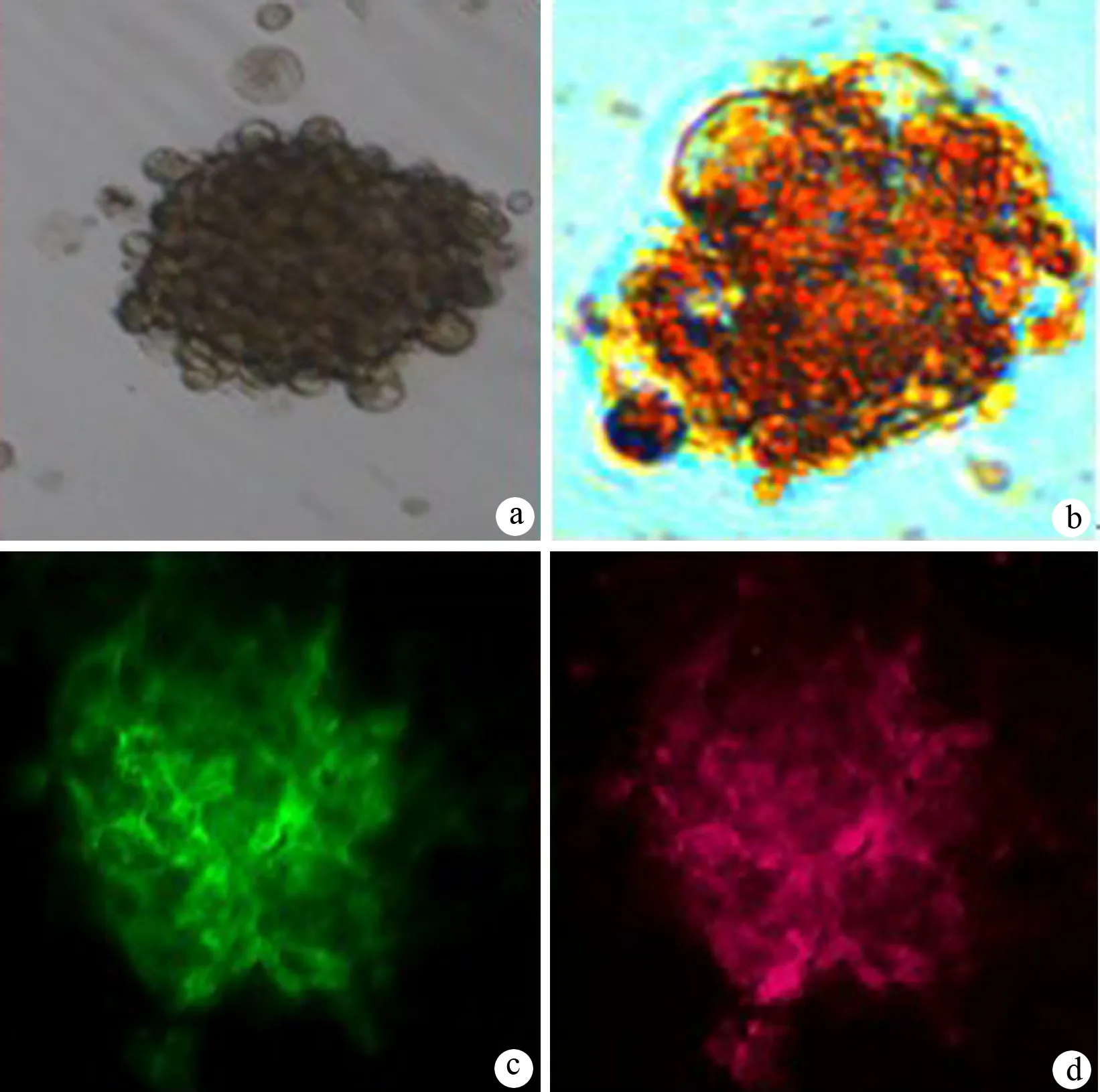
图3MSCs诱导后细胞的形态(a、b)及C肽(c)、胰岛素(d)表达(免疫荧光 ×400)
四、胰岛相关基因mRNA的表达
联合组细胞在诱导0、7、10、17 d和17 d加高糖刺激1 h后均可检测到胰岛相关基因PDX1、ngn3、insulin、glut-2、NKX6.1 mRNA的表达(图4)。

图4 诱导后细胞胰岛相关基因mRNA的表达(RT-PCR)
五、胰岛素和C肽的分泌
Adxsi-CMV-PDX1组、空病毒+细胞因子组及对照组细胞培养不同时间及用高糖刺激,其胰岛素分泌量均无明显变化,波动在(3.6±2.4)mU/L~(4.5±3.7)mU/L。联合组细胞诱导第10、17天时,培养液上清中胰岛素含量显著升高,高糖刺激1 h后,胰岛素的分泌量更高(表1)。
只有联合组在培养第10、17天表达C肽,分别为(0.13±0.04)ng/ml和(1.61±0.41)ng/ml,高糖刺激后C肽分泌高达(3.72±1.52)ng/ml,其他时段及其他各组细胞的培养上清液中均未检测到C肽,差异显著(P<0.05)。
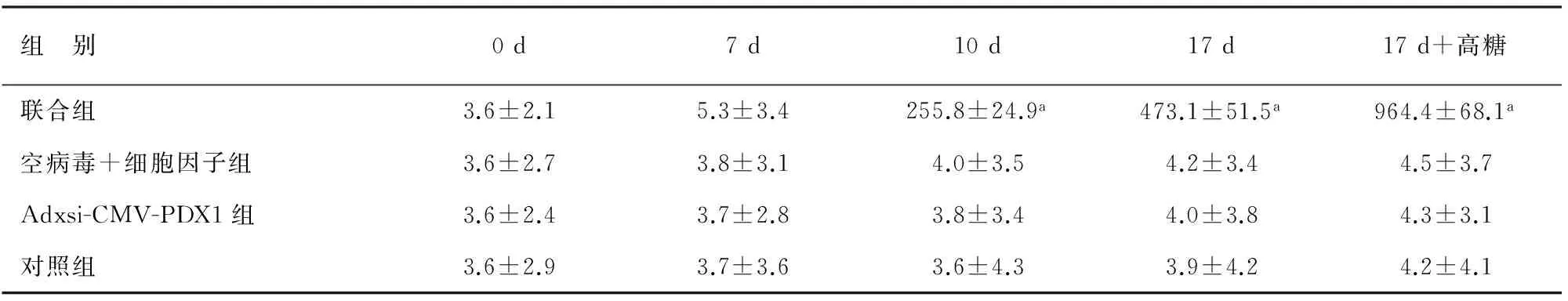
表1 各组细胞各时段培养液上清中胰岛素分泌量(X±SD, mU/L)
注:与其他组相比,aP<0.05
六、胰岛素阳性细胞率
联合组胰岛素阳性细胞率为(11.6±4.8)%,对照组为0。两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
讨 论
Kaneto等[6]报道,PDX1不能诱导MSCs表达胰岛素mRNA。本实验单独用携带PDX1的重组腺病毒感染脐带MSCs 17 d也未能检测到胰岛素mRNA。最新研究[7-10]已经明确,从β前体细胞到成熟β细胞的发育过程除需PDX1之外,尚需NKX6.1、ngn3、Mafa、NKX2.2、Foxa1等转录因子的时序表达、相互作用,此外,许多细胞因子也可以促进这一分化过程[11-13]。
本实验结果显示,PDX1转入MSCs 7 d后仅有ngn3 mRNA表达,联合EGF与B27刺激3 d后,激活脐带MSCs向β细胞定向分化所需的NKX6.1的表达,并启动了胰岛素mRNA的表达,细胞形状与β细胞非常相似。经双硫腙染成亮红色,说明诱导后的MSCs细胞的胞质内富含锌离子,具备β细胞前体细胞的特征。再联合其他因子诱导后细胞的胰岛素水平和C肽分泌水平显著升高,高糖刺激后胰岛素分泌量更高,C肽分泌量也增加,glut2 mRNA也开始表达。
insulin、glut2、GK和Mafa是β细胞成熟的4个重要标志物,而ngn3在成熟的β细胞中并不表达。本实验诱导的胰岛样细胞表达insulin、glut2和ngn3 mRNA,说明诱导的β细胞尚未完全成熟。有研究报道,转入外源性PDX1、ngn3和Mafa 3个基因可以将成年鼠胰腺外分泌细胞分化为胰岛β样细胞,胰岛素阳性细胞百分率可达20%[14]。因此,要提高诱导效率,还需要进一步优化诱导方案。
[1] Jiang J,Au M,Lu K,et al.Generation of insulin-producing islet-like clusters from human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells,2007,25:1940-1953.
[2] Segev H,Fishman B,Ziskind A,et al.Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing clusters.Stem Cells,2004,22:265-274.
[3] Melloul D.Transcription factors in islet development and physiology:role of PDX-1 in beta-cell function.Ann NY Acad Sci USA,2004,1014:28-37.
[4] Kajiyama H,Hamazaki TS,Tokuhara M,et al.Pdx1-transfected adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiate into insulin-producing cells in vivo and reduce hyperglycemia in diabetic mice.Int J Dev Biol,2010,54:699-705.
[5] Hisanaga E,Park KY,Yamada S,et al.A simple method to induce differentiation of murine bone marrow mesenchymal cells to insulin-producingcells using conophylline and betacellulin-delta4.Endocr J,2008,55:535-543.
[6] Kaneto H,Nakatani Y,Miyatsuka T,et al.PDX-1/VP16 fusion protein,together with neuroD or Ngn3,markedly induces insulin gene transcription and ameliorates glucose tolerance.Diabetes,2005,54:1009-1022.
[7] Wescott MP,Rovira M,Reichert M,et al.Pancreatic ductal morphogenesis and the Pdx1 homeodomain transcription factor.Mol Biol Cell,2009,20:4838-4844.
[8] Smith SB,Watada H,German MS.Neurogenin3 activates the islet differentiation program while repressing its own expression.Mol Endocrinol,2004,18:142-149.
[9] Mellitzer G,Bonne S,Luco RF,et al.IA1 is NGN3-dependent and essential for differentiation of the endocrine pancreas.EMBO J,2006,25:1344-1352.
[10] Song YD,Lee EJ,Yashar P,et al.Islet cell differentiation in liver by combinatorial expression of transcription factors Neurogenin-3,BETA2,and RIPE3b1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2007,354:334-339.
[11] Miettinen P,Ormio P,Hakonen E,et al.EGF receptor in pancreatic beta-cell mass regulation.Biochem Soc Trans,2008,36:280-285.
[12] Yasuda M,Yamamoto M,Ochiai H,et al.Effects of growth factors on development of fetal islet B-cells in vitro.J Vet Med Sci,2007,
69:807-811.
[13] Li L,Li F,Qi H,et al.Coexpression of Pdx1 and betacellulin in mesenchymal stem cells could promote the differentiation of nestin-positive epithelium-like progenitors and pancreatic islet-like spheroids.Stem Cells Dev,2008,17:815-823.
[14] Zhou Q,Brown J,Kanarek A,et al.In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to beta-cells.Nature,2008,455:627-632.
2010-07-26)
(本文编辑:屠振兴)
PDX1geneandcytokinesinducehumanumbilicalcordmesenchymalstemcellstodifferentiateintoisletβ-likecellsinvitro
WANGBo,WUHan-qing,WUHe-shui,WANGChun-you.
DepartmentofPancreaticSurgery,UnionHospital,TongjiMedicalCollege,HuazhongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,Wuhan430022,China
WUHe-shui,Email:heshuiwu@163.com
ObjectiveTo explore the method how PDX1 gene modified mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from human umbilical cord can be differentiated into islet β-like cells in vitro.MethodsRecombined adenovirus vectors inserted with PDX1 (Adxsi-CMV-PDX1) was transfected into MSCs and multiple cytokines was combined to induce differentiation. The expressions of PDX1, insulin, ngn3, glut2, NKX6.1 were examined by RT-PCR and immunofluorescence staining. The levels of insulin and C peptide secretion were examined by chemiluminescence immunoassay. Flow cytometry was used to determine the positive rate of insulin cells.ResultsAfter Adxsi-CMV-PDX1 transfection and cytokines induction, MSCs were transformed from short spindle shape to long spindle shape and aggregated into islet-like cell clusters. Dithizone staining of these cells showed bright red color. PDX1, ngn3, NKX6.1, insulin, glut 2 mRNA were expressed in cells 17d after induction. Insulin and C peptide were expressed in cytoplasm. The levels of insulin and C peptide in cell culture supernatant were (473.1±51.5)mU/L and (1.61±0.41)ng/ml; the levels of insulin and C peptide secretion were (964.4±68.1)mU/L, (3.72±1.52) ng/mL, respectively, with 25 mmol/L glucose stimulation for one hour. Insulin (+) cells rate (11.6±4.8)%.ConclusionsAdxsi-CMV-PDX1 combined with cytokines can induce MSCs from human umbilical cord to differentiate into islet β-like cells. They can secret insulin and C peptide, and have the sensitivity to the stimulation of glucose.
Umbilical cord; Mesenchymal stem cells; Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox factor;Islet β-like cells; Cell differentiation
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2011.01.015
430022 湖北武汉,华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院胰腺外科
吴河水,Email:heshuiwu@163.com

