3-羟基肉桂酸构筑的锌(Ⅱ)和镉(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、晶体结构和荧光性质
张春艳傅君丹温一航
(浙江师范大学物理化学研究所,浙江省固体表面反应化学重点实验室,金华321004)
3-羟基肉桂酸构筑的锌(Ⅱ)和镉(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、晶体结构和荧光性质
张春艳傅君丹温一航*
(浙江师范大学物理化学研究所,浙江省固体表面反应化学重点实验室,金华321004)
用水热法合成得到2个配合物,{[ML2(bipy)(H2O)2]·2bipy}n(M=Cd 1,Zn 2;HL=3-羟基肉桂酸,bipy=4,4′-联吡啶),并对它们进行了红外分析、元素分析,热重分析和单晶结构分析。配合物1和2为异质同晶,单斜晶系,P2/c空间群。中心金属M为六配位,相邻的MⅡ通过4,4′-联吡啶桥联形成沿b轴延伸的一维链状结构,此外还存在未配位的4,4′-联吡啶作为客体分子位于链与链之间。通过对配合物1和2的固态荧光测试表明,它们在绿光区均显示发光效应。
3-羟基肉桂酸;4,4′-联吡啶;一维链状;荧光
In recent years,extensive attention has been focused on the design and synthesis of d10metalcarboxylate metal-organic frameworks(MOFs)for their various geometry chemistry of motifs,photoluminescent properties and other potential applications in molecular-based materials[1-4].Furthermore,due to the various coordination types of the trans-cinnamic acid,it has made significant contribution in the development of organic solid state chemistry[5].So far,the complexes of trans-cinnamic acid with several metal ions have been reported,due to its diverse coordination modes of carboxylate[6-16].And bipy have been attracted considerable interests for the formation of extended structures by bridging metal nodes and is very important for the prep-aration of open frameworks with dimensionalities[17-20].
In our work,interest attaches to the synthesis and characterization of metal-organic complexes with 3-hydroxycinnamic acid based on the following considerations[21]:The carboxylate group conjugated with benzene ring through C=C double bond,which will make the electronic density delocalized in the ligand and it may become more rigidly when coordinated with metal ions; the exist of phenolic hydroxyl group and benzene ring in the ligand will probable form hydrogen bonding and π-π stacking interactions in the crystal lattices. Therefore,the ligand should be interesting in regard to their coordination chemistry and supramolecular chemistry.Herein,two new coordination polymers, namely,{[ML2(bipy)(H2O)2]·2bipy}n(M=Cd 1;Zn 2) have been synthesized by hydrothermal reaction of metal salt with HL and bipy under suitable condition. The crystal structures,thermal stabilities and solidstate luminescent properties of these two complexes are reported here.
1 Experimental
1.1 M aterials and instrumentation
All starting materials and solvents for synthesis were obtained commercially and used without further purification.IR spectra were recorded on an FTIR-8700 spectrometer with KBr pellets in the range of 4 000~ 400 cm-1.Eleme(Ⅱ)ntary analyses were performed on a PE-2400(Ⅱ)element analysis instrument.The crystal data collections were carried out on a Bruker SMART APEX-ⅡCCD diffractometer.Thermogravimetric analyses were determined on a Mettler-Toledo TGA/ SDTA 851ein the 25~700℃(10℃·min-1)range under oxygen atmosphere.Luminescence spectra were performed on a HITACHI F-2500 Fluorescence Spectrometer in solid state at room temperature.
1.2 Synthesis of 1
A mixture of Cd(Ac)2·2H2O(0.1333 g,0.5 mmol), 3-hydroxycinnamic acid(0.164 g,1.0 mmol),4,4′-bipyridine(0.156 g,1.0 mmol)and methanol-water(15 mL,V/V 1∶4)was sealed in a 25 mL stainless steel reactor with a Telflon liner and heated at 433 K for 72 h.After cooling to room temperature at a rate of 2℃per hour,the yellow crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained in 43%yield.Elemental Anal.Found (%):C,61.15;H,4.43;N,8.95.Calcd.For C48H42N6O8Cd(%):C,61.12;H,4.49;N,8.91.IR(KBr,cm-1): 3 415,1 638,1 605,1 580,1 543,1 511,1 451,1 387, 1279,1220,989,867,807,685,629.
1.3 Synthesis of 2
The preparation of 2 was similar to that of 1 except that ZnSO4·7H2O(0.143 8 g,0.5 mmol)was used instead of Cd(Ac)2·2H2O.The colorless crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained in 41%yield. Elemental Anal.Found(%):C,63.45;H,4.80;N,9.30. Calcd.For C48H42N6O8Zn(%):C,64.32;H,4.72;N,9.38. IR(KBr,cm-1):3421,1637,1610,1597,1581,1558, 1 404,1 419,1 387,1 357,1 280,1 048,992,802,711, 617.
1.4 Crystal structure determ ination
Data collections were performed on a Bruker SMART APEX-Ⅱdiffractometer equipped with a CCD detector using a graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071073 nm)at room temperature.Structures were solved by direct methods and expanded with difference Fourier synthesis.Anisotropic displacement parameters were applied to all non-hydrogen atoms in full-matrix least-squares refinements based on F2.The hydrogen atoms were assigned with isotropic displacement factors and included in the final refinement cycles by the use of geometrical restrains.All calculations were performed with SHELX-97 package[22].Crystal data and structural refinement parameters for 1,2 are summarized in Table 1 and selected bond lengths and angles are listed in Table 2.
CCDC:818712,1;818713,2.

Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for the title comp lexes
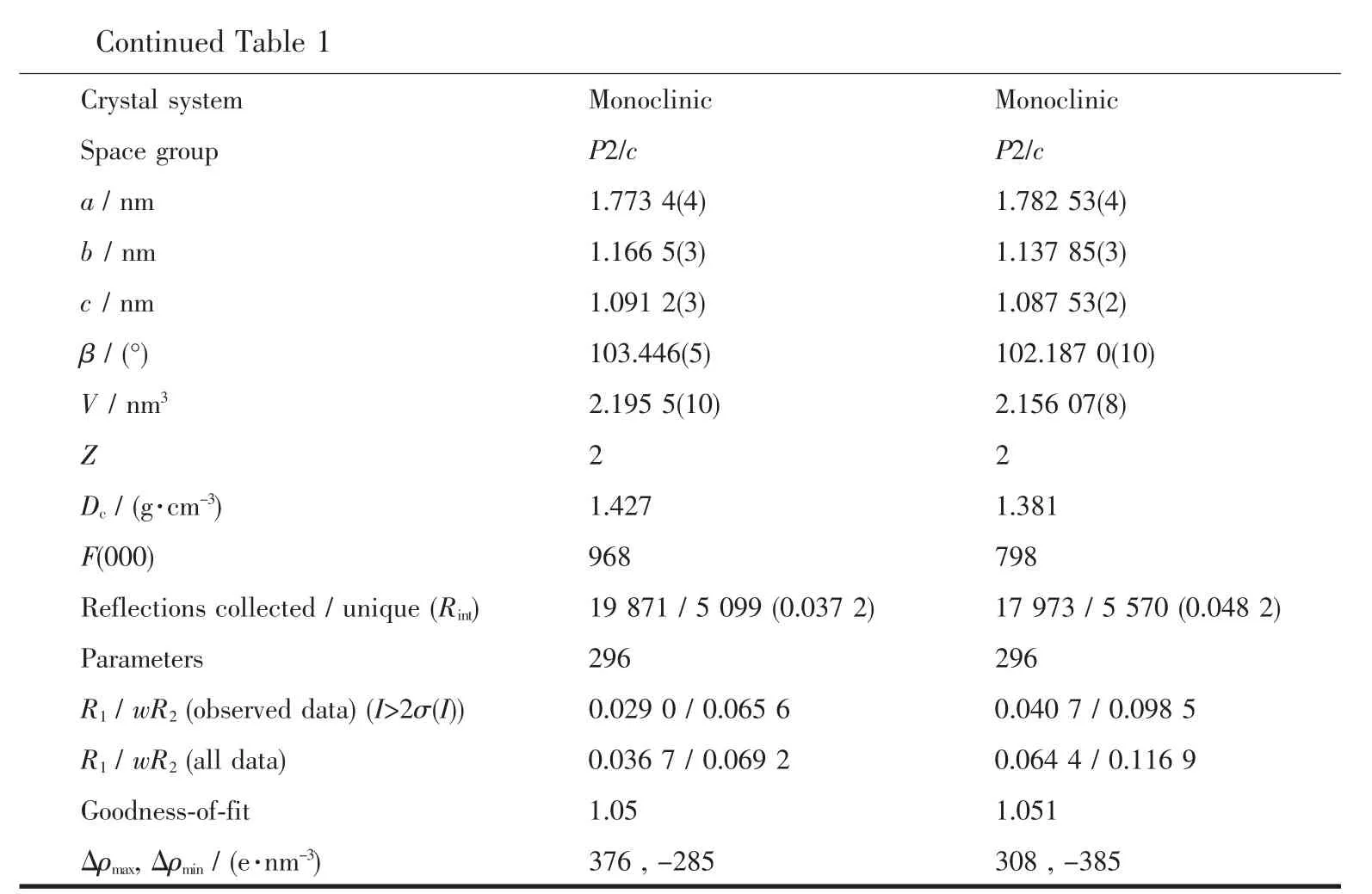
Continued Table 1 Crystal system Monoclinic Monoclinic Space group P2/c P2/c a/nm 1.773 4(4)1.782 53(4) b/nm 1.166 5(3)1.137 85(3) c/nm 1.091 2(3)1.087 53(2) β/(°)103.446(5)102.187 0(10) V/nm32.195 5(10)2.156 07(8) Z 2 2 Dc/(g·cm-3)1.427 1.381 F(000)968 798 Reflections collected/unique(Rint)19 871/5 099(0.037 2)17 973/5 570(0.048 2) Parameters 296 296 R1/wR2(observed data)(I>2σ(I))0.029 0/0.065 6 0.040 7/0.098 5 R1/wR2(all data)0.036 7/0.069 2 0.064 4/0.116 9 Goodness-of-fit 1.05 1.051 Δρmax,Δρmin/(e·nm-3)376,-285 308,-385
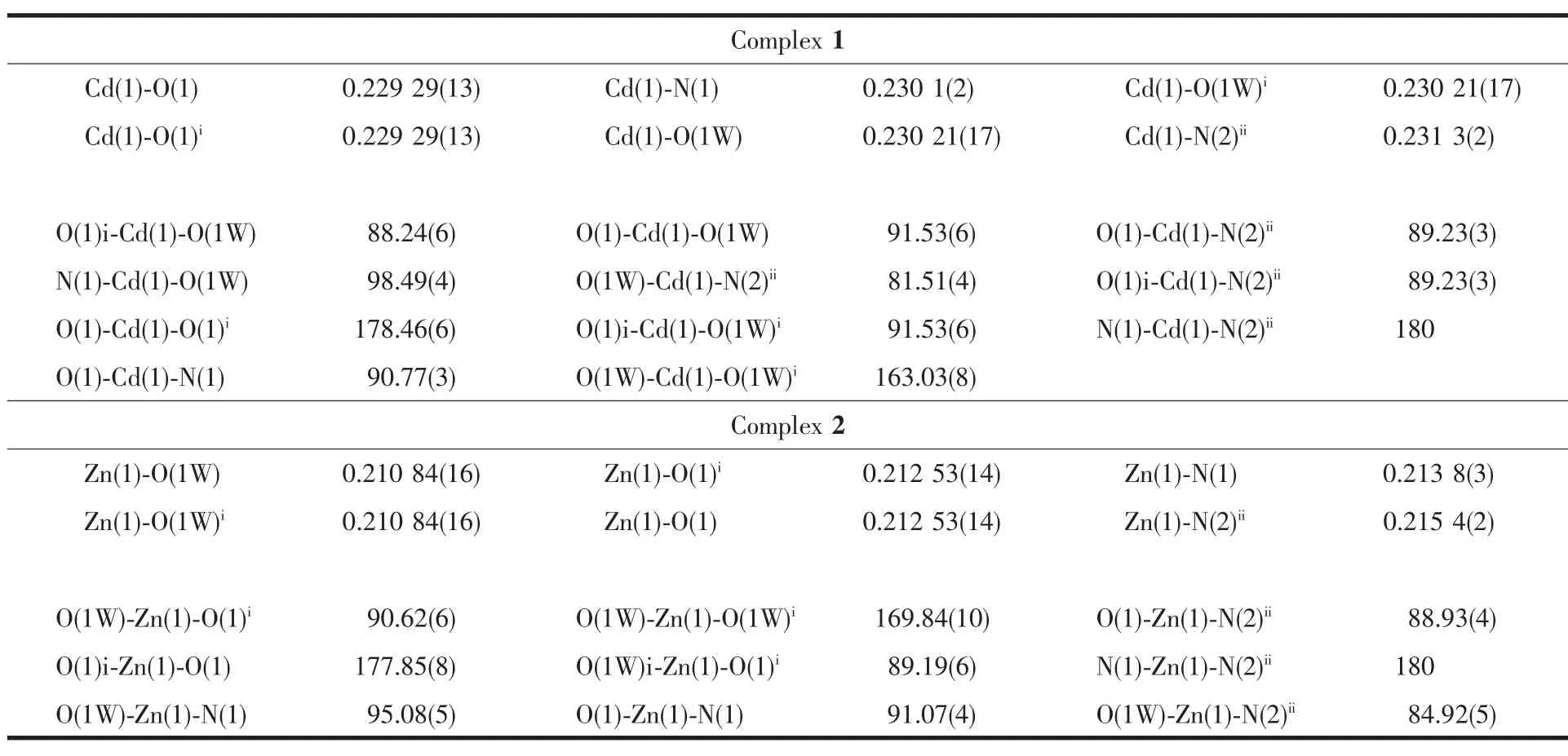
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for the title com plexes
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Description of structures
The single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses show that complexes 1 and 2 are isostructural,and both crystallize in monoclinic system,P2/c space group.The structural motif consists of one metal ion,two L ligands, two coordinated water molecules,one coordinated and two discreted bipy molecules.As representative,the structure of complex 1 is described here in detail.
As shown in Fig.1,the Cd(Ⅱ)center with a distorted octahedral coordination environment,is surrounded by two N atoms from two bipy ligands,two carboxylate O atoms and two water molecules.Each two Cd(Ⅱ)ions are linked together by bipy ligands(Cd-N 0.230 1(2)and 0.2313(2)nm),form a linear chain structure along b axis with Cd…Cd separation of 1.1665(3)nm(Fig.2a). The dihedral angel between two pyridyl rings is about 26.93°.The L ligands are symmetrically arranged in two sides of the chains with Cd-O bond length being0.22929(13)nm and the O-Cu-O bond angle being 178.46(5)°.In addition,non-coordinated bipy as guest molecules intersperse between the chains.
The 3D structure of complex 1 connected by weak interactions is shown in Fig.2b.There exist extensive O-H…O and O-H…N hydrogen bonds involving coordinated water molecules,L ligands and free bipy molecules in 1(Table 3).Furthermore,there are relatively short distances(centroid-centroid separation 0.368 30(6)nm)between adjacent bipy molecules, implying strong π-π stacking interactions in complex 1. All these weak interactions in complex 1 result in a 3D network structure and lead the whole network structure system stable.
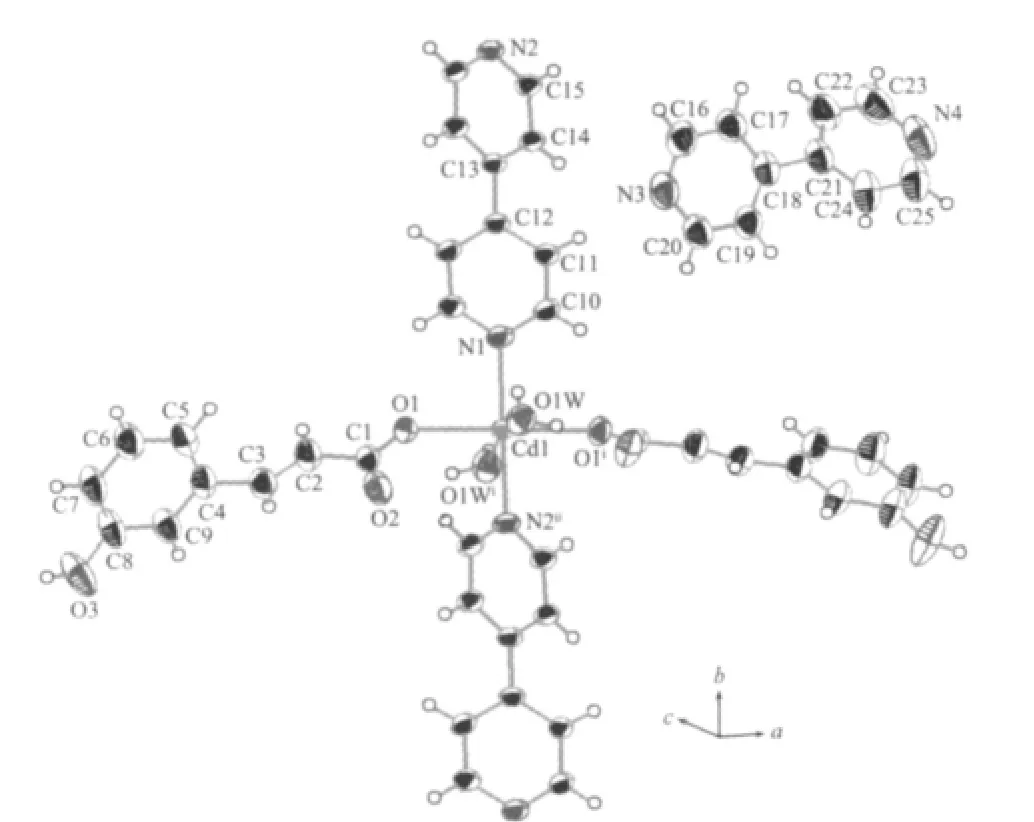
Fig.1 Coordination environments of Cd atoms in complex 1 showing 30%probability ellipsoids and the atom-labeling scheme
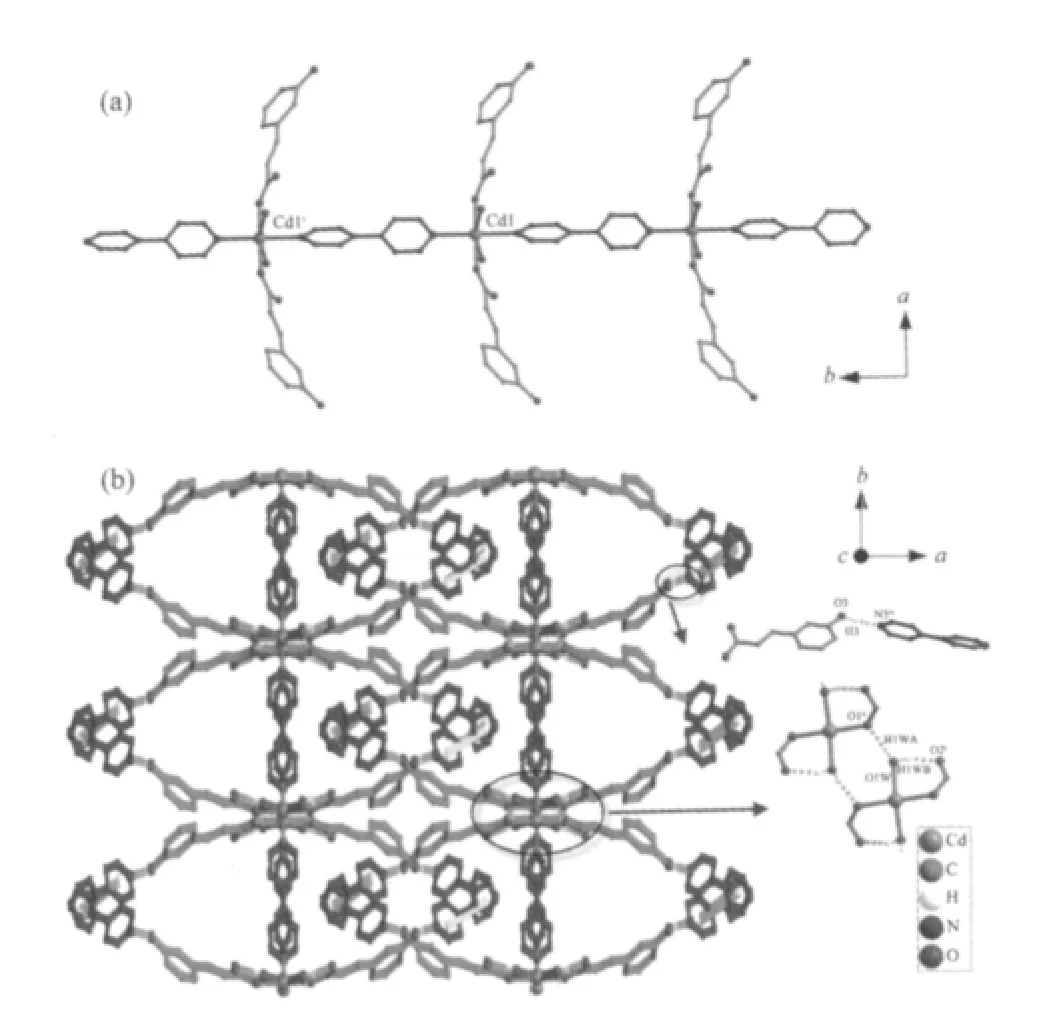
Fig.2 (a)1D chain viewed along the b axis in complex 1; (b)Packing of complex 1
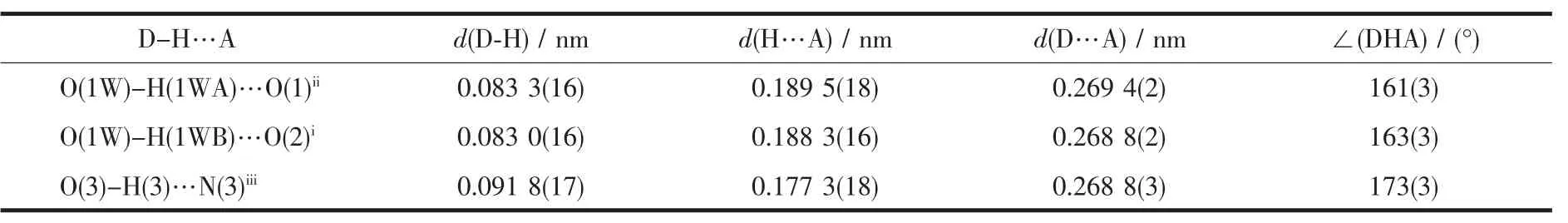
Table 3 Hydrogen bonds for complex 1
2.2 Lum inescence properties
The d10metal complexes have been shown to exhibit some photoluminescent properties[23-24].The solid-state luminescent properties of HL ligand and title complexes were investigated at room temperature and their emission spectra are given in Fig.3.For title complexes,the fluorescent emission spectra exhibit intense photoluminescence at 540 nm upon excited at 550 nm,and 560 nm upon excited at 574 nm, respectively.In order to understand the nature of the emission bands of title complexes,we further measuredthe emission spectrum of the free HL ligand,which shows one peak emission at 504 nm.The maximum emission bands of title complexes are red-shifted compared to free HL ligand.Therefore,the emission band of title complexes may be mainly assigned to π*-π charge transfer[25].
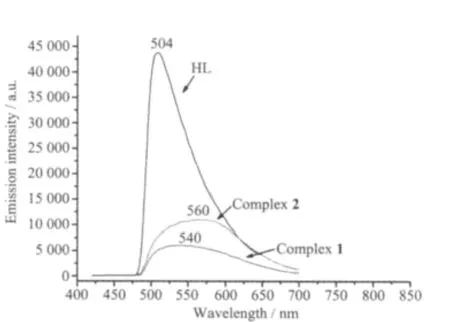
Fig.3 Fluorescence emission spectra of HL ligand and two complexes in the solid state at room temperature
2.3 Thermogravimetric analysis
Owing to the similarity of the structures for the two complexes,complex 2 was selected for thermogravimetric analysis(TGA)to examine the thermal stability of complexes.The experiment for sample 2 was heated to 700℃in O2atmosphere with a rate of 10℃·min-1. The TGA curve for 2(Fig.4)shows that the first weight loss of 25.18%from 120 to 200℃corresponds to the removal of one discrete bipy molecule and one pyridine-ring of another discrete bipy molecule(calcd. 26.14%).Further decomposition occurs in the range of 200~460℃,that is attributed to the elimination of two water molecules and two L ligands(obsd.60.04%, calcd.60.56%).The remaining product may be ZnO (obsd.11.05%,calcd.9.18%).The loss of all aqua molecules at relatively high temperature indicates the presence of the strong hydrogen bonding interactions in complex 2[26].
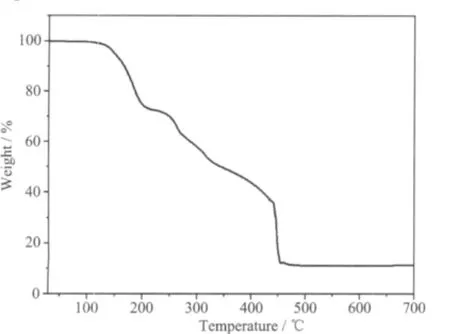
Fig.4 TGA curve of the complex 2
[1]Dakanali M,Kefalas E T,Raptopoulou C P,et al.Inorg. Chem.,2003,42:2531-2537
[2]Liu X J,Fang Q R,Zhu G S,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2004,7:31-34
[3]Zheng C G,Xie Y L,Xiong R G,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2001,4:405-408
[4]Liu Y H,Lu Y L,Wu H C,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2002,41:2592-2597
[5]Yang Y S,Gong M L,Li Y Y,et al.J.Alloys Compd.,1994, 207/208:112-114
[6]Crowther D,Chowdhury M,Kariuki B M.J.Mol.Struct., 2008,872:64-71
[7]Darshak R,Trivedi P,Dastidar P.Cryst.Growth Des.,2006,6: 114-121
[8]Ballabh A,Trivedi D R,Dastidar P.Chem.Mater.,2006,18: 3795-3800
[9]Natarajan A,Mague J T,Venkatesan K,et al.Org.Lett., 2005,7:1895-1898
[10]Trivedi D R,Ballabh A,Dastidar P.J.Mater.Chem.,2005, 15:2606-2614
[11]Gossauer A,Nydegger F,Kiss T,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc., 2004,126:1764-1783
[12]Gupta M,Bagaria A,Mishra A,et al.Adv.Mater.,2007,19: 858-861
[13]Barreiro E,Casas J S,Couce M D,et al.Eur.J.Med.Chem., 2008,43:2489-2497
[14]Casasa J,Castieirasa A,Couceb M D,et al.Polyhedron,2008, 27:2436-2446
[15]Zhang C Y,Fu J D,Wen Y H.Acta Cryst.,2010,E66:m1003-m1004
[16]Chowdhury M,Kariuki B M.Cryst.Growth Des.,2006,6:74-780
[17]Fu R B,Xiang S C,Hu S M,et al.Chem.Commun.,2005,5: 5292-5294
[18]Reger D L,Semeniuc R F,Smith M D.Cryst.Growth Des., 2005,5:177-182
[19]Lu W G,Su C Y,Lu T B,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2006,128: 34-35
[20]Zhang J,Xie Y R,Ye Q,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2003: 2572-2577
[21]Li H,Hu C W.J.Mol.Struct.,2004,177:4501-4507
[22]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97,Program for the Solution and the Refinement of Crystal Structure, University of Grttingen,Germany,1997.
[23]Wang X W,Chen J Z,Liu J H.Cryst.Growth Des.,2007,7: 1227-1229
[24]Yang E C,Zhao H K,Ding B,et al.Cryst.Growth Des., 2007,7:2009-2015
[25]Wen L L,Dang D B,Duan C Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2005,44: 7161-7170
[26]Barea E,Navarro J A R,Salas J M.Polyhedron,2003,22: 3051-3057
Hydrothermal Syntheses,Crystal Structures and Lum inescent Properties of Zn(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)Com plexes Based on 3-Hydroxycinnam ic Acid
ZHANG Chun-Yan FU Jun-Dan WEN Yi-Hang*
(Zhejiang Key Laboratory for Reactive Chemistry on Solid Surfaces,Institute of Physical Chemistry,Zhejiang Normal University,Jinhua,Zhejiang 321004,China)
Two linear structure metal-organic complexes,{[ML2(bipy)(H2O)2]·2bipy}n(M=Cd 1;Zn 2),based on 3-hydroxycinnamic acid(HL)and 4,4′-bipyridine(bipy)were synthesized and characterized by IR,elemental analyses,thermogravimetric analyses and X-ray diffraction technique.Two complexes are isostructural, crystallized in monoclinic system,P2/c space group.The center metal ion is six-coordinated by two nitrogen atoms from the bridging bipy ligands,two oxygen atoms from two L ligands,and two water molecules,forming a distorted octahedral geometry.The MⅡions and bipy ligands link each other to form a 1D linear chain that infinitely propagates along b axis,and discrete bipy as guest molecules intersperses between the chains.The luminescent properties in the solid state and thermogravimetric analyses(TGA)of two complexes are also discussed.CCDC:818712,1;818713,2.
3-hydroxycinnamic acid;4,4′-bipyridine;linear chain;luminescent
O614.24+1;O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2011)11-2308-05
2011-03-28。收修改稿日期:2011-07-26。
浙江师范大学博士启动资金资助项目。
*通讯联系人。E-mail:wyh@zjnu.edu.cn;会员登记号:S060017686M。

